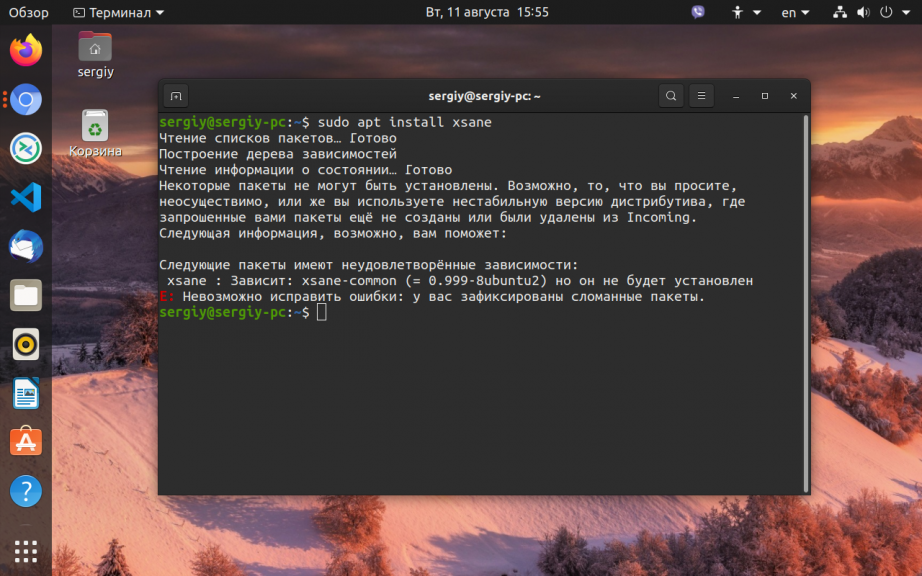
Во время установки программ с помощью пакетного менеджера apt в любом из дистрибутивов, использующих этот пакетный менеджер, вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой, что у вас зафиксированы сломанные пакеты. Это пакеты, которые не установились полностью потому что им не хватает зависимостей или процесс установки был по какой-либо причине прерван.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим что делать с такой ошибкой, как её исправить, а также я дам ссылки на другие материалы на сайте, которые помогут справится с проблемой.
Как исправить у вас зафиксированы сломанные пакеты?
1. Обновите списки пакетов
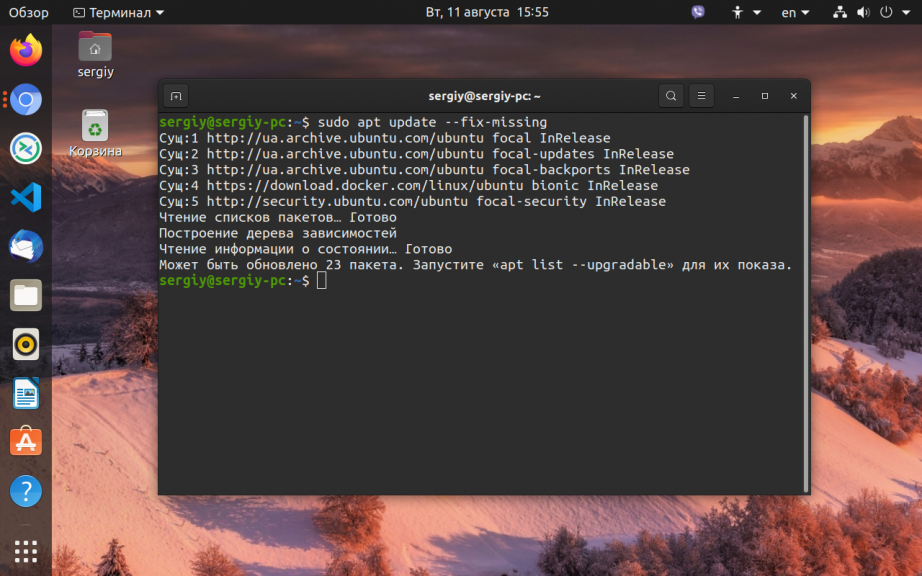
Возможно вам не удалось установить нужные пакеты потому что списки репозиториев устарели, и там ещё не было нужных пакетов. Для обновления списка пакетов выполните:
sudo apt update --fix-missing
2. Установите битые пакеты
После обновления списка пакетов из репозиториев может помочь установка битых пакетов. Этот шаг поможет особенно если вы устанавливали пакет с помощью dpkg и теперь нужно доустановить его зависимости с помощью пакетного менеджера. Для этого есть специальная команда:
sudo apt install -f
3. Очистите лишние пакеты
Установке могут мешать лишние пакеты, которые больше не нужны в системе. Для их удаления выполните:
sudo apt clean
Затем:
sudo apt autoremove
Утилита отобразит список всех битых пакетов, которые не установлены, вы можете попытаться их удалить с помощью команды:
sudo dpkg --remove -force --force-remove-reinstreq имя_пакета
4. Используйте dpkg
Вместо apt вы можете использовать команду dpkg чтобы посмотреть какие пакеты вызывают проблему. Просто выполните:
sudo dpkg --configure -a
Команда покажет проблемные пакеты, а потом вы сможете их удалить той же командой:
sudo dpkg --remove -force --force-remove-reinstreq имя_пакета
5. Разрешите зависимости
Битые пакеты чаще всего появляются из-за того, что пакетный менеджер не может найти для них нужные зависимости. Если вам всё же очень нужно установить такой пакет, просто разрешите эти зависимости. Для этого можно скачать и установить их вручную или если вы уверенны, что зависимости в пакете указаны неверно, можно скачать его распаковать и удалить мешающие зависимости. Подробнее об этом читайте в этой статье.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрели что делать если в вашей системе появились битые пакеты и как их исправить. Здесь решение проблемы очень сильно зависит от вашей ситуации, но здесь приведены основные варианты решения, которые должны помочь вернуть пакетный менеджер к работе. Иногда рекомендуют удалить пакет вручную из базы данных dpkg /var/lib/dpkg/status, однако лучше этого не делать и найти путь решить проблему по другому, ручное редактирование подобных файлов может создать ещё больше проблем.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
