«403 Forbidden» – наиболее распространенная ошибка при работе с NGINX. В этой статье мы расскажем о причинах возникновения 403 forbidden NGINX, а также о том, как найти ее причину и исправить основную проблему.
- Об ошибке
- Поиск файла конфигурации NGINX
- Некорректный индексный файл
- Автоиндекс
- Права доступа к файлам
- Идентификация пользователя NGINX
- Установите права собственности на файл
- Установите права доступа
«403 Forbidden» – это универсальная ошибка NGINX, которая указывает на то, что вы запросили что-то, а NGINX (по ряду причин) не может это предоставить. «403» является кодом состояния HTTP, который означает, что веб-сервер получил и понял ваш запрос, но не может предпринять никаких дальнейших действий.
По умолчанию файлы конфигурации NGINX находятся в папке /etc/nginx. Если вы просмотрите этот каталог, то найдете несколько конфигурационных файлов для различных модулей сервера.
Главный файл конфигурации – /etc/nginx/nginx.conf. Он содержит основные директивы для NGINX и является аналогом файла httpd.conf для Apache.
Чтобы отредактировать этот файл, используйте команду:
CentOS 7: sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/test.example.com.conf Ubuntu 16.04: sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/test.example.com.conf
Одна из наиболее распространенных причин ошибки 403 forbidden NGINX – некорректная настройка индексного файла.
nginx.conf указывает, какие индексные файлы должны загружаться, и в каком порядке. Например, приведенная ниже строка указывает NGINX искать index.html, затем index.htm, затем index.php:
index index.html index.htm index.php;
Если ни один из этих трех файлов не будет найден в каталоге, NGINX вернет ошибку «403 Forbidden».
Примечание. Имена файлов чувствительны к регистру. Если nginx.conf указывает index.html, а файл называется Index.html, это приведет к ошибке «403 Forbidden».
Если вы хотите использовать имя индексного файла, которое ваш веб-сервер NGINX не распознает, отредактируйте nginx.conf и добавьте имя файла в строку конфигурации индекса.
Например, чтобы добавить index.py в список распознаваемых индексных файлов, отредактируйте эту строку следующим образом:
index index.html index.htm index.php index.py;
Сохраните изменения, а затем перезапустите NGINX командой:
Альтернативным решением является разрешение индекса директории. Индекс директории означает, что если индексный файл не найден, сервер отобразит все содержимое директории.
По соображениям безопасности индекс директории в NGINX по умолчанию отключен.
При «403 forbidden NGINX», если вы хотите показать индекс директории в ситуациях, когда NGINX не может найти (идентифицировать) файл, отредактируйте nginx.conf, как описано выше, и добавьте в него две следующие директивы:
Autoindex on; Autoindex_exact_size off;
Эти директивы должны быть добавлены в блок location. Можно либо добавить их в существующий блок location/, либо добавить новый. Окончательный результат должен выглядеть так:
location / {
[pre-existing configurations, if applicable]
autoindex on;
autoindex_exact_size off;
}
Также можно активировать индексирование директории в определенной папке, если не хотите, чтобы она была доступна для всего сайта:
location /myfiles {
autoindex on;
autoindex_exact_size off;
}
Сохраните изменения в файле, затем перезапустите NGINX командой:
Некорректные права доступа к файлам являются еще одной причиной ошибки «403 Forbidden NGINX». Для использования с NGINX рекомендуется стандартная настройка: для каталогов – 755 и для файлов – 644. Пользователь NGINX также должен быть владельцем файлов.
Для начала нужно определить, от имени какого пользователя запущен NGINX. Для этого используйте команду:
В этом примере рабочий процесс NGINX работает от имени пользователя nginx.
