Overview
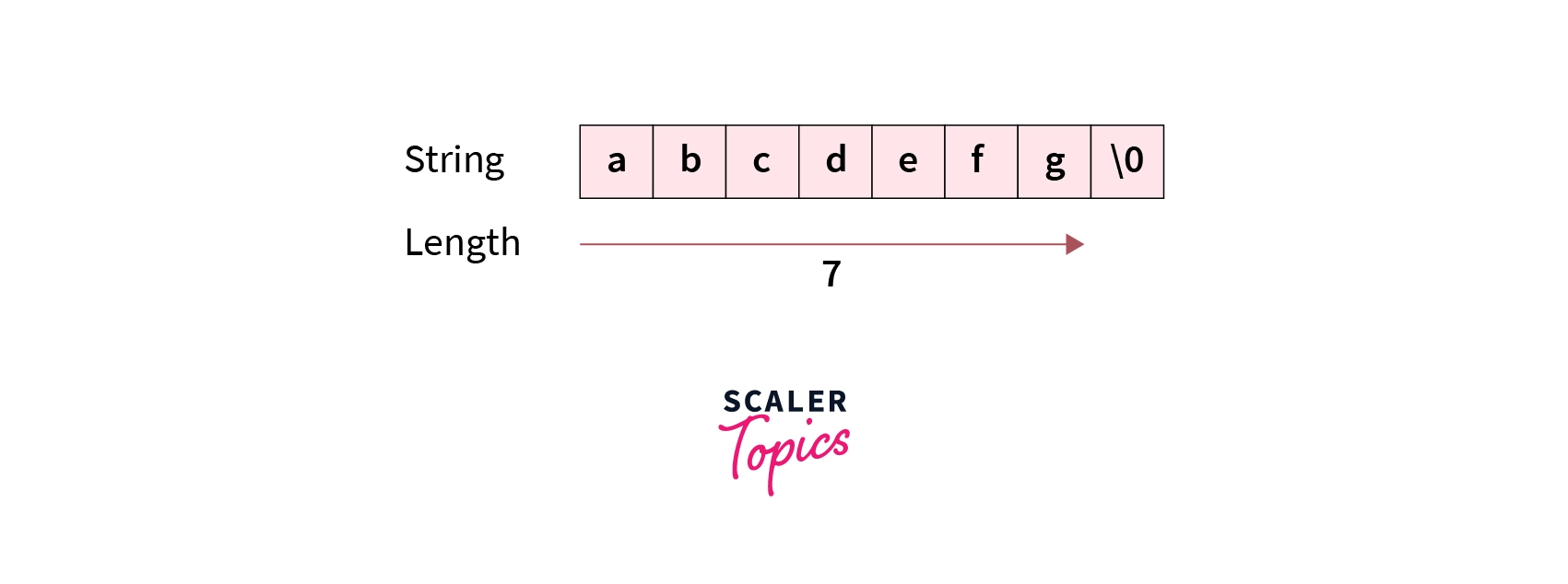
In C, a string is an array of characters that is terminated with a null character “”. The length of a string will be determined by counting all the characters in the string (except for the null character).
Scope of Article
- In this article, we will learn to find the length of a String in C.
- All the methods to find the length of a String will be explained in this article.
- Every method will be explained using syntax, images, and examples.
Introduction
The string length in C is equal to the count of all the characters in it (except the null character “”).
