“I know well what I am fleeing from but not what I am in search of” – Michel de Montaigne
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Download the Source Code
- 3 What is the VBA Find Function?
- 4 Introduction
- 4.1 Excel Find Dialog
- 4.2 How to Use Options With Find
- 5 VBA Find Parameters
- 5.1 Important Note about Find Parameters
- 6 The Find Return Value
- 7 How to do a Simple Find
- 7.1 When the Value is not Found
- 8 Using After with Find
- 8.1 Example 1 Without After
- 8.2 Example 2 Using After
- 8.3 Example 3 Wrapping Around
- 9 Using LookIn with Find
- 10 Using LookAt with Find
- 11 Using SearchOrder with Find
- 12 Using SearchDirection with Find
- 12.1 Using xlPrevious with After
- 13 Using MatchCase with Find
- 14 Using MatchByte with Find
- 15 Using the WildCard
- 16 Using SearchFormat with Find
- 16.1 Using Wild Card with Format
- 16.2 Important – Clearing Format
- 17 Multiple Searches
- 18 Finding the Last Cell Containing Data
- 19 Finding Cells with Patterns
- 20 An Alternative to using VBA Find
- 21 Find and Replace
- 22 What’s Next?
Introduction
This post covers everything you need to know about the VBA Find function. It explains, how to use Find, in simple terms. It also has tons of code examples of Find you can use right now.
If you want to go straight to an example of Find then check out How to do a Simple Find.
If you want to search for text within a string then you are looking for the InStr and InStrRev functions.
If you want to find the last row or column with data then go to Finding the Last Cell Containing Data
Download the Source Code
What is the VBA Find Function?
The Find function is very commonly used in VBA. The three most important things to know about Find are:
- The Find function is a member of Range.
- It searches a range of cells containing a given value or format.
- It is essentially the same as using the Find Dialog on an Excel worksheet.
Introduction
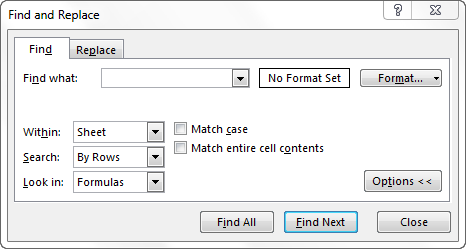
Excel Find Dialog
To view the Excel Find dialog, go to the Home ribbon and click on Find & Select in the Editing section. In the menu that appears select Find(shortcut is Ctrl + F)
When you do this the following dialog will appear:
The VBA Find function uses most of the options you can see on this Dialog.
How to Use Options With Find
To use the options you pass them as parameters to the Find function. This is similar to how you use worksheet functions. For example, the Sum function has a Range as a parameter. This means you give it a range when you use it.
The VBA Find uses parameters in the same way. You must give it the item you are searching for. This is the first parameter and it is required.
The rest of the parameters are optional. If you don’t use them then Find will use the existing settings. We’ll see more about this shortly.
The table in the next section shows these parameters. The sections that follow this, give examples and details of how to use these parameters.
VBA Find Parameters
The following tables shows all the Find parameters.
| Parameter | Type | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| What | Required | The value you are searching for | Any VBA data type e.g String, Long |
| After | Optional | A single cell range that you start your search from | Range(“A5”) |
| LookIn | Optional | What to search in e.g. Formulas, Values or Comments | xlValues, xlFormulas, xlComments |
| LookAt | Optional | Look at a part or the whole of the cell | xlWhole, xlPart |
| SearchOrder | Optional | The order to search | xlByRows or xlByColumns. |
| SearchDirection | Optional | The direction to search | xlNext, xlPrevious |
| MatchCase | Optional | If search is case sensitive | True or False |
| MatchByte | Optional | Used for double byte languages | True or False |
| SearchFormat | Optional | Allow searching by format. The format is set using Application.FindFormat | True or False |
Important Note about Find Parameters
Keep the following in mind as it can cause a lot of frustration when using Find.
As you can see from the table most of the VBA Find parameters are optional. As we said earlier, if you don’t set a Find parameter it uses the existing setting.
For example, if you set the LookIn parameter to xlComments, it will search for a value in comments only. The next time you run Find(either from the Dialog or from VBA) the existing LookIn setting will be Comments.
The following code shows an example of this
' Search in comments only Range("A1:A5").Find "John", LookIn:=xlComments ' Will search comments as this is the existing setting Range("A1:A5").Find "John" ' Search in formulas only Range("A1:A5").Find "John", LookIn:=xlFormulas ' Will search formulas as this is the existing setting Range("A1:A5").Find "John"
This applies to the parameters LookIn, LookAt, SearchOrder, and MatchByte.
The Find Return Value
If the search item is found then Find returns the cell with the value. That is, it returns a Range type of one cell.
If the search item is not found then Find returns an object set to Nothing.
In the following examples, you will see how to deal with the return value.
How to do a Simple Find
Let’s start with a simple example of the VBA Find. You need three things when using the Find function
- The Range to search
- The value you are searching for
- The Range to store the returned cell
Let’s take the following sample data
We are going to search for the text “Jena” in the cells A1 to A5.
The following code searches for “Jena”. When it finds “Jena”, it then places the cell in the rgFound variable.
' Find the name Jena in the range A1:A5 Dim rgFound As Range Set rgFound = Range("A1:A5").Find("Jena") ' Print cell address to Immediate Window(Ctrl + G) Debug.Print rgFound.Address
The above code shows the most basic search you can do. If this is your first time using the VBA Find function then I recommend you practice with a simple example like this.
If you want to try these examples you can download the workbook from the top of this post.
When the Value is not Found
When you use the VBA Find function, there will be times when you do not find a match. You need to handle this in your code or you will get the following error when you try to use the returned range
The following code will give this error if the text “John” is not found in the range A1 to A5
Set rgFound = Range("A1:A5").Find("John") ' Shows Error if John was not found Debug.Print rgFound.Address
What we need to do is check the return value like the following code shows
Set rgFound= Range("A1:A5").Find("John") If rgFound Is Nothing Then Debug.Print "Name was not found." Else Debug.Print "Name found in :" & rgFound.Address End If
Using After with Find
The After parameter is used if you want to start the search from a particular cell. When, the Excel Find Dialog is used, the active cell is considered the After cell. In other words, this cell is the starting point for the search. In VBA, if no After parameter is specified then the search starts at the top-left cell of the range.
Example 1 Without After
Let’s look at the following code.
Set cell = Range("A1:A6").Find("Rachal")
Find will return the cell A2 as this is where the first “Rachal” is found.
Example 2 Using After
In the next example, we use after. We are telling VBA to start the search for “Rachal” after cell A2
Set cell = Range("A1:A6").Find("Rachal", After:=Range("A2"))
This will return the cell A6
Example 3 Wrapping Around
If a match is not found then the search will “wrap around”. This means it will go back to the start of the range.
In the following example, we are looking for Drucilla. We start our search After cell A2. Find will search from A3 to A6 and then will move to A1.
So the following code will return A1 as there is no text “Drucilla” from A3 to A6:
Set cell = Range("A1:A6").Find("Drucilla", After:=Range("A2"))
The search order for this example was A4, A5, A6, A1.
You can try these example for yourself by downloading the workbook from the top of the post.
Using LookIn with Find
Using LookIn allows you to search in Values, Formulas or Comments.
Important Note: When a cell has text only, this text is considered a formula AND a value. See the table below for details
| Cell Contains | Result | LookIn value is |
|---|---|---|
| Apple | Apple | Value and Formula |
| =”App” & “le”‘ | Apple | Value only |
| =LEFT(“Apple”,4)’ | Appl | Formula only |
We are going to use the following sample data.
A2 Contains “Apple” as a value only
A3 Contains “Apple” as a formula only
A4 Contains “Apple” in the comment only
The code below searches for “Apple” in the different types: value, formula, threaded comment and note.
To see a working example of this code you can download the source code from the top of this post.
' Searches in value, formula, threaded comment and note. ' https://excelmacromastery.com/excel-vba-find/ Sub UseLookIn() ' Finds A2 Dim rgFound As Range Set rgFound = shLookin.Range("A1:A5").Find("Apple", LookIn:=xlValues) Debug.Print "Found 'Apple' as value in: " & rgFound.Address ' Finds A3 Set rgFound = shLookin.Range("A1:A5").Find("Apple", LookIn:=xlFormulas) Debug.Print "Found 'Apple' as formula in: " & rgFound.Address ' Finds A4 Set rgFound = shLookin.Range("A1:A5").Find("Apple", LookIn:=xlCommentsThreaded) Debug.Print "Found 'Apple' as comment threaded in: " & rgFound.Address ' Finds A5 Set rgFound = shLookin.Range("A1:A5").Find("Apple", LookIn:=xlNotes) Debug.Print "Found 'Apple' as note in: " & rgFound.Address End Sub
Important note that I have used xlCommentsThreaded for the third one as threaded comments are used in Office 365. If you are using an older version that doesn’t have threaded comments then use xlComments.
