.index()Returns: Integer
Description: Search for a given element from among the matched elements.
-
version added: 1.4.index()
-
This signature does not accept any arguments.
-
-
version added: 1.4.index( selector )
-
selector
A selector representing a jQuery collection in which to look for an element.
-
-
version added: 1.0.index( element )
-
element
The DOM element or first element within the jQuery object to look for.
-
Return Values
If no argument is passed to the .index() method, the return value is an integer indicating the position of the first element within the jQuery object relative to its sibling elements.
If .index() is called on a collection of elements and a DOM element or jQuery object is passed in, .index() returns an integer indicating the position of the passed element relative to the original collection.
If a selector string is passed as an argument, .index() returns an integer indicating the position of the first element within the jQuery object relative to the elements matched by the selector. If the element is not found, .index() will return -1.
Detail
The complementary operation to .get(), which accepts an index and returns a DOM node, .index() can take a DOM node and returns an index. Suppose we have a simple unordered list on the page:
If we retrieve one of the three list items (for example, through a DOM function or as the context to an event handler), .index() can search for this list item within the set of matched elements:
|
1 2 |
|
We get back the zero-based position of the list item:
Index: 1
Similarly, if we retrieve a jQuery object consisting of one of the three list items, .index() will search for that list item:
|
1 2 |
|
We get back the zero-based position of the list item:
Index: 1
Note that if the jQuery collection used as the .index() method’s argument contains more than one element, the first element within the matched set of elements will be used.
|
1 2 |
|
We get back the zero-based position of the first list item within the matched set:
Index: 1
If we use a string as the .index() method’s argument, it is interpreted as a jQuery selector string. The first element among the object’s matched elements which also matches this selector is located.
|
1 2 |
|
We get back the zero-based position of the list item:
Index: 1
If we omit the argument, .index() will return the position of the first element within the set of matched elements in relation to its siblings:
|
1 |
|
Again, we get back the zero-based position of the list item:
Index: 1
Examples:
On click, returns the index (zero-based) of that div in the page.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
|
Demo:
Returns the index for the element with ID bar.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
|
Demo:
Returns the index for the first item in the jQuery collection.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
|
Demo:
Returns the index for the element with ID bar in relation to all <li> elements.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
|
Demo:
Returns the index for the element with ID bar in relation to its siblings.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
|
Demo:
Returns -1, as there is no element with ID foobar.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
|
Demo:
Содержание:
-
.index()
- .index()
- .index( selector )
- .index( element )
- Обсуждение
- Примеры
.index()Возвращает: Integer
Описание: Возвращает индекс заданного элемента в наборе (2 и 3 вариант использования) или относительно соседних элементов (1 вариант использования).
-
Добавлен в версии: 1.4.index()
-
This signature does not accept any arguments.
-
-
Добавлен в версии: 1.4.index( selector )
-
selector
A selector representing a jQuery collection in which to look for an element.
-
-
Добавлен в версии: 1.0.index( element )
-
element
The DOM element or first element within the jQuery object to look for.
-
Return Values
If no argument is passed to the .index() method, the return value is an integer indicating the position of the first element within the jQuery object relative to its sibling elements.
If .index() is called on a collection of elements and a DOM element or jQuery object is passed in, .index() returns an integer indicating the position of the passed element relative to the original collection.
If a selector string is passed as an argument, .index() returns an integer indicating the position of the first element within the jQuery object relative to the elements matched by the selector. If the element is not found, .index() will return -1.
Detail
The complementary operation to .get(), which accepts an index and returns a DOM node, .index() can take a DOM node and returns an index. Suppose we have a simple unordered list on the page:
If we retrieve one of the three list items (for example, through a DOM function or as the context to an event handler), .index() can search for this list item within the set of matched elements:
|
1 2 |
|
We get back the zero-based position of the list item:
Index: 1
Similarly, if we retrieve a jQuery object consisting of one of the three list items, .index() will search for that list item:
|
1 2 |
|
We get back the zero-based position of the list item:
Index: 1
Note that if the jQuery collection used as the .index() method’s argument contains more than one element, the first element within the matched set of elements will be used.
|
1 2 |
|
We get back the zero-based position of the first list item within the matched set:
Index: 1
If we use a string as the .index() method’s argument, it is interpreted as a jQuery selector string. The first element among the object’s matched elements which also matches this selector is located.
|
1 2 |
|
We get back the zero-based position of the list item:
Index: 1
If we omit the argument, .index() will return the position of the first element within the set of matched elements in relation to its siblings:
|
1 |
|
Again, we get back the zero-based position of the list item:
Index: 1
Примеры использования
How do I get the index of clicked item in the code below?
