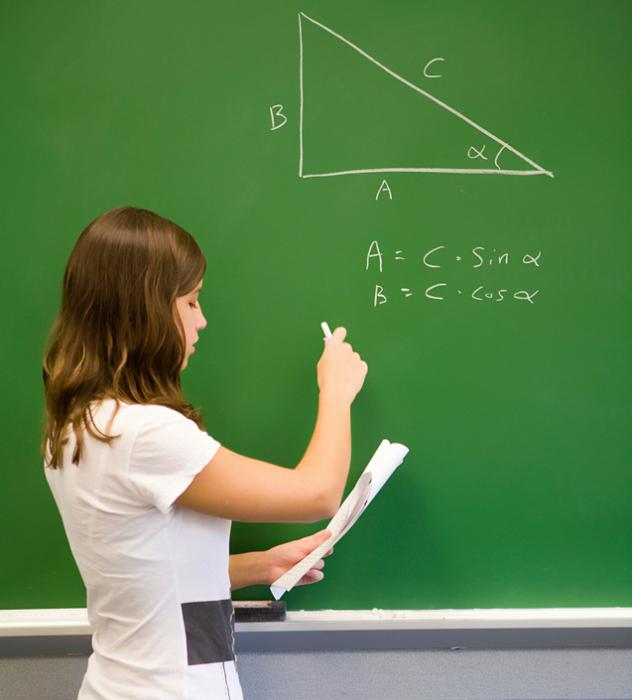
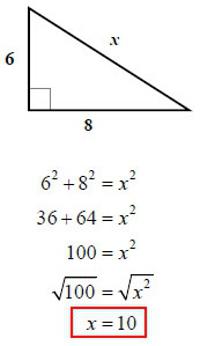После изучения темы про прямоугольные треугольники ученики часто выбрасывают из головы всю информацию о них. В том числе и то, как найти гипотенузу, не говоря уже о том, что это такое.
И напрасно. Потому что в дальнейшем диагональ прямоугольника оказывается этой самой гипотенузой, и ее нужно найти. Или диаметр окружности совпадает с самой большой стороной треугольника, один из углов которого прямой. И найти ее без этого знания невозможно.
Существует несколько вариантов того, как найти гипотенузу треугольника. Выбор метода зависит от исходного набора данных в условии задачи величин.
Способ под номером 1: даны оба катета
Это самый запоминающийся метод, потому что использует теорему Пифагора. Только иногда ученики забывают, что по этой формуле находится квадрат гипотенузы. Значит, чтобы найти саму сторону, нужно будет извлечь квадратный корень. Поэтому формула для гипотенузы, которую принято обозначать буквой «с», будет выглядеть так:
с = √ (а2 + в2), где буквами «а» и «в» записаны оба катета прямоугольного треугольника.
Способ под номером 2: известен катет и угол, который к нему прилежит
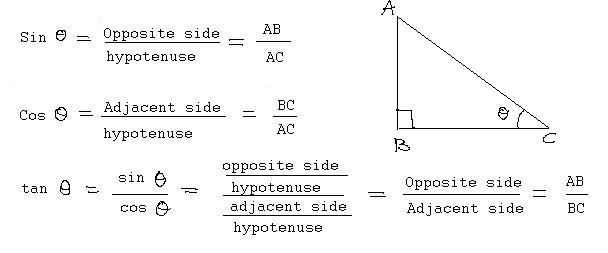
Для того чтобы узнать, как найти гипотенузу, потребуется вспомнить тригонометрические функции. А именно косинус. Для удобства будем считать, что даны катет «а» и прилежащий к нему угол α.
Теперь нужно вспомнить, что косинус угла прямоугольного треугольника равен отношению двух сторон. В числителе будет стоять значение катета, а в знаменателе — гипотенузы. Из этого следует, что последнюю можно будет сосчитать по формуле:
с = а / cos α.
Способ под номером 3: даны катет и угол, который лежит напротив него
Чтобы не запутаться в формулах, введем обозначение для этого угла — β, а сторону оставим прежнюю «а». В этом случае потребуется другая тригонометрическая функция – синус.
Как и в предыдущем примере, синус равен отношению катета к гипотенузе. Формула этого способа выглядит так:
с = а / sin β.