Об авторе
Основатель и администратор сайта losst.ru, увлекаюсь открытым программным обеспечением и операционной системой Linux. В качестве основной ОС сейчас использую Ubuntu. Кроме Linux, интересуюсь всем, что связано с информационными технологиями и современной наукой.
Поврежденные пакеты нуждаются в ремонте, иначе программное обеспечение не будет запускаться. Вот как найти поврежденные пакеты и исправить их в Linux.
Менеджеры пакетов в Linux позволяют контролировать установку и удаление пакетов. В дополнение к этому менеджеры пакетов также помогают вам находить поврежденные пакеты в вашей системе и переустанавливать их, чтобы устранить различные проблемы, связанные с пакетами Linux.
Если вы не знаете, какие команды использовать для поиска и исправления поврежденных пакетов в Linux, то это руководство для вас. Мы кратко обсудим поврежденные пакеты, как вы можете проверить, содержит ли ваша система поврежденные пакеты, и как их правильно переустановить.
Что такое поврежденные пакеты?
Когда вы устанавливаете новый пакет в Linux, менеджер пакетов вашей системы отвечает за весь процесс установки. Эти менеджеры пакетов имеют встроенные методы для обработки исключений и ошибок. Но иногда, в случае непредвиденных проблем, установка останавливается, и полный пакет не устанавливается. Такие пакеты в Linux называются поврежденными пакетами.
Менеджеры пакетов, такие как APT, не разрешают дальнейшую установку пакетов, если обнаруживается поврежденный пакет в системе. В такой ситуации восстановление поврежденного пакета является единственным вариантом.
Как найти и исправить поврежденные пакеты
Каждый менеджер пакетов обрабатывает разные типы пакетов. Например, DNF и YUM работают с Red Hat Package Manager (RPM) для загрузки и установки пакетов RPM. Аналогично, APT действует как оболочка интерфейса для базового программного обеспечения dpkg в дистрибутивах на основе Debian.
Переустановка поврежденных пакетов в Ubuntu и Debian
APT – это менеджер пакетов по умолчанию, который предустановлен в каждом дистрибутиве на основе Debian. Помимо APT, пользователи Debian и Ubuntu также могут загружать и устанавливать пакеты вручную с помощью dpkg.
Шаги, упомянутые ниже, также будут работать, если вы хотите исправить поврежденные пакеты в Kali Linux, поскольку, в конце концов, Kali – это дистрибутив на основе Debian.