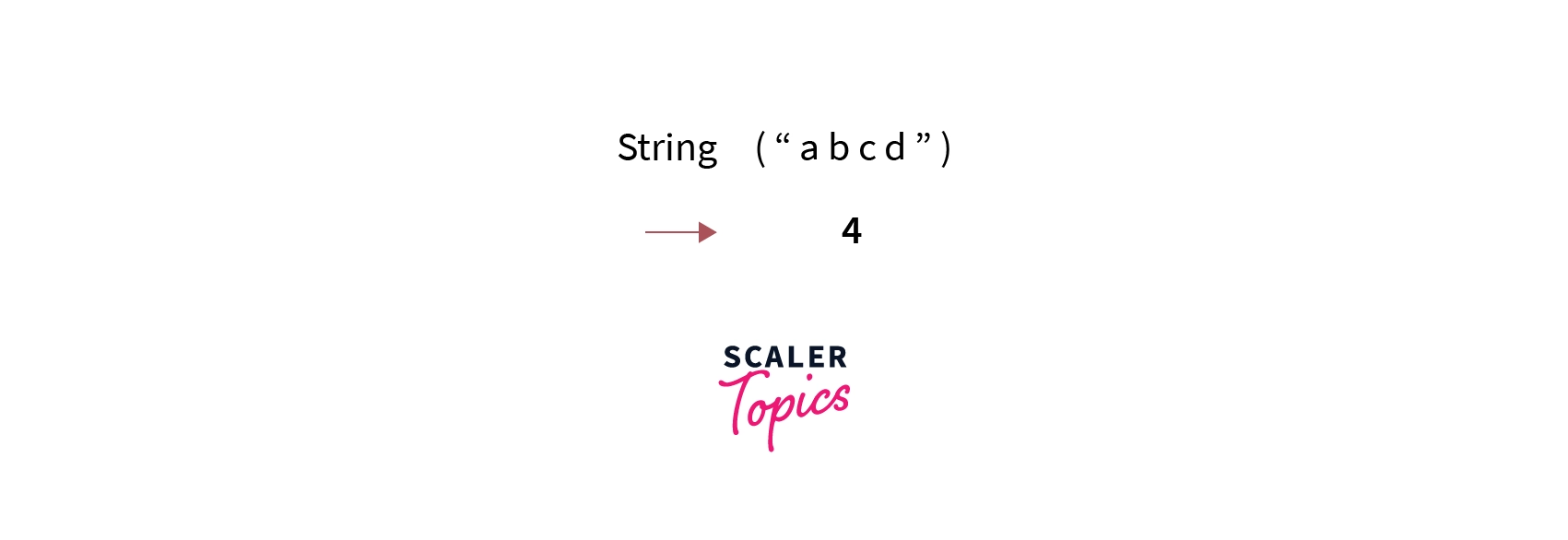
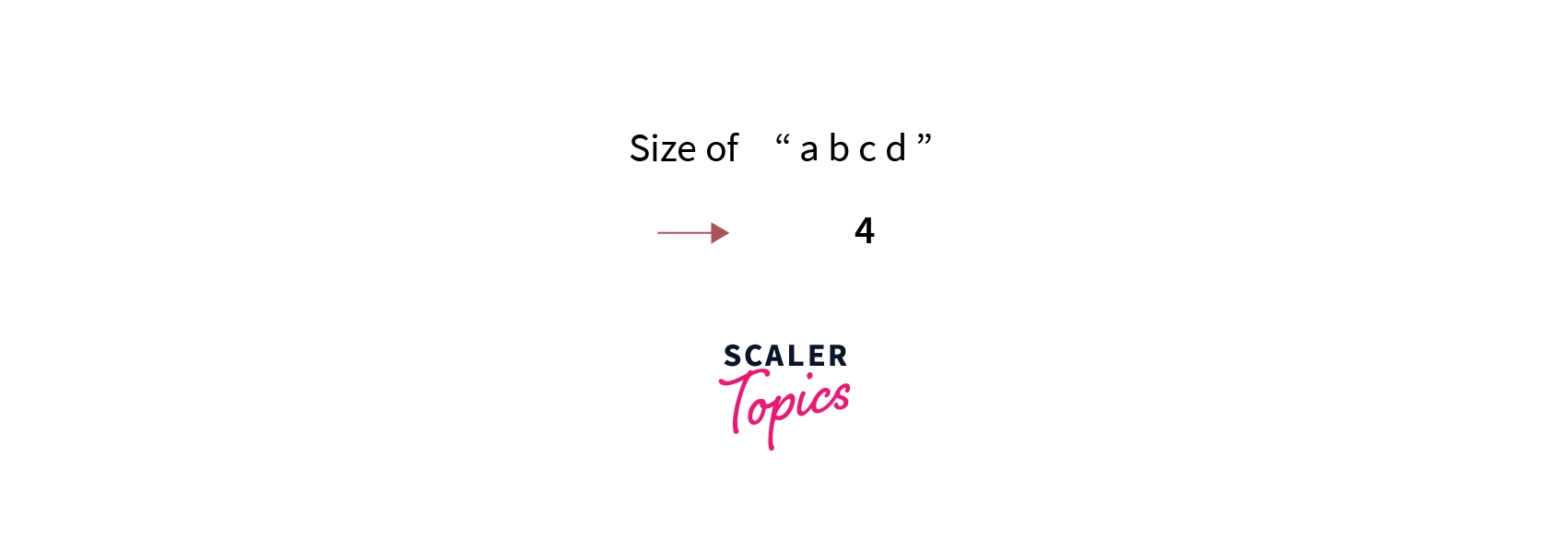
For Example, the string “gfddf” has a length of 5 and the string “4343” has a length of 4.