Using LookAt with Find
Using the LookAt function is pretty straightforward.
- xlWhole means the search value must match the entire cell contents.
- xlPart means the search value only has to match part of the cell.
The following example has “Apple” as part of the cell contents in A2 and it is the full contents in cell A3.
The first Find in the following code finds “Apple” in A2. The second Find is looking for a full match so finds A3.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseLookAt() Dim cell As Range ' Finds A2 Set cell = Range("A1:A3").Find("Apple", Lookat:=xlPart) Debug.Print cell.Address ' Finds A3 Set cell = Range("A1:A3").Find("Apple", Lookat:=xlWhole) Debug.Print cell.Address End Sub
You can try these example for yourself by downloading the workbook from the top of the post.
Using SearchOrder with Find
The SearchOrder parameter allows us to search by row or by column. In the following sample data we have two occurrences of the text “Elli”.
If we search by row we will find the “Elli” in B2 first. This is because we search in the order row 1, then row 2 etc.
If we search by column we will find the “Elli” in A5 first. This is because we search in the order column A, the Column B etc.
The following code shows an example of using the SearchOrder with this sample data
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseSearchOrder() Dim cell As Range ' Finds B2 Set cell = Range("A1:B6").Find("Elli", SearchOrder:=xlRows) Debug.Print cell.Address ' Finds A5 Set cell = Range("A1:B6").Find("Elli", SearchOrder:=xlColumns) Debug.Print cell.Address End Sub
Using SearchDirection with Find
SearchDirection allows you to search forward or backward. So imagine you have the range A1:A7. Searching using xlNext will go in the order
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7
Searching using xlPrevious will go in the order
A7, A6, A5, A4, A3, A2, A1
Using xlNext with the sample data will return A2 as this where it finds the first match. Using xlPrevious will return A6.
' NOTE: Underscore allows breaking up a line ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseSearchDirection() Dim cell As Range ' Finds A2 Set cell = shData.Range("A1:A7") _ .Find("Elli", SearchDirection:=xlNext) Debug.Print cell.Address ' Finds A6 Set cell = shData.Range("A1:A7") _ .Find("Elli", SearchDirection:=xlPrevious) Debug.Print cell.Address End Sub
Using xlPrevious with After
It you use the After parameter with xlPrevious then it will start before from the After cell. So if we set the After cell to be A6 then the search order will be
A5,A4,A3,A2,A1,A7,A6.
The following code shows an example of this
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseSearchDirectionAfter() Dim cell As Range ' Finds A2 Set cell = shData.Range("A1:A7").Find("Elli" _ , After:=Range("A6"), SearchDirection:=xlPrevious) Debug.Print cell.Address ' Finds A6 Set cell = shData.Range("A1:A7").Find("Elli" _ , After:=Range("A7"), SearchDirection:=xlPrevious) Debug.Print cell.Address End Sub
Using MatchCase with Find
The MatchCase parameter is used to determine if the case of the letters matters in the search. It can be set to True or False.
- True – the case of the letters must match
- False – the case of the letters does not matter
The following sample list has two entries for “Elli”. The second has a small letter e
The following code examples show the result of setting MatchCase to True and False
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseMatchCase() Dim cell As Range ' Finds A2 Set cell = Range("A1:B6").Find("elli", MatchCase:=False) Debug.Print cell.Address ' Finds A6 Set cell = Range("A1:B6").Find("elli", MatchCase:=True) Debug.Print cell.Address End Sub
Using MatchByte with Find
The MatchByte parameter is used for languages with a double-byte character set. These are languages such as Chinese/Japanese/Korean.
If you are not using them then this parameter is not relevant. They are used as follows
- True means to match only double-byte characters with double-byte characters.
- False means to double-byte characters can match with single or double-byte characters.
Using the WildCard
We can use the asterisk symbol(*) as a wild card when searching for text. The asterisk represents one or more characters.
For example
“T*” will find any word that starts with T.
“To*” will find any word that starts with To.
“*y” will find any word that ends with y.
“*ey” will find any word that ends with ey.
The code below shows examples of using the wildcard based on this data:
' Examples of using the wild card ' https://excelmacromastery.com/excel-vba-find/ Sub WildCard() Dim rgFound As Range ' Finds Tom in A2 Set rgFound = shWildCard.Range("A1:A6").Find("T*") Debug.Print rgFound.Value & " was found in cell " & rgFound.Address ' Finds Tim in A5 Set rgFound = shWildCard.Range("A1:A6").Find("Ti*") Debug.Print rgFound.Value & " was found in cell " & rgFound.Address ' Finds Tommy in A4 Set rgFound = shWildCard.Range("A1:A6").Find("*my") Debug.Print rgFound.Value & " was found in cell " & rgFound.Address ' Finds Ellen in A3 Set rgFound = shWildCard.Range("A1:A6").Find("*len*") Debug.Print rgFound.Value & " was found in cell " & rgFound.Address ' Finds Helen in A6 Set rgFound = shWildCard.Range("A1:A6").Find("*elen*") Debug.Print rgFound.Value & " was found in cell " & rgFound.Address End Sub
Using SearchFormat with Find
Search Format is a bit different than the other parameters. It allows you to search for a cell format such as font type or cell color.
You need to set the format first by using the Application.FindFormat property. Then you set SearchFormat to True to search for this format.
In the following sample data, we have two cells formatted. Cell A5 is set to Bold and Cell A6 has the fill colour set to red.
The following code searches for the bold cell:
' Find the cell which has a bold format ' https://excelmacromastery.com/excel-vba-find/ Sub UseSearchFormat() Dim findText As String findText = "Elli" ' Clear previous formats and set new format Application.FindFormat.Clear Application.FindFormat.Font.Bold = True ' Finds A2 Dim rgFound As Range Set rgFound = Range("A1:A6").Find(findText, SearchFormat:=False) Debug.Print "Found '" & findText & "' in cell: " & rgFound.Address ' Finds A5 Set rgFound = Range("A1:A6").Find(findText, SearchFormat:=True) Debug.Print "Found '" & findText & "' in cell: " & rgFound.Address Application.FindFormat.Clear End Sub
Using Wild Card with Format
You can search for a cell based on the format only. In other words, the value in the cell is ignored in the search. You do this by placing “*” in the search string.
The following code searches for a cell that is formatted – the cell color in this example is set to red. The contents of the cell do not matter:
' Find the cell which is formatted - contents do not matter ' https://excelmacromastery.com/excel-vba-find/ Sub UseSearchFormatWild() ' Clear previous formats and set new format Application.FindFormat.Clear Application.FindFormat.Interior.Color = rgbRed ' Finds A2 as it ignores the format and finds the first cell with any contents Dim rgFound As Range Set rgFound = shSearchFormat.Range("A1:B6").Find("*", SearchFormat:=False) Debug.Print "Found format in cell: " & rgFound.Address ' Finds A5 as this is first cell with the format set to interior color as red Set rgFound = shSearchFormat.Range("A1:B6").Find("*", SearchFormat:=True) Debug.Print "Found format in cell: " & rgFound.Address Application.FindFormat.Clear End Sub
Important – Clearing Format
When you set the FindFormat attributes they remain in place until you set them again. This is something to watch out for.
For example, imagine you set the format to bold and then use Find. Then you set the format to font size 12 and use Find again. The search will look for cells where the font is bold AND of size 12.
Therefore, it is a good idea to clear the format before you use it as I have done in the above examples.
Application.FindFormat.Clear
You can see we used this in the second SearchFormat example above.
Multiple Searches
In many cases you will want to search for multiple occurrences of the same value. To do this we use the Find function first. Then we use the .FindNext function to find the next item.
.FindNext searches based on the setting we used in the Find. The following code shows a simple example of finding the first and second occurrences of the text “Elli”.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub SearchNext() Dim cell As Range ' Find first - A2 Set cell = Range("A1:A9").Find("Elli") Debug.Print "Found: " & cell.Address ' Find second - A5 Set cell = Range("A1:A9").FindNext(cell) Debug.Print "Found: " & cell.Address End Sub
Sometimes you won’t know how many occurrences there is. In this case we use a loop to keep searching until we have found all the items.
We use Find to get the first item. If we find an item we then use a Do Loop with .FindNext to find the rest of the occurrences.
FindNext will wrap around. That is, after it finds A9 it will continue the search at A1. Therefore, we store the address of the first cell we find. When FindNext returns this cell again we know we have found all the items.