$('selector').click(function (event) {
// get index in collection of the clicked item ...
});
With Firebug I saw this: jQuery151017197709735298827: 2 (I’ve clicked in the second element).
Keavon
6,7179 gold badges50 silver badges79 bronze badges
asked Apr 4, 2011 at 22:59
This will alert the index of the clicked selector (starting with 0 for the first):
$('selector').click(function(){
alert( $('selector').index(this) );
});
answered Apr 4, 2011 at 23:16
AntAnt
3,8671 gold badge15 silver badges14 bronze badges
4
$('selector').click(function (event) {
alert($(this).index());
});
jsfiddle
answered Apr 4, 2011 at 23:17
2
Siblings
$(this).index() can be used to get the index of the clicked element if the elements are siblings.
<div id="container">
<a href="#" class="link">1</a>
<a href="#" class="link">2</a>
<a href="#" class="link">3</a>
<a href="#" class="link">4</a>
</div>
Not siblings
If no argument is passed to the
.index()method, the return value is an integer indicating the position of the first element within the jQuery object relative to its sibling elements.
Pass the selector to the index(selector).
$(this).index(selector);
Example:
Find the index of the <a> element that is clicked.
<tr>
<td><a href="#" class="adwa">0001</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a href="#" class="adwa">0002</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a href="#" class="adwa">0003</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a href="#" class="adwa">0004</a></td>
</tr>
Fiddle
answered Mar 22, 2016 at 10:06
![]()
TusharTushar
85.3k21 gold badges159 silver badges177 bronze badges
1
Just do this way:-
$('ul li').on('click', function(e) {
alert($(this).index());
});
OR
$('ul li').click(function() {
alert($(this).index());
});
answered Apr 26, 2012 at 11:05
Siva CharanSiva Charan
17.9k9 gold badges60 silver badges95 bronze badges
answered Nov 3, 2020 at 17:28
if you are using .bind(this), try this:
let index = Array.from(evt.target.parentElement.children).indexOf(evt.target);
$(this.pagination).find("a").on('click', function(evt) {
let index = Array.from(evt.target.parentElement.children).indexOf(evt.target);
this.goTo(index);
}.bind(this))
answered Oct 8, 2018 at 14:00
Достаточно интересные методы –
и
1 |
.index() |
, особенно в сочетании друг с другом. Поэтому и решил объединить рассмотрение этих методов. Каждый по отдельности – методы просты и мало показательны.
Но для начала вкратце (по другому и не получиться) опищу каждый из методов, по возможности своими словами.
Работа метода
проста – он возвращает индекс (порядковый номер) указанного элемента среди группы ему подобных.
Синтаксис метода
также простой:
index([element])или
.index(selector)И пример для иллюстрации:
<ul class="test">
<li class="primo">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="secondo">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="tetro">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="quattro">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="cinque">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="sei">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="sedici">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="ten">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
</ul>Сделать выборку всех элементов
и вернуть индекс элемента
1 |
li |
с классом
1 |
.cinque |
:
var listIndex = $('.cinque');
console.log('Index of ' + $('li').index(listIndex));Найти элемент с классом
среди соседних элементов и вернуть его индекс:
console.log('Index of ' + $('.sei').index());Как видим, способы получения индекса элемента разные, а результат один.
Метод eq
Метод
прямопротивоположен методу
1 |
.index() |
. Этот метод возвращает элемент (как объект) по его индексу (порядковому номеру).
Если взять предыдущую HTML-разметку, то такой javascript-код:
$('li').eq(1).html("Secondo");… изменит содержимое второго по счету элемента
на “Secondo”. Почему второго? Как можно догадаться, результатом выборки
1 |
$('li')
|
является массив элементов; а в массиве индексирование элементов начинается с нуля (0).