Note:
In C, a String is an array of characters that is terminated with a null character “” to indicate the end of the string.
How to Find the String Length in C?
We can find the length of a String by counting all the characters in it (before the null character) using a for loop. We can also use the built-in string.h library function strlen() or the sizeof() operator.
Let us understand how to use these methods in the coming sections.
String Length in C using a User-Defined Function
We can find the length of a string using a user-defined function by iterating over the string in a for loop and incrementing the count of characters (length) by 1 till it reaches the null character “” and then returning the count.
Let’s take a look at its implementation:
Code
// finding the length of a string using a user-defined function #include <stdio.h> // The User-defined method int str_length(char str[]) { // initializing count variable (stores the length of the string) int count; // incrementing the count till the end of the string for (count = 0; str[count] != ''; ++count); // returning the character count of the string return count; } // Driver code int main() { // initializing the array to store string characters char str[1000]; // inputting the string printf("Enter the string: "); scanf("%s", str); // assigning the count of characters in the string to the length of the string int length = str_length(str); // printing the length of string printf("The length of the string is %d", length); return 0; }Output
Enter the string: 567lens The length of the string is 7Explanation:
In the above example, we are finding the length of a string by iterating over it in a for loop and incrementing the count by 1 in each iteration till it reaches the null character. The value of count after the end of the for loop will be equal to the length of the string.
String Length in C Using Built-In Library Function
The length of a string can be found using the built-in library function strlen() in string.h header file. It returns the length of the string passed to it (ignoring the null character).
Syntax
The string is passed to the strlen() function, which returns its length.
Let us take a look at its implementation.
Code
// finding the length of a string using the strlen() function from the string.h library #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main() { char str[1000]; // initializing the array to store string characters // inputting the string printf("Enter the string: "); scanf("%s", str); // initializing the length variable int length; // Using the strlen() function to return the length of the string and assign it to the length variable length = strlen(str); // printing the length of string printf("The length of the string is %d", length); return 0; }Output :
Enter the string: 5654dds The length of the string is 7In the above example, we are finding the length of a string by using the string.h library function strlen(), which returns the length of the string passed to it.
String Length in C Using the sizeof() Operator
We can also find the length of a string using the sizeof() Operator in C. The sizeof is a unary operator which returns the size of an entity (variable or value).
Syntax
The value is written with the sizeof operator which returns its size (in bytes).
Let us take a look at its implementation:
Code
// finding the length of a string using the sizeof operator #include <stdio.h> int main() { // initializing the string literal char str[] = "g4343"; // printing the string printf("The given string is %sn", str); // initializing the length variable int length; // using the sizeof operator to find the length of the string length = sizeof str; // printing the length of string printf("The length of the string is %d", length-1); return 0; }Output
The given string is g4343 The length of the string is 5In the above example, we are finding the length of the string “g4343” using the sizeof operator in C. The sizeof operator returns its length as 6 in the output as It returns the size of an operand, not the string length (including null values). But here, if we print length-1 then we get the length of the string.
Conclusion
- In C, the length of a string is the count of all its characters except the null character “”.
- We can find the length of the string using a for loop by counting each character in each iteration.
- The built-in library function strlen() is used to return the length of a string passed to it.
- We can also find the length of a C String using the sizeof operator.
I’m trying to find a way to find the length of an integer (number of digits) and then place it in an integer array. The assignment also calls for doing this without the use of classes from the STL, although the program spec does say we can use “common C libraries” (gonna ask my professor if I can use cmath, because I’m assuming log10(num) + 1 is the easiest way, but I was wondering if there was another way).
