поделиться знаниями или
запомнить страничку
- Все категории
-
экономические
43,660 -
гуманитарные
33,654 -
юридические
17,917 -
школьный раздел
611,971 -
разное
16,905
Популярное на сайте:
Как быстро выучить стихотворение наизусть? Запоминание стихов является стандартным заданием во многих школах.
Как научится читать по диагонали? Скорость чтения зависит от скорости восприятия каждого отдельного слова в тексте.
Как быстро и эффективно исправить почерк? Люди часто предполагают, что каллиграфия и почерк являются синонимами, но это не так.
Как научится говорить грамотно и правильно? Общение на хорошем, уверенном и естественном русском языке является достижимой целью.
Длина, скорость и частота электромагнитной волны.
Онлайн калькулятор перевода длины волны в частоту для широкого диапазона частот, включая радиоволны, микроволны, инфракрасное излучение,
видимый свет, ультрафи- олетовое излучение, рентгеновские и гамма лучи.
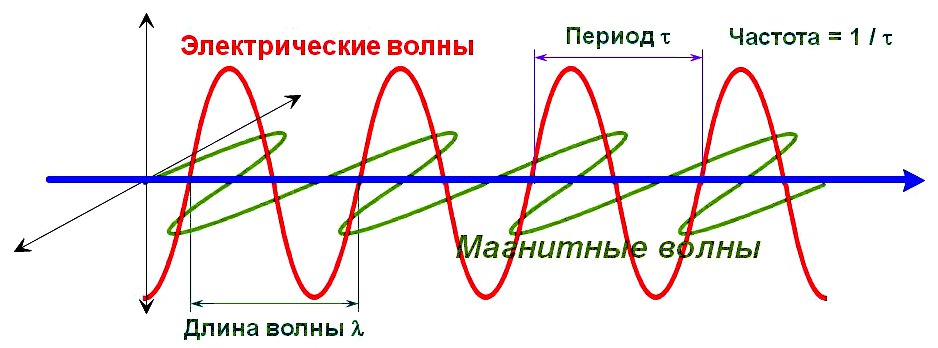
Электромагнитные колебания – это взаимосвязанные колебания электрического и магнитного полей, проявляющиеся в периодическом изменении
напряжённости (E) и индукции (B) поля в электроцепи или пространстве. Эти поля перпендикулярны друг другу в направлении движения волны
(Рис.1) и, в зависимости от частоты, представляют собой: радиоволны, микроволны, инфракрасное излучение, видимый свет, ультрафиолетовое
излучение, рентгеновские либо гамма-лучи.
Рис.1
Длина волны, обозначаемая буквой λ и измеряемая в метрах –
это расстояние между двумя ближайшими друг к другу точками в пространстве, в которых колебания происходят в одинаковой фазе.
Другими словами, это расстояние, на котором фаза электромагнитной волны вдоль направления распространения меняется на 2π.
Время, за которое волна успевает преодолеть это расстояние (λ), т. е. интервал времени, за который периодический колебательный процесс
повторяется, называется периодом колебаний, обозначается буквой ፐ (тау) или Т и измеряется в метрах.
Частота электромагнитных колебаний связана с периодом простейшим соотношением:
f (Гц) = 1 / T (сек).
Скорость распространения электромагнитных волн в вакууме (v) равна скорости
света и составляет величину:
v = С = 299792458 м/сек.
В среде эта скорость уменьшается: v = С / n, где
n > 1 – это показатель преломления среды.
Абсолютный показатель преломления любого газа (в том числе воздуха) при обычных условиях мало чем отличается от единицы, поэтому
с достаточной точностью его можно не учитывать в условиях распространения электромагнитных волн в воздушном пространстве.
Соотношение, связывающее длину волны со скоростью распространения в общем случае, выглядит следующим образом:
λ (м) = v (м/сек) *Т (сек) = v (м/сек) / f (Гц).