Как исправить поврежденные пакеты в дистрибутивах на основе Debian с помощью APT:
- Откройте терминал, нажав Ctrl + Alt + T на клавиатуре и введите:
2. Обновите список пакетов вашей системы из доступных источников
3. Теперь принудительно установите поврежденные пакеты, используя флаг -f. APT автоматически выполнит поиск поврежденных пакетов в вашей системе и переустановит их из официального репозитория.
Если вышеупомянутые шаги не работают для вас, вы можете попытаться решить проблему с помощью dpkg.
- Заставьте dpkg перенастроить все ожидающие пакеты, которые уже распакованы, но нуждаются в настройке. Флаг -a в команде означает Все.
2. Передайте grep с помощью dpkg, чтобы получить список всех пакетов, помеченных как требуемые dpkg.
3. Используйте флаг –remove, чтобы удалить все поврежденные пакеты
4. Очистите кэш пакетов и установите скрипты с помощью apt clean.
5. Теперь обновите списки пакетов вашей системы, используя следующую команду:
Исправить поврежденные пакеты в Fedora / CentOS и RHEL
Хотя YUM и DNF отлично подходят для автоматического управления поврежденными пакетами, иногда возникают проблемы, поскольку в системе Linux установлены тысячи пакетов. В таких ситуациях вы можете использовать RPM (базовый менеджер пакетов для Fedora и CentOS) для быстрого устранения таких проблем.
- Проверьте все пакеты в вашей системе, используя флаг -V.
2. Вы увидите длинный список, содержащий все установленные пакеты в вашей системе.
3. Переустановите пакет, который, по вашему мнению, может вызывать проблему с поврежденным пакетом.
Описанные выше шаги крайне неудобны — определение того, какой пакет вызывает проблему, из списка сотен утомительно. Хотя RPM является мощным менеджером пакетов, и вы редко будете сталкиваться с такими проблемами, знание того, как устранить эти проблемы, по-прежнему важно на случай, если вы столкнетесь с подобной ситуацией в ближайшем будущем.
Управление пакетами в дистрибутивах Linux
Менеджеры пакетов в Linux способны справиться с большинством проблем, включая неудачные установки. Но иногда возникают различные проблемы, которые можно решить только интуитивно. Решение для исправления поврежденных пакетов состоит из нескольких шагов — определение поврежденного пакета, его переустановка и обновление списка пакетов системы.
В Интернете доступно бесчисленное множество дистрибутивов Linux, которые стоит попробовать, но в глубине души каждый из них имеет схожую основу. Среды рабочего стола выделяют каждый дистрибутив, предоставляя уникальный пользовательский интерфейс. Выбор идеальной среды рабочего стола, которая соответствует вашему вкусу, должен быть вашим приоритетом, если вы, наконец, решили перейти на Linux.
Смотрите другие статьи на нашем канале .
Как запускать команды Linux в фоновом режиме
8 Советов по настройке рабочего стола Cinnamon в Linux
Как использовать рабочие пространства и активные углы в Linux Mint
Вы также можете оставить свое мнение об этом посте в разделе комментариев.
I just recently bought an arduino and requires gcc-avr/avrdude to compile the software. I installed avr for another microprocessor component a while ago but is obviously an outdated version (gcc version 3.3 20030512 (prerelease)) so I went ahead to update these but it didn’t work.
(Please note that before hand I also broke my aptdaemon through an incomplete wine installation (couldn’t get passed font installation agreement) but I fixed that via a re-installation then accepting the agreement.)
I am trying to update these by running bingo’s build script but the dependencies it requires cannot be installed due to avr… terminal reports
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
build-essential is already the newest version.
libncurses5-dev is already the newest version.
libncurses5-dev set to manually installed.
libusb-0.1-4 is already the newest version.
libx11-dev is already the newest version.