Для того чтобы не запутаться в тригонометрических функциях, можно запомнить простое мнемоническое привило: если в задаче идет речь о противолежащем угле, то нужно использовать синус, если — о прилежащем, то косинус. Следует обратить внимание на первые гласные в ключевых словах. Они образуют пары о-и или и-о.
Способ под номером 4: по радиусу описанной окружности
Теперь, для того чтобы узнать, как найти гипотенузу, потребуется вспомнить свойство окружности, которая описана около прямоугольного треугольника. Оно гласит следующее. Центр окружности совпадает с серединой гипотенузы. Если сказать по-другому, то самая большая сторона прямоугольного треугольника равна диагонали окружности. То есть удвоенному радиусу. Формула для этой задачи будет выглядеть так:
с = 2 * r, где буквой r обозначен известный радиус.
Это все возможные способы того, как находить гипотенузу прямоугольного треугольника. Пользоваться в каждой конкретной задаче нужно тем методом, который больше подходит по набору данных.
Пример задачи №1
Условие: в прямоугольном треугольнике проведены медианы к обоим катетам. Длина той, которая проведена к большей стороне, равна √52. Другая медиана имеет длину √73. Требуется вычислить гипотенузу.
Решение.
Так как в треугольнике проведены медианы, то они делят катеты на два равных отрезка. Для удобства рассуждений и поиска того, как найти гипотенузу, нужно ввести несколько обозначений. Пусть обе половинки большего катета будут обозначены буквой «х», а другого — «у».
Теперь нужно рассмотреть два прямоугольных треугольника, гипотенузами у которых являются известные медианы. Для них нужно дважды записать формулу теоремы Пифагора:
(2у)2 + х2 = (√52)2
и
(у)2 + (2х)2 = (√73)2.
Эти два уравнения образуют систему с двумя неизвестными. Решив их, легко можно будет найти катеты исходного треугольника и по ним его гипотенузу.
Сначала нужно все возвести во вторую степень. Получается:
4у2 + х2 = 52
и
у2 + 4х2 = 73.
Из второго уравнения видно, что у2 = 73 – 4х2. Это выражение нужно подставить в первое и вычислить «х»:
4(73 – 4х2) + х2 = 52.
После преобразования:
292 – 16 х2 + х2 = 52 или 15х2 = 240.
Из последнего выражения х = √16 = 4.
Теперь можно вычислить «у»:
у2 = 73 – 4(4)2 = 73 – 64 = 9.
у = 3.
По данным условия получается, что катеты исходного треугольника равны 6 и 8. Значит, можно воспользоваться формулой из первого способа и найти гипотенузу:
√(62 + 82) = √(36 + 64) = √100 = 10.
Ответ: гипотенуза равна 10.
Пример задачи №2
Условие: вычислить диагональ, проведенную в прямоугольнике с меньшей стороной, равной 41. Если известно, что она делит угол на такие, которые соотносятся как 2 к 1.
Решение.
В этой задаче диагональ прямоугольника является наибольшей стороной в треугольнике с углом 90º. Поэтому все сводится к тому, как найти гипотенузу.
В задаче идет речь об углах. Это значит, что нужно будет пользоваться одной из формул, в которых присутствуют тригонометрические функции. А сначала требуется определить величину одного из острых углов.
Пусть меньший из углов, о которых идет речь в условии, будет обозначен α. Тогда прямой угол, который делится диагональю, будет равен 3α. Математическая запись этого выглядит так:
90º = 3 α.
Из этого уравнения просто определить α. Он будет равен 30º. Причем он будет лежать напротив меньшей стороны прямоугольника. Поэтому потребуется формула, описанная в способе №3.
Гипотенуза равна отношению катета к синусу противолежащего угла, то есть:
41 / sin 30º = 41 / (0,5) = 82.
Ответ: гипотенуза равна 82.
Ученик
(145),
закрыт
1 год назад
Алексей Бараев
Гений
(69534)
1 год назад
Определение сторон и углов треугольника в общем случае называется «решением треугольников». У любого треугольника три стороны и три внутренних угла по определению. Итого 6 параметров. Для того, чтобы «решить» треугольник необходимо и достаточно знать три параметра из шести. Если все-таки разговор про телрему Пифагора, то она про прямоугольные треугольники, то есть один угол уже известен, опять-таки из определения. Для того, чтобы найти гипотенузу, нужно знать два катета (уголь между ними известен).