Перейдите на уровень выше корневой директории документа сайта. Например, если корневая директория вашего сайта /usr/share/nginx/example.com, перейдите в /usr/share/nginx с помощью команды:
Измените права собственности на все файлы в директориях нижних уровней на пользователя nginx с помощью команды:
sudo chown -R nginx:nginx *
403 forbidden NGINX – как исправить: установите права доступа для каждой директории на 755 с помощью команды:
sudo chmod 755 [имя директории]
Например, чтобы установить права доступа для директории example.com, используется команда:
sudo chmod 755 example.com
Затем перейдите в корневой каталог веб-документа:
sudo chmod 755 example.com
Измените права доступа для всех файлов в этой директории с помощью команды:
- Private Cloud
- Public Cloud
-
- Cloud Servers
- Cloud Networks
- Cloud Load Balancers
- DNS
-
- Object Storage
- Cloud Block Storage
- Cloud File Sharing
-
- Identity Authentication
- Cloud Image Service
- Key Management
-
- Certified Kubernetes
-
- Orchestration
-
- Big Data Services
-
- Solutions
-
- OpenStack Consulting
- OpenStack Upgrades
-
- Kubernetes Enablement
- Managed Zuul
-
- Resources
-
- Blog
- Ebooks & White Papers
- Tutorials
-
- Success Stories
- FAQs
- Videos
-
- VEXXHOST
-
- Company
- Data Center Locations
- Brand Guide
-
- Newsroom
- Events
- Careers
-
HTTP errors are pesky and typically hard to resolve without the right tools. However, with proper investigation and tools, you can easily identify the source of a problem and fix it just as fast. In order to debug or fix 403 Forbidden Nginx errors, all you have to do is check the correct error logs and take the proper action to resolve it. We’ll go over how to check the error logs and the possible scenarios that typically cause these errors.
Finding Error Logs
If you know exactly where the error logs of your Nginx server are, you can skip onto the next section. If you’re not sure where to find the error logs of your Nginx server, then be sure to continue this section.
The path for error logs can change a lot depending on how Nginx was installed on the server and the Linux distribution. If you do not know where your error logs are and you have a hard time going through Nginx configuration, we can use a very small and useful Linux tool with the name of lsof which gives us all the open files associated to a specific process. This will help us find the error log for your web server.
The first step of this is to check for the process ID of the main Nginx process, you can run the following command and except output somewhat similar to the one indicated below:
$ ps x | grep nginx
29229 ? S 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx
The first column of each row is the process ID, as we can see, the main/master process ID is 29229 in this case, however this will change in every system. Once you have the process ID, you will be able to use the lsof too to get all open files associated to this process by running the following. We’ve trimmed the output to the part you should be looking for, as there might be a lot more data when you run that command:
$ lsof -p 29229
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
nginx 29229 root cwd DIR 202,1 4096 2 /
nginx 29229 root rtd DIR 202,1 4096 2 /
nginx 29229 root txt REG 202,1 843656 1182 /usr/sbin/nginx
...
nginx 29229 root 2w REG 202,1 0 262748 /var/log/nginx/error.log
...
As you can see from the above output, we can see that one of the files that are open by this Nginx installation is /var/log/nginx/error.log which (by the file name) does look like an error log. We’ve now identified the path of our Nginx error log and we can move onto finding the reason behind our pesky HTTP error.
Fixing Nginx HTTP errors
Once you have the correct error log file, it’s time to watch for errors. In our experience, the best way to do this is by running a continuous stream of the error log in your shell screen using the tail utility.
$ tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
Once you’ve ran this command, tail will continuously output any newly appended content to the error.log as it comes in until you hit Control + C. We recommend that you clear the entire shell screen to make it easy to identify newly appended content. You can do this in Windows (PuTTY) by right clicking the PuTTY menu bar and clicking on “Clear Scrollback” or on Mac OS X by clicking Command + K.
Now, you will need to replicate the issue that you are getting. The error should be printed out right away after you replicate the issue. For example, if you have a 403 Forbidden error, then you should refresh the page that is causing the problem so that a new error log entry can be appended. Once that is done, you’ll see a new line in the error log which should hopefully lead you to the right path to fixing the issue. We’re going to cover a few of the most common issues below.
Incorrect Directory Settings
The error below can be caused by two different reasons: incorrect directory index or disallowed directory listing.
