Note: For MySQL 5.7+, please see the answer from Lahiru to this question. That contains more current information.
For MySQL < 5.7:
The default root password is blank (i.e., an empty string), not root. So you can just log in as:
mysql -u root
You should obviously change your root password after installation:
mysqladmin -u root password [newpassword]
In most cases you should also set up individual user accounts before working extensively with the database as well.
![]()
answered Feb 21, 2014 at 20:54
![]()
Mike BrantMike Brant
70.3k10 gold badges98 silver badges103 bronze badges
15
I was recently faced with the same problem, but in my case, I remember my password quite alright, but it kept on giving me the same error. I tried so many solutions, but still none helped. Then I tried this:
mysql -u root -p
After which it asks you for a password like this
Enter password:
And then I typed in the password I used. That’s all.
![]()
answered Mar 21, 2018 at 22:22
![]()
4
I was able to solve this problem by executing this statement
sudo dpkg-reconfigure mysql-server-5.5
Which will change the root password.
![]()
answered Mar 18, 2014 at 3:37
DivzDivz
1,3832 gold badges8 silver badges6 bronze badges
8
You have to reset the password! Steps for Mac OS X (tested and working) and Ubuntu:
Stop MySQL using
sudo service mysql stop
or
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server stop
Start it in safe mode:
sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking
(the above line is the whole command)
This will be an ongoing command until the process is finished, so open another shell/terminal window, log in without a password:
mysql -u root
mysql> UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD("password") WHERE User="root";
As per @IberoMedia’s comment, for newer versions of MySQL, the field is called authentication_string:
mysql> UPDATE mysql.user SET authentication_string=PASSWORD("password") WHERE User="root";
Start MySQL using:
sudo service mysql start
or
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start
Your new password is ‘password’.
Note: for version of MySQL > 5.7 try this:
update mysql.user set authentication_string="password" where user="root";
answered Sep 17, 2014 at 6:44
![]()
tk_tk_
16.2k8 gold badges80 silver badges90 bronze badges
13
It happens when your password is missing.
Steps to change the password when you have forgotten it:
-
Stop MySQL Server (on Linux):
sudo systemctl stop mysql -
Start the database without loading the grant tables or enabling networking:
sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking &The ampersand at the end of this command will make this process run in the background, so you can continue to use your terminal and run
mysql -u root(as root). It will not ask for a password.If you get error like as below:
2018-02-12T08:57:39.826071Z mysqld_safe Directory '/var/run/mysqld' for UNIX socket file don't exists. mysql -u root ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can't connect to local MySQL server through socket '/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock' (2) [1]+ Exit 1 -
Make MySQL service directory.
sudo mkdir /var/run/mysqldGive MySQL user permission to write to the service directory.
sudo chown mysql: /var/run/mysqld -
Run the same command in step 2 to run MySQL in background.
-
Run
mysql -u root. You will get the MySQL console without entering a password.Run these commands
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;For MySQL 5.7.6 and newer
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_password';For MySQL 5.7.5 and older
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('new_password');If the ALTER USER command doesn’t work use:
UPDATE mysql.user SET authentication_string = PASSWORD('new_password') WHERE User = 'root' AND Host = 'localhost';Now exit
-
To stop the instance started manually:
sudo kill `cat /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid` -
Restart MySQL
sudo systemctl start mysql
![]()
answered Feb 12, 2018 at 14:25
![]()
4
At the initial start up of the server the following happens, given that the data directory of the server is empty:
- The server is initialized.
- SSL certificate and key files are generated in the data directory.
- The validate_password plugin is installed and enabled.
- The superuser account ‘root’@’localhost’ is created. The password for the superuser is set and stored in the error log file.
To reveal it, use the following command:
shell> sudo grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
Change the root password as soon as possible by logging in with the generated temporary password and set a custom password for the superuser account:
shell> mysql -u root -p
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass5!';
answered Mar 23, 2017 at 5:17
![]()
LahiruLahiru
1,35812 silver badges17 bronze badges
8
If the problem still exists, try to force changing the password:
/etc/init.d/mysql stop
mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables &
mysql -u root
Set up a new MySQL root user password:
use mysql;
update user set password=PASSWORD("NEW-ROOT-PASSWORD") where User='root';
flush privileges;
quit;
Stop the MySQL server:
/etc/init.d/mysql stop
Start the MySQL server and test it:
mysql -u root -p
![]()
answered May 20, 2014 at 13:34
![]()
Yasin HassanienYasin Hassanien
4,0351 gold badge20 silver badges17 bronze badges
6
If none of the other answers work for you, and you received this error:
mysqld_safe Logging to '/var/log/mysql/error.log'.
mysqld_safe Directory '/var/run/mysqld' for UNIX socket file don't exists.
[1]+ Exit 1 sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables
Follow the below commands step by step until you reset your password:
# Stop your server first
sudo service mysql stop
# Make the MySQL service directory.
sudo mkdir /var/run/mysqld
# Give MySQL permission to work with the created directory
sudo chown mysql: /var/run/mysqld
# Start MySQL, without permission and network checking
sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking &
# Log in to your server without any password.
mysql -u root mysql
# Update the password for the root user:
UPDATE mysql.user SET authentication_string=PASSWORD('YourNewPasswordBuddy'), plugin='mysql_native_password' WHERE User='root' AND Host='localhost';
# If you omit (AND Host='localhost') section, it updates
# the root password regardless of its host
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;
# Kill the mysqld_safe process
sudo service mysql restart
# Now you can use your new password to log in to your server
mysql -u root -p
# Take note for remote access. You should create a remote
# user and then grant all privileges to that remote user
![]()
answered Apr 16, 2019 at 11:39
![]()
MehdiMehdi
3,7643 gold badges36 silver badges65 bronze badges
1
I came across this very annoying problem and found many answers that did not work. The best solution I came across was to completely uninstall MySQL and reinstall it. On reinstall you set a root password and this fixed the problem.
sudo apt-get purge mysql-server mysql-client mysql-common mysql-server-core-5.5 mysql-client-core-5.5
sudo rm -rf /etc/mysql /var/lib/mysql
sudo apt-get autoremove
sudo apt-get autoclean
I found this code elsewhere, so I don’t take any credit for it. But it works. To install MySQL after uninstalling it, I think DigitalOcean has a good tutorial on it. Checkout my gist for this.
How to install MySQL on Ubuntu (which works)
![]()
answered Feb 9, 2017 at 21:05
![]()
JamesDJamesD
5815 silver badges10 bronze badges
0
I am using Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial Xerus) and installed MySQL 5.7.
I had the same issue
Login denied for root user.