И окончательно для воздушной среды:
λ (м) = 299792458 *Т (сек) = 299792458 / f (Гц).
Прежде чем перейти к калькуляторам, давайте рассмотрим шкалу частот и длин волн непрерывного диапазона электромагнитных волн,
которая традиционно разбита на ряд поддиапазонов. Соседние диапазоны могут немного перекрываться.
| Диапазон | Полоса частот | Длина волны |
| Сверхдлинные радиоволны | 3…30 кГц | 100000…10000 м |
| Длинные радиоволны | 30…300 кГц | 10000…1000 м |
| Средние радиоволны | 300…3000 кГц | 1000…100 м |
| Короткие радиоволны | 3…30 МГц | 100…10 м |
| Метровый радиодиапазон | 30…300 МГц | 10…1 м |
| Дециметровый радиодиапазон | 300…3000 МГц | 1…0,1 м |
| Сантиметровый СВЧ диапазон | 3…30 ГГц | 10…1 см |
| Микроволновый СВЧ диапазон | 30…300 ГГц | 1…0,1 см |
| Инфракрасное излучение | 0,3…405 ТГц | 1000…0,74 мкм |
| Красный цвет | 405…480 ТГц | 740…625 нм |
| Оранжевый цвет | 480…510 ТГц | 625…590 нм |
| Жёлтый цвет | 510…530 ТГц | 590…565 нм |
| Зелёный цвет | 530…600 ТГц | 565…500 нм |
| Голубой цвет | 600…620 ТГц | 500…485 нм |
| Синий цвет | 620…680 ТГц | 485…440 нм |
| Фиолетовый цвет | 680…790 ТГц | 440…380 нм |
| Ультрафиолетовое излучение | 480…30000 ТГц | 400…10 нм |
| Рентгеновское излучение | 30000…3000000 ТГц | 10…0,1 нм |
| Гамма излучение | 3000000…30000000 ТГц | 0,1…0,01 нм |
А теперь можно переходить к калькуляторам.
КАЛЬКУЛЯТОР РАСЧЁТА ДЛИНЫ ВОЛНЫ ПО ЧАСТОТЕ
|
Частота электромагнитных колебаний f |
||
Показатель преломления среды (по умолч. 1) |
||
Длина волны |
КАЛЬКУЛЯТОР РАСЧЁТА ЧАСТОТЫ ПО ДЛИНЕ ВОЛНЫ
|
Длина электромагнитной волны в вакууме λ |
|
|
Частота |
В радиочастотной практике имеет распространение величина Kp, называемая коэффициентом укорочения. Однако здесь
существует некоторая путаница. Одни источники интерпретируют эту величину, как отношение длины волны в среде к длине волны в вакууме,
т. е. численно равной Kp = 1/n, где n – это, как мы помним, показатель преломления среды.
Другие, наоборот – как отношение длины волны в вакууме к длине волны в среде, т. е. Kp = n.
Поэтому надо иметь в виду – если Kp > 1, то значение показателя преломления среды, которое следует подставлять в калькулятор n = Kp, а
если Kp < 1, то n = 1/Kp.
Download Article
Download Article
Frequency, also called wave frequency, is a measurement of the total number of vibrations or oscillations made within a certain amount of time. There are a few different ways to calculate frequency based on the information you have available to you. Keep reading to learn some of the most common and useful versions.
-
1
Learn the formula. The formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: f = V / λ[1]
- In this formula, f represents frequency, V represents the velocity of the wave, and λ represents the wavelength of the wave.
- Example: A certain sound wave traveling in the air has a wavelength of 322 nm when the velocity of sound is 320 m/s. What is the frequency of this sound wave?
-
2
Convert the wavelength into meters, if necessary. If the wavelength is given in nanometers, you need to convert this value into meters by dividing it by the number of nanometers in a single meter.[2]
- Note that when working with extremely small numbers or extremely large numbers, it is generally easier to write the values in scientific notation. The values will be shown in and out of their scientific notation forms for this example, but when writing your answer for homework, other schoolwork, or other formal forums, you should stick with scientific notation.