2013/08/31 15:03:43 [error] 29231#0: *2098806 directory index of "/usr/share/nginx/static/" is forbidden, client: 1.1.1.1, server: domain.com, request: "GET / HTTP/1.1", host: "domain.com"
If you are trying to list all the files in a folder, you will get that error if the directory does not have directory listing enabled. You can enable directory listing by adding the following line to your Nginx configuration, you can read more about this option here: http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_autoindex_module.html
autoindex on;
The other possibility for that error to come up is if your index setting is incorrect, so for example, you have a index.php file in that folder, however, your index setting is setup to index.htm and index.html. This means that only these files are checked if no specific file is provided. If you alter it to something like the following, your index.php file should work:
index index.htm index.html index.php;
Incorrect Permissions
The error below is generally caused by incorrect Unix permissions, you will need to make sure you have the correct permissions for the entire path.
2013/09/01 00:31:57 [error] 29231#0: *2115270 open() "/usr/share/nginx/static/forbidden" failed (13: Permission denied), client: 1.1.1.1, server: domain.com, request: "GET /forbidden HTTP/1.1", host: "domain.com"
As you see, the file that we are trying to access is /usr/share/nginx/static/forbidden. In order for Nginx to access it with no problems at all, Nginx must have read permissions for that specific file as well as execute for all the folders above it. This means that /, /usr, /usr/share, /usr/share/nginx and /usr/share/nginx/static must be executable by Nginx and the file /usr/share/nginx/static/forbidden must be readable by Nginx in this case.
Conclusion
We’ve gone through quite a few tools such as tail and lsof. These are just one of the tools which are offered by Linux which allow system administrators to resolve and debug issues much faster and easier. The most important factor in resolving system issues is being able to identify the issue properly, resolution is usually the easiest part once the problem is identified. The larger the toolset of the system administrator, the faster they can identify and fix those problems.
Would you like to know about Zuul, a CI/CD project gating tool? Download our white paper and get reading!
Are you stuck with Nginx 403 forbidden error? We can help you in fixing it.
This error occurs mainly due to incorrect set up of index file and wrong file permissions.
At Bobcares, we often receive requests to fix this error as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s discuss how our Support Engineers fix this error easily for our customers.
Why does Nginx 403 forbidden error occur?
Before discussing how to fix the error, let’s have a look at the error.
Usually, it is quite common to find the 403 forbidden error when dealing with Nginx.
And, this error occurs when Nginx cannot deliver the requested process.
Also, the location of the Nginx configuration files is by default /etc/nginx.
The major causes of this error are incorrect settings in the index file and wrong file permissions.
How we fix the forbidden error?
Now, let’s check the major causes in detail and discuss their respective fixes by our Support Engineers.
Wrong file permissions
One major cause of Nginx 403 error is the incorrect file permissions.
By default, the standard permission for the directory is 755 and that of the file is 644.
And, any error with these permissions will result in 403 forbidden.
Also, it is necessary that the Nginx user must be the owner of the files.
We change the ownership of all the files to the Nginx user with the command,
sudo chown -R nginx:nginx *Also, we change the permissions of each directory to 755 using the command,
sudo chmod 755 [directory name]Similarly, we go to the directory and change the permissions of all the files using the following command.
sudo chmod 644 *Incorrect setting up of index file
The Nginx configuration file will specify the index files to load and the order in which they should load.
And, incorrect set up of the index file will cause this error. For instance, we will give it as follows,
The above line shows that the index.html will load first and then the index.php file.
If these files are not found in the directory, it will result in a 403 forbidden error.
Similarly, if we want to load another index file, we will add it along with the list of recognized index files.
[Need more assistance to fix this error?- We’re available 24/7.]
Conclusion
In short, Nginx 403 forbidden error occurs due to incorrect set up of index file and wrong file permissions. In today’s writeup, we discussed how our Support Engineers fix this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = “owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM”;
Introduction to Nginx Forbidden
We are facing the Nginx forbidden error many times in our application; we are facing this error while using the nginx server. Also, most time, this is not related to the nginx server. Nginx forbidden error contains error code 403, which means we have no permission to access specified web parts. So this error will cause many reasons in our application; investigating the error cause is very important.