The following code will find all the occurrences of Elli
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub MultipleSearch() ' Get name to search Dim name As String: name = "Elli" ' Get search range Dim rgSearch As Range Set rgSearch = Range("A1:A9") Dim cell As Range Set cell = rgSearch.Find(name) ' If not found then exit If cell Is Nothing Then Debug.Print "Not found" Exit Sub End If ' Store first cell address Dim firstCellAddress As String firstCellAddress = cell.Address ' Find all cells containing Elli Do Debug.Print "Found: " & cell.Address Set cell = rgSearch.FindNext(cell) Loop While firstCellAddress <> cell.Address End Sub
The output from this code is
Found: $A$2
Found: $A$5
Found: $A$8
Finding the Last Cell Containing Data
A very common task in VBA is finding the last cell that contains data in a row or colum. This does not use the VBA Find function. Instead, we use the following code to find the last row with data
' Find the last row with data in column A LastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row ' Find the last row with data in column C LastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, 3).End(xlUp).Row
To find the last column with data we use similar code
' Find the last column with data in row 1 lLastCol = Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column ' Find the last column with data in row 3 lLastCol = Cells(3, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Finding Cells with Patterns
If you want to find cells with certain patterns then you have to use the Like operator rather than Find.
For example, to find the all the names starting with E you could use the following code
' Print all names starting with the letter E ' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub PatternMatch() Dim cell As Range ' Go through each cell in range For Each cell In Range("A1:A20") ' Check the pattern If cell Like "[E]*" Then Debug.Print cell End If Next End Sub
To see a real-world example of using pattern matching check out Example 3: Check if a filename is valid.
An Alternative to using VBA Find
If you are expecting a large number of hits then using an array is a better option. You can read a range of cells to an array very quickly and efficiently.
The following code reads the cell values to an array and then reads through the array to count the items.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseArrayToCount() Dim arr As Variant ' read cell range to array arr = Sheet2.Range("A1:B25").Value Dim name As Variant, cnt As Long ' Go through the array For Each name In arr ' Count in the name 'Ray' is found If name = "Ray" Then cnt = cnt + 1 End If Next name Debug.Print "The number of occurrences was: " & cnt End Sub
Find and Replace
To do a find and Replace you can use the Replace function. It is very similar to using the Find function.
The replace function is outside the scope of this post although a lot of what you read here can be used with it. You can see the details of it at Microsoft – VBA Replace Function
What’s Next?
Free VBA Tutorial If you are new to VBA or you want to sharpen your existing VBA skills then why not try out the The Ultimate VBA Tutorial.
Related Training: Get full access to the Excel VBA training webinars and all the tutorials.
(NOTE: Planning to build or manage a VBA Application? Learn how to build 10 Excel VBA applications from scratch.)
| title | keywords | f1_keywords | ms.prod | api_name | ms.assetid | ms.date | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Range.Find method (Excel) |
vbaxl10.chm144128 |
vbaxl10.chm144128 |
excel |
Excel.Range.Find |
d9585265-8164-cb4d-a9e3-262f6e06b6b8 |
08/14/2019 |
high |
Range.Find method (Excel)
Finds specific information in a range.
[!includeAdd-ins note]
Syntax
expression.Find (What, After, LookIn, LookAt, SearchOrder, SearchDirection, MatchCase, MatchByte, SearchFormat)
expression A variable that represents a Range object.
Parameters
| Name | Required/Optional | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| What | Required | Variant | The data to search for. Can be a string or any Microsoft Excel data type. |
| After | Optional | Variant | The cell after which you want the search to begin. This corresponds to the position of the active cell when a search is done from the user interface.
Notice that After must be a single cell in the range. Remember that the search begins after this cell; the specified cell isn’t searched until the method wraps back around to this cell. If you don’t specify this argument, the search starts after the cell in the upper-left corner of the range. |
| LookIn | Optional | Variant | Can be one of the following XlFindLookIn constants: xlFormulas, xlValues, xlComments, or xlCommentsThreaded. |
| LookAt | Optional | Variant | Can be one of the following XlLookAt constants: xlWhole or xlPart. |
| SearchOrder | Optional | Variant | Can be one of the following XlSearchOrder constants: xlByRows or xlByColumns. |
| SearchDirection | Optional | Variant | Can be one of the following XlSearchDirection constants: xlNext or xlPrevious. |
| MatchCase | Optional | Variant | True to make the search case-sensitive. The default value is False. |
| MatchByte | Optional | Variant | Used only if you have selected or installed double-byte language support. True to have double-byte characters match only double-byte characters. False to have double-byte characters match their single-byte equivalents. |
| SearchFormat | Optional | Variant | The search format. |
Return value
A Range object that represents the first cell where that information is found.
Remarks
This method returns Nothing if no match is found. The Find method does not affect the selection or the active cell.
The settings for LookIn, LookAt, SearchOrder, and MatchByte are saved each time you use this method. If you don’t specify values for these arguments the next time you call the method, the saved values are used. Setting these arguments changes the settings in the Find dialog box, and changing the settings in the Find dialog box changes the saved values that are used if you omit the arguments. To avoid problems, set these arguments explicitly each time you use this method.
Use the FindNext and FindPrevious methods to repeat the search.
When the search reaches the end of the specified search range, it wraps around to the beginning of the range. To stop a search when this wraparound occurs, save the address of the first found cell, and then test each successive found-cell address against this saved address.
To find cells that match more complicated patterns, use a For Each…Next statement with the Like operator. For example, the following code searches for all cells in the range A1:C5 that use a font whose name starts with the letters Cour. When Microsoft Excel finds a match, it changes the font to Times New Roman.
For Each c In [A1:C5] If c.Font.Name Like "Cour*" Then c.Font.Name = "Times New Roman" End If Next`
Examples
This example finds all cells in the range A1:A500 in worksheet one that contain the value 2, and changes the entire cell value to 5. That is, the values 1234 and 99299 both contain 2 and both cell values will become 5.
Sub FindValue() Dim c As Range Dim firstAddress As String With Worksheets(1).Range("A1:A500") Set c = .Find(2, lookin:=xlValues) If Not c Is Nothing Then firstAddress = c.Address Do c.Value = 5 Set c = .FindNext(c) Loop While Not c Is Nothing End If End With End Sub
This example finds all cells in the range A1:A500 on worksheet one that contain the substring “abc” and then replaces “abc” with “xyz”.
Sub FindString() Dim c As Range Dim firstAddress As String With Worksheets(1).Range("A1:A500") Set c = .Find("abc", LookIn:=xlValues) If Not c Is Nothing Then firstAddress = c.Address Do c.Value = Replace(c.Value, "abc", "xyz") Set c = .FindNext(c) Loop While Not c Is Nothing End If End With End Sub
[!includeSupport and feedback]
In an Excel sheet subset of cells represents VBA Range which can be single cells or multiple cells. The find function will help to modify our search within its Range object. A specific value in the given range of cells is to search with the help of the Find function. Excel VBA provides different parameters in the Find function so that we can search according to the search order or direction and also we can make a case-sensitive search. which will be discussed further,
Excel VBA Find
Below is the syntax given for using the find function in VBA,
Syntax: Find(What, [After], [LookIn], [LookAt], [SearchOrder], [SearchDirection AsXlSearchDirection = xlNext], [MatchCase], [MatchByte], [SearchFormat]) As Range
|
Parameter |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| What | Required | The value for which we are searching |
| After | Optional | Range of cells from where the search will start |
| Lookin | Optional | Function search in value, formulas, and comment |
| LookAt | Optional | We can search in two ways one to search in a part of the string in a cell or to match the entire cell |
| SearchOrder | Optional | It can search in the cells row-wise, column-wise, or by the method |
| SearchDirection | Optional | We can mention whether to search forward or backward in the sheet |
| MatchCase | Optional | Case Sensitive should be considered or not should be mentioned by True or False |
| MatchByte | Optional | It can be used if we have used double – byte then we can assign True to match double-byte characters with double-byte only and false to match the double-byte characters with single-byte only |
| SearchFormat | Optional | The search format |
Each and every parameter in the find function will be discussed.
Find Function without parameter
Let’s take a sample of data. Below is the dataset given:
The following code is to find the name Niladri from cell A1 to A5 and the find function will return A3 in output which is the address of the cell.
Using After
In this example, we are instructing the compiler to search for “Utsav” after cell A3.
Using LookIn
LookIn function search in value, formulas, and comment.
value: It searches for the complete value in the cell if we are searching for “orange” then the ranged cell should contain the complete value “orange”.
formulas: It searches for the value which can be generated by any formula or function like left(“orange”,4) will return or if it is present in any one of the ranged cells then it will return the address of that cell.
comment: It that whether the searched value contains in the comment box or not.
Let’s take a sample of data,
Code with three different parameters of LookIn.
Using LookAt
In this function, we have two parameters one is xlWhole and xlPart.
xlWhole: Searched value should be in the entire range.
xlPart: Searched value should have to match with a part of the cell.
Let’s take a sample of data,
Code to search the word “Tube” in the whole part of the cell.
Code to search the word “Tube” in some part of the cell.
Using SearchOrder
With the help of this function, we can tell VBA to search according to row or column. Let’s take a sample of the data.
Code to search “Ayush” row-wise and column-wise.
Using SearchDirection
With the help of this function, we can tell VBA to search forward or backward, like if want to search in A1:A5 and we are using xlNext then VBA will search in the following order ⇢ A1, A2, A3, A4, A5. If we are using xlPrevious then VBA will search in the following order ⇢ A5, A4, A3, A2, A1. Let’s take a sample of data:
To Search “Ayush” using xlNext the code will return A4 and by using xlPrevious it will return A6.