342 324
Ученик
(154)
1 год назад
Если вам дан короткий катет (противолежащий углу в 30 градусов), просто умножьте длину этого катета на 2, чтобы найти длину гипотенузы. Например, если короткий катет равен 4, то гипотенуза равна 8.
Download Article
Download Article
All right triangles have one right (90-degree) angle, and the hypotenuse is the side that is opposite or the right angle, or the longest side of the right triangle.[1]
The hypotenuse is the longest side of the triangle, and it’s also very easy to find using a couple of different methods. This article will teach you how to find the length of the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem when you know the length of the other two sides of the triangle. It will then teach you to recognize the hypotenuse of some special right triangles that often appear on tests. It will finally teach you to find the length of the hypotenuse using the Law of Sines when you only know the length of one side and the measure of one additional angle.
-
1
Learn the Pythagorean Theorem. The Pythagorean Theorem describes the relationship between the sides of a right triangle.[2]
It states that for any right triangle with sides of length a and b, and hypotenuse of length c, a2 + b2 = c2.[3]
-
2
Make sure that your triangle is a right triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem only works on right triangles, and by definition only right triangles can have a hypotenuse. If your triangle contains one angle that is exactly 90 degrees, it is a right triangle and you can proceed.
- Right angles are often notated in textbooks and on tests with a small square in the corner of the angle. This special mark means “90 degrees.”
Advertisement
-
3
Assign variables a, b, and c to the sides of your triangle. The variable “c” will always be assigned to the hypotenuse, or longest side. Choose one of the other sides to be a, and call the other side b (it doesn’t matter which is which; the math will turn out the same). Then copy the lengths of a and b into the formula, according to the following example:
- If your triangle has sides of 3 and 4, and you have assigned letters to those sides such that a = 3 and b = 4, then you should write your equation out as: 32 + 42 = c2.
-
4
Find the squares of a and b. To find the square of a number, you simply multiply the number by itself, so a2 = a x a. Find the squares of both a and b, and write them into your formula.[4]
- If a = 3, a2 = 3 x 3, or 9. If b = 4, then b2 = 4 x 4, or 16.
- When you plug those values into your equation, it should now look like this: 9 + 16 = c2.
-
5
Add together the values of a2 and b2. Enter this into your equation, and this will give you the value for c2. There is only one step left to go, and you will have that hypotenuse solved!
- In our example, 9 + 16 = 25, so you should write down 25 = c2.
-
6
Find the square root of c2. Use the square root function on your calculator (or your memory of the multiplication table) to find the square root of c2. The answer is the length of your hypotenuse![5]
- In our example, c2 = 25. The square root of 25 is 5 (5 x 5 = 25, so Sqrt(25) = 5). That means c = 5, the length of our hypotenuse!
Advertisement
-
1
Learn to recognize Pythagorean Triple Triangles. The side lengths of a Pythagorean triple are integers that fit the Pythagorean Theorem. These special triangles appear frequently in geometry text books and on standardized tests like the SAT and the GRE. If you memorize the first 2 Pythagorean triples, in particular, you can save yourself a lot of time on these tests because you can immediately know the hypotenuse of one of these triangles just by looking at the side lengths![6]
- The first Pythagorean triple is 3-4-5 (32 + 42 = 52, 9 + 16 = 25). When you see a right triangle with legs of length 3 and 4, you can instantly be certain that the hypotenuse will be 5 without having to do any calculations.
- The ratio of a Pythagorean triple holds true even when the sides are multiplied by another number. For example a right triangle with legs of length 6 and 8 will have a hypotenuse of 10 (62 + 82 = 102, 36 + 64 = 100). The same holds true for 9-12-15, and even 1.5-2-2.5. Try the math and see for yourself!
- The second Pythagorean triple that commonly appears on tests is 5-12-13 (52 + 122 = 132, 25 + 144 = 169). Also be on the lookout for multiples like 10-24-26 and 2.5-6-6.5.
-
2
Memorize the side ratios of a 45-45-90 right triangle. A 45-45-90 right triangle has angles of 45, 45, and 90 degrees, and is also called an Isosceles Right Triangle. It occurs frequently on standardized tests, and is a very easy triangle to solve. The ratio between the sides of this triangle is 1:1:Sqrt(2), which means that the length of the legs are equal, and the length of the hypotenuse is simply the leg length multiplied by the square root of two.[7]
- To calculate the hypotenuse of this triangle based on the length of one of the legs, simply multiply the leg length by Sqrt(2).
