width, height = map(int, input().split())
def rectanglePerimeter(width, height):
return ((width + height)*2)
print(rectanglePerimeter(width, height))
Running it like this produces:
% echo "1 2" | test.py
6
I suspect IDLE is simply passing a single string to your script. The first input() is slurping the entire string. Notice what happens if you put some print statements in after the calls to input():
width = input()
print(width)
height = input()
print(height)
Running echo "1 2" | test.py produces
1 2
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/unutbu/pybin/test.py", line 5, in <module>
height = input()
EOFError: EOF when reading a line
Notice the first print statement prints the entire string '1 2'. The second call to input() raises the EOFError (end-of-file error).
So a simple pipe such as the one I used only allows you to pass one string. Thus you can only call input() once. You must then process this string, split it on whitespace, and convert the string fragments to ints yourself. That is what
width, height = map(int, input().split())
does.
Note, there are other ways to pass input to your program. If you had run test.py in a terminal, then you could have typed 1 and 2 separately with no problem. Or, you could have written a program with pexpect to simulate a terminal, passing 1 and 2 programmatically. Or, you could use argparse to pass arguments on the command line, allowing you to call your program with
test.py 1 2
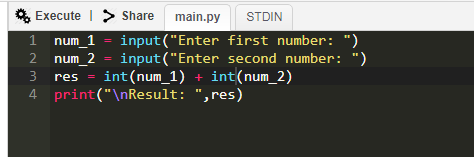
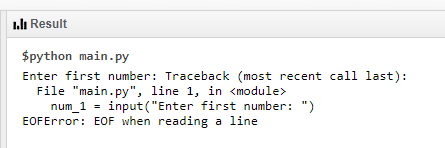
Только только притронулся к изучению Python, и уже застрял с ошибкой. Помогите)
-
Вопрос заданболее двух лет назад
-
25315 просмотров
В вашем случае, вы вероятно используете Python 2, потому что на Python 3 данный код выполняется корректно.
first = int(input('First number: '))
second = int(input('Second number: '))
result = first + second
print(result)
Так же проблема может заключаться в том, что некоторые терминалы неправильно обрабатывают ввод
(Хотя я сам с таким не сталкивался, но читал что и такое бывает в нашем мире)
Пригласить эксперта
При использовании input по достижении конца файла или если нажимаете Ctrl+Z и потом Enter, будет сгенерировано исключение EOFError. Чтобы избежать аварийного завершения программы нужно обработать исключение:
try:
a=input(“Enter Your data:”)
print(a)
except EOFError:
print(“Exception handled”)
То есть, когда внутри блока возникнет исключение EOFError, управление будет передано в блок except и после исполнения инструкций в этом блоке программа продолжит нормальную работу.
-
Показать ещё
Загружается…
17 мая 2023, в 21:58
1000 руб./за проект
17 мая 2023, в 21:51
800 руб./за проект
17 мая 2023, в 21:34
500 руб./в час
Минуточку внимания
When using the input() or raw_input() function in Python, you might see the following error:
EOFError: EOF when reading a line
This error usually occurs when the input() function reached the end-of-file (E0F) without reading any input.
There are two scenarios where this error might occur:
- When you interrupt the code execution with
CTRL + Dwhile aninput()function is running - You called the
input()function inside awhileloop - You’re using an Online Python IDE and you don’t provide any input in STDIN
This tutorial will show how to fix this error in each scenario.
1. Interrupting code execution with CTRL + D
Suppose you have a Python code as follows:
my_input = input("Enter your name: ")
print("Hello World!")
Next, you run the program, and while Python is asking for input, you pressed CTRL + D. You get this output:
Enter your name: Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 1, in <module>
my_input = input("Enter your name: ")
EOFError
This is a natural error because CTRL + D sends an end-of-file marker to stop any running process.
The error simply indicates that you’re not passing anything to the input() function.
To handle this error, you can specify a try-except block surrounding the input() call as follows:
try:
my_input = input("Enter your name: ")
except EOFError as e:
print(e)
print("Hello World!")
Notice that there’s no error received when you press CTRL+D this time. The try-except block handles the EOFError successfully.
2. Calling input() inside a while statement
This error also occurs in a situation where you need to ask for user input, but you don’t know how many times the user will give you input.
For example, you ask the user to input names into a list as follows:
names = list()
while True:
names.append(input("What's your name?: "))
print(names)
Next, you send one name to the script from the terminal with the following command:
echo "nathan" | python3 main.py
Output:
What's your name?: ['nathan']
What's your name?: Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 11, in <module>
names.append(input("What's your name?: "))
EOFError: EOF when reading a line
When the input() function is called the second time, there’s no input string to process, so the EOFError is raised.
To resolve this error, you need to surround the code inside the while statement in a try-except block as follows:
names = list()
while True:
try:
names.append(input("What's your name?: "))
except EOFError as e:
print(names)
break
This way, the exception when the input string is exhausted will be caught by the try block, and Python can proceed to print the names in the list.
Suppose you run the following command:
echo "nathan n john" | python3 main.py
Output:
What's your name?:
What's your name?:
What's your name?: ['nathan ', ' john']
When Python runs the input() function for the third time, it hits the end-of-file marker.
The except block gets executed, printing the names list to the terminal. The break statement is used to prevent the while statement from running again.
3. Using an online IDE without supplying the input
When you run Python code using an online IDE, you might get this error because you don’t supply any input using the stdin box.
Here’s an example from ideone.com:
You need to put the input in the stdin box as shown above before you run the code, or you’ll get the EOFError.
Sometimes, online IDEs can’t handle the request for input, so you might want to consider running the code from your computer instead.
Conclusion
This tutorial shows that the EOFError: EOF when reading a line occurs in Python when it sees the end-of-file marker while expecting an input.
To resolve this error, you need to surround the call to input() with a try-except block so that the error can be handled by Python.
I hope this tutorial is helpful. Happy coding! 👍
Before starting how to fix EOF When Reading a Line using Python, it’s crucial to understand what causes it, or what even is it in the first place.
An EOF error occurs when you try to read from the end of a file. This can happen because there are no more lines left, or if your program expected some other value instead.
It might be due for example an encoding mistake made by accident while transferring data over Bluetooth connections etcetera!
EOFError(End Of File Error) is a type of exception handling error that Python raises because of either of the following reasons:
- When the input() function is interrupted in both Python 2.7 and Python 3.6+
- When the input() function reaches the end of the line unexpectedly in Python 2.7
- You forgot to enclose your code within a special statement like a for loop or while loop
- You did not close the parentheses properly i.e number of brackets is either more or less than it should be
The BaseException class is the base class of the Exception class which in turn inherits the EOFError class. Technically speaking, EOFError is not an error, but it is an exception.
When the built-in functions such as read() or input() return a string that is empty (unable to read any data), then the EOFError exception is raised.
Or in simple words, EOFError is raised when our program is trying to read or modify something but is unable to do so.
EXAMPLES OF EOFError
# You may also use like int(input()) # or alternative way n = "10" print(n * 10)