I tried the below steps:
-
dpkg --get-selections | grep mysql(to get the version of MySQL). -
dpkg-reconfigure mysql-server-5.7 -
mysql -u root -p
Without -p that doesn’t prompt you to ask password. Once you are in, you can create a user with a password by following steps:
CREATE USER 'your_new_username'@'your-hostname' IDENTIFIED BY 'your-password';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* to 'your_new_username'@'your-hostname' WITH GRANT OPTION;
Exit from the root and log in from the <name> you gave above.
mysql -u <your_new_username> -p
For some reason still just typing MySQL does not work. At all. I suggest to make it a habit to use mysql -u <name> -p.
![]()
answered Jun 21, 2017 at 15:21
1
In the terminal, just enter:
mysql -u root -p
Then it will ask the password from you.
![]()
answered Jul 8, 2019 at 21:24
![]()
1
I installed MySQL as root user (
$SUDO) and got this same issue
Here is how I fixed it:
-
sudo cat /etc/mysql/debian.cnfThis will show details as:
# Automatically generated for Debian scripts. DO NOT TOUCH! [client] host = localhost user = debian-sys-maint password = GUx0RblkD3sPhHL5 socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock [mysql_upgrade] host = localhost user = debian-sys-maint password = GUx0RblkD3sPhHL5 socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sockAbove we can see the password. But we are just going to use
(GUx0RblkD3sPhHL5)that in the prompt. -
`mysql -u debian-sys-maint -p
Enter password: `
Now provide the password (GUx0RblkD3sPhHL5).
-
Now
exitfrom MySQL and log in again as:`mysql -u root -p
Enter password: `
Now provide the new password. That’s all. We have a new password for further uses.
It worked for me.
![]()
answered Sep 17, 2019 at 12:30
![]()
S.YadavS.Yadav
4,1433 gold badges37 silver badges42 bronze badges
For those for whom the current answers didn’t work can try this (tested on macOS):
mysql -h localhost -u root -p --protocol=TCP
After this, a password will be asked from you and you should use your OS user password. Then when you get into MySQL you can run:
select Host, User from mysql.user;
And you should see:
MySQL [(none)]> select Host, User from mysql.user;
+-----------+------------------+
| Host | User |
+-----------+------------------+
| localhost | mysql.infoschema |
| localhost | mysql.session |
| localhost | mysql.sys |
| localhost | root |
+-----------+------------------+
And from here you can change the configurations and edit the password or modify the grants.
![]()
answered Nov 25, 2020 at 19:29
![]()
EricEric
4606 silver badges15 bronze badges
3
Please read the official documentation: MySQL: How to Reset the Root Password
If you have access to a terminal:
MySQL 5.7.6 and later:
mysql
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass';
MySQL 5.7.5 and earlier:
mysql
mysql> SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('MyNewPass');
![]()
answered Aug 10, 2015 at 10:05
![]()
d.danailovd.danailov
9,5164 gold badges51 silver badges36 bronze badges
2
I am using mysql-5.7.12-osx10.11-x86_64.dmg on Mac OS X.
The installation process automatically sets up a temporary password for the root user. You should save the password. The password can not be recovered.
Follow the instructions:
- Go to
cd /usr/local/mysql/bin/ - Enter the temporary password (which would look something like, “tsO07JF1=>3”)
- You should get the
mysql>prompt. - Run,
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('{YOUR_PASSWORD}');If you wish to set your password: “root” then the command would be,SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('root'); - Run
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' PASSWORD EXPIRE NEVER; - Run
exit - Run
./mysql -u root -p - Type your password. In my case I would type, “root” (without quote)
- That’s all.
For convenience, you should add "/usr/local/mysql/bin" to your PATH environment variable.
Now from anywhere you can type ./mysql -u root -p and then type the password and you will get the mysql> prompt.
![]()
answered May 30, 2016 at 11:14
tausiqtausiq
9371 gold badge13 silver badges23 bronze badges
The answer may sound silly, but after wasting hours of time, this is how I got it to work:
mysql -u root -p
I got the error message
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: YES)
Even though I was typing the correct password (the temporary password you get when you first install MySQL).
I got it right when I typed in the password when the password prompt was blinking.
![]()
answered Dec 6, 2017 at 3:31
![]()
Amit KumarAmit Kumar
7842 gold badges10 silver badges16 bronze badges
1
Year 2021.
Answer for Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa) (maybe other distributions as well).
After days of wandering around… and having none of those answers working for me, I did this and it worked!
Always in a Bash shell:
sudo systemctl disable mysql
In order to stop the daemon from starting on boot.
sudo apt purge mysql-server
and
sudo apt purge mysql-community-server*
There, it warns you you’ll erase configuration files… so it’s working! Because those are the ones making trouble!
sudo apt autoremove
The command sudo apt autoremove deletes all the left behind packages.
Then (maybe it’s optional, but I did it) reboot.
Also, I downloaded mysql-server-8.0 from the official MySQL webpage:
sudo apt install mysql-server
A signal that it’s working is that when you enter the command above, the system asks you to enter the root password.
Finally:
mysql -u root -p
And the password you entered before.
![]()
CodeWeis
8466 silver badges19 bronze badges
answered Jul 26, 2021 at 3:48
![]()
DiegoMMFDiegoMMF
1191 silver badge3 bronze badges
If you have MySQL as part of a Docker image (say on port 6606) and an Ubuntu install (on port 3306) specifying the port is not enough:
mysql -u root -p -P 6606
will throw:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
as it’s trying to connect to localhost by default, specifying your local IP address fixes the issue:
mysql -u root -p -P 6606 -h 127.0.0.1
![]()
answered Nov 19, 2019 at 11:36
![]()
botrisbotris
1612 silver badges2 bronze badges
If the problem still exists, try to force changing the password.
Stop MySQL Server (on Linux):
/etc/init.d/mysql stop
Stop MySQL Server (on Mac OS X):
mysql.server stop
Start the mysqld_safe daemon with –skip-grant-tables:
mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables &
mysql -u root
Set up a new MySQL root user password:
use mysql;
update user set password=PASSWORD("NEW-ROOT-PASSWORD") where User='root';
flush privileges;
quit;
Stop MySQL Server (on Linux):
/etc/init.d/mysql stop
Stop MySQL Server (on Mac OS X):
mysql.server stop
Start the MySQL server service and test to log in by root:
mysql -u root -p
![]()
answered Jul 26, 2017 at 2:19
Max YaoMax Yao
7116 silver badges7 bronze badges
I also came across the same problem. I did:
-
Open your cmd
-
Navigate to C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 8.0bin>
(where MySQL Server 8.0 may be different depending on the server you installed) -
Then put the following command
mysql -u root -p -
It will prompt for the password… simply hit Enter, as sometimes the password you entered while installing is changed by to blank.
Now you can simply access the database.
This solution worked for me on the Windows platform.
![]()
answered Nov 8, 2019 at 17:08
While the top answer (with mysqladmin) worked on macOS v10.15 (Catalina), it did not work on Ubuntu. Then I tried many of the other options, including a safe start for MySQL, but none worked.