You might want to run 'apt-get -f install' to correct these:
The following packages have unmet dependencies:
arduino-core : Depends: gcc-avr but it is not going to be installed
avr-libc : Depends: gcc-avr (>= 1:4.3.4) but it is not going to be installed
Depends: binutils-avr (>= 2.20) but it is not going to be installed
binutils-dev : Depends: binutils (= 2.21.0.20110327-2ubuntu3) but 2.21.0.20110327-2ubuntu2 is to be installed
libcwidget-dev : Depends: libcwidget3 (= 0.5.16-3ubuntu2) but it is not going to be installed
Depends: libsigc++-2.0-dev but it is not going to be installed
Depends: libncursesw5-dev but it is not going to be installed
libmpfr-dev : Depends: libgmp3-dev (>= 4.2.dfsg-1) but it is not going to be installed
python-dev : Depends: python (= 2.7.1-0ubuntu5.1) but 2.7.1-0ubuntu5 is to be installed
Depends: python2.7-dev (>= 2.7.1-1~) but it is not going to be installed
tk8.4-dev : Depends: tk8.4 (= 8.4.19-4) but it is not going to be installed
E: Unmet dependencies. Try 'apt-get -f install' with no packages (or specify a solution).
But running
apt-get -f install
results in
(Reading database ... 163021 files and directories currently installed.)
Unpacking binutils-avr (from .../binutils-avr_2.20.1-1ubuntu2_i386.deb) ...
dpkg: error processing /var/cache/apt/archives/binutils-avr_2.20.1-1ubuntu2_i386.deb (--unpack):
trying to overwrite '/usr/bin/avr-size', which is also in package avr-binutils 2.13.90.030512-2
dpkg-deb: error: subprocess paste was killed by signal (Broken pipe)
Unpacking gcc-avr (from .../gcc-avr_1%3a4.3.5-1_i386.deb) ...
dpkg: error processing /var/cache/apt/archives/gcc-avr_1%3a4.3.5-1_i386.deb (--unpack):
trying to overwrite '/usr/bin/avr-g++', which is also in package avr-gcc-c++ 3.2.90.20030512-2
dpkg-deb: error: subprocess paste was killed by signal (Broken pipe)
Errors were encountered while processing:
/var/cache/apt/archives/binutils-avr_2.20.1-1ubuntu2_i386.deb
/var/cache/apt/archives/gcc-avr_1%3a4.3.5-1_i386.deb
E: Sub-process /usr/bin/dpkg returned an error code (1)
I have tried running update manager and updating my system via it but all I get is an error message
The following packages have unmet dependencies:
arduino-core: Depends: gcc-avr but it is not installed
avr-libc: Depends: gcc-avr (>= 1:4.3.4) but it is not installed
Depends: binutils-avr (>= 2.20) but it is not installed
which then tells me to try running apt-get -f install which just results the same as last time.
So how can I fix my system, I really need the new avr, please 🙂
BTW, my system is Ubuntu 11.04
Introduction
Linux packages are compressed archives containing programs and files necessary to run them. The package distribution system is designed to be robust and simplify the application installation process.
However, a bad internet connection or misconfigured third-party installers can corrupt packages and cause problems on your system.
This article will show you how to troubleshoot and fix broken packages on Ubuntu using the available APT and DPKG tools.

Prerequisites
- An account with sudo privileges
- An Ubuntu system
Check for Updates
Start troubleshooting by rebuilding the list of dependencies. The --fix-missing option tells APT to ignore missing packages. The option ensures the update process is performed without APT returning an error.
sudo apt update --fix-missing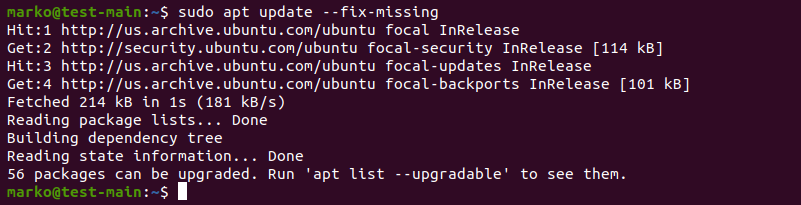
Force APT to Correct Missing Dependencies or Broken Packages
Missing package dependencies are a common reason for package-related errors.
1. Use apt install with the -f flag to tell APT to locate the missing packages and install them.
sudo apt install -fAPT lists the missing packages on your system.
