Загрузить PDF
Загрузить PDF
Все прямоугольные треугольники имеют один прямой угол (90 градусов), а противоположная ему сторона называется гипотенузой.[1]
Гипотенуза — самая длинная сторона треугольника, и найти ее можно различными способами. В этой статье мы расскажем вам, как найти гипотенузу по теореме Пифагора (когда известны длины двух других сторон треугольника), по теореме синусов (когда известны длина катета и угол) и в некоторых частных случаях (часто такие задания встречаются на контрольных и тестах).
-

1
Теорема Пифагора связывает все стороны прямоугольного треугольника.[2]
Согласно данной теореме, в любом прямоугольном треугольнике с катетами «а» и «b» и гипотенузой «с»: a2 + b2 = c2.[3]
-

2
Убедитесь, что данный вам треугольник является прямоугольным, так как теорема Пифагора применима только к прямоугольным треугольникам. В прямоугольных треугольниках один из трех углов всегда равен 90 градусам.
- Прямой угол в прямоугольном треугольнике обозначается значком в виде квадрата.
-

3
Обозначьте стороны треугольника. Катеты обозначьте как «а» и «b» (катеты — стороны, пересекающиеся под прямым углом), а гипотенузу — как «с» (гипотенуза — самая большая сторона прямоугольного треугольника, лежащая напротив прямого угла). Затем подставьте данные вам значения в формулу.
- Например, катеты треугольника равны 3 и 4. В этом случае а = 3, b = 4, а формула выглядит так: 32 + 42 = c2.
-

4
Возведите в квадрат значения катетов («a» и «b»). Для этого просто умножьте число само на себя:
- Если a = 3, то a2 = 3 x 3 = 9. Если b = 4, то b2 = 4 x 4 = 16.
- Подставьте эти значения в формулу: 9 + 16 = с2.
-

5
Сложите найденные квадраты катетов (a2 и b2), чтобы вычислить квадрат значения гипотенузы (с2).
- В нашем примере 9 + 16 = 25, поэтому с2 = 25.
-

6
Найдите квадратный корень с2. Используйте калькулятор, чтобы извлечь квадратный корень из найденного значения. Так вы вычислите гипотенузу треугольника.
- В нашем примере с2 = 25. Квадратный корень из 25 равен 5 (так как 5 х 5 = 25, поэтому √25 = 5). Это означает, что гипотенуза с = 5.
Реклама
-

1
Определение пифагоровой тройки. Пифагорова тройка — это три числа (длины трех сторон), которые удовлетворяют теореме Пифагора. Очень часто треугольники с такими сторонами приводятся в учебниках и на тестах. Если вы запомните первые несколько пифагоровых троек, вы сэкономите много времени на тестах или экзаменах, потому что сможете вычислить гипотенузу, просто взглянув на длины катетов.[4]
- Первая пифагорова тройка: 3-4-5 (32 + 42 = 52, 9 + 16 = 25). Если дан треугольник с катетами 3 и 4, то вы можете с уверенностью заявить, что гипотенуза равна 5 (без необходимости делать какие-либо расчеты).
- Пифагоровы тройки работают даже в том случае, когда числа умножены или разделены на один коэффициент. Например, если катеты равны 6 и 8, гипотенуза равна 10 (62 + 82 = 102, 36 + 64 = 100). То же самое верно для 9-12-15 и даже для 1,5-2-2,5.
- Вторая пифагорова тройка: 5-12-13 (52 + 122 = 132, 25 + 144 = 169). Также к этой тройке относятся, например, числа 10-24-26 и 2,5-6-6,5.
-

2
Равнобедренный прямоугольный треугольник. Это такой треугольник, углы которого равны 45,45 и 90 градусам. Соотношение между сторонами этого треугольника равно 1:1:√2. Это означает, что гипотенуза в таком треугольнике равна произведению катета и квадратного корня из 2.
- Чтобы вычислить гипотенузу такого треугольника, просто умножьте длину любого катета на √2.[5]
- Это соотношение особенно удобно, когда в задачах вместо числовых значений даются переменные.
- Чтобы вычислить гипотенузу такого треугольника, просто умножьте длину любого катета на √2.[5]
-