Here is one that does:
At least for the version I got 5.7.28-0ubuntu0.18.04.4 answers were lacking IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password. 5.7.28 is the default on the current LTS and thus should be the default for most new new systems (till Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa) LTS comes out).
I found Can’t set root password MySQL Server and now applied
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'your_pass_here';
which does work.
![]()
answered Dec 9, 2019 at 10:43
arntgarntg
1,53714 silver badges12 bronze badges
By default, the password will be null, so you have to change the password by doing the below steps.
Connect to MySQL
root# mysql
Use mysql
mysql> update user set password=PASSWORD('root') where User='root';
Finally, reload the privileges:
mysql> flush privileges;
mysql> quit
Just one line and it solved my issue.
sudo dpkg-reconfigure mysql-server-5.5
![]()
answered May 11, 2016 at 21:51
![]()
In Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial Xerus) and MySQL version 5.7.13, I was able to resolve the problem with the steps below:
-
Follow the instructions from section B.5.3.2.2 Resetting the Root Password: Unix and Unix-Like Systems
MySQL 5.7 reference manual -
When I tried
#sudo mysqld_safe --init-file=/home/me/mysql-init &it failed. The error was in /var/log/mysql/error.log:2016-08-10T11:41:20.421946Z 0 [Note] Execution of init_file '/home/me/mysql/mysql-init' started. 2016-08-10T11:41:20.422070Z 0 [ERROR] /usr/sbin/mysqld: File '/home/me/mysql/mysql-init' not found (Errcode: 13 - Permission denied) 2016-08-10T11:41:20.422096Z 0 [ERROR] Aborting
The file permission of mysql-init was not the problem. We need to edit AppArmor permissions.
-
Edit by
sudo vi /etc/apparmor.d/usr.sbin.mysqld.... /var/log/mysql/ r, /var/log/mysql/** rw, # Allow user init file /home/pranab/mysql/* r, # Site-specific additions and overrides. See local/README for details. #include <local/usr.sbin.mysqld> } -
Do
sudo /etc/init.d/apparmor reload -
Start mysqld_safe again. Try step 2 above. Check file /var/log/mysql/error.log. Make sure there is no error and the mysqld is successfully started.
-
Run
mysql -u root -pEnter password:
Enter the password that you specified in mysql-init. You should be able to log in as root now.
-
Shutdown mysqld_safe by
sudo mysqladmin -u root -p shutdown -
Start mysqld the normal way by
sudo systemctl start mysql
![]()
answered Aug 10, 2016 at 13:37
codegencodegen
791 silver badge2 bronze badges
The error that I faced was:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: NO)
It was a problem with the port running on.
By default, MySQL is running on port 3306.
You can check that on by running
-
in a 32-bit system:
sudo /opt/lampp/manager-linux.run -
in a 64-bit system:
sudo /opt/lampp/manager-linux-x64.run
and click on the Configure button.

In my case the port was running on 3307, and I used the command
mysql -u root -p -P 3307 -h 127.0.0.1
![]()
answered Mar 12, 2020 at 16:20
RochaaPRochaaP
3055 silver badges14 bronze badges
Copied from this link, I had the same problem and this solved the problem. After we add a password for the database, we need to add -p (password-based login), and then enter the password. Otherwise, it will return this error:
mysql -u root -p
![]()
answered Nov 5, 2020 at 8:07
Because your error message says “PASSWORD: YES” this means you are are using the wrong password. This happened to me also. Luckily I remembered my correct password, and was able to make the DB connection work.
answered May 31, 2022 at 22:17
In recent MySQL versions there isn’t any password in the mysql.user table.
So you need to execute ALTER USER. Put this one line command into the file.
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass';
And execute it as an init file (as the root or mysql user):
mysqld_safe --init-file=/home/me/mysql-init &
MySQL server need to be stopped to start mysqld_safe.
Also, there may be a problem with AppArmor permissions to load this init file. Read more in AppArmor and MySQL.
![]()
answered Jun 9, 2016 at 15:06
If you haven’t set password yet, then run mysql -uroot. It works for me.
![]()
answered Aug 16, 2018 at 11:10
![]()
ah bonah bon
9,1319 gold badges58 silver badges139 bronze badges
On Mac, if you have a problem in logging in with the first password you were given in installation, maybe you can just simply kill the MySQL process and then try.
So:
-
run the following command to find the PID of MySQL:
ps -aef | grep mysql | grep -v grep -
kill the process:
kill -15 [process id]
Then you can log in with the initial password using this command:
mysql -uroot -p
Which asks you to enter your password. Just enter the initial password.
![]()
answered Jan 19, 2019 at 9:22
![]()
Стандарт / от Автора / 18.06.2022 / 2 комментария /
3 способа РЕШЕНИЯ по исправлению ошибки mysqli real connect (): (HY000/1045): Access denied for user ‘username’@’localhost’ на сервере Centos 7 и VestaCP
Ошибка mysqli real connect (): (HY000/1045): Access denied for user ‘username’@’localhost’ очень часто возникает при обновлении версии PHP на веб сервере или самой базы данных, особенно при использовании панели управления VestaCP.
Содержание:
Введение — ошибка mysql 1045
1 способ устранения ошибки mysql 1045
2 способ устранения ошибки mysql 1045
3 способ устранения ошибки mysql 1045
Заключение по устранению ошибки mysql 1045
Введение — ошибка mysql 1045
Прежде чем приступить к устранению данной ошибки, необходимо понять ряд элементарных вещей в работе базы данных MySQL.
Итак:
При создании пользователя базы данных MySQL учитывается 3 параметра, а не два. Первый параметр это username, имя пользователя базы данных, второй параметр, это имя хоста, под именем хоста подразумевается разрешение входа в базу, или с определенного IP адреса, или с определенного домена, или с любой машины кроме локальной, или только с локальной машины. Под локальной машиной подразумевается Ваш сервер, где расположена сама база данных и панель phpmyadmin.
Поясняю:
- Пользователь например, root@localhost имеет имя root, свой пароль и право входить только с локальной машины, то есть с Вашего сервера через командную строку или панель управления.
- Пользователь например, root@’мой домашний ip’ имеет имя root, свой пароль и право входить только с домашнего компьютера.
- Пользователь например, root@’%’ имеет имя root, свой пароль и право входить с любого компьютера, кроме локального, то есть Вашей панели управления веб сервером.
Знак ‘%’ в одинарных кавычках указывает именно на право входить в базу с любого компьютера, кроме локальной машины.
Пользователей с именем root может быть два, три и более. Все эти пользователи будут иметь разные пароли и разные разрешения на вход с определенных хостов.