- Knowing this ratio comes in especially handy when your test or homework question gives you the side lengths in terms of variables instead of integers.
-
3
Learn the side ratios of a 30-60-90 right triangle. This triangle has angle measurements of 30, 60, and 90 degrees, and occurs when you cut an equilateral triangle in half. The sides of the 30-60-90 right triangle always maintain the ratio 1:Sqrt(3):2, or x:Sqrt(3)x:2x. If you are given the length of one leg of 30-60-90 right triangle and are asked to find the hypotenuse, it is very easy to do:[8]
- If you are given the length of the shortest leg (opposite the 30-degree angle,) simply multiply the leg length by 2 to find the length of the hypotenuse. For instance, if the length of the shortest leg is 4, you know that the hypotenuse length must be 8.
- If you are given the length of the longer leg (opposite the 60-degree angle,) multiply that length by 2/Sqrt(3) to find the length of the hypotenuse. For instance, if the length of the longer leg is 4, you know that the hypotenuse length must be 4.62.
Advertisement
-
1
Understand what “Sine” means. The terms “sine,” “cosine,” and “tangent” all refer to various ratios between the angles and/or sides of a right triangle. In a right triangle, the sine of an angle is defined as the length of the side opposite the angle divided by the hypotenuse of the triangle. The abbreviation for sine found in equations and on calculators is sin.[9]
-
2
Learn to calculate sine. Even a basic scientific calculator will have a sine function. Look for a key marked sin. To find the sine of angle, you will usually press the sin key and then enter the angle measurement in degrees. On some calculators, however, you must enter the degree measurement first and then the sin key. You will have to experiment with your calculator or check the manual to find out which it is.
- To find the sine of an 80 degree angle, you will either need to key in sin 80 followed by the equal sign or enter key, or 80 sin. (The answer is -0.9939.)
- You can also type in “sine calculator” into a web search, and find a number of easy-to-use calculators that will remove any guesswork.[10]
-
3
Learn the Law of Sines. The Law of Sines is a useful tool for solving triangles. In particular, it can help you find the hypotenuse of a right triangle if you know the length of one side, and the measure of one other angle in addition to the right angle. For any triangle with sides a, b, and c, and angles A, B, and C, the Law of Sines states that a / sin A = b / sin B = c / sin C.[11]
- The Law of Sines can actually be used to solve any triangle, but only a right triangle will have a hypotenuse.
-
4
Assign the variables a, b, and c to the sides of your triangle. The hypotenuse (longest side) must be “c”. For the sake of simplicity, label the side with the known length as “a,” and the other “b”. Then assign variables A, B, and C to the angles of the triangle. The right angle opposite the hypotenuse will be “C”. The angle opposite side “a” is angle “A,” and the angle opposite side “b” is “B”.
-
5
Calculate the measurement of the third angle. Because it is a right angle, you already know that C = 90 degrees, and you also know the measure of A or B. Since the internal degree measurement of a triangle must always equal 180 degrees, you can easily calculate the measurement of the third angle using the following formula: 180 – (90 + A) = B. You can also reverse the equation such that 180 – (90 + B) = A.
- For example, if you know that A = 40 degrees, then B = 180 – (90 + 40). Simplify this to B = 180 – 130, and you can quickly determine that B = 50 degrees.
-
6
Examine your triangle. At this point, you should know the degree measurements of all three angles, and the length of side a. It is now time to plug this information into the Law of Sines equation to determine the lengths of the other two sides.
- To continue our example, let’s say that the length of side a = 10. Angle C = 90 degrees, angle A = 40 degrees, and angle B = 50 degrees.
-
7
Apply the Law of Sines to your triangle. We just need to plug our numbers in and solve the following equation to determine the length of hypotenuse c: length of side a / sin A = length of side c / sin C. This might still look a bit intimidating, but the sine of 90 degrees is a constant, and always equals 1! Our equation can thus be simplified to: a / sin A = c / 1, or just a / sin A = c.[12]
-
8
Divide the length of side a by the sine of angle A to find the length of the hypotenuse! You can do this in two separate steps, by first calculating sin A and writing it down, and then dividing by a. Or you can key it all into the calculator at the same time. If you do, remember to include parentheses after the division sign.[13]
For example, key in either 10 / (sin 40) or 10 / (40 sin), depending on your calculator.- Using our example, we find that sin 40 = 0.64278761. To find the value of c, we simply divide the length of a by this number, and learn that 10 / 0.64278761 = 15.6, the length of our hypotenuse!