3
Половина равностороннего прямоугольного треугольника. Это такой треугольник, углы которого равны 30,60 и 90 градусам. Соотношение между сторонами этого треугольника равно 1:√3:2 или х:х√3:2х. Чтобы найти гипотенузу в таком треугольнике выполните одно из следующих действий:[6]
- Если вам дан короткий катет (противолежащий углу в 30 градусов), просто умножьте длину этого катета на 2, чтобы найти длину гипотенузы. Например, если короткий катет равен 4, то гипотенуза равна 8.
- Если вам дан длинный катет (противолежащий углу в 60 градусов), просто умножьте длину этого катета на 2/√3, чтобы найти длину гипотенузы. Например, если короткий катет равен 4, то гипотенуза равна 4,62.
Реклама
-

1
Поймите, что означает «синус». Синус, косинус и тангенс угла — это основные тригонометрические функции, связывающие углы и стороны в прямоугольном треугольнике. Синус угла равен отношению противолежащей стороны к гипотенузе. Обозначается синус как sin.[7]
-

2
Научитесь вычислять синус. Чтобы вычислить синус, на калькуляторе найдите клавишу sin, нажмите ее, а затем введите значение угла. В некоторых калькуляторах сначала нужно нажать клавишу перехода к работе с функциями, а затем нажать клавишу sin. Поэтому поэкспериментируйте с калькулятором или проверьте его документацию.
- Чтобы найти синус угла в 80 градусов, нажмите «sin», «8», «0», «=» или нажмите «8», «0», «sin», «=» (ответ: -0,9939).
- Вы также можете найти онлайн-калькулятор, введя в поисковой системе «вычисление синуса» (без кавычек).[8]
-

3
Запомните теорему синусов. Теорема синусов является полезным инструментом для вычисления углов и сторон любого треугольника. В частности, она поможет вам найти гипотенузу прямоугольного треугольника, если вам дан катет и угол, отличный от прямого. Согласно теореме синусов, в любом треугольнике со сторонами a, b, c и углами A, B, C верно равенство a / sin A = b / sin B = c / sin С.[9]
- Теорема синусов применяется к любым треугольникам, а не только к прямоугольным (но только в прямоугольном треугольнике есть гипотенуза).
-

4
Обозначьте стороны треугольника через «а» (известный катет), «b» (неизвестный катет), «с» (гипотенуза). Затем обозначьте углы треугольника через «А» (напротив катета «а»), «В» (напротив катета «b»), «С» (напротив гипотенузы).
-

5
Найдите третий угол. Если вам дан один из острых углов прямоугольного треугольника (А или В), а второй угол всегда равен 90 градусам (С = 90), то третий угол вычисляется по формуле 180 – (90 + А) = B (помните, что сумма углов в любом треугольнике равна 180 градусам). При необходимости уравнение можно изменить и так: 180 – (90 + B) = A.
- Например, если угол A = 40 градусам, то B = 180 – (90 + 40) = 180 – 130 = 50 градусов.
-

6
На данном этапе вам известны значения всех трех углов и длина катета «а». Теперь вы можете подставить эти значения в формулу теоремы синусов, чтобы найти две другие стороны.
- В нашем примере допустим, что катет а = 10, а углы равны C = 90˚, A = 40˚, В = 50˚.
-

7
Подставьте данные и найденные значения в теорему синусов, чтобы найти гипотенузу: катет «а»/синус угла «A» = гипотенуза «с»/синус угла «С». При этом sin 90˚ = 1. Таким образом, уравнение упрощается до: а/sinA = с/1 или с = а/sinA.
-

8
Разделите длину катета «а» на синус угла «А», чтобы найти длину гипотенузы. Для этого сначала найдите синус угла, а затем выполните деление. Или вы можете воспользоваться калькулятором, введя 10/(sin40) или 10/(40sin) (не забудьте про скобки).
- В нашем примере sin 40 = 0,64278761, а с = 10/0,64278761 = 15,6.
Реклама
Об этой статье
Эту страницу просматривали 312 249 раз.
Была ли эта статья полезной?
Гипотенуза — сторона в прямоугольном треугольнике, находящаяся напротив прямого угла. Две других стороны — катеты. В прямоугольном треугольнике гипотенуза всегда длиннее катетов.