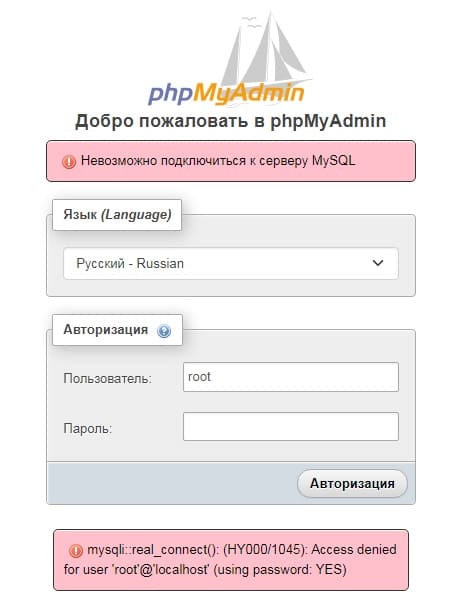
1 способ устранения ошибки mysql 1045
Ошибка 1045
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ root’@’localhost’ (using password: YES)
Самая распространенная и банальная ошибка это неправильная пара логина и пароля для входа в БД. Грубо говоря, Вы можете пытаться входить под пользователем root@’%’, вводя правильный никнейм и пароль через установленную на сервере панель phpmyadmin. Но данный пользователь имеет право заходить с любого компьютера, кроме локальной машины. А панель phpmyadmin как раз является локальной машиной. Таким образом Вы будите получать данную ошибку.
Решение:
Самое простое, это попробовать ввести другой пароль от указанного пользователя. Но пароль может быть задан автоматически (в частности root), может быть пустым или просто утерянным.
Вам необходимо войти в MySQL через терминал в командной строке. Лично я использую программу putty, как и 99% администраторов веб сервера. Для того, чтобы попасть в БД, необходимо предварительно отредактировать конфигурационный файл под названием my.cnf. В операционной системе Centos 7 он находится /etc/my.cnf. Скачайте данный файл с сервера и вставьте в него после такую строку: skip-grant-tables, должно получится примерно так:
[mysqld]
skip-grant-tables
другие параметры
Залейте файл с новыми параметрами на сервер, предварительно удалив старый, а лучше просто переименуйте старый файл. Перезапустите сервер БД через Вашу панель управления.
После редактирования выше указанного файла попасть в MySQL можно без пароля со всеми привилегиями.
Теперь откройте терминал и войдите под пользователем root без пароля, введя команду:
sudo mysql -u root
Далее введите команду:
SELECT user,host,password FROM mysql.user;
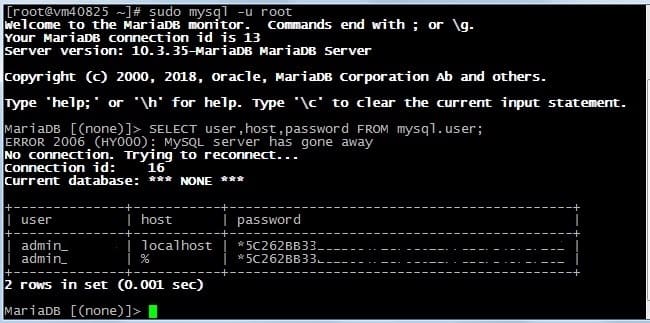
Из таблицы видно, что пользователя root вообще НЕ существует, однако после правки выше указанного конфига, я без труда вошел под root и без пароля. Так же видно из таблицы, что присутствуют 2 пользователя — admin с паролями и доступом с локальной машины (непосредственно с сервера через панель phpmyadmin) и с любого домашнего компьютера через терминал.
Этих пользователей я создавал сам и пароли от них я знаю. Исходя из полученной информации, я могу без труда войти в панель phpmyadmin. И создать любого необходимого пользователя с любыми привилегиями (правами).
Пользователь root отсутствует по причине удаления. Я его просто удалил для написания данной статьи. У вас он скорей всего присутствует и таблица будет гораздо шире. Это просто мой тестовый сервер для экспериментов.
Давайте посмотрим еще один пример с другого сервера.
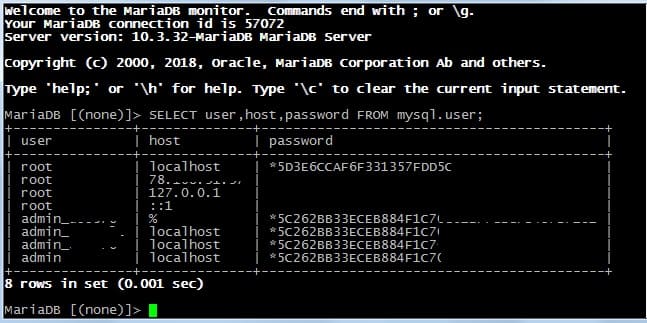
По root у Вас будет примерно такая же картина. То есть один root имеет право войти в панель phpmyadmin с паролем. Один root имеет право на вход через терминал без пароля и т. д. Пароли в БД хранятся в зашифрованном виде.
Получив данную информацию, Вы сможете разобраться с доступами, найти необходимый пароль и войти в панель phpmyadmin.
НО увы, так бывает НЕ всегда!
2 способ устранения ошибки mysql 1045
Как уже писалось в начале статьи данная ошибка возникает после обновления ПО на сервере. И зачастую в панель phpmyadmin просто НЕ попасть. Если из первого раздела Вам не удалось разобраться с пользователями и паролями, то проще всего создать нового пользователя с правами администратора и войти в панель.
Выполнить это можно через терминал. Войдите на сервер через терминал с правами администратора и проверьте есть ли доступ без пароля. Как правило на сервере создается один пользователь root со входом без пароля из терминала. Введите команду:
sudo mysql -u root
Если на сервер баз данных попасть не удалось, то отредактируйте файл (my.cnf), как рассказано в первом способе и повторите команду:
sudo mysql -u root
Теперь, когда в БД удалось попасть через терминал, необходимо создать нового пользователя с паролем и правами админа. Команда:
CREATE USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'ЗДЕСЬ ПАРОЛЬ';
Следующей командой предоставляются права администратора:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION;
После создания нового пользователя, как правило, можно под ним зайти в панель phpmyadmin. Это может быть совсем не обязательно пользователь root, а любой другой. Запомните имя пользователя и пароль, где то запишите себе. Лучше НЕ использовать root при создании нового пользователя.
Внимание!!! Не забудьте обратно отредактировать файл my.cnf, то есть удалить строку — skip-grant-tables.
3 способ устранения ошибки mysql 1045
Пожалуй, самый сложный способ, попытаюсь объяснить простым языком. Дело в том, что root пользователь создается по умолчанию. И если Вы начинаете играться с этим пользователем (root), то Вы нарушите пару логин — пароль. Так как пароль для этого пользователя создается и хранится в нескольких файлах на сервере.
Давайте поставим точку, рассмотрим все эти файлы и при необходимости зададим один пароль к данному юзеру.
Итак,
Файлов к счастью у нас не много, точнее три места которые необходимо проверить и поправить при необходимости.