What is Nginx Forbidden 403?
For debugging and fixing the error of 403 nginx forbidden, we need to check the correct error logs and take proper action. The nginx forbidden 403 error is the nginx server’s way of telling the user that we are requesting for resource, but we cannot give it to us. Nginx forbidden 403 is technically not an error, but it contains the status code of http. Response code of 403 headers is intentionally returned in multiple cases, like the user is blocked from requesting the page, resource, or whole site of the application.
How to Fix Nginx 403 Forbidden Error?
When dealing with web resources and servers, we encounter errors that cause at the time of performing configurations and maintenance. At the time of meeting this error, we need to fix the same as soon as possible.
Nginx 403 forbidden error is nothing but will generate the status code and display it on the user’s screen when a client tries to access part of the web server with insufficient permission.
The figure below shows the error message that will occur on the user’s screen when this error occurs.
Below is the cause of the nginx 403 forbidden error and how we can fix the same user-specified action. To improve the issue of nginx forbidden 403, first, we need to install the nginx server in our system.
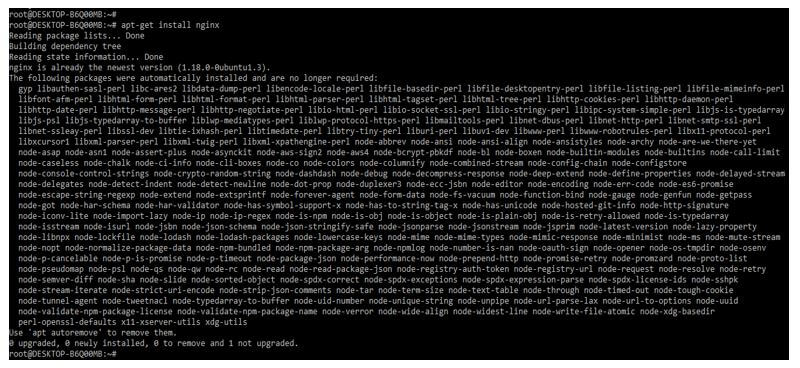
Below we are installing the nginx server on the ubuntu system. We are installing the nginx server by using the apt-get command as follows.
Code:
apt-get install nginxOutput:
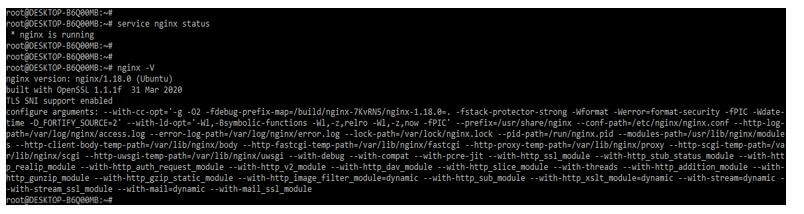
After installing the nginx server, we check the nginx installed version by using the following command. We can check the nginx version and the running status of the nginx server.
Code:
nginx –VOutput:
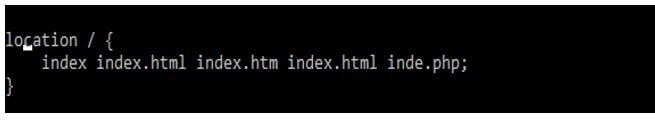
The common cause of this error is an incorrect configuration file of the index section. The nginx will specify which index file we need to load and the order in which we are loading; it determines that the index file is not in the directory. So we need to define the below index file and load it; we need to define the index files into the location directive as follows.
Code:
location / {
index index.html index.htm index.html inde.php;
}Output:
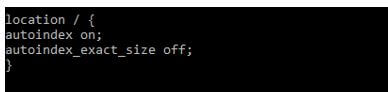
The index page was located in the directory from which the auto index parameter was off. Therefore, we can on the auto index parameter of the index by using the following way as follows.