Теорема Пифагора: квадрат гипотенузы равен сумме квадратов катетов (формула: c² = a² + b², где c — гипотенуза, a и b — катеты). Очень часто для вычисления гипотенузы используется именно эта теорема.
Как найти гипотенузу?
Как найти гипотенузу, зная катеты?
Если известны оба катета (две другие стороны прямоугольного треугольника), можно применить Теорему Пифагора.
Теорема Пифагора — в прямоугольном треугольнике квадрат гипотенузы равен сумме квадратов катетов. Формула: c² = a² + b² (при c — гипотенуза, a и b — катеты).
Например:

Один катет равен 3 см, другой — 4 см. Таким образом, а = 3, b = 4, подставляем в формулу:
c² = 3² + 4² <=> c² = 9 + 16 <=> c² = 25 <=> c = √25 <=> c = 5.
Ответ: длина гипотенузы 5 см (или x = 5).
Как найти катет в прямоугольном треугольнике
По той же формуле можно найти и длину одного неизвестного катета, нужно только немного её изменить:
Начальная формула: c² = a² + b² (при c — гипотенуза, a и b — катеты), и найти катет можно по этой:

Например: Один катет равен 3 см, а гипотенуза — 5 см. Нужно узнать длину второго катета.
Применяем формулу b = √c² — a² ⇔
b = √5² — 3² ⇔ b = √25 — 9 ⇔ b = √16 ⇔ b = 4.
Как найти гипотенузу, зная катет и угол?
Если есть противолежащий катет — теорема синусов
Если в условии задачи дан угол и противолежащий катет, то ищем гипотенузу по Теореме синусов: стороны треугольника пропорциональны синусам противолежащих углов.
Примечание: гипотенуза есть только в прямоугольном треугольнике, однако теорему синусов можно применять к любым треугольникам (не только к прямоугольным).
Формула:


Например:

Известна одна сторона треугольника 𝐴𝐶 = √2 и ∠β = 45º.
∠α = 90º (т.к. мы ищем гипотенузу, то второй угол в треугольнике прямой, значит имеет 90º).
Так как во всех треугольниках сумма всех углов равна 180º, то можем узнать оставшийся ∠c.
Значит: ∠c = 180º — (90º + 45º) = 45º.
Подставляем в формулу (a/sinα = b/sinβ = c/sinγ) известные:
BC/sin90º = AC/sin45º = AB/sin45º
В таблице вы найдёте значения для синуса:
| sin 45º | √2/2 |
| sin 60º | √3/2 |
| sin 90º | 1 |
В условии задачи нам дано: 𝐴𝐶 = √2, значит:
BC/sin90º = √2/sin45º = AB/sin45º
Подставляем значения синуса из таблицы:
BC/1 = √2/(√2/2) = AB/(√2/2) (забудем на время про катет AB) ⇔
BC = √2/(√2/2) ⇔ BC = 2 (гипотенуза равна 2)
Если хотите вычислить катет, уже зная другой катет и гипотенузу:
AB/(√2/2) = 2 ⇔ AB = √2
Ответ: гипотенуза BC равна 2 см, а катет AB √2 см.
Если есть прилежащий катет — по косинусу
Если в условии задачи дан угол и прилежащий катет, то ищем гипотенузу по косинусу (в прямоугольном треугольнике, косинус острого угла (cos) — это отношение прилежащего катета (b) к гипотенузе(c), таким образом cos a = b/c, из этого получается c = b / cos α).
Т.е. гипотенуза (c) = прилежащий катет (b) / косинус угла или c = b / cos α.
Например:

Известна одна сторона треугольника AB = 1 и ∠β = 45º. Нужно вычислить гипотенузу (BC).
Помним, что гипотенуза (c) = прилежащий катет (b) / косинус угла или c = b / cos α. Т.е.: BC = AB / cosβ ⇔ BC = 1/ cos 45º.
Смотрим в таблице, чему равен cos 45º.
BC = 1/ (√2/2) = √2
Ответ: гипотенуза BC равна √2 см.
Как найти гипотенузу равнобедренного треугольника
В равнобедренном треугольнике есть гипотенуза только в том случае, если он одновременно и прямоугольный, т.к. гипотенуза есть только в прямоугольных треугольниках (и его основание будет гипотенузой).
Чтобы найти такую гипотенузу, нужно любой из двух одинаковых катетов возвести в квадрат, умножить на 2 и посчитать квадратный корень: b = √2a² (где b — гипотенуза, а — катет). Это следствие из теоремы Пифагора.
Например:

Катет равнобедренного треугольника равен 7см. Нужно найти гипотенузу.
Формула b = √2a². Подставляем:
b = √2*7² = √2*49 ≈ √98 ≈ 9.899
Если забудете эту формулу, можно использовать уже знакомую формулу Пифагора для гипотенузы (c² = a² + b²):
c² = a² + b²
c² = 7² + 7²
c² = 49 + 49
c² = 98
c = √98
c ≈ 9.899
Ответ: гипотенуза равна 9.899.
Узнайте больше про Теорему Пифагора, Теорему косинусов, а также, что такое Тангенс и Аксиома.
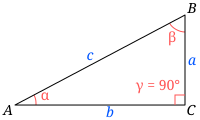
Прямоугольный треугольник и его гипотенуза (c), а также катеты a и b.
Гипотенуза (греч. ὑποτείνουσα, натянутая[1]) — самая длинная сторона прямоугольного треугольника, противоположная прямому углу.
Длина гипотенузы прямоугольного треугольника может быть найдена с помощью теоремы Пифагора: Квадрат длины гипотенузы равен сумме квадратов длин катетов. Например, если длина одного из катетов равна 3 м (квадрат его длины равен 9 м²), а длина другого — 4 м (квадрат его длины равен 16 м²), то сумма их квадратов равна 25 м². Длина гипотенузы в этом случае равна квадратному корню из 25 м², то есть 5 м.
Вычисление длины гипотенузы[править | править код]
Длину гипотенузы можно найти, применив теорему Пифагора.
Пусть 


Если известна длина одного из катетов 

для противолежащего угла
, и
для прилежащего угла
.
См. также[править | править код]
- Синус
- Треугольник
- Тригонометрия
Примечания[править | править код]
- ↑ Александрова Н. В. Математические термины.(справочник). М..: Высшая школа, 1978, с. 26.
Download Article
Download Article
All right triangles have one right (90-degree) angle, and the hypotenuse is the side that is opposite or the right angle, or the longest side of the right triangle.[1]
The hypotenuse is the longest side of the triangle, and it’s also very easy to find using a couple of different methods. This article will teach you how to find the length of the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem when you know the length of the other two sides of the triangle. It will then teach you to recognize the hypotenuse of some special right triangles that often appear on tests. It will finally teach you to find the length of the hypotenuse using the Law of Sines when you only know the length of one side and the measure of one additional angle.
-

1
Learn the Pythagorean Theorem. The Pythagorean Theorem describes the relationship between the sides of a right triangle.[2]
It states that for any right triangle with sides of length a and b, and hypotenuse of length c, a2 + b2 = c2.[3]
-

2
Make sure that your triangle is a right triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem only works on right triangles, and by definition only right triangles can have a hypotenuse. If your triangle contains one angle that is exactly 90 degrees, it is a right triangle and you can proceed.
- Right angles are often notated in textbooks and on tests with a small square in the corner of the angle. This special mark means “90 degrees.”
Advertisement
-

3
Assign variables a, b, and c to the sides of your triangle. The variable “c” will always be assigned to the hypotenuse, or longest side. Choose one of the other sides to be a, and call the other side b (it doesn’t matter which is which; the math will turn out the same). Then copy the lengths of a and b into the formula, according to the following example:
- If your triangle has sides of 3 and 4, and you have assigned letters to those sides such that a = 3 and b = 4, then you should write your equation out as: 32 + 42 = c2.
-