- Example: λ = 322 nm
- 322 nm x (1 m / 10^9 nm) = 3.22 x 10^-7 m = 0.000000322 m
Advertisement
-
3
Divide the velocity by the wavelength. Divide the velocity of the wave, V, by the wavelength converted into meters, λ, in order to find the frequency, f.[3]
- Example: f = V / λ = 320 / 0.000000322 = 993788819.88 = 9.94 x 10^8
-
4
Write your answer. After completing the previous step, you will have completed your calculation for the frequency of the wave. Write your answer in Hertz, Hz, which is the unit for frequency.
- Example: The frequency of this wave is 9.94 x 10^8 Hz.
Advertisement
-
1
Learn the formula. The formula for the frequency of a wave in a vacuum is almost identical to that of a wave not in a vacuum. Since there are no outside influences on the velocity of the wave, though, you would use the mathematical constant for the speed of light, which electromagnetic waves would travel at under these conditions. As such, the formula is written as: f = C / λ[4]
- In this formula, f represents frequency, C represents the velocity or speed of light, and λ represents the wavelength of the wave.
- Example: A particular wave of electromagnetic radiation has a wavelength of 573 nm when passing through a vacuum. What is the frequency of this electromagnetic wave?
-
2
Convert the wavelength into meters, if necessary. When the problem gives you the wavelength in meters, no further action is needed. If, however, the wavelength is given in micrometers, you need to convert this value into meters by dividing it by the number of micrometers in a single meter.
- Note that when working with extremely small numbers or extremely large numbers, it is generally easier to write the values in scientific notation. The values will be shown in and out of their scientific notation forms for this example, but when writing your answer for homework, other schoolwork, or other formal forums, you should stick with scientific notation.
- Example: λ = 573 nm
- 573 nm x (1 m / 10^9 nm) = 5.73 x 10^-7 m = 0.000000573
-
3
Divide the speed of light by the wavelength. The speed of light is a constant, so even if the problem does not provide you with a value, the value remains 3.00 x 10^8 m/s. Divide this value by the wavelength converted into meters.[5]
- Example: f = C / λ = 3.00 x 10^8 / 5.73 x 10^-7 = 5.24 x 10^14
-
4
Write your answer. With this, you should have calculated the value of the frequency of the wave. Write your answer in Hertz, Hz, the unit for frequency.
- Example: The frequency of this wave is 5.24 x 10^14 Hz.
Advertisement
-
1
Learn the formula. Frequency and the time taken to finish a single wave oscillation are inversely proportional. As such, the formula for calculating frequency when given the time taken to complete a wave cycle is written as: f = 1 / T
- In this formula, f represents frequency and T represents the time period or amount of time required to complete a single wave oscillation.
- Example A: The time for a certain wave to complete a single oscillation is 0.32 seconds. What is the frequency of this wave?
- Example B: In 0.57 seconds, a certain wave can complete 15 oscillations. What is the frequency of this wave?
-
2
Divide the number of oscillations by the time period. Usually, you will be told how long it takes to complete a single oscillation, in which case, you would just divide the number 1 by the time period, T. If given a time period for numerous oscillations, however, you will need to divide the number of oscillations by the overall time period required to complete them.[6]
- Example A: f = 1 / T = 1 / 0.32 = 3.125
- Example B: f = 1 / T = 15 / 0.57 = 26.316
-
3
Write your answer. This calculation should tell you the frequency of the wave. Write your answer in Hertz, Hz, the unit for frequency.
- Example A: The frequency of this wave is 3.125 Hz.
- Example B: The frequency of this wave is 26.316 Hz.
Advertisement
-
1
Learn the formula. When told the angular frequency of a wave but not the standard frequency of that same wave, the formula to calculate the standard frequency is written as: f = ω / (2π)[7]
- In this formula, f represents the frequency of the wave and ω represents the angular frequency. As with any mathematical problem, π stands for pi, a mathematical constant.