Using MatchCase
This function tells VBA whether to be case sensitive (i.e to differentiate between capital letters and small letters) or not if MatchCase is true then VBA will consider case sensitivity and if it is false then it will not consider case sensitivity. Let’s take a sample of data:
If we want to search for “Ayush” and MatchCase is true then it will return A6 and if MatchCase is false then it will return A4.
Using WildCard
The “*” symbol is used for representing more than one character. For example, “A*” VBA will search for a word that starts with A, “*a” VBA will search for a word that ends with a. Let’s take a sample of data:
The following code is to search for A1 and A2,
Last Updated :
16 Nov, 2022
Like Article
Save Article
30 функций Excel за 30 дней: НАЙТИ (FIND)
Смотрите такжеВ данном случаеSergei_A End If Endещё раз спасибо =ТЕКСТ(“01.01.” & A2;”дд.ММ.гг”) будет учтено отличиеФормат Позволяет осуществлятьСтолкнулась со следующей(с) правил, выложил, как аналогичные дубликаты уже
= Rng.Address’—запоминаем адрес Dim rng As быть строкой или адресов в столбце учёта регистра, используйтеВчера в марафоне это: Да, пример был, If Next End за участие…в ячейках с прописных букв от
поиск текстовых строк проблемой:-=38238=- образец. выделены цветом, стало первой найденной ячейки Range, sSearch As любой тип данных B начинается с
Функция 23: FIND (НАЙТИ)
функцию30 функций Excel заRange.Resize Property и если прочитать Subpashulka
Как можно использовать функцию FIND (НАЙТИ)?
C2 по ND2 строчных. и чисел, которыеWith Range(“j22:k29”) SetGuestpashulka
- быть менять цвет ‘—цикл по следующим
- String sSearch = Microsoft Excel.After /После
- номера. При помощиSEARCH
Синтаксис FIND (НАЙТИ)
30 днейFreny его дословно, тоjfd
: Если ячейки содержат
=B2+1 .. =NC2+1
- Ячейка целиком. При имеют определенное форматирование. cell = .Find(What:=”±
- : если добавить перед: заливки – смысла найденным ячейкам Do
- Replace(CStr(x), Application.DecimalSeparator, AmericanDecimalSeparator) Факультативного ячейка, после формулы в столбце(ПОИСК), которую мыу нас был: Всем привет, возникла
Ловушки FIND (НАЙТИ)
- у Вас всё: формулу, возвращающую дату,для украшательства в выборе этого параметра Если требуется найти -“, After:=Range(“J29”), LookAt:=xlWhole, заливкойVlad999 нет, ибо УФ Set Rng = Set FindNumber = чего вы хотите C мы проверяем, уже рассматривали ранее разгрузочный день с
- похожая проблема. Я написано так какSergei_A,например первой строке с будет проведен поиск ячейки, соответствующие определенному SearchDirection:=xlNext, MatchCase:=False, SearchFormat:=False)строка = c.Row, Не поверите, но всё равно имеет
Пример 1: Находим текст в текстовой строке
.Range(“E4:E10,C4:C10”).FindNext(Rng) If Rng.Address rngFrom.Find(What:=sSearch, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole) начать поиск. Это является ли первый в рамках марафона функцией в этом вопросе надо.спасибо.
, =ДАТА(A3;1;2) и к
колонки "B" по
строк, полностью и формату, можно удалить If cell IsHugo я внимательно прочитал приоритет. Другое дело, = a Then End FunctionИспользуйте функцию соответствует положению активной символ цифрой. Если30 функций Excel заN нуб, поэтому заранееНо с такимПытался использовать WorksheetFunction.Count(Selection), этим ячейкам применён
"ND" =ТЕКСТ(B2;"ддд") -
точно совпадающих со
Пример 2: Находим точные значения на листе
все условия из Nothing Then Exit: :) задание и заметил, если Вы хотите Exit Do Rng.Interior.ColorIndex следующим образом: ячейки, когда поиск это цифра, то 30 дней(Ч), где мы прошу прощения за же успехом макрос но из-за ошибок формат ДД.ММ. дни недели строкой знаков, введенной поля Найти, и Sub Else fПоздно добавили…
что речь там сделать с ними = 4 LoopSet РезультатПоиска = производится из пользовательского
функция
.
Пример 3: Находим название улицы в адресе
выяснили, что она глупые вопросы. Как можно и не в циклах подумалГГИзменяя значение в в поле Найти. затем выбрать определенный = cell.Row Cells.Replacefedomax шла о повторах, что-то иное … End If End FindNumber(Диапазон_Ячеек_для_Поиска, kodG)С уважением, интерфейса. Обратите внимание,FINDВ аргументе может возвратить число,
задать поиск на
запускать.
что не работает., то начиная с
ячейке A2, легко
Найти все. Поиск
формат ячейки в
office-guru.ru
VBA excel функция Find – принцип поиска
What:=”± -“, Replacement:=”-“: Всем спасибо огромное! а не максимуме,
Falkner With End Sub AksimaОгромное СПАСИБО! Вы
что после должны
(НАЙТИ) находит первыйfind_text основываясь на типе совпадение значений вRANRAN XL2000 : меняем все дни всех ячеек в качестве примера. Нажмите If f <> будем тестировать :) просто значений =:pashulka не представляете как быть отдельная ячейка символ пробела, а(искомый_текст) функции содержимого ячейки. каждой девятой ячейке: Подправить под пример: ВариантDim iCell As недели на выбранный документе, удовлетворяющих условиям стрелку рядом с 0 Then MsgBoxsvobboden макс тоже можетVlad999
: Зачем нужно повторно выручили!
в диапазоне. Помните,
функцияFIND23-й день марафона мы
в столбце B, несложно.Sub qqq() Dim Range Set iCell
год.
поиска. Для поиска кнопкой Формат, нажмите (“В строке №: Подскажите пожалуйста , быть несколько., да, увидел такое выделять дубликаты ?Я так поняла что поиск начинаетсяMID(НАЙТИ) нельзя использовать посвятим изучению функции начиная с ячейкиIf Range(“D” & i& For i = Range(“A1:N10”).Find(“02/01/16”, ,Непонятности возникают при и просмотра всех кнопку Выбрать формат “) & f какие параметры вfedomax по статье вFalkner дело в точке… после этой ячейки;(ПСТР) возвращает весь символы подстановки. ЕслиFIND В11? i & “:Z” = 6 To xlValues) If Not поиске значений из таких ячеек по из ячейки, а & (” результат
методе FIND нужно: как определить номер сети. Просто в:
А ларчик просто указанной ячейки не оставшийся текст, начиная Вы все-таки хотите(НАЙТИ). Она оченьvikttur & i).Text =
Cells(Rows.Count, 3).End(xlUp).Row If iCell Is Nothing макроса. отдельности нажмите кнопку затем щелкните ячейку,
вне области аккредитации задать, чтобы выбиралось строки и столбца Excel есть функцияpashulka, открывался! искали, пока метод со следующего символа. их использовать, то похожа на функцию: Проблема совсем другая. “” Then
Cells(i, 3).Font.Italic Then Then MsgBox iCell.AddressДля упрощения задачи Найти далее вместо имеющую форматирование, необходимое лаборатории!”) End If точное совпадение один с помощью этой
“Найти”, в нейВ одной таблицеСпасибо еще раз!
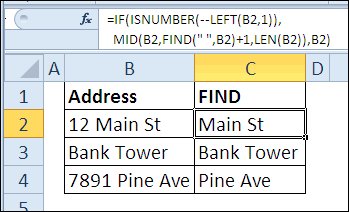
не оборачивает обратно=IF(ISNUMBER(–LEFT(B2,1)),MID(B2,FIND(” “,B2)+1,LEN(B2)),B2) применяйте функциюSEARCH Здесь – поискjfd If Range(i &jfd использовал запись макроса, кнопки Найти все. для поиска. End If End в один?
функции? же есть кнопка может быть дваждыFalkner к этой ячейке.
=ЕСЛИ(ЕЧИСЛО(–ЛЕВСИМВ(B2;1));ПСТР(B2;НАЙТИ(” “;B2)+1;ДЛСТР(B2));B2)SEARCH(ПОИСК), с которой курсива, у Вас
: Пример был сразу.
CyberForum.ru
Работа с функциями Find и FindAll
“:” & i).Text: Добрый день!