4
Find the squares of a and b. To find the square of a number, you simply multiply the number by itself, so a2 = a x a. Find the squares of both a and b, and write them into your formula.[4]
- If a = 3, a2 = 3 x 3, or 9. If b = 4, then b2 = 4 x 4, or 16.
- When you plug those values into your equation, it should now look like this: 9 + 16 = c2.
-

5
Add together the values of a2 and b2. Enter this into your equation, and this will give you the value for c2. There is only one step left to go, and you will have that hypotenuse solved!
- In our example, 9 + 16 = 25, so you should write down 25 = c2.
-

6
Find the square root of c2. Use the square root function on your calculator (or your memory of the multiplication table) to find the square root of c2. The answer is the length of your hypotenuse![5]
- In our example, c2 = 25. The square root of 25 is 5 (5 x 5 = 25, so Sqrt(25) = 5). That means c = 5, the length of our hypotenuse!
Advertisement
-

1
Learn to recognize Pythagorean Triple Triangles. The side lengths of a Pythagorean triple are integers that fit the Pythagorean Theorem. These special triangles appear frequently in geometry text books and on standardized tests like the SAT and the GRE. If you memorize the first 2 Pythagorean triples, in particular, you can save yourself a lot of time on these tests because you can immediately know the hypotenuse of one of these triangles just by looking at the side lengths![6]
- The first Pythagorean triple is 3-4-5 (32 + 42 = 52, 9 + 16 = 25). When you see a right triangle with legs of length 3 and 4, you can instantly be certain that the hypotenuse will be 5 without having to do any calculations.
- The ratio of a Pythagorean triple holds true even when the sides are multiplied by another number. For example a right triangle with legs of length 6 and 8 will have a hypotenuse of 10 (62 + 82 = 102, 36 + 64 = 100). The same holds true for 9-12-15, and even 1.5-2-2.5. Try the math and see for yourself!
- The second Pythagorean triple that commonly appears on tests is 5-12-13 (52 + 122 = 132, 25 + 144 = 169). Also be on the lookout for multiples like 10-24-26 and 2.5-6-6.5.
-

2
Memorize the side ratios of a 45-45-90 right triangle. A 45-45-90 right triangle has angles of 45, 45, and 90 degrees, and is also called an Isosceles Right Triangle. It occurs frequently on standardized tests, and is a very easy triangle to solve. The ratio between the sides of this triangle is 1:1:Sqrt(2), which means that the length of the legs are equal, and the length of the hypotenuse is simply the leg length multiplied by the square root of two.[7]
- To calculate the hypotenuse of this triangle based on the length of one of the legs, simply multiply the leg length by Sqrt(2).
- Knowing this ratio comes in especially handy when your test or homework question gives you the side lengths in terms of variables instead of integers.
-

3
Learn the side ratios of a 30-60-90 right triangle. This triangle has angle measurements of 30, 60, and 90 degrees, and occurs when you cut an equilateral triangle in half. The sides of the 30-60-90 right triangle always maintain the ratio 1:Sqrt(3):2, or x:Sqrt(3)x:2x. If you are given the length of one leg of 30-60-90 right triangle and are asked to find the hypotenuse, it is very easy to do:[8]
- If you are given the length of the shortest leg (opposite the 30-degree angle,) simply multiply the leg length by 2 to find the length of the hypotenuse. For instance, if the length of the shortest leg is 4, you know that the hypotenuse length must be 8.
- If you are given the length of the longer leg (opposite the 60-degree angle,) multiply that length by 2/Sqrt(3) to find the length of the hypotenuse. For instance, if the length of the longer leg is 4, you know that the hypotenuse length must be 4.62.
Advertisement
-