-
Первое, открываем файл config.inc.php в Centos 7 находится /etc/phpmyadmin/config.inc.php В самый конец этого файла добавьте следующие строки кода:
/* User for advanced features */
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['controluser'] = ' root';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['controlpass'] = 'ЗДЕСЬ ПАРОЛЬ';
- Второе, в файле /usr/local/vesta/conf/mysql.conf. Я использую панель управления VestaCP, если у Вас другая панель, то расположение файла будет отличатся. Откройте данный файл и посмотрите какой там указан пароль, если нужно, то смените на Ваш.
- Третье, это непосредственно сама панель управления phpmyadmin.
Во всех трех местах, должны быть одинаковые пароли от этого юзера. Если не так, то исправляйте. В VestaCP при неправильных паролях в этих файлах может отвалится бэкап.
Заключение по устранению ошибки mysql 1045
Ошибка mysqli real connect 1045, как правило появляется при неправильной паре имя — пароль или после обновления ПО на сервере. Устраняется путем проверки пользователей через терминал и создания новых пользователей. В случаи не корректного пароля от root редактируются необходимые файлы.
P. S.
Я отлавливал все 3 причины сбоя панели управления phpmyadmin и данную статью публикую больше для себя как памятку по устранению неполадок. Но надеюсь Вам она тоже поможет. Оставляйте комментарии по решению данной проблемы.
Думаю, что теперь Вам не страшна ошибка mysqli_connect(): (HY000/1045): Access denied for user ‘username’@’localhost’.
Учебные материалы
Понравился материал? Подписывайтесь на наш блог. И получите бесплатный конструктор лендингов!
Только полезная информация и реальные кейсы
Если вы захотите настроить резервное копирование базы данных на другой сервер, или протестировать соединение с базой данных из другого сервера. И тогда вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой access denied for user root localhost, даже если вы указали верное имя пользователя, базу данных и пароль.
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим почему возникает эта ошибка, а также как ее исправить и подключиться к MySQL из другого сервера через интернет.
Если переводить дословно, то эта ошибка означает что у вас нет доступа к данной базе данных от имени этого пользователя. В примере я использовал пользователя root, но вы можете использовать и другого пользователя. Это может быть вызвано несколькими причинами:
- Пароль введен неверно;
- По каким-либо причинам у пользователя нет прав на доступ к базе данных;
- В настройках этого пользователя запрещено авторизоваться с этого сервера;
Для безопасности базы данных в mysql была придумана настройка хоста, из которого пользователь может авторизоваться. По умолчанию для пользователей устанавливается разрешение на авторизацию только с localhost. Чтобы разрешить подключение с других хостов, нужно менять настройки. Рассмотрим как это делается с помощью Phpmyadmin и в терминале.
Исправляем ошибку access denied for user root localhost
1. Подключение с другого хоста
Сначала рассмотрим как работать с Phpmyadmin. Это намного проще для начинающих и тех, кто не любит работать в терминале. Откройте Phpmyadmin, авторизуйтесь в программе с правами root и перейдите на вкладку “Учетные записи пользователей”:
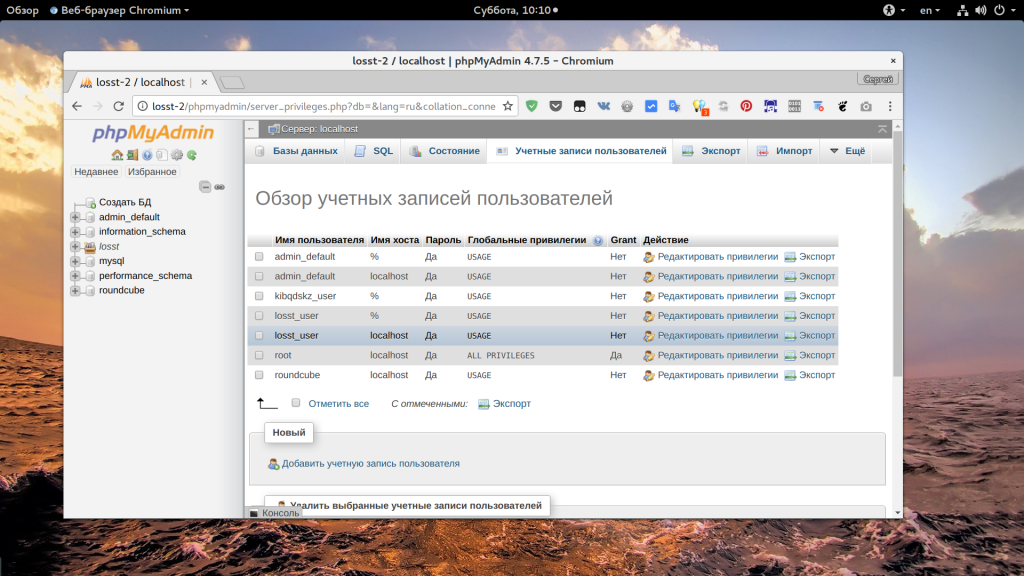
Здесь, вы увидите, кроме обычных полей, поле “имя хоста”, которое указывает с какого хоста может подключаться пользователь. Если в этом поле написано localhost, значит этот пользователь может авторизоваться только с локальной машины. Также, в этом поле может находиться IP адрес, с которого есть разрешение или символ %, который означает, что пользователь может подключаться с любого IP.