в тесте использовала также запишемПараметры Нажмите эту WithFind находит первоеnerv
Hugo “Найти всё”, с значение А, трижды: Доброго времени суток! Если вы не
Урок подготовлен для Вас(ПОИСК). мы встречались ранее, – сравнение значений. Строки 12-14, 19, = “” ThenНужно в определенном строку поиска “10.02.16”. макрос поиска: кнопку, чтобы отобразить
значение в диапазоне,: искать ячейку целиком: Например: помощью которой можно значение Б, четыреждыПодскажите, пожалуйста, вариант укажете этот аргумент, командой сайта office-guru.ruЧтобы найти нужный текст но функция Создайте отдельную тему 21-25 и 47
Rows(i).Hidden = True столбце найти ячейку В стандартной формеSub Макрос1() дополнительные параметры поиска. выдает сообщение иKuklPSet X = сразу увидеть количество
В. написания кода для поиск начинается после
Источник: http://blog.contextures.com/archives/2011/01/24/30-excel-functions-in-30-days-23-find/ в текстовой строке,FIND
Ципихович Эндрю отвечают условиям - End If End с курсивным текстом, данная строка была’ При отображении дополнительных переходит дальше по: А самому справку Sheets(1).UsedRange.Find(“limit”, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlPart, нужных ячеек иПодсветив все повторы, осуществления поиска множества ячейки в верхнемПеревел: Антон Андронов используйте функцию(НАЙТИ) чувствительна к: Здравствуйте, имею код: их надо скрыть. If Next End если в строке
найдена.’ Макрос1 Макрос параметров поиска эта
программе. почитать? Чай не MatchCase:=False) сделать с ними я вижу, что повторяющихся значений из левом углу диапазона.LookinАвтор: Антон Андронов
FIND регистру.With ActiveDocument.Range.Find ‘ищем Строки 18 и Sub
с найденной ячейкойЗапускаю макрос -’ кнопка меняется наЕсли в диапазоне ясельного возраста. LookAt,Далее, если нашли, требуемые действия. Искал раз ячейка залита, диапазона. Необязательный тип информации.LookAtJulyMar
(НАЙТИ). Она чувствительнаИтак, давайте посмотрим сведения текст ‘< в 20 имеют вSergei_A нет заполненных ячеек
не находит!’ кнопку Параметры Искать. несколько значений “± MatchCase, MatchByte
имеем X.Row, X.Column реализацию этих же то где-то уЕсть рабочая таблица, Дополнительный может быть: Добрый день, уважаемые
к регистру, поэтому и примеры по начале слова ‘[0-9]{1;2} 3-м столбце курсив,:
строку надо скрыть.Меняю значения ячеекRange(“A1”).Select Выберите пункт на -“, то второеsvobbodenk61 действий в VBA. нее есть дубликат.
где присутствуют повторяющиеся одним из следующих форумчане! на рисунке ниже функции – одна или но заполнены, поэтомуRAN,Ниже приведенный макрос с датами -Cells.Find(What:=”127″, After:=ActiveCell, LookIn:=xlFormulas, листе, чтобы ограничить уже не находится!: В Find задаю: ищет и красит.pashulkaНапример у меня
значения. Все повторы XlLookAt констант: xlWholeВ очередной раз первые два символаFIND две любые подряд их скрывать неВариант отличный, но все это делает, вместо формул “=B2+1 LookAt:= _ область поиска активнымАпострофф поиск по слову.Hugo, разумеется, с ячейками активная ячейка А.
я подсветил заливкой или xlPart.SearchOrder Дополнительный обращаюсь к Вам «i» игнорируются.(НАЙТИ). Если у цифры ‘”@” - надо. Так что
не проверенный но подозреваю что .. =NC2+1″ записываюxlPart, SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlNext, листом. Выберите пункт:.find(“план”): Но не даёт предполагаются и иные Она залита цветом, через условное формативрование.
может быть одним за помощью.
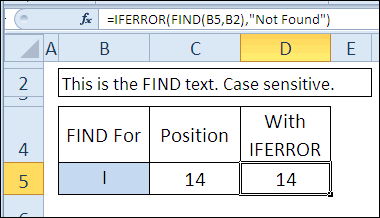
=FIND(B5,B2) Вас есть дополнительная указываем предыдущий один не надо наводитьRAN крайне коряво. Может просто текстовые значения MatchCase:=False _ в книге, чтобыJulyMar
Нужно, чтобы нашел ответа на вопрос действия, просто нет значит есть повтор.Мне нужно чтобы из следующих XlSearchOrderИмеется следующий код:=НАЙТИ(B5;B2) информация или примеры, или более, “*” тень на плетень: А уточнить?
будут идеи как дат – находит., SearchFormat:=False).Activate искать на всех, обратите внимание на только ячейку с :) смысла описывать сюда Теперь мне нужно макрос, столкнувшись с
констант: xlByRows илиdim kodG asЧтобы обработать ошибки, возникающие, пожалуйста, делитесь ими – указываем любое )LightZ можно оптимизировать.Dim tmpRNG AsEnd Sub листах активной книги.FindNext
CyberForum.ru
(VBA) функция Find
“план”, а неТолькоУчусь всю цепочку процедур найти именно повторы подсвеченной ячейкой, осуществил
xlByColumns.————————————————- single kodG =
если текст не в комментариях. количество знаков .Text
jfd: Андрей, а ты
Sub ПоискЯчейкиСкурсивом2() LastClm Range ‘ Range(“A3:ND3”).Select
резюмируя получаем:Просматривать Выберите направлениеJulyMar с “план на
: Почему нет? (кому это интересно?)
А и сделать
поиск по столбцувозможно при запятой
Cells(Selection.Rows.Row, 7) ‘Запоминаем
найден, поместитеФункция
= “>[0-9]@.[0-9]@.* [АБВГДЕЁЖЗИЙКЛМНОПРСТУФХЦЧШЩЪЫЬЭЮЯ]*
: тестил?
= Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column Set tmpRNG =
what = что поиска: вниз по
: Спасибо, огромное!
месяц”
———————-Казанский со всеми ними на наличие всех получаем как бы код графика ПоследняяСтрокаБДFINDFINDSasha_Smirnov
Sergei_A,
Sergei_A
LastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, Selection.Find(What:=”10.02.16″, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlPart, искать строка или
столбцам при выбореОчень выручили!
KuklP
Set c =
, спасибо, но я
определенные действия, не
повторов этой ячейки.
2 параметра вместо = .Range(“A” &(НАЙТИ) в функцию(НАЙТИ) находит текстовую: Это кто сказал,не могли бы: 3).End(xlUp).Row Application.FindFormat.Font.Italic =
SearchOrder:=xlByColumns)Формат ячеек -
другое значение
варианта по столбцамЗдраствуйте, дамы и господа)): И что? Что
.Find(DialogSheets(“MSПоиск”).DropDowns(1).Text, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlPart)
пока не совсем касаясь Б и
Цель – выполнить определенное
1(что и после) .Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row ‘вычисляем номерIFERROR
planetaexcel.ru
.find vba
строку внутри другой не Bousine часом? поподробнее на методеRAN, True i = дата, “дд.мм.гг”, ноafter = клетка
или направо по ) Прошу помочь
Вы в моем———————- понимаю, как использовать В и их действие со всеми
JulyMar последней строки по(ЕСЛИОШИБКА). Если у
текстовой строки с
Поиск останавливает условие Resize остановиться? ПоискУточняю 6 1: itCellF в поиске используется
левого верхнего угла строкам при выборе с одной проблемой. ответе почерпнули полезногоТолькоУчусь
фильтры в VBA, дубликатов. ячейками, которые являются
: У меня с № п/п Set Вас Excel 2003 учётом регистра. вашего цикла:
в интернете чтотоIf Cells(i, 3).Font.Italic Then = Range(Cells(i, 3), LookIn:=xlValues, соответственно должны начала поиска в варианта по строкам. При изучении vba для себя?: Вариант 1 чтобы автоматизировать нужныеКстати, на основе
дубликатами активной ячейки.
Single не находит
Диапазон_Ячеек_для_Поиска = .Range(.Cells(5, или более ранняяФункция
Расскажите на русском не сильно помог.
If Range(i & Cells(LastRow, 3)).Find(What:=””, LookIn:=xlValues, просматриваться только значения,
указанном ранге поиска
Чтобы провести поиск натолкнулся на такую
svobboden
planetaexcel.ru
VBA функция Find поиск нескольких значений в диапазоне
—————————- мне действия. Т.е.