1
Understand what “Sine” means. The terms “sine,” “cosine,” and “tangent” all refer to various ratios between the angles and/or sides of a right triangle. In a right triangle, the sine of an angle is defined as the length of the side opposite the angle divided by the hypotenuse of the triangle. The abbreviation for sine found in equations and on calculators is sin.[9]
-

2
Learn to calculate sine. Even a basic scientific calculator will have a sine function. Look for a key marked sin. To find the sine of angle, you will usually press the sin key and then enter the angle measurement in degrees. On some calculators, however, you must enter the degree measurement first and then the sin key. You will have to experiment with your calculator or check the manual to find out which it is.
- To find the sine of an 80 degree angle, you will either need to key in sin 80 followed by the equal sign or enter key, or 80 sin. (The answer is -0.9939.)
- You can also type in “sine calculator” into a web search, and find a number of easy-to-use calculators that will remove any guesswork.[10]
-

3
Learn the Law of Sines. The Law of Sines is a useful tool for solving triangles. In particular, it can help you find the hypotenuse of a right triangle if you know the length of one side, and the measure of one other angle in addition to the right angle. For any triangle with sides a, b, and c, and angles A, B, and C, the Law of Sines states that a / sin A = b / sin B = c / sin C.[11]
- The Law of Sines can actually be used to solve any triangle, but only a right triangle will have a hypotenuse.
-

4
Assign the variables a, b, and c to the sides of your triangle. The hypotenuse (longest side) must be “c”. For the sake of simplicity, label the side with the known length as “a,” and the other “b”. Then assign variables A, B, and C to the angles of the triangle. The right angle opposite the hypotenuse will be “C”. The angle opposite side “a” is angle “A,” and the angle opposite side “b” is “B”.
-

5
Calculate the measurement of the third angle. Because it is a right angle, you already know that C = 90 degrees, and you also know the measure of A or B. Since the internal degree measurement of a triangle must always equal 180 degrees, you can easily calculate the measurement of the third angle using the following formula: 180 – (90 + A) = B. You can also reverse the equation such that 180 – (90 + B) = A.
- For example, if you know that A = 40 degrees, then B = 180 – (90 + 40). Simplify this to B = 180 – 130, and you can quickly determine that B = 50 degrees.
-

6
Examine your triangle. At this point, you should know the degree measurements of all three angles, and the length of side a. It is now time to plug this information into the Law of Sines equation to determine the lengths of the other two sides.
- To continue our example, let’s say that the length of side a = 10. Angle C = 90 degrees, angle A = 40 degrees, and angle B = 50 degrees.
-

7
Apply the Law of Sines to your triangle. We just need to plug our numbers in and solve the following equation to determine the length of hypotenuse c: length of side a / sin A = length of side c / sin C. This might still look a bit intimidating, but the sine of 90 degrees is a constant, and always equals 1! Our equation can thus be simplified to: a / sin A = c / 1, or just a / sin A = c.[12]
-

8
Divide the length of side a by the sine of angle A to find the length of the hypotenuse! You can do this in two separate steps, by first calculating sin A and writing it down, and then dividing by a. Or you can key it all into the calculator at the same time. If you do, remember to include parentheses after the division sign.[13]
For example, key in either 10 / (sin 40) or 10 / (40 sin), depending on your calculator.- Using our example, we find that sin 40 = 0.64278761. To find the value of c, we simply divide the length of a by this number, and learn that 10 / 0.64278761 = 15.6, the length of our hypotenuse!
Advertisement
-
1
Identify the formula to use. There are many variations of the formula for the area of a right triangle. You may already be familiar with the formula Area = 1/2 x base x height. But the known parameters determines which formulas you can work with. You can find the most commonly used formulas for calculating the area of right and non right angles with worked examples in this article[14]
. The variation that directly relates the area to the hypotenuse is- Rearrange formula to make hypotenuse the subject. The variable “c” represents the hypotenuse.

- Rearrange formula to make hypotenuse the subject. The variable “c” represents the hypotenuse.
-
2
Assign the variables.
represents an angle on the right angle other than the 90 degree angle. So it is up to you to assign any of the other two angles as
. The other variable in the formula is the area, which as the name suggests refers to the area of the triangle.
-
3
Apply the formula to your triangle. We just need to plug in the variables to the formula and solve the following equation to determine the length of hypotenuse c.
Advertisement
Practice Problems and Answers
Add New Question
-
Question
How do you find the length of the hypotenuse in the Pythagorean Theorem?