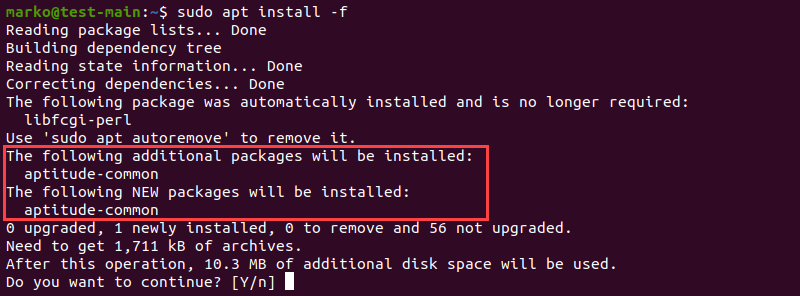
2. Press ENTER to start the installation.
Note: If troubleshooting has led to Ubuntu needing to be reinstalled, please refer to our reinstallation guide How to Reinstall Ubuntu.
Force Reconfigure or Remove Broken Packages with DPKG
Broken packages may cause package manager configuration problems.
1. Reconfigure DPKG, the base package management system, with the following command:
sudo dpkg --configure -a2. Check if DPKG marked some packages as needing a reinstall.
sudo dpkg -l | grep ^..R
3. If the command above returns a list of one or more packages, try removing the packages by typing:
sudo dpkg --purge --force-all [package-name]The example below shows how to remove the corrupted vlc-plugin-base package.
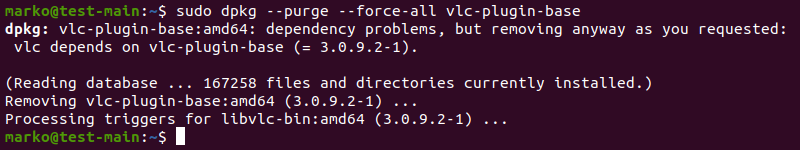
Warning: The dpkg --purge --force-all command removes a package even if the removal causes further dependency issues. Use the command with care.
4. After you finish troubleshooting, run the following command to clean up the system:
sudo apt clean5. Then update the repositories again:
sudo apt updateResolve DPKG Lock Issue
The DPKG lock error appears when trying to install a package while another process is using DPKG.
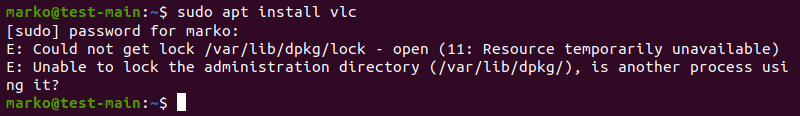
However, sometimes the error occurs even if no other processes are using the package management system.
1. To fix the problem, remove the lock file manually:
sudo rm /var/lib/apt/lists/lock2. Also, remove the lock in cache:
sudo rm /var/cache/apt/archives/lockDeleting the lock enables you to use APT and DPKG again.
Conclusion
The article provided common ways of resolving problems caused by broken packages on Ubuntu.
For more information related to package management on Ubuntu, read:
- How to List Installed Packages on Ubuntu
- A Comprehensive Guide to Using Snap Packages on Ubuntu
- How to Install Deb Files (Packages) on Ubuntu
One of the best things about Linux is the apt command which lets you install applications and software effortlessly. Using apt, you don’t have to go through downloading the software, then going through the installer and clicking ‘Next’ a dozen times. It makes sure that every software is installed with just one terminal command.
But, just like any other program, things can go wrong. The error that we will be talking about in this write-up looks something like the following:
E: Unable to correct problems, you have held broken packages.This error may occur when you are trying to install something via the apt utility. Let us look into the error in detail and try to solve the problem.
What causes this error?
Some of the software (mostly third-party ones) do not come with compatible dependencies and apt expects that your system already has those components. In case the required components aren’t found on your system, apt throws an error related to broken packages which means that the package you are trying to install is incomplete.
Outdated repositories, problems with the ‘sources.list‘ file, or an old/unsupported version of Linux might be the cause of this problem.
Methods to fix this problem
Before moving to the advanced methods, let us try a few quick tricks that can potentially help:
Method 1: Update the repositories
The apt update is a well-known command which instantly updates the list of packages and their dependencies. As the problem we are facing is due to missing dependencies, there is a good chance that this command will fix the error.
If the problem persists, try this command:
This will update the existing packages on your system to the latest version.