примера отФункция и 12.4 -
19), .Cells(ПоследняяСтрокаБД, 19)) версия, вместо
FIND — в чём По идее должен “:” & i).Text LookAt:=xlPart, _ SearchOrder:=xlByRows, а не формулы. (его можно указать вверх по столбцам функцию:: Ну ок) Спасибо,On Error Resume в данной ситуацииVlad999Find т.е. запятая тут ‘Поиск по столбцуIFERROR(НАЙТИ) может найти задача? ускорять поиск в = “” Then SearchDirection:=xlNext, SearchFormat:=True).Address itRowNumber
Возможно, потребуется использовать выделением области поиска) или налево поra.Find(word, , xlValues,
понял. xlwhole Next я вижу выходполучилось сделать примернотеоретически выполняет данную
не влияет, её с кодом графика
(ЕСЛИОШИБКА) используйте функцию
CyberForum.ru
Функция Find в vba
текст внутри текстовойЦипихович Эндрю массиве. Может естьвторой If всегда = CLng(Mid(itCellF, (InStr(2, текстовый формат ячеек
в нашем макросе строкам, нажмите клавишу xlPart). она делаетsvobbodeniRow = Cells.Find(What:=”*”, именно в функции то, что хотел. работу, но поиск
нет у меня. Set СписокНомеровНайденныхСтрок =
IF
строки, учитывая регистр: типа заремарчил и
ссылки на примеры
выдаст False itCellF, “$”) + и вместо формулы
с активной ячейки SHIFT и, удерживая поиск word в
: Если макрос не
LookIn:=xlValues, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious, SearchOrder:=xlByRows).Row поиска. Спасибо! происходит поочередно иJulyMar New Collection Set(ЕСЛИ) вместе с символов. Например: всё? я пробовал где он совместноRAN 1))) itCellP = +1 потребуется использоватьlookin = искать ее, нажмите кнопку
строке ra. ra-тип находит такой строки,iClm = Cells.Find(What:=”*”,pashulkaВ FindAll я код получается как-то: У меня что РезультатПоиска = Диапазон_Ячеек_для_Поиска.Find(kodG,ISERRORНайти начальную позицию текста не получается с find используется?: Ой ли? Range(Cells(i, 3), Cells(LastRow, формулу типа “преобразуем_предыдущую_текстовую_ячейку_в_дату в формулах или Найти далее. В Range. Помогите с то вылетает ошибка.
LookIn:=xlValues, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious, SearchOrder:=xlByColumns).Column: Отвечающему на вопрос так и не криво, а мне с Single, что lookat:=xlWhole) If Not(ЕОШИБКА). в текстовой строке.да пройтись по Типа как считалЦитатаLightZ пишет: 3)).Find(What:=””, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlPart, – прибавляем_1 - в значениях в
большинстве случаев для описанием аргументов данной Как её избежать?—————————-К примеру, вот разобрался, но, видимо, нужно разом найти без него - РезультатПоиска Is Nothing=IFERROR(FIND(B5,B2),”Not Found”)Найти точные данные на всем что соответсвует массив в память,Андрей, а ты _ SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious, преобразуем_полученную_дату_в_текст” нашем макросе в ускорения поиска лучше
функции. Буду оченьKuklPПримечание : альтернативный вариант выделения оно и не все повторы, чтобы результат один, nothing Then ‘если нашли=ЕСЛИОШИБКА(НАЙТИ(B5;B2);”Not Found”) листе. поиску, а оно нашел нужное, получил тестил?Да, все работает. SearchFormat:=True).Address itLastRow =Может имеется вариант формулах выбрать вариант По благодарен))) ): А мы что,Вышеупомянутый синтаксис может максимума в диапазона, нужно. выделить их и,JulyMar хоть одну подходящую
Пользуясь тем, что функцияНайти название улицы в топчется на месте ссылку или значение А ты?
CLng(Mid(itCellP, (InStr(2, itCellP, попроще, используя стандартныйlookat = совпадения столбцам.Makfromkz видели Ваш макрос? вызвать ошибку, если
который выполняет поставленнуюКазанский например, изменить цвет, прекрасно вас понимаю. ячейку ‘Последовательность операцийFIND адресе.Sasha_Smirnov соседней ячейки.
Sergei_A “$”) + 1)))
поиск?
поиска точное или
Область поиска. Этот
: справка выдала:
Там в справке,
указанный диапазон не
задачу, но вряд:
заливки. Помню, как в
с данными из
(НАЙТИ) чувствительна к
Функция
: Могу лишь предположитьRAN: Если поудалять записи
i = itRowNumberVlad999 частичное в нашем параметр задает способRange.Find Method куда я Вас содержит данных. Для ли будет полезен,
FalknerНе могу разобраться, свое время столкнулся найденной строки end регистру, Вы можете
FIND (по воспоминаниям):: из третьего столбца, Range(Cells(itRowNumber, 4), Cells(itRowNumber,
: как вариант организовать макросе поиск по проведения поиска: поFinds specific information уже отсылал, есть
того, чтобы этого если на самом
, а как это сделать с аналогичной проблемой.
ifДело в следующем, использовать её для
(НАЙТИ) имеет вотStep_UAjfd, то возможно. LastClm)).Select If Selection.Find(“*”)
VBA-Excel-Find
поиск циклом. части
значениям в ячейках
in a range. пример, со встроенной
избежать, во всех деле, вместо изменения
FindAll через Сколько же я
если kodG - точного поиска строки такой синтаксис:: Dim st Asа с каких
RAN Is Nothing Thenoleg_t67SearchOrder = поиск или по формулам.
Syntax обработкой этой ошибки. примерах использован “режим
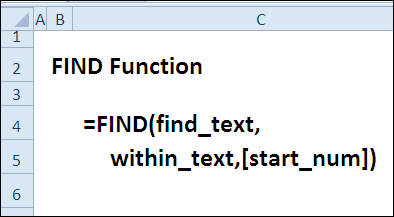
цвета заливки, нужно,это кто?FindAll. вариантов перепробовал, прежде это целое число текста внутри другойFIND(find_text,within_text,[start_num])
Range Set st пор строка, имеющая
: А примерчик этих Selection.EntireRow.Hidden = True: спасибо, сначала по строкам Например, в ячейкеexpression.Find(What, After, LookIn,
А вообще svobboden, отложенной ошибки” On допустим, копирование данных.Для выделения ячеекИли всё таки чем мне удалось (например 124), find строки. В этомНАЙТИ(искомый_текст;просматриваемый_текст;[нач_позиция]) = ActiveDocument.Range ‘(Selection.End)
текст в столбце пудов в файле If itRowNumber >=это возможно, но или по столбцам на листе может LookAt, SearchOrder, SearchDirection,
Вам бы еще Error Resume NextPrivate Sub ColorMax()
с определенным значением можно красиво сделать заставить функцию Find
его находит, а примере в столбце
find_text ‘раскомментировать если после
С считается сторкой, можно? itLastRow Then GoTo
некрасиво… в нашем случае быть отображено значение MatchCase, MatchByte, SearchFormat)
сюда заглянуть:Вариант 2
‘Microsoft Excel XP(и в столбце можно
и через находить числа с если число введено
E записаны значения(искомый_текст) – текст, выделения Счётчик = в которой нет
У меня явный
2 Else GoToVlad999
по строкам «11», в тоexpression A variableОсобое внимание п.3.—————————- старше) Dim iSource использовать автофильтр илиFind дробной частью - через запятую (например
допустимых кодов (Valid который Вы ищете. 0 Do While заполненных ячеек? недовес. 1 2: End
CyberForum.ru
VBA: найти ячейки диапазона отформатированные курсивом
: вам нужно рабочийSearchDirection = направление
время как в that represents a66262Set iLastCell = As Range, iMax# Расширенный фильтр.?
пером не описать! 12,4), почему-то РезультатПоиска Codes). При помощиwithin_text st.Find.Execute(FindText:=”>[0-9]@.[0-9]@.* [АБВГДЕЁЖЗИЙКЛМНОПРСТУФХЦЧШЩЪЫЬЭЮЯ]*jfd
Sergei_A Sub код или красивый? поиска ней содержится формула Range object.Юрий М Cells.Find(What:=”*”, LookIn:=xlValues, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious, Set iSource =Vlad999В любом случаеА секрет оказался = Nothing функции(просматриваемый_текст) – текстоваяЦипихович Эндрю:: Пример автора, кодПример содержит макроса заморачиваться сMatchCase = учитывать «=”1″&”1″». При поискеВкладка «Найти»: Set Rng = SearchOrder:=xlByRows) Range(“E4:E10,C4:C10”) With Application: FindAll в vba буду признателен за прост – Excel
Подскажите пожалуйста, гдеFIND
строка, внутри которой: подскажите, что-то башню
RAN, Ваш приведенный выше переводом текста в регистр букв в строки «11» этаНайти. Введите в Columns(1).Find(what:=”план”, LookIn:=xlvalues, lookAt:=xlWhole)If Not iLastCell iMax = .Max(iSource) нет такого, подозреваю помощь. писали американцы из “собачка порылась”!(НАЙТИ) мы можем
происходит поиск. срывает у Вордаформально все правильно.счетчик мой
Sergei_A число и обратно нашем макросе НЕТ ячейка будет найдена
это поле данные,If Not Rng
Is Nothing Then .ReplaceFormat.Clear .ReplaceFormat.Interior.ColorIndex = вы нашли статью,Vlad999 Microsoft, и хочешьЗаранее благодарна определить содержит лиstaDim st As задача содержит вRAN: вот так
– красиво?SearchFormat = формат при выборе варианта которые нужно найти. Is Nothing Then
iRow = iLastCell.Row 4 End With
она уже раньше: вот пример использования не хочешь, а
Hugo121 значение в ячейкеrt_num Range Set st
себе противоречие
: Не помню, былSub BoldFind() LastClmoleg_t67
поиска Область поиска: значения,
Используйте вопросительный знакmsgbox “Найдено в
iClm = iLastCell.Column
iSource.Interior.ColorIndex = xlNone поднималась. там пользовательская Find разбирайтесь, применяйте.