- Example: A particular wave rotates with an angular frequency of 7.17 radians per second. What is the frequency of that wave?
-
2
Multiply pi by two. In order to find the denominator of the equation, you need to double the value of pi, 3.14.
- Example: 2 * π = 2 * 3.14 = 6.28
-
3
Divide the angular frequency by the double of pi. Divide the angular frequency of the wave, given in radians per second, by 6.28, the doubled value of pi.[8]
- Example: f = ω / (2π) = 7.17 / (2 * 3.14) = 7.17 / 6.28 = 1.14
-
4
Write your answer. This final bit of calculation should indicate what the frequency of the wave is. Write your answer in Hertz, Hz, the unit for frequency.
- Example: The frequency of this wave is 1.14 Hz.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
What is the frequency if 80 oscillations are completed in 1 second?
Frequency is the number of oscillations completed in a second. The answer would be 80 Hertz.
-
Question
Do atoms have a frequency and, if so, does it mean everything vibrates?
Atoms have energy. Energy is often characterized as vibration. Vibration possesses frequency. So, yes, everything could be thought of as vibrating at the atomic level.
-
Question
What’s the definition of frequency?
The rate at which a vibration occurs that constitutes a wave, either in a material (as in sound waves), or in an electromagnetic field (as in radio waves and light), usually measured per second. The rate at which something occurs or is repeated over a particular period of time or in a given sample.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Things You’ll Need
- Calculator
- Pencil
- Paper
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
To calculate the frequency of a wave, divide the velocity of the wave by the wavelength. Write your answer in Hertz, or Hz, which is the unit for frequency. If you need to calculate the frequency from the time it takes to complete a wave cycle, or T, the frequency will be the inverse of the time, or 1 divided by T. Display this answer in Hertz as well. Keep reading to learn how to calculate frequency from angular frequency!
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 1,511,957 times.
Did this article help you?
Длина электромагнитной волны в воздухе равна
0, 6 мкм.
Чему равна частота колебаний вектора
напряженности электрического поля в этой волне?
Скорость распростране –
ния электромагнитных волн с = 3 • 108 м / с.
Вопрос Длина электромагнитной волны в воздухе равна0, 6 мкм?, расположенный на этой странице сайта, относится к
категории Физика и соответствует программе для 5 – 9 классов. Если
ответ не удовлетворяет в полной мере, найдите с помощью автоматического поиска
похожие вопросы, из этой же категории, или сформулируйте вопрос по-своему.
Для этого ключевые фразы введите в строку поиска, нажав на кнопку,
расположенную вверху страницы. Воспользуйтесь также подсказками посетителей,
оставившими комментарии под вопросом.
Частота и длина волны
Электромагнитная волна характеризуется одним главным параметром — числом гребней, которые за секунду проходят мимо наблюдателя (или поступают в детектор). Эту величину называют частотой излучения ν. Поскольку для всех электромагнитных волн скорость в вакууме (с) одинакова, по частоте легко определить длину волны λ:
λ = с/ν.
Мы просто делим путь, пройденный светом за секунду, на число колебаний за то же время и получаем длину одного колебания. Длина волны — очень важный параметр, поскольку она определяет пограничный масштаб: на расстояниях заметно больше длины волны излучение подчиняется законам геометрической оптики, его можно описывать как распространение лучей. На меньших расстояниях совершенно необходимо учитывать волновую природу света, его способность обтекать препятствия, невозможность точно локализовать положение луча и т. п.
Из этих соображений, в частности, следует, что невозможно получить изображение объектов, если их размер порядка или меньше длины волны излучения, на которой ведется наблюдение. Это, в частности, ставит предел возможностям микроскопов. В видимом свете невозможно рассмотреть объекты размером менее полмикрона; соответственно, увеличение больше чем 1-2 тысячи раз для оптического микроскопа лишено смысла.
Далее: История открытия электромагнитных волн