Ah, and this doesn’t have to handle negative numbers. Solely non-negative numbers.
I’m attempting to create a variant “MyInt” class that can handle a wider range of values using a dynamic array. Any tips would be appreciated! Thanks!
LihO
41k11 gold badges99 silver badges166 bronze badges
asked Mar 26, 2014 at 0:13
5
Not necessarily the most efficient, but one of the shortest and most readable using C++:
std::to_string(num).length()
answered Feb 9, 2016 at 10:42
RiotRiot
15.5k4 gold badges59 silver badges66 bronze badges
1
The number of digits of an integer n in any base is trivially obtained by dividing until you’re done:
unsigned int number_of_digits = 0;
do {
++number_of_digits;
n /= base;
} while (n);
answered Mar 26, 2014 at 0:17
Kerrek SBKerrek SB
461k92 gold badges869 silver badges1075 bronze badges
3
There is a much better way to do it
#include<cmath>
...
int size = trunc(log10(num)) + 1
....
works for int and decimal
answered Aug 4, 2017 at 16:02
kunzkunz
1,0351 gold badge11 silver badges27 bronze badges
3
If you can use C libraries then one method would be to use sprintf, e.g.
#include <cstdio>
char s[32];
int len = sprintf(s, "%d", i);
answered Mar 26, 2014 at 0:16
Paul RPaul R
208k35 gold badges386 silver badges555 bronze badges
2
“I mean the number of digits in an integer, i.e. “123” has a length of 3″
int i = 123;
// the "length" of 0 is 1:
int len = 1;
// and for numbers greater than 0:
if (i > 0) {
// we count how many times it can be divided by 10:
// (how many times we can cut off the last digit until we end up with 0)
for (len = 0; i > 0; len++) {
i = i / 10;
}
}
// and that's our "length":
std::cout << len;
outputs 3
answered Mar 26, 2014 at 0:18
LihOLihO
41k11 gold badges99 silver badges166 bronze badges
0
Closed formula for the longest int (I used int here, but works for any signed integral type):
1 + (int) ceil((8*sizeof(int)-1) * log10(2))
Explanation:
sizeof(int) // number bytes in int
8*sizeof(int) // number of binary digits (bits)
8*sizeof(int)-1 // discount one bit for the negatives
(8*sizeof(int)-1) * log10(2) // convert to decimal, because:
// 1 bit == log10(2) decimal digits
(int) ceil((8*sizeof(int)-1) * log10(2)) // round up to whole digits
1 + (int) ceil((8*sizeof(int)-1) * log10(2)) // make room for the minus sign
For an int type of 4 bytes, the result is 11. An example of 4 bytes int with 11 decimal digits is: “-2147483648”.
If you want the number of decimal digits of some int value, you can use the following function:
unsigned base10_size(int value)
{
if(value == 0) {
return 1u;
}
unsigned ret;
double dval;
if(value > 0) {
ret = 0;
dval = value;
} else {
// Make room for the minus sign, and proceed as if positive.
ret = 1;
dval = -double(value);
}
ret += ceil(log10(dval+1.0));
return ret;
}
I tested this function for the whole range of int in g++ 9.3.0 for x86-64.
answered May 18, 2015 at 15:20
lvellalvella
12.5k11 gold badges52 silver badges106 bronze badges
3
int intLength(int i) {
int l=0;
for(;i;i/=10) l++;
return l==0 ? 1 : l;
}
Here’s a tiny efficient one
answered Dec 8, 2015 at 11:50
NaheelNaheel
4873 silver badges13 bronze badges
1
Being a computer nerd and not a maths nerd I’d do:
char buffer[64];
int len = sprintf(buffer, "%d", theNum);
answered Mar 26, 2014 at 0:17
John3136John3136
28.7k4 gold badges49 silver badges68 bronze badges
1
Would this be an efficient approach? Converting to a string and finding the length property?
int num = 123
string strNum = to_string(num); // 123 becomes "123"
int length = strNum.length(); // length = 3
char array[3]; // or whatever you want to do with the length
answered Apr 10, 2015 at 20:18
Aris94Aris94
712 silver badges8 bronze badges
1
How about (works also for 0 and negatives):
int digits( int x ) {
return ( (bool) x * (int) log10( abs( x ) ) + 1 );
}
answered Dec 10, 2017 at 8:53
Best way is to find using log, it works always
int len = ceil(log10(num))+1;
answered May 13, 2018 at 6:16
tsukyonomi06tsukyonomi06
4541 gold badge5 silver badges15 bronze badges
2
Code for finding Length of int and decimal number:
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int len,num;
cin >> num;
len = log10(num) + 1;
cout << len << endl;
return 0;
}
//sample input output
/*45566
5
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 3.292 s
Press any key to continue.