Методы eq и index
Рассмотренные выше примеры использования методов
и
1 |
.index() |
просты и понятны. И неинтересны.
Гораздо более интеерсным примером является случай объединения обоих методов в jQuery-цепочке.
Приведу такой гипотетический пример:
<ul class="test">
<li class="test__item primo">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="test__item secondo">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="test__item tetro">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="test__item quattro">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="test__item cinque">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="test__item sei">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="test__item sedici">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
<li class="test__item">
<a href="#" class="test__link">test item link</a>
</li>
</ul>$('.test__item').click(function(){
$('li').eq($(this).index()).html($(this).index()).siblings().html("test item link");
});Javascript-код, написанный выше, читается таким образом:
- сделать выборку всех элементов с классом
1
.test__item
- при клике мыши на любом из этих элементов выполнить функцию:
- сделать выборку всех элементов
1
li
- вернуть индекс активного элемента из выборки –
1
$(this).index()
- вернуть активный элемент по его индексу –
1
.eq($(this).index())
- для возвращенного элемента
1
.eq($(this).index())
1
html($(this).index())
- всем соседним (sibling) элементам установить значение в –
1
.siblings().html("test item link")
- сделать выборку всех элементов
Пример рабочий, поэтому его можно свободно попробовать.
В принципе, на этом все.

Definition of jQuery index
The jQuery index() function is used to return the index of the specific element with respect to the selector. The jQuery index() function is a built-in function in jQuery. The jQuery index() function searches for the specified element among the matched elements, if the element is found it, then it returns the index of the element, if the element is not found in the matched elements, then it returns -1. If no parameter is passed to the index() function, then it returns the position of the first element present within the jQuery object.
Syntax:
$(selector). index(element);Parameters:
- element – This is an optional parameter. It specifies the element which is to search and return the index value with respect to the selector.
- Return value – The return value of this function is the index value of the specified element.
Working of the jQuery index() Function
The JQuery index() function accepts one parameter, the parameter is the element that is to search in the matched elements. Suppose we have an element used on the page next we need to find the index of a specific element like “div”. So we can use the index() function as “$( “div” ).index( );”, which will return a number that indicates the index of “div” element in the page.
Examples
Example of jQuery index() function to get the index value of the specific element –
Example #1
Code:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.0.js"></script>
<title> This is an example for jQuery index( ) function </title>
<script>
$(document).ready(function() {
$("li").click(function() {
$("li").css( {"color": "black"} );
$(this).css( {"color" : "red"} );
$( "#p1" ).text("The $("li").index() is : " + $(this).index());
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h3> This an example of index() function: </h3>
<div> Click the below list of elements to get their index value among their list. </div>
<h2> The List of Vegetables are : </h2>
<ol>
<li> Corn </li>
<li> Mushroom </li>
<li> Broccoli </li>
<li> Cucumber </li>
</ol>
<h2> The List of Fruits are : </h2>
<ol>
<li> Apple </li>
<li> Banana </li>
<li> Cherry </li>
<li> Pome </li>
</ol>
<p id = "p1"> </p>
</body>
</html>An output of the above code is –
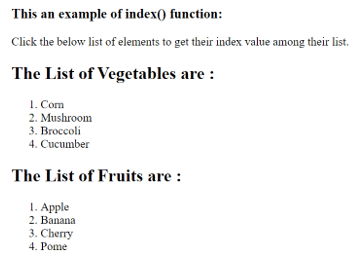
Once we click on the list of elements, the respective outputs are –
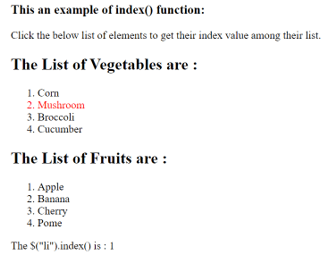

In the above code, there are two order lists created for the vegetables and fruits. Next, the index() function is used to get the index of selected or clicked list elements as “$( this ).index();”. Note that both the lists are different, so the element gives the index value with respect to its list, as we can see in the above output.