Advertisement
-
1
Identify the formula to use. There are many variations of the formula for the area of a right triangle. You may already be familiar with the formula Area = 1/2 x base x height. But the known parameters determines which formulas you can work with. You can find the most commonly used formulas for calculating the area of right and non right angles with worked examples in this article[14]
. The variation that directly relates the area to the hypotenuse is- Rearrange formula to make hypotenuse the subject. The variable “c” represents the hypotenuse.
- Rearrange formula to make hypotenuse the subject. The variable “c” represents the hypotenuse.
-
2
Assign the variables.
represents an angle on the right angle other than the 90 degree angle. So it is up to you to assign any of the other two angles as
. The other variable in the formula is the area, which as the name suggests refers to the area of the triangle.
-
3
Apply the formula to your triangle. We just need to plug in the variables to the formula and solve the following equation to determine the length of hypotenuse c.
Advertisement
Practice Problems and Answers
Add New Question
-
Question
How do you find the length of the hypotenuse in the Pythagorean Theorem?
Grace Imson, MA
Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco
Grace Imson is a math teacher with over 40 years of teaching experience. Grace is currently a math instructor at the City College of San Francisco and was previously in the Math Department at Saint Louis University. She has taught math at the elementary, middle, high school, and college levels. She has an MA in Education, specializing in Administration and Supervision from Saint Louis University.
Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco
Expert Answer
Support wikiHow by
unlocking this expert answer.One common mistake is forgetting to square the terms. In the Pythagorean Theorem, all three terms are squared. Many people go too fast and forget to find the square before the sum of ‘a’ and ‘b,’ which gives them an incorrect answer.
-
Question
Is there a calculator for finding the length of the hypotenuse?
This answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff Editor
Staff Answer
Support wikiHow by
unlocking this staff-researched answer.Google provides a right angle triangle calculator that allows you to solve for the hypotenuse. Simply search for “hypotenuse calculator” and plug your numbers into the calculator at the top of the search results. You can also use the hypotenuse calculator at Omincalculator.com.
-
Question
How can you find the length of the hypotenuse given the length of 1 side and an angle?
This answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff Editor
Staff Answer
Support wikiHow by
unlocking this staff-researched answer.If you know you are dealing with a right triangle, then you already know that one of the angles is 90°. Since the angles must add up to 180°, you can solve for the missing angle using the formula 90 + X = 180. Once you have all 3 angles, you can use that information and the known length of 1 side to use the law of sines and find the length of the hypotenuse.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
About This Article
Article SummaryX
If you need to find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle, you can use the Pythagorean theorem if you know the length of the other two sides. Square the length of the 2 sides, called a and b, then add them together. Take the square root of the result to get the hypotenuse. If you want to learn how to find the hypotenuse using trigonometric functions, keep reading the article!
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 1,375,273 times.
Did this article help you?
Гипотенуза — сторона в прямоугольном треугольнике, находящаяся напротив прямого угла. Две других стороны — катеты. В прямоугольном треугольнике гипотенуза всегда длиннее катетов.
Теорема Пифагора: квадрат гипотенузы равен сумме квадратов катетов (формула: c² = a² + b², где c — гипотенуза, a и b — катеты). Очень часто для вычисления гипотенузы используется именно эта теорема.
Как найти гипотенузу?
Как найти гипотенузу, зная катеты?
Если известны оба катета (две другие стороны прямоугольного треугольника), можно применить Теорему Пифагора.
Теорема Пифагора — в прямоугольном треугольнике квадрат гипотенузы равен сумме квадратов катетов. Формула: c² = a² + b² (при c — гипотенуза, a и b — катеты).
Например:
Один катет равен 3 см, другой — 4 см. Таким образом, а = 3, b = 4, подставляем в формулу:
c² = 3² + 4² <=> c² = 9 + 16 <=> c² = 25 <=> c = √25 <=> c = 5.
Ответ: длина гипотенузы 5 см (или x = 5).