Grace Imson, MA
Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco
Grace Imson is a math teacher with over 40 years of teaching experience. Grace is currently a math instructor at the City College of San Francisco and was previously in the Math Department at Saint Louis University. She has taught math at the elementary, middle, high school, and college levels. She has an MA in Education, specializing in Administration and Supervision from Saint Louis University.

Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco
Expert Answer
Support wikiHow by
unlocking this expert answer.One common mistake is forgetting to square the terms. In the Pythagorean Theorem, all three terms are squared. Many people go too fast and forget to find the square before the sum of ‘a’ and ‘b,’ which gives them an incorrect answer.
-
Question
Is there a calculator for finding the length of the hypotenuse?

This answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.

wikiHow Staff Editor
Staff Answer
Support wikiHow by
unlocking this staff-researched answer.Google provides a right angle triangle calculator that allows you to solve for the hypotenuse. Simply search for “hypotenuse calculator” and plug your numbers into the calculator at the top of the search results. You can also use the hypotenuse calculator at Omincalculator.com.
-
Question
How can you find the length of the hypotenuse given the length of 1 side and an angle?

This answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.

wikiHow Staff Editor
Staff Answer
Support wikiHow by
unlocking this staff-researched answer.If you know you are dealing with a right triangle, then you already know that one of the angles is 90°. Since the angles must add up to 180°, you can solve for the missing angle using the formula 90 + X = 180. Once you have all 3 angles, you can use that information and the known length of 1 side to use the law of sines and find the length of the hypotenuse.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
About This Article
Article SummaryX
If you need to find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle, you can use the Pythagorean theorem if you know the length of the other two sides. Square the length of the 2 sides, called a and b, then add them together. Take the square root of the result to get the hypotenuse. If you want to learn how to find the hypotenuse using trigonometric functions, keep reading the article!
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 1,376,552 times.
Did this article help you?
Гипотенуза – это самая длинная сторона прямоугольного треугольника. Она лежит напротив прямого угла. Длина гипотенузы может быть найдена различными способами.

Если известна длина обоих катетов, то ее размер вычисляется по теореме Пифагора: сумма квадратов двух катетов равняется квадрату гипотенузы.

Соответственно длина гипотенузы в прямоугольном треугольнике вычисляется по формуле:

![]() К примеру: катет a = 3 см, катет b = 4 см.
К примеру: катет a = 3 см, катет b = 4 см.
Чтобы найти длину гипотенузы в прямоугольном треугольнике, подставим числа в формулу.  =5 см
=5 см
Преобразовав эту формулу можно найти и длину одного неизвестного катета.
 ,
, 
| Катет a= | Катет b= | |
| Ответ: Гипотенуза= 5.000 |
В случае если известна длина катета A и гипотенузы C, угол α можно определить по формуле:
Второй угол будет вычисляться так: β = 180°-90°-α. Зная, что сумма всех углов составляет 180°, вычитаем прямой угол и уже известный.
![]() К примеру: A = 3 см, C=5 см, подставляем значения в формулу:
К примеру: A = 3 см, C=5 см, подставляем значения в формулу:  =0,6
=0,6
По таблицу синусов угол α будет приблизительно равен 36°, соответственно угол β = 54°.
Если по условиям даны параметры двух катетов, то можно найти острый угол по следующей формуле:

![]() К примеру: A = 3 см, B = 4 см
К примеру: A = 3 см, B = 4 см
Подставляем значения в формулу  =0,75
=0,75
По таблице тангенсов угол α будет равняться 36°, соответственно угол β = 54°.
Также стороны прямоугольного треугольника можно найти по различным формулам в зависимости от количества известных переменных.
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
При расчете параметров прямоугольного треугольника важно обращать внимание на известные значения и решать задачу по самой простой формуле.