Example of jQuery array indexOf() function to get the index of the elements from the selector with passing parameter value for the search –
Example #2
Code:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset = "utf-8">
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.0.js"></script>
<title> This is an example for jQuery index( ) function </title>
<script>
$(document).ready(function() {
$("p").click(function() {
$("p").css( {"color" : "black", "border" : "0px solid black"} );
$(this).css( {"color" : "red", "border" : "2px solid black"} );
alert("The $("p").index( "p" ) is : " + $(this).index("p")+ "nThe $(".c1").index( "p" ) is : " + $(".c1").index("p"));
});
$("span").click(function() {
$("span").css( {"color" : "black", "border" : "0px solid black"} );
$(this).css( {"color" : "red", "border" : "2px solid black"} );
alert("The $("span").index( "span" ) is : " + $(this).index("span")+ "nThe $(".c1").index( "span" ) is : " + $(".c1").index("span"));
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h3> This an example of index() function: </h3>
<p> This is a first paragraph without any class. </p>
<span class = "c1" > This is a first span box with class "c1". </span>
<p class = "c1" > This is a second paragraph with class "c1". </p>
<span class = "c1" > This is a second span box with class "c1". </span>
<br>
</body>
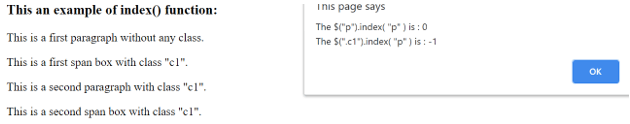
</html>An output of the above code is –

Once we click on the first p element, the output is –
Once we click on the first span element, the output is –

Once we click on the second p element, the output is –
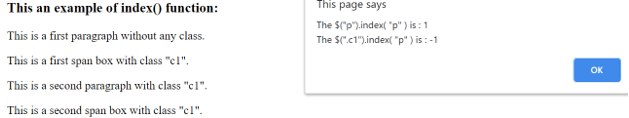
Once we click on the second span element, the output is –
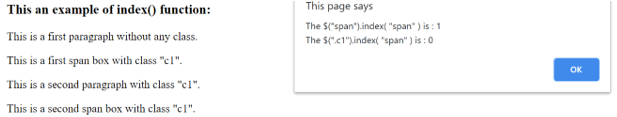
In the above code, the “h3” “p” and “span” elements are used, “p” and “span” used with the class as well. Next, the index() function is used to get the index of selected or clicked elements with and without class. The code “$( “.c1” ).index( “span”);” selects the elements who have class “c1” and among these select “span” element index in the selected list. We can see in the above output the result for a different combination.
Example of jQuery array indexOf() function to get the index of the multiple elements –
Example #3
Code:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset = "utf-8">
<script src = "https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.0.js"></script>
<title> This is an example for jQuery index( ) function </title>
<script>
$(document).ready(function() {
$("button").click(function() {
alert("$("p").index() : " +$("p").index() + "n$("p, h3").index() : " +$("p, h3").index() + "n$("h3, p").index() : " +$("h3, p").index());
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h3> This an example of index() function: </h3>
<p> This is paragraph. </p>
<span > This is a span box. </span>
<br>
<br>
<button> Get the index of an element </button>
</body>
</html>An output of the above code is –

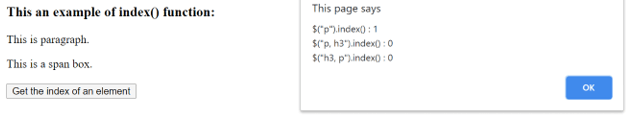
In the above code, the “h3” “p” and “span” elements are used. Next, the index() function is used to get the index of “p” which returned 1, then used to get the index of “p” and “h3” in one call which returned the index of “h3” that is the lowest index and also try third time alternatively, there also return the “h3” index that is the lowest index. So among the multiple selectors, it gives the lowest index, as we can see in the above output.
Conclusion
The jQuery index() function is a built-in function, which is used to returns the index of the specific element with respect to the selector.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to jQuery index. Here we discuss the description, syntax, parameters, working of the JQuery index() function, and examples with code implementation respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
- jQuery removeClass()
- jQuery Deferred
- jQuery window
- jQuery move element