Как найти катет в прямоугольном треугольнике
По той же формуле можно найти и длину одного неизвестного катета, нужно только немного её изменить:
Начальная формула: c² = a² + b² (при c — гипотенуза, a и b — катеты), и найти катет можно по этой:

Например: Один катет равен 3 см, а гипотенуза — 5 см. Нужно узнать длину второго катета.
Применяем формулу b = √c² — a² ⇔
b = √5² — 3² ⇔ b = √25 — 9 ⇔ b = √16 ⇔ b = 4.
Как найти гипотенузу, зная катет и угол?
Если есть противолежащий катет — теорема синусов
Если в условии задачи дан угол и противолежащий катет, то ищем гипотенузу по Теореме синусов: стороны треугольника пропорциональны синусам противолежащих углов.
Примечание: гипотенуза есть только в прямоугольном треугольнике, однако теорему синусов можно применять к любым треугольникам (не только к прямоугольным).
Формула:
Например:
Известна одна сторона треугольника 𝐴𝐶 = √2 и ∠β = 45º.
∠α = 90º (т.к. мы ищем гипотенузу, то второй угол в треугольнике прямой, значит имеет 90º).
Так как во всех треугольниках сумма всех углов равна 180º, то можем узнать оставшийся ∠c.
Значит: ∠c = 180º — (90º + 45º) = 45º.
Подставляем в формулу (a/sinα = b/sinβ = c/sinγ) известные:
BC/sin90º = AC/sin45º = AB/sin45º
В таблице вы найдёте значения для синуса:
| sin 45º | √2/2 |
| sin 60º | √3/2 |
| sin 90º | 1 |
В условии задачи нам дано: 𝐴𝐶 = √2, значит:
BC/sin90º = √2/sin45º = AB/sin45º
Подставляем значения синуса из таблицы:
BC/1 = √2/(√2/2) = AB/(√2/2) (забудем на время про катет AB) ⇔
BC = √2/(√2/2) ⇔ BC = 2 (гипотенуза равна 2)
Если хотите вычислить катет, уже зная другой катет и гипотенузу:
AB/(√2/2) = 2 ⇔ AB = √2
Ответ: гипотенуза BC равна 2 см, а катет AB √2 см.
Если есть прилежащий катет — по косинусу
Если в условии задачи дан угол и прилежащий катет, то ищем гипотенузу по косинусу (в прямоугольном треугольнике, косинус острого угла (cos) — это отношение прилежащего катета (b) к гипотенузе(c), таким образом cos a = b/c, из этого получается c = b / cos α).
Т.е. гипотенуза (c) = прилежащий катет (b) / косинус угла или c = b / cos α.
Например:
Известна одна сторона треугольника AB = 1 и ∠β = 45º. Нужно вычислить гипотенузу (BC).
Помним, что гипотенуза (c) = прилежащий катет (b) / косинус угла или c = b / cos α. Т.е.: BC = AB / cosβ ⇔ BC = 1/ cos 45º.
Смотрим в таблице, чему равен cos 45º.
BC = 1/ (√2/2) = √2
Ответ: гипотенуза BC равна √2 см.
Как найти гипотенузу равнобедренного треугольника
В равнобедренном треугольнике есть гипотенуза только в том случае, если он одновременно и прямоугольный, т.к. гипотенуза есть только в прямоугольных треугольниках (и его основание будет гипотенузой).
Чтобы найти такую гипотенузу, нужно любой из двух одинаковых катетов возвести в квадрат, умножить на 2 и посчитать квадратный корень: b = √2a² (где b — гипотенуза, а — катет). Это следствие из теоремы Пифагора.
Например:
Катет равнобедренного треугольника равен 7см. Нужно найти гипотенузу.
Формула b = √2a². Подставляем:
b = √2*7² = √2*49 ≈ √98 ≈ 9.899
Если забудете эту формулу, можно использовать уже знакомую формулу Пифагора для гипотенузы (c² = a² + b²):
c² = a² + b²
c² = 7² + 7²
c² = 49 + 49
c² = 98
c = √98
c ≈ 9.899
Ответ: гипотенуза равна 9.899.