The code mentioned above will return an EOFError if no input is given to the online IDE, which means that there is no data for the program to work with.
Hence the error.
animals = ["cat", "dog", "mouse", "monkey"]
for i in animals:
print(i)

In this code, we iterate through the “animals” list successfully but still, the IDE prompts an EOFError. This is because we haven’t put any code within our for-loop.
This is also the case with other statements, meaning that EOFError will be raised if we don’t specify any code within the while-loop, if-else statements, or a function.

To avoid this error we have to write some code, however small it is, within the loop. Or, if we don’t want to specify any code within the statement.
We can use the “pass” statement which is usually used as a placeholder for future code.
print("hello")
This code will also raise an EOFError since the number of parentheses opened and closed are not equal. To tackle this issue simply add a closing bracket at the end of the print statement.
We will be good to go. Another example of the same kind of problem is:
animals = ["cat", "dog", "mouse", "monkey"]
Since the closing square bracket is missing, the IDE will raise an EOFError.
animals = {'mammal':'cat', "fish":"shark"}
print(animals)

The same will be the case with dictionaries if the number of curly brackets is uneven.
Read more: How to Check if File Exists Using Python?
Read file
The most common reason for this is that you have reached the end of the file without reading all of the data.
To fix this, make sure that you read all of the data in the file before trying to access its contents. You can do this by using a loop to read through the file’s contents.
Alternatively, you can use a function like len() to find out how many bytes are in the file so that you can ensure that you read through all of them.
Fix EOFError: EOF When Reading a Line using Python
Conclusion
The statement “SyntaxError: unexpected EOF while parsing” is thrown by the IDE when the interpreter reaches the end of a program before every line of code has been executed.
To solve this error our first step should be to make sure that all statements such as for-loop, while-loop, if statements, etc contain some code. Next, we should make sure that all the parentheses have properly closed.
Read more: Ways To Use Python If Not



So as we can see in the pictures above, despite having produced the expected output, our test case fails due to a runtime error EOFError i.e., End of File Error. Let’s understand what is EOF and how to tackle it.
What is EOFError
In Python, an EOFError is an exception that gets raised when functions such as input() or raw_input() in case of python2 return end-of-file (EOF) without reading any input.
When can we expect EOFError
We can expect EOF in few cases which have to deal with input() / raw_input() such as:
-
Interrupt code in execution using
ctrl+dwhen an input statement is being executed as shown below

-
Another possible case to encounter EOF is, when we want to take some number of inputs from user i.e., we do not know the exact number of inputs; hence we run an infinite loop for accepting inputs as below, and get a Traceback Error at the very last iteration of our infinite loop because user does not give any input at that iteration
n=int(input())
if(n>=1 and n<=10**5):
phone_book={}
for i in range(n):
feed=input()
phone_book[feed.split()[0]]=feed.split()[1]
while True:
name=input()
if name in phone_book.keys():
print(name,end="")
print("=",end="")
print(phone_book[name])
else:
print("Not found")
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
The code above gives EOFError because the input statement inside while loop raises an exception at last iteration
Do not worry if you don’t understand the code or don’t get context of the code, its just a solution of one of the problem statements on HackerRank 30 days of code challenge which you might want to check
The important part here is, that I used an infinite while loop to accept input which gave me a runtime error.
How to tackle EOFError
We can catch EOFError as any other error, by using try-except blocks as shown below :
try:
input("Please enter something")
except:
print("EOF")
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
You might want to do something else instead of just printing “EOF” on the console such as:
n=int(input())
if(n>=1 and n<=10**5):
phone_book={}
for i in range(n):
feed=input()
phone_book[feed.split()[0]]=feed.split()[1]
while True:
try:
name=input()
except EOFError:
break
if name in phone_book.keys():
print(name,end="")
print("=",end="")
print(phone_book[name])
else:
print("Not found")
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
In the code above, python exits out of the loop if it encounters EOFError and we pass our test case, the problem due to which this discussion began…

Hope this is helpful
If you know any other cases where we can expect EOFError, you might consider commenting them below.