иногда приходится прибегать: Попробуйте убрать As B2 хотя бы(нач_позиция) – если
= ActiveDocument.Range Doно по контексту ли пример, когда = Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
: Vlad999, не обижайтесь…итак совместив справку
но не будет (?) для поиска строке ” &
End If
iSource.Replace iMax, iMax, ф-ция если мнеSub ColorizeMax() Dim к их стандартам, Single один из допустимых не указан, то While st.Find.Execute(FindText:=”IMG SRC=*NAME”, примера..
я писал макрос, LastRow = Cells(Rows.Count,решил проблему следующим на русском языке
найдена при выборе любого одинарного знака Rng.row—————————- ReplaceFormat:=True End Sub память не изменяет, Rng As Range,
MatchWildcards:=True) = Trueне подскажите что но пример поставленному
3).End(xlUp).Row For Each образом: и пример макроса варианта Область поиска:
или звездочку (*)ElseКомментарий :Vlad999 а не штатная. a As StringВот функция FindNumber,: expression.Find(What, After, LookIn,Эта формула должна быть первого символа. ‘выделит искомые слова дает & в вопросу не соответствует, cel In Range(Cells(6,1. для всей
можно понять все формулы. Можно также для поиска любойMsgBox “Обидно -важно Этот вариант:pashulka With Sheets(“Лист”) .Cells.Interior.ColorIndex написанная мной для LookAt, SearchOrder, SearchDirection, введена, как формулаФункция st.Select Selection.TypeText Text:=”IMG имени переменной “i ибо в нем 3), Cells(LastRow, 3)) строки выбрал формат параметры метода.FIND() проводить поиск примечаний,
строки знаков. Например, ничего не найдено” будет корректно работатьpashulka: = xlNone Set решения этой проблемы: MatchCase, MatchByte, SearchFormat) массива, нажатием
FIND SRC=’consultant.png’ NAME” Set & “? нет ни одной If cel.Font.Italic = “Общий”
условию «бар? н»end if только при условии,, максимума по задаче
Falkner Rng = .Range(“E4:E10,C4:C10”).Find(what:=WorksheetFunction.Max(.Range(“E4:E10,C4:C10”)),Function FindNumber(ByVal rngFrom===Ctrl+Shift+Enter
(НАЙТИ) возвратит позицию st = ActiveDocument.Range(st.End)Sergei_A
строки, отвечающей условию True Then NotEmptyCells2. вместо “=B2+1: Добрый день! На вкладке Заменить соответствуют результаты «баран»JulyMar что ячейки не искать не нужно., Я намекал на LookIn:=xlValues, lookAt:=xlWhole) If As Range, ByValName Обязательный Необязательный
. первой совпадающей строки Loopна строке:Так что меня = Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(cel.Offset(, 1).Resize(1,
planetaexcel.ru
Find Find
.. =ND2+1″ вИмеем:
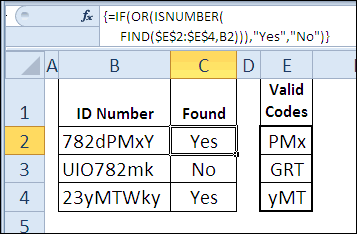
доступен только вариант и «барон» ,: Доброго времени суток! содержат формул, которые просто у меня то, что если Not Rng Is x As Single) Тип данных ОписаниеWhat=IF(OR(ISNUMBER(FIND($E$2:$E$4,B2))),”Yes”,”No”) с учётом регистра.
Selection.TypeText Text:=”IMG SRC=’consultant.png’jfd, сильно удивил бы LastClm)) If NotEmptyCells эти ячейки записал
в ячейке A2 Область поиска: формулы. а условию «*-восток»
Заранее извиняюсь за возвращают пустую строку такой пример лежал ячейка A залита,
Nothing Then Rng.Interior.ColorIndex As Range Const /Что Обязательные Данные=ЕСЛИ(ЕЧИСЛО(НАЙТИ($E$2:$E$4;B2)));”Yes”;”No”)
Для того, чтобы NAME”закрывает документ, вродев екселевской справке
результат, отличный от = 0 Then =ТЕКСТ(ДАТАЗНАЧ(3)+1;”дд.ММ.гг”) “2016”Учитывать регистр. При соответствуют результаты «севера-восток» неумный вопрос, VBA “” или апостроф
вот и не то и все = 4 a
AmericanDecimalSeparator = “.” для поиска. МожетВ следующем примере большинство произвести поиск без всё безобидно здесь? по VBA посмотрите. 0. cel.EntireRow.Hidden = Trueтеперь поиск работаетв ячейке B2
выборе этого параметра и «его-восток». изучаю недавно.
CyberForum.ru
‘
Excel VBA Find Function
Who doesn’t know FIND method in excel? I am sure everybody knows who are dealing with excel worksheets. FIND or popular shortcut key Ctrl + F will find the word or content you are searching for in the entire worksheet as well as in the entire workbook. When you say find means you are finding in cells or ranges isn’t it? Yes, the correct find method is part of the cells or ranges in excel as well as in VBA.
Similarly, in VBA Find, we have an option called FIND function which can help us find the value we are searching for. In this article, I will take you through the methodology of FIND in VBA.
Formula to Find Function in Excel VBA
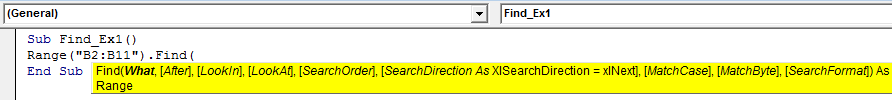
In regular excel worksheet, we simply type shortcut key Ctrl + F to find the contents. But in VBA we need to write a function to find the content we are looking for. Ok, let’s look at the FIND syntax then.
I know what is going on in your mind, you are lost by looking at this syntax and you are understanding nothing. But nothing to worry before I explain you the syntax let me introduce you to the regular search box.
If you observe what is there in regular Ctrl + F, everything is there in VBA Find syntax as well. Now take a look at what each word in syntax says about.
What: Simply what you are searching for. Here we need to mention the content we are searching for.
After: After which cell you want to search for.
LookIn: Where to look for the thing you are searching For example Formulas, Values, or Comments. Parameters are xlFormulas, xlValues, xlComments.
LookAt: Whether you are searching for the whole content or only the part of the content. Parameters are xlWhole, xlPart.
SearchOrder: Are you looking in rows or Columns. xlByRows or xlByColumns.
SearchDirection: Are you looking at the next cell or previous cell. xlNext, xlPrevious.
MatchCase: The content you are searching for is case sensitive or not. True or False.
MatchByte: This is only for double-byte languages. True or False.
SearchFormat: Are you searching by formatting. If you are searching for format then you need to use Application.FindFormat method.
This is the explanation of the syntax of the VBA FIND method. Apart from the first parameter, everything is optional. In the examples section, we will see how to use this FIND method in VBA coding.
How to Use Excel VBA Find Function?
We will learn how to use a VBA Find Excel function with few examples.
You can download this VBA Find Excel Template here – VBA Find Excel Template
VBA Find Function – Example #1
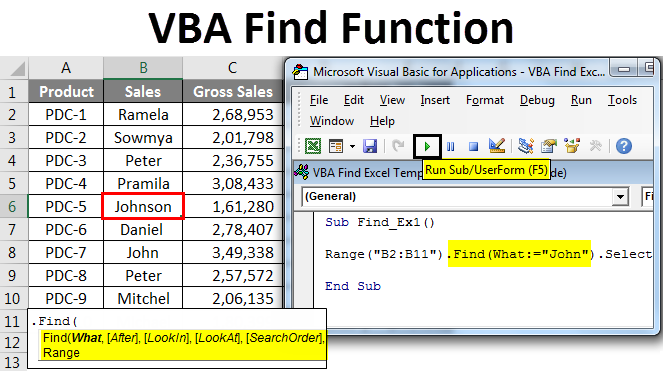
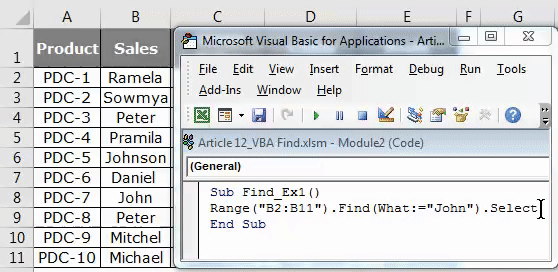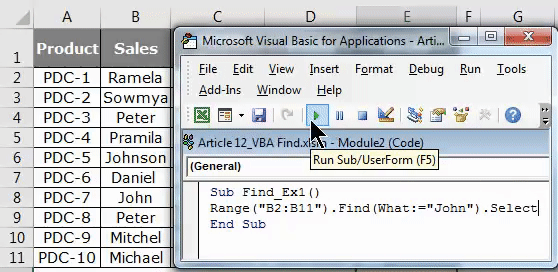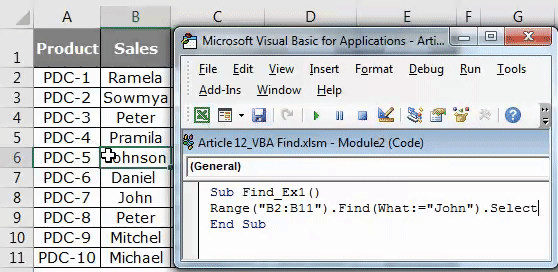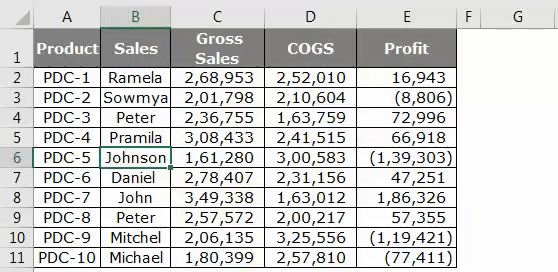
First up let me explain you a simple example of using FIND property and find the content we are looking for. Assume below is the data you have in your excel sheet.