Узнайте больше про Теорему Пифагора, Теорему косинусов, а также, что такое Тангенс и Аксиома.
|
Я не понял насчет какого треугольника вы спрашиваете, но раз в вопросе указано катеты и гипотенуза, то наверняка это прямоугольный треугольник. А найти гипотенузу по двум известным катетам очень просто. Для этого необходимо знать теорему Пифагора, она заключается в том, что: Квадрат гипотенузы равен сумме квадратов катетов. То есть, найдете гипотенузу в квадрате, а затем вычислите квадратный корень из получившегося числа. Вот вам и будет гипотенуза. автор вопроса выбрал этот ответ лучшим Искатель приключений 7 лет назад Для расчета длины гипотенузы треугольника при известной длине двух катетов, необходимо воспользоваться достаточно известной теоремой Пифагора. Согласно её, квадрата гипотенузы, равен сумме квадратов катета. Формула очень простая в использование, её проходят еще учась в школе. Владимир З 9 лет назад Вопрос не из простых, долго думал, потом придумал. Нужно сложить квадраты катетов и из этой суммы извлечь квадратный корень, если сумма получилась не отрицательной. Иначе придется оперировать с комплексными числами. Rnd 3 месяца назад Определение длины гипотенузы в прямоугольном треугольнике – это задача, решаемая с помощью удивительной теоремы Пифагора. Согласно теореме, квадрат длины гипотенузы является суммой квадратов длин двух катетов. На примере, если один из катетов имеет длину 3 метра (что дает квадрат длины 9 метров квадратных), а другой катет имеет длину 4 метра (что дает квадрат длины 16 метров квадратных), то сумма их квадратов равна 25 метров. Таким образом, длина гипотенузы равна квадратному корню из 25 метров квадратных, что составляет 5 метров. Алиса в Стране 5 лет назад Для решения этой задачки нам не обойтись без применения знаменитой теоремы Пифагора, которая связывает между собой квадрат гипотенузы и квадраты катетов. Нам нужно просто вспомнить простую формулу: квадрат гипотенузы прямоугольного треугольника (в других треугольниках гипотенуз не бывает, как и катетов, впрочем) равен сумме квадратов катетов. А сама гипотенуза равна квадратному корню из этой суммы. Пример решения задачи можно посмотреть на картинке: Skiyers 8 лет назад Для этого пользуются теоремой Пифагора. Известно, что Поэтому, если ваши катеты, например, 3 и 4 сантиметра, то вам нужно возвести в квадрат эти два числа (получится 9 и 16), сплюсовать (получится 25) и взять квадратный корень из этого числа (5). Кстати, такой треугольник называется “классическим” или “египетским“, и именно на нем проще всего обьяснять эту теорему оттого, что все числа получаются целыми, можно даже не пользоваться калькулятором. Невозмутимый Дождь 4 года назад Находя гипотенузу любого прямоугольного треугольника, необходимо, по теореме Пифагора, зная остальные его стороны, то есть катеты, суммировать квадраты последних и получить сумму, соответствующую длине искомой гипотенузы. Например, у нас есть катеты 3 см и 4 см. Гипотенуза этого треугольника равна 5 см, она несколько длиннее каждого из катетов, поскольку её квадрат (25) равен сумме двух квадратов – 16 и 9. Артём Денисов 7 лет назад Когда нам известны катеты в треугольнике и нужно найти гипотенузу, то следует применить теорему Пифагора. Исходя из теоремы, известно, что гипотенуза – это сума квадратов катетов (то есть нужно просто сложить суму катетов, но в квадрате и получится гипотенуза). Например, один катет равен 3, а другой – 4. 3^2+4^2 (9+16) = 25 (берем под корень) = 5. Galina7v7 7 лет назад Теорема Пифагора никого не оставит в покое,если вопрос касается прямоугольного треугольника.Варианта 3:1)известна гипотенуза с и 1-й катет а.Найти 2-й катет b:b=V(c^2-a^2). 2)известно :гипотенуза с и 2-й катет b.Найти :катет а:a=V(c^2-b^2). 3)вариант задачи:известны катеты a и b.Найти гипотенузу c=V(a^2+b^2). Надежда Кот 6 лет назад Если необходимо найти длину гипотенузы прямоугольного треугольника, то надо вспомнить, что гипотенуза может быть найдена с помощью хорошо известной теоремы Пифагора, которая говорит нам, что квадрат длины гипотенузы равен сумме квадратов длин катетов. Нужно воспользоваться простым и проверенным веками способом – теоремой Пифагора. Согласно теореме Пифагора, квадрат гипотенузы равен сумме квадратов катетов. Таким образом, для решения нужно вычислить квадратный корень из суммы квадратов катетов Знаете ответ? |