Code:
location / {
autoindex on;
autoindex_exact_size off;
}Output:
After changing the configuration, we need to reboot the nginx server to take the effect of the changed port. Before restarting the nginx server, we execute the nginx –t command to check whether the nginx configuration file contains any error or not.
Code:
nginx –t
service nginx restartOutput:
Nginx 403 Forbidden HTTP
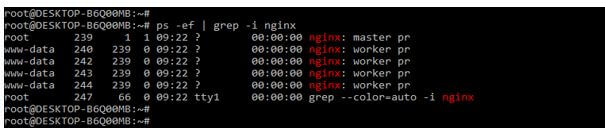
It http contains the different causes of these errors. First, we check the process ID of our nginx server to check the server state it is running or not; we can use the following command to find the process ID.
Code:
ps –ef | grep –i nginxOutput:
The error of nginx 403 forbidden also occurs due to directory restrictions by using IP. We need to check; we need to check the config file in case we have to allow or deny the rule of blocking the network. We must comment that line into the configuration file if we deny any IP. Or we can let all the network traffic of our website by allowing all rules as follows. We need to define this rule in the location directive of the nginx configuration file.
Code:
location / {
# deny 192.168.1.1;
# allow 192.168.1.0/24;
allow all;
}Output:
Http 403 forbidden error will occur by using multiple reasons, but all the errors are the same, like we have no access to the data directory or file we are accessing. So when we encounter an nginx forbidden error, we need to try debugging the mistake using the suggested suggestions.
Incorrect Setting Nginx Forbidden
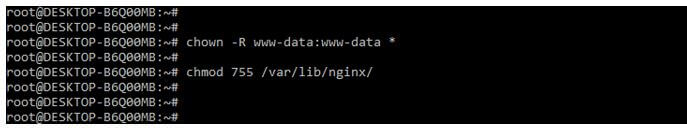
The nginx 403 forbidden will also result in setting incorrect permission of folders and files. Nginx will successfully serve specific resources and files to the client; nginx will contain the read, write and execute permissions on the entire path. To resolve this error, we need to change the permission of the data directory to 755 and file permission to 644. In addition, we need to ensure that the user who was running owns the nginx files.
Code:
chown -R www-data:www-data *
chmod 755 /var/lib/nginx/Output:
This error may occur from the server side as well as the client side.
To resolve the client-side issue, we need to perform the following client-side operations as follows:
- First, we must ensure that we are accessing the correct location on the web.
- We need to clear the browser cache when this type of issue occurs.
- We must ensure that a proxy or firewall will allow us to access the web resources.
If suppose we are unsure how to fix the issue of nginx forbidden, then we can investigate the same by using the error log.
Conclusion
The nginx forbidden 403 error is the nginx server’s way of telling the user that we are requesting for resource, but we cannot give it to us. Nginx forbidden error contains error code 403, which means we have no permission to access specified web parts.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Nginx Forbidden. Here we discuss the introduction and how to fix the nginx 403 forbidden error with an incorrect setting. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
- Nginx Add_header
- Nginx Location Directive
- Nginx WAF
- Nginx FastCGI
The 403 Forbidden error is the most common error encountered while working on Nginx web server. But most of the time, it is not related to Nginx itself. 403 Forbidden error means that you don’t have permission to access certain directory or a web page. This error can be caused due to many reason. And in this article we will identify the source of the error and then we will learn how to Fix it.
About 403 Error
Let’s understand “403 Forbidden” error in details.
“403 Forbidden” is an error which indicates that you have requested for something that NGINX cannot deliver. This error is actually an HTTP status code which simply means that the web server has received and understood the request which is made, but cannot process further.
1. Wrong Directory or File permissions
Incorrect file permissions are one of the most common cause of this “403 Forbidden” error. In case of NGINX, the standard permission settings for directories and and file are 755 and 644 respectively. Moreover, the NGINX user also needs to be the owner of the directory and files.