*/
answered Apr 7, 2018 at 5:22
Tanim_113Tanim_113
3111 gold badge3 silver badges11 bronze badges
There are no inbuilt functions in C/C++ nor in STL for finding length of integer but there are few ways by which it can found
Here is a sample C++ code to find the length of an integer, it can be written in a function for reuse.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
long long int n;
cin>>n;
unsigned long int integer_length = 0;
while(n>0)
{
integer_length++;
n = n/10;
}
cout<<integer_length<<endl;
return 0;
}
Here is another way, convert the integer to string and find the length, it accomplishes same with a single line:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
long long int n;
cin>>n;
unsigned long int integer_length = 0;
// convert to string
integer_length = to_string(n).length();
cout<<integer_length<<endl;
return 0;
}
Note: Do include the cstring header file
answered Mar 2, 2021 at 7:20
The easiest way to use without any libraries in c++ is
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num, length = 0;
cin >> num;
while(num){
num /= 10;
length++;
}
cout << length;
}
answered Sep 24, 2021 at 10:35
1
You can also use this function:
int countlength(int number)
{
static int count = 0;
if (number > 0)
{
count++;
number /= 10;
countlength(number);
}
return count;
}
answered Sep 20, 2022 at 11:44
1
#include <math.h>
int intLen(int num)
{
if (num == 0 || num == 1)
return 1;
else if(num < 0)
return ceil(log10(num * -1))+1;
else
return ceil(log10(num));
}
answered Feb 21 at 13:59
RefaelRefael
6,5839 gold badges35 silver badges54 bronze badges
1
Most efficient code to find length of a number.. counts zeros as well, note “n” is the number to be given.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,len= 0;
cin>>n;
while(n!=0)
{
len++;
n=n/10;
}
cout<<len<<endl;
return 0;
}
answered Sep 26, 2019 at 12:00
2
Let us assume I have declared the variable ‘i’ of certain datatype (might be int, char, float or double) …
NOTE: Simply consider that ‘i’ is declared and dont bother if it is an int or char or float or double datatype. Since I want a generic solution I am simply mentioning that variable ‘i’ can be of any one of the datatypes namely int, char, float or double.
Now can I find the size of the variable ‘i’ without sizeof operator?
Simson
3,2982 gold badges23 silver badges38 bronze badges
asked Sep 8, 2009 at 11:10
codingfreakcodingfreak
4,44711 gold badges47 silver badges60 bronze badges
5
You can use the following macro, taken from here:
#define sizeof_var( var ) ((size_t)(&(var)+1)-(size_t)(&(var)))
The idea is to use pointer arithmetic ((&(var)+1)) to determine the offset of the variable, and then subtract the original address of the variable, yielding its size. For example, if you have an int16_t i variable located at 0x0002, you would be subtracting 0x0002 from 0x0006, thereby obtaining 0x4 or 4 bytes.
However, I don’t really see a valid reason not to use sizeof, but I’m sure you must have one.
answered Sep 8, 2009 at 11:13
João SilvaJoão Silva
88.8k29 gold badges150 silver badges158 bronze badges
9
It’s been ages since I wrote any C code and I was never good at it, but this looks about right:
int i = 1;
size_t size = (char*)(&i+1)-(char*)(&i);
printf("%zin", size);
I’m sure someone can tell me plenty of reasons why this is wrong, but it prints a reasonable value for me.
answered Sep 8, 2009 at 11:16
Joachim SauerJoachim Sauer
301k57 gold badges553 silver badges612 bronze badges
14
This works..