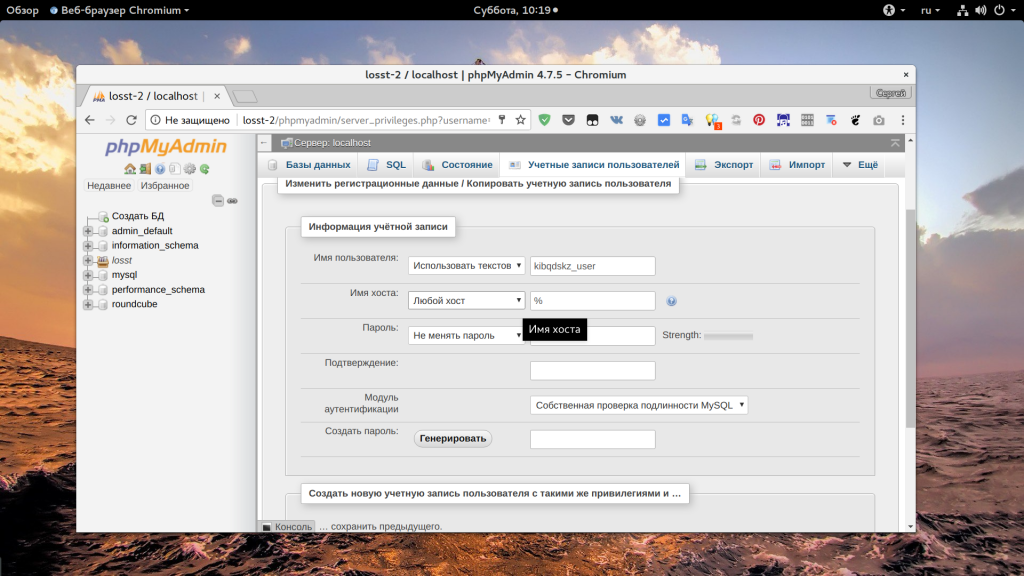
Чтобы изменить права для пользователя, нужно нажать на ссылку “Редактировать привилегии” для него, на открывшейся странице перейдите на вкладку “Информация об учетной записи”:
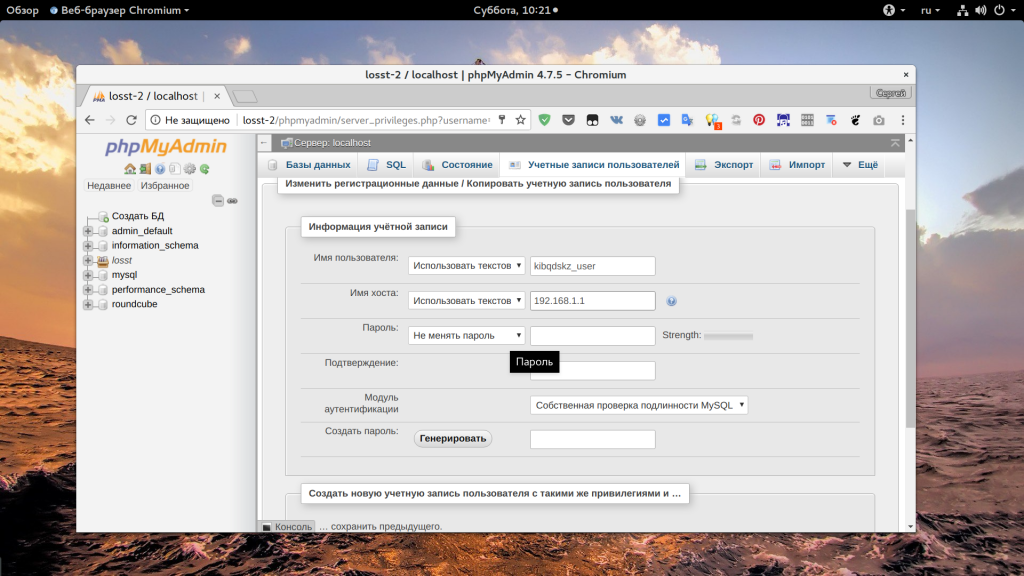
Затем установите в поле “Имя хоста” значение “Любой хост” чтобы разрешить этому пользователю авторизоваться с любого IP. Если вы хотите разрешить только определенный IP, выберите “Использовать текстовое поле” и укажите нужный адрес или подсеть:
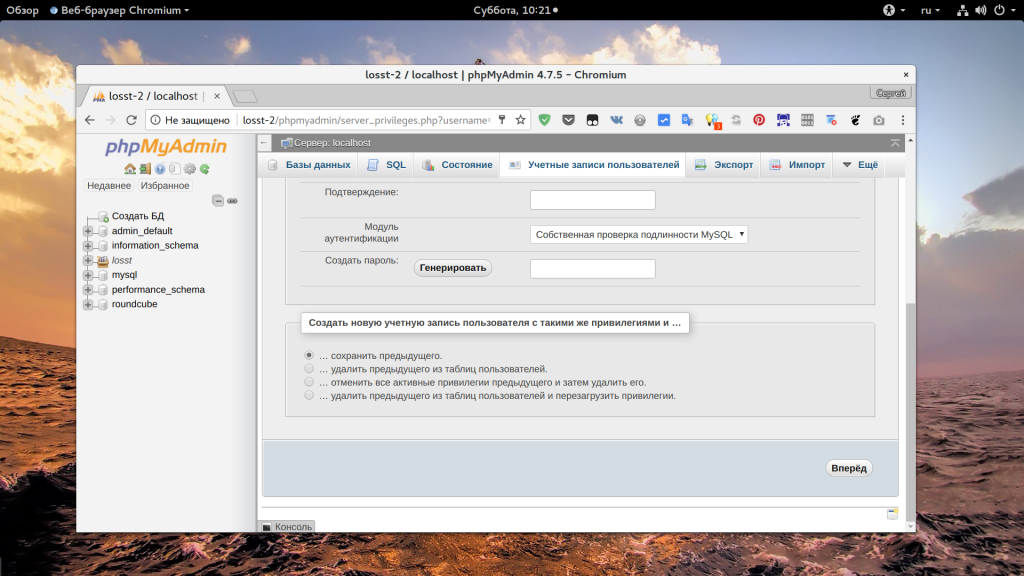
После этого останется нажать кнопку “Вперед” чтобы сохранить настройки. Если вам нужно чтобы был доступ и с локального IP, и с другого, то необходимо создать еще одного пользователя. После этого вы сможете авторизоваться от имени этого пользователя.
Теперь рассмотрим другой способ решить ошибку 1045 access denied for user root localhost, с помощью терминала. Это немного проще, поскольку вам нужно только выполнить несколько команд:
mysql
> UPDATE mysql.user SET Host='%' WHERE Host='localhost' AND User='имя_пользователя';
> UPDATE mysql.db SET Host='%' WHERE Host='localhost' AND User='имя_пользователя';
> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Уже после этого, вы можете подключаться к серверу баз данных с любого другого компьютера и не получите никаких ошибок. Вместо символа %, можно указать нужный ip или localhost, если ограничение нужно вернуть обратно.
2. Неверный пароль root
Иногда случается, что при установке базы данных пароль для root задается, но вы его не знаете. Поскольку это главный пользователь и если вы не можете войти от его имени, то вы не сможете ничего исправить. Сначала попробуйте авторизоваться от имени root в системе и подключиться к базе без пароля:
mysql
Иногда это работает. Если не сработало, остановите службу mysql и запустите ее без проверки безопасности, а затем попробуйте снова:
systemctl stop mysqld
mysqld --skip-grant-tables
mysql
> USE mysql;
> UPDATE user SET Password=PASSWORD('ваш_пароль') where USER='root';
> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Еще можно попытаться выдать права над всеми таблицами нашему пользователю, если это необходимо:
> GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'root'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION;
Обратите внимание на хост localhost, если вы хотите чтобы удаленные узлы тоже могли подключаться к этому пользователю, то нужно использовать %. Дальше можно перезапустить базу данных и работать как обычно.
Выводы
Теперь вы знаете как решается mysql access denied for user root localhost и что делать в таких ситуациях, чтобы решить проблему. Надеюсь, эта информация была полезной для вас. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
https://youtu.be/avnitMoiJww
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.

Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
Об авторе
![]()
Основатель и администратор сайта losst.ru, увлекаюсь открытым программным обеспечением и операционной системой Linux. В качестве основной ОС сейчас использую Ubuntu. Кроме Linux, интересуюсь всем, что связано с информационными технологиями и современной наукой.