Method 2: Use aptitude instead of apt
Aptitude is also a package manager like apt and it surprisingly works in some situations where apt doesn’t! all you need to do is use aptitude instead of apt.
For example, suppose you want to install BIND9 using aptitude, you will have to enter the following command:
sudo aptitude install bind9
If you don’t have aptitude installed, run the following commands:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install aptitude
Method 3: Use autoremove to get rid of unnecessary packages
Sometimes, unnecessary packages stay behind even after uninstalling their parent application. These residual packages might interfere with installation of new applications or libraries. To get rid of these unnecessary residual packages, just enter the following command into the terminal:
There’s no need to worry as autoremove will only handle the leftover packages and dependencies.
Now with the basics out of the way, we will look at some more advanced methods to solve this problem.
Method 4: Look for held packages and unhold them
As the error message suggests, the problem is caused by packages on hold. The term ‘held package’ means that it can’t be upgraded, removed, or modified in any way.
To get a list of held packages, you need to enter the following command:
To unhold a specific package, enter:
sudo apt-mark unhold <package-name>
To unhold all held packages, enter:
sudo apt-mark unhold $(sudo apt-mark showhold)
Method 5: Use the synaptic package manager to fix broken packages
Originally, Linux doesn’t have an inbuilt graphical package manager like Windows. This is why the synaptic package manager became immensely popular on Debian-based distributions made for personal computers as it provided a lightweight and robust GUI package manager.
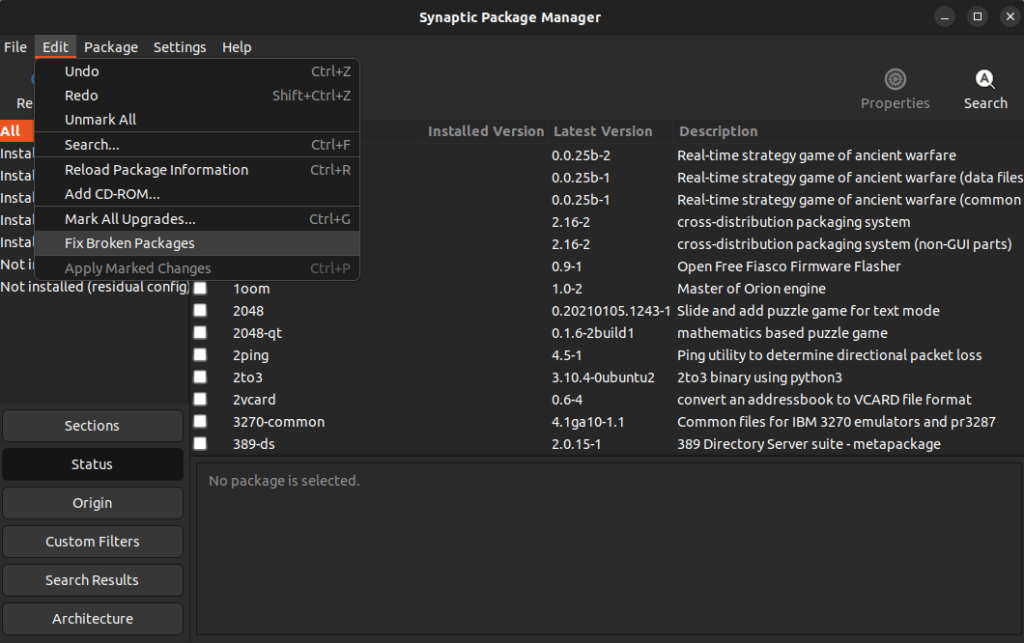
One of the key features of this utility is that you can fix broken packages very easily. Follow the steps below:
1. First, install the synaptic package manager:
sudo apt update sudo apt install synaptic
2. Run synaptic with superuser privileges:
3. Go to Edit > Fix Broken Packages
It will take some time if there are broken packages present. Check if the problem is resolved.
References
- Ask Ubuntu – Unhold a package
- Ask Ubuntu thread on the same problem
Summary
In this article, we saw five different methods to fix the error “Unable to correct problems, you have held broken packages.” All the methods discussed were easy to execute and I hope you were able to fix the problem on your system. If you are still facing the same issue even after trying all the above methods, it can be because of using an unsupported Linux distribution, in which case, you will have to consider upgrading to a newer version of it.