Identify the NGINX User
To begin, we first need to identify the NGINX user. To check the user, run:
ps -ef | grep nginx
Output:
userwv+ 6016 26683 0 19:28 ttyS0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx root 26734 1 0 Mar20 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin; www-data 26739 26734 0 Mar20 ? 00:01:53 nginx: worker process
In our case, we can identify the NGINX worker processe in the third row of the first column.
We can see that the NGINX worker process is running as the user www-data.
Set File Ownership
Since we already know that the standard permission for the directory in case of Nginx is 755 and that of the file is 644. We need to set the file ownership.
For example, if the root folder of your website is /var/www/html/example.com/public_html/, run:
+
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/example.com/public_html/
Set Directory Permissions
Now we need to set 755 permissions on each directory in this location.
sudo chmod 755 [directory name]
In our case, we need to set permission on example.com directory. To achieve that, run:
sudo chmod 755 example.com
Now, navigate to the root directory of the website by running:
cd example.com
Now change the file permission to 644 by running:
sudo chmod 644 *
2. Incorrect Index File
The “403 Forbidden” error can appear if the index file is not set properly.
+
Navigate to the NGINX configuration file and check whether you have updated correct index file or not. To do that, open our NGINX configuration file for example.com, by running:
sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com
For example, if you’re running a WordPress based website, inside the server block your index should be:
index index.php;
If you’re running an HTML based website, your default file must contain .html extension. e.g.,
index index.html;
Chances are there that you might have forgotten to add this line inside the server block. If you have included this line of code, you must check whether you have spelled it correctly or not.
Moreover, you also must keep in mind that these file names are case-sensitive. If the default file name is index.html but the file is named mentioned in NGINX configuration is Index.html, this will throw “403 Forbidden” error.
If you are running some web application that NGINX is not able to recognize, you can edit configuration file and add the file extension.
For example, if you’re running a python based application, you can add index.py to the list of recognized index files:
index index.py;
In case you’re running a web application that uses multiple programming languages, you can add:
index index.php index.html index.py;
Now, update the changes in the configuration file and restart NGINX by running:
sudo nginx -s reload
or
sudo service nginx restart
Autoindex
It is an alternative solution which is useful if you don’t have any index file or no index file is found by NGINX.
The the server will scan and list all of the contents of your website’s root directory by autoindex method. But for security reasons, the directory index is turned off in NGINX by default.
You can turn on this feature by just adjusting a few lines of code. You just need to turn on and turn of the autoindex and autoindex_exact_size respectively.
autoindex on; autoindex_exact_size off;
Now you can add these configurations to the location block. The final result will look like:
location / {
[pre-existing configurations, if applicable]
autoindex on;
autoindex_exact_size off;
}
To activate the directory indexing for some other directories, you can add the forward slash (/) and then the name of the directory. For example:
location /some_directory {
autoindex on;
autoindex_exact_size off;
}
Now, save the changes and reload the NGINX.
sudo nginx -s reload
3. Directory restrictions by IP
Inside your nginx.conf file, check if you have applied allow/deny rule that may be blocking your network. For example:
location / {
# block Oxygen's Computer.
deny 192.168.1.1;
# allow anyone else in 192.168.1.0/24
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
# drop rest of the connections
deny all;
}
4. No index files
This could be a silliest mistake if you don’t have any file name as ‘index (index.php, index.html, index.py)’ inside the root directory of your website. This could also be a reason that your website is throwing a 403 Forbidden Error.
Additional Resources
- HTTP Status Codes on W3C
You might also want to check some other fixes:
- Error Establishing a Database Connection in WordPress Fix
- Fix 502 Bad Gateway Nginx Error in Ubuntu
- Fix: 504 Gateway Timeout Nginx Error
- PHP5-FPM 502 Bad Gateway Error (connect() to unix:/var/run/php5-fpm.sock failed (2: No such file or directory)
- Your PHP installation appears to be missing the MySQL extension which is required by WordPress
I hope you these 4 ways will help you to Fix 403 Forbidden Error.
Which of these ways helped you get rid of this error? Let us know in the comment section below.