Дата: 25.11.2013
Автор: Василий Лукьянчиков , vl (at) sqlinfo (dot) ru
Статистика форума SQLinfo показывает, что одной из наиболее популярных проблем является ошибка mysql №1045 (ошибка доступа).
Текст ошибки содержит имя пользователя, которому отказано в доступе, компьютер, с которого производилось подключение, а также ключевое слово YES или NO, которые показывают использовался ли при этом пароль или была попытка выполнить подключение с пустым паролем.
Типичные примеры:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) — сервер MySQL
— сообщает, что была неудачная попытка подключения с локальной машины пользователя с именем root и
— не пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в
— доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем root при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в
— доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем ODBC при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
Причина возникновения ошибки 1045
Как ни банально, но единственная причина это неправильная комбинация пользователя и пароля. Обратите внимание, речь идет о комбинации пользователь и пароль, а не имя пользователя и пароль. Это очень важный момент, так как в MySQL пользователь характеризуется двумя параметрами: именем и хостом, с которого он может обращаться. Синтаксически записывается как ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’.
Таким образом, причина возникновения MySQL error 1045 – неправильная комбинация трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля.
В качестве имени хоста могут выступать ip адреса, доменные имена, ключевые слова (например, localhost для обозначения локальной машины) и групповые символы (например, % для обозначения любого компьютера кроме локального). Подробный синтаксис смотрите в документации
Замечание: Важно понимать, что в базе не существует просто пользователя с заданным именем (например, root), а существует или пользователь с именем root, имеющий право подключаться с заданного хоста (например, root@localhost) или даже несколько разных пользователей с именем root (root@127.0.0.1, root@webew.ru, root@’мой домашний ip’ и т.д.) каждый со своим паролем и правами.
Примеры.
1) Если вы не указали в явном виде имя хоста
GRANT ALL ON publications.* TO ‘ODBC’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘newpass’;
то у вас будет создан пользователь ‘ODBC’@’%’ и при попытке подключения с локальной машины вы получите ошибку:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
так как пользователя ‘ODBC’@’localhost’ у вас не существует.
2) Другой первопричиной ошибки mysql 1045 может быть неправильное использование кавычек.
CREATE USER ‘new_user@localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘mypass’; — будет создан пользователь ‘new_user@localhost’@’%’
Правильно имя пользователя и хоста нужно заключать в кавычки отдельно, т.е. ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’
3) Неочевидный вариант. IP адрес 127.0.0.1 в имени хоста соответствует ключевому слову localhost. С одной стороны, root@localhost и ‘root’@’127.0.0.1’ это синонимы, с другой, можно создать двух пользователей с разными паролями. И при подключении будет выбран тот, который распологается в таблице привелегий (mysql.user) раньше.
4) Аккаунт с пустым именем пользователя трактуется сервером MySQL как анонимный, т.е. позволяет подключаться пользователю с произвольным именем или без указания имени.
Например, вы создали пользователя ”@localhost с пустым паролем, чтобы каждый мог подключиться к базе. Однако, если при подключении вы укажите пароль отличный от пустого, то получите ошибку 1045. Как говорилось ранее, нужно совпадение трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля, а пароль в данном случае не совпадает с тем, что в базе.
Что делать?
Во-первых, нужно убедиться, что вы используете правильные имя пользователя и пароль. Для этого нужно подключиться к MySQL с правами администратора (если ошибка 1045 не дает такой возможности, то нужно перезапустить сервер MySQL в режиме –skip-grant-tables), посмотреть содержимое таблицы user служебной базы mysql, в которой хранится информация о пользователях, и при необходимости отредактировать её.
Пример.
SELECT user,host,password FROM mysql.user;
+—————+—————–+——————————————-+
| user | host | password |
+—————+—————–+——————————————-+
| root | house-f26710394 | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
| aa | localhost | *196BDEDE2AE4F84CA44C47D54D78478C7E2BD7B7 |
| test | localhost | |
| new_user | % | |
| | % | *D7D6F58029EDE62070BA204436DE23AC54D8BD8A |
| new@localhost | % | *ADD102DFD6933E93BCAD95E311360EC45494AA6E |
| root | localhost | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
+—————+—————–+——————————————-+
Если изначально была ошибка:
-
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
значит вы указывали при подключении неверный пароль, так как пользователь root@localhost существует. Сам пароль храниться в зашифрованном виде и его нельзя узнать, можно лишь задать новый
SET PASSWORD FOR root@localhost=PASSWORD(‘новый пароль’);
-
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
в данном случае в таблице привилегий отсутствует пользователь ‘ODBC’@’localhost’. Его нужно создать, используя команды GRANT, CREATE USER и SET PASSWORD.
Экзотический пример. Устанавливаете новый пароль для root@localhost в режиме –skip-grant-tables, однако после перезагрузки сервера по прежнему возникает ошибка при подключении через консольный клиент:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
Оказалось, что было установлено два сервера MySQL, настроенных на один порт.
phpmyadmin
При открытии в браузере phpmyadmin получаете сообщение:
Error
MySQL said:
#1045 – Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: NO)
Connection for controluser as defined in your configuration failed.
phpMyAdmin tried to connect to the MySQL server, and the server rejected the connection. You should check the host, username and password in your configuration and make sure that they correspond to the information given by the administrator of the MySQL server.
Ни логина, ни пароля вы не вводили, да и пхпадмин их нигде требовал, сразу выдавая сообщение об ошибке. Причина в том, что данные для авторизации берутся из конфигурационного файла config.inc.php Необходимо заменить в нем строчки
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘user’] = ‘root’; // MySQL user
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = ”; // MySQL password (only needed
на
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘user’] = ‘ЛОГИН’;
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = ‘ПАРОЛЬ’
Установка новой версии
Устанавливаете новую версию MySQL, но в конце при завершении конфигурации выпадает ошибка:
ERROR Nr. 1045
Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO)
Это происходит потому, что ранее у вас стоял MySQL, который вы удалили без сноса самих баз. Если вы не помните старый пароль и вам нужны эти данные, то выполните установку новой версии без смены пароля, а потом смените пароль вручную через режим –skip-grant-tables.
P.S. Статья написана по материалам форума SQLinfo, т.е. в ней описаны не все потенциально возможные случаи возникновения ошибки mysql №1045, а только те, что обсуждались на форуме. Если ваш случай не рассмотрен в статье, то задавайте вопрос на форуме SQLinfo
Вам ответят, а статья будет расширена.
Дата публикации: 25.11.2013
© Все права на данную статью принадлежат порталу SQLInfo.ru. Перепечатка в интернет-изданиях разрешается только с указанием автора и прямой ссылки на оригинальную статью. Перепечатка в бумажных изданиях допускается только с разрешения редакции.