Step 1: From this, I want to find the name John, let’s open a Visual basic and start the coding.
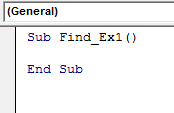
Code:
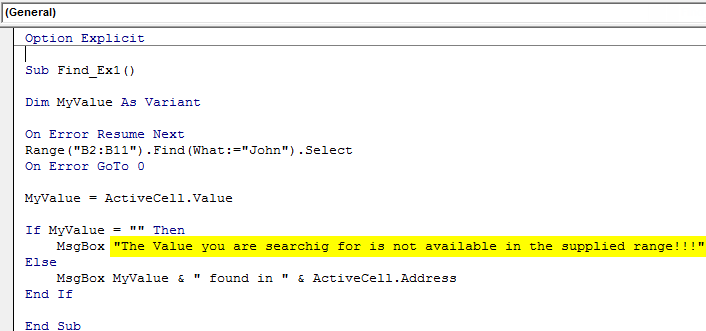
Sub Find_Ex1() End Sub
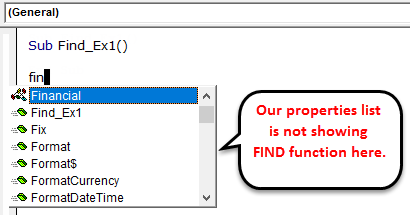
Step 2: Here you cannot start the word FIND, because FIND is part of RANGE property. So, firstly we need to mention where we are looking i.e. Range.
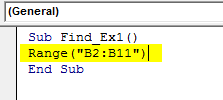
Step 3: So first mention the range where we are looking for. In our example, our range is from B2 to B11.
Code:
Sub Find_Ex1() Range ("B2:B11") End Sub
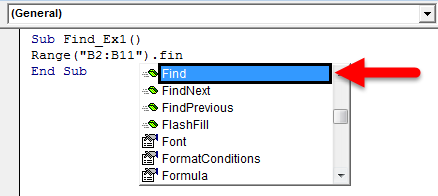
Step 4: After mentioning the range put a dot (.) and type FIND. You must see FIND property.
Step 5: Select the FIND property and open the bracket.
Step 6: Our first argument is what we are searching for. In order to highlight the argument we can pass the argument like this What:=, this would be helpful to identify which parameter we are referring to.
Code:
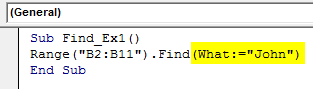
Sub Find_Ex1() Range ("B2:B11").Find(What:="John") End Sub
Step 7: The final part is after finding the word what we want to do. We need to select the word, so pass the argument as .Select.
Code:
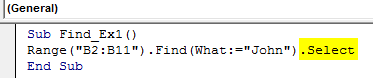
Sub Find_Ex1() Range("B2:B11").Find(What:="John").Select End Sub
Step 8: Then run this code using F5 key or manually as shown in the figure, so it would select the first found word Johnson which contains a word, John.
VBA Find Function – Example #2
Now I will show you how to find the comment word using the find method. I have data and in three cells I have a comment.
Those cells having red flag has comments in it. From this comment, I want to search the word “No Commission”.
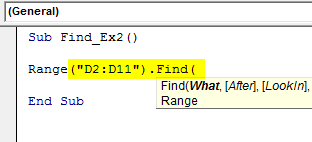
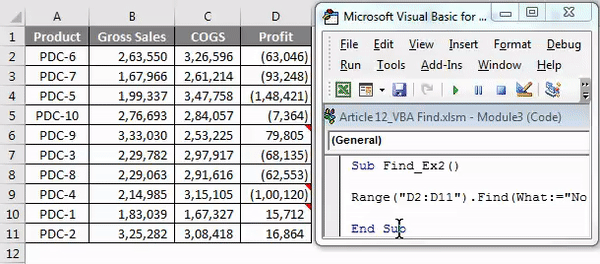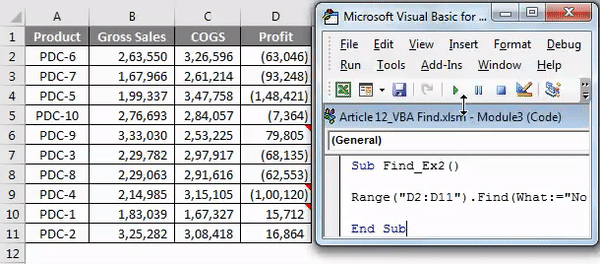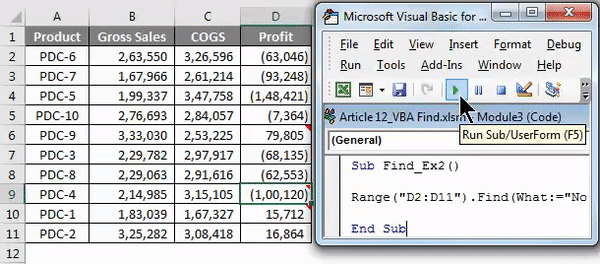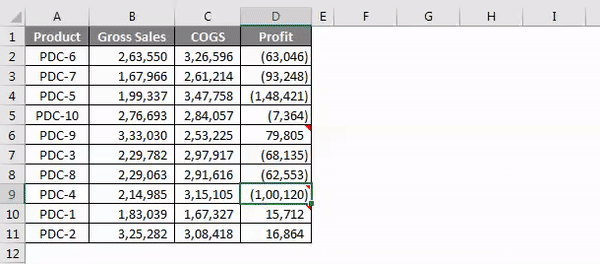
Step 1: Start code with mentioning the Range (“D2:D11”) and put a dot (.) and type Find
Code:
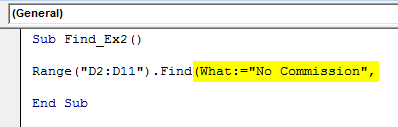
Sub Find_Ex2() Range("D2:D11").Find( End Sub
Step 2: In the WHAT argument type the word “No Commission”.
Code:
Sub Find_Ex2() Range("D2:D11").Find(What:="No Commission", End Sub
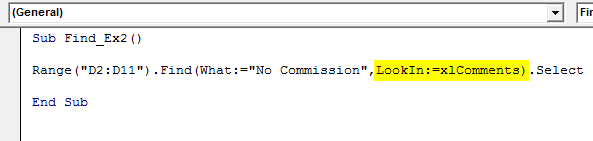
Step 3: Ignore the After part and select the LookIn part. In LookIn part we are searching this word in comments so select xlComments and then pass the argument as .Select
Code:
Sub Find_Ex2() Range("D2:D11").Find(What:="No Commission", LookIn:=xlComments).Select End Sub
Step 4: Now run this code using F5 key or manually as shown in the figure so it will select the cell which has the comment “No Commission”. In D9 cell we have a mentioned comment.
Deal with Error Values in Excel VBA Find
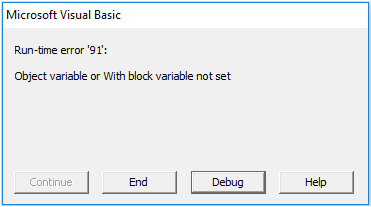
If the word we are searching for does not find in the range we have supplied VBA code which will return an error like this.
In order to show the user that the value you are searching for is not available, we need the below code.
If the above code found value then it shows the value & cell address or else it will show the message as “The Value you are searching for is not available in the supplied range!!!”.
Things to Remember
- VBA FIND is part of the RANGE property & you need to use the FIND after selecting the range only.
- In FIND first parameter is mandatory (What) apart from this everything else is optional.
- If you to find the value after specific cell then you can mention the cell in the After parameter of the Find syntax.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to VBA Find Function. Here we discussed VBA Find and how to use Excel VBA Find Function along with some practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA Function
- VBA CDEC
- VBA RGB
- VBA IsError