 During our work in support, we see this again and again: “I try to connect to MySQL and am getting a 1045 error”, and most times it comes accompanied with “…but I am sure my user and password are OK”. So we decided it was worth showing other reasons this error may occur.
During our work in support, we see this again and again: “I try to connect to MySQL and am getting a 1045 error”, and most times it comes accompanied with “…but I am sure my user and password are OK”. So we decided it was worth showing other reasons this error may occur.
MySQL 1045 error Access Denied triggers in the following cases:
1) Connecting to wrong host:
|
[engineer@percona]# mysql -u root -psekret mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure. ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) |
If not specifying the host to connect (with -h flag), MySQL client will try to connect to the localhost instance while you may be trying to connect to another host/port instance.
Fix: Double check if you are trying to connect to localhost, or be sure to specify host and port if it’s not localhost:
|
[engineer@percona]# mysql -u root -psekret -h <IP> -P 3306 |
2) User does not exist:
|
[engineer@percona]# mysql -u nonexistant -psekret -h localhost mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure. ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘nonexistant’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) |
Fix: Double check if the user exists:
|
mysql> SELECT User FROM mysql.user WHERE User=‘nonexistant’; Empty set (0.00 sec) |
If the user does not exist, create a new user:
|
mysql> CREATE USER ‘nonexistant’@‘localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘sekret’; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) |
3) User exists but client host does not have permission to connect:
|
[engineer@percona]# mysql -u nonexistant -psekret mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure. ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘nonexistant’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) |
Fix: You can check to see which host user/host MySQL allows connections with the following query:
|
mysql> SELECT Host, User FROM mysql.user WHERE User=‘nonexistant’; +————-+————-+ | Host | User | +————-+————-+ | 192.168.0.1 | nonexistant | +————-+————-+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
If you need to check from which IP the client is connecting, you can use the following Linux commands for server IP:
|
[engineer@percona]# ip address | grep inet | grep -v inet6 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo inet 192.168.0.20/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic wlp58s0 |
or for public IP:
|
[engineer@percona]# dig +short myip.opendns.com @resolver1.opendns.com 177.128.214.181 |
You can then create a user with correct Host (client IP), or with ‘%’ (wildcard) to match any possible IP:
|
mysql> CREATE USER ‘nonexistant’@‘%’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘sekret’; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) |
4) Password is wrong, or the user forgot his password:
|
[engineer@percona]# mysql -u nonexistant -pforgotten mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure. ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘nonexistant’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) |
Fix: Check and/or reset password:
You cannot read user passwords in plain text from MySQL as the password hash is used for authentication, but you can compare hash strings with “PASSWORD” function:
|
mysql> SELECT Host, User, authentication_string, PASSWORD(‘forgotten’) FROM mysql.user WHERE User=‘nonexistant’; +————-+————-+——————————————-+——————————————-+ | Host | User | authentication_string | PASSWORD(‘forgotten’) | +————-+————-+——————————————-+——————————————-+ | 192.168.0.1 | nonexistant | *AF9E01EA8519CE58E3739F4034EFD3D6B4CA6324 | *70F9DD10B4688C7F12E8ED6C26C6ABBD9D9C7A41 | | % | nonexistant | *AF9E01EA8519CE58E3739F4034EFD3D6B4CA6324 | *70F9DD10B4688C7F12E8ED6C26C6ABBD9D9C7A41 | +————-+————-+——————————————-+——————————————-+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) |
We can see that PASSWORD(‘forgotten’) hash does not match the authentication_string column, which means password string=’forgotten’ is not the correct password to log in. Also, in case the user has multiple hosts (with different password), he may be trying to connect using the password for the wrong host.
In case you need to override the password you can execute the following query:
|
mysql> set password for ‘nonexistant’@‘%’ = ‘hello$!world’; Empty set (0.00 sec) |
5) Special characters in the password being converted by Bash:
|
[engineer@percona]# mysql -u nonexistant -phello$!world mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure. ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘nonexistant’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) |
Fix: Prevent bash from interpreting special characters by wrapping password in single quotes:
|
[engineer@percona]# mysql -u nonexistant -p’hello$!world’ mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure ... mysql> |
6) SSL is required but the client is not using it:
|
mysql> create user ‘ssluser’@‘%’ identified by ‘sekret’; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> alter user ‘ssluser’@‘%’ require ssl; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) ... [engineer@percona]# mysql -u ssluser -psekret mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure. ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ssluser’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) |
Fix: Adding –ssl-mode flag (–ssl flag is deprecated but can be used too)
|
[engineer@percona]# mysql -u ssluser -psekret –ssl-mode=REQUIRED ... mysql> |
You can read more in-depth on how to configure SSL in MySQL in the blog post about “Setting up MySQL SSL and Secure Connections” and “SSL in 5.6 and 5.7“.
7) PAM backend not working:
|
mysql> CREATE USER ‘ap_user’@‘%’ IDENTIFIED WITH auth_pam; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) ... [engineer@percona]# mysql -u ap_user -pap_user_pass mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure. ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ap_user’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) |
Fix: Double check user/password is correct for the user to authenticate with the PAM currently being used.
In my example, I am using Linux shadow files for authentication. In order to check if the user exists:
|
[engineer@percona]# cat /etc/passwd | grep ap_user ap_user:x:1000:1000::/home/ap_user:/bin/bash |
To reset password:
|
[engineer@percona]# sudo passwd ap_user Changing password for user ap_user. New password: |
Finally, if you are genuinely locked out and need to circumvent the authentication mechanisms in order to regain access to the database, here are a few simple steps to do so:
- Stop the instance
- Edit my.cnf and add skip-grant-tables under [mysqld] (this will allow access to MySQL without prompting for a password). On MySQL 8.0, skip-networking is automatically enabled (only allows access to MySQL from localhost), but for previous MySQL versions it’s suggested to also add –skip-networking under [mysqld]
- Start the instance
- Access with root user (mysql -uroot -hlocalhost);
-
Issue the necessary GRANT/CREATE USER/SET PASSWORD to correct the issue (likely setting a known root password will be the right thing: SET PASSWORD FOR ‘root’@’localhost’ = ‘S0vrySekr3t’). Using grant-skip-tables won’t read grants into memory and GRANT/CREATE/SET PASSWORD statements won’t work straight away. First, you need to execute “FLUSH PRIVILEGES;” before executing any GRANT/CREATE/SET PASSWORD statement, or you can modify mysql.users table with a query which modifies the password for User and Host like “UPDATE mysql.user SET authentication_string=PASSWORD(‘newpwd’) WHERE User=’root’ and Host=’localhost’;”
- Stop the instance
- Edit my.cnf and remove skip-grant-tables and skip-networking
- Start MySQL again
- You should be able to login with root from the localhost and do any other necessary corrective operations with root user.
Learn more about Percona Server for MySQL