int main() {
int a; //try changing this to char/double/float etc each time//
char *p1, *p2;
p1 = &a;
p2 = (&a) + 1;
printf("size of variable is:%dn", p2 - p1);
}
soktinpk
3,7482 gold badges21 silver badges33 bronze badges
answered Oct 21, 2014 at 2:06
2
int *a, *b,c,d;/* one must remove the declaration of c from here*/
int c=10;
a=&c;
b=a;
a++;
d=(int)a-(int)b;
printf("size is %d",d);
answered Apr 6, 2011 at 16:51
2
I hope that below code would solve your problem in c++ without using sizeof() operator
for any variables like (int, char, float, double, char, short and many more…)
here I take integer,
int a;
then
show it as byte addressable output,
cout<<(char *)(&a + 1) - (char *)(&a);
answered Jan 22, 2020 at 15:13
Ankit SinghAnkit Singh
3543 silver badges5 bronze badges
This should work.
#define xsizeof(x) (char *)(&x+1) - (char *)&x
answered May 16, 2021 at 17:10
Vijay S BVijay S B
1,2411 gold badge12 silver badges24 bronze badges
Try this,
#define sizeof_type( type ) ((size_t)((type*)1000 + 1 )-(size_t)((type*)1000))
For the following user-defined datatype,
struct x
{
char c;
int i;
};
sizeof_type(x) = 8
(size_t)((x*)1000 + 1 ) = 1008
(size_t)((x*)1000) = 1000
answered Nov 12, 2010 at 7:38
joshjosh
13.6k12 gold badges49 silver badges58 bronze badges
This should give you the size of your variable
#define mySizeof(type) ((uint)((type *)0+1))
Dan Oberlam
2,4259 gold badges36 silver badges54 bronze badges
answered Jun 12, 2014 at 0:51
1
Program to find Size of the variable without using sizeof operator
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int *p,*q;
int no;
p=&no;
printf("Address at p=%un",p);
q=((&no)+1);
printf("Address at q=%un",q);
printf("Size of int 'no': %d Bytesn",(int)q-(int)p);
char *cp,*cq;
char ch;
cp=&ch;
printf("nAddress at cp=%un",cp);
cq=cp+1;
printf("Address at cq=%un",cq);
printf("Size of Char=%u Byten",(int)cq-(int)cp);
float *fp,*fq;
float f;
fp=&f;
printf("nAddress at fp=%un",fp);
fq=fp+1;
printf("Address at fq=%un",fq);
printf("Size of Float=%u Bytesn",(int)fq-(int)fp);
return 0;
}
Jakuje
24.3k12 gold badges65 silver badges74 bronze badges
answered Dec 15, 2015 at 19:08
Debashis SahooDebashis Sahoo
5,2084 gold badges36 silver badges41 bronze badges
#define GET_SIZE(myvar) ((char)( ((char*)(&myvar+1) )- ((char*)&myvar) ))
EsmaeelE
2,2316 gold badges22 silver badges31 bronze badges
answered Sep 21, 2022 at 12:55
1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
struct size1
{
int a;
char b;
float c;
};
void main()
{
struct size1 *sptr=0; //declared one pointer to struct and initialise it to zero//
sptr++;
printf("size:%dn",*sptr);
getch();
}
answered Sep 30, 2011 at 18:28
Below statement will give generic solution:
printf("%lin", (void *)(&i + 1) - (void *)(&i));
i is a variable name, which can be any data type (char, short, int, float, double, struct).
JJJ
32.8k20 gold badges89 silver badges102 bronze badges
answered Jul 20, 2016 at 8:53
1
|
n971030 188 / 120 / 4 Регистрация: 23.01.2010 Сообщений: 1,320 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
Как узнать длину строки?08.02.2012, 22:25. Показов 104029. Ответов 7 Метки нет (Все метки)
Как узнать длинну строки
выше код дает сбой, кажеться он поределят поток а не количество сиволов в переменной xc
0 |
|
Programming Эксперт 94731 / 64177 / 26122 Регистрация: 12.04.2006 Сообщений: 116,782 |
08.02.2012, 22:25 |
|
Ответы с готовыми решениями:
Как узнать длину строки в байтах? using (FileStream fs = File.Create(fileName)) Как узнать длину строки в динамическом двухмерном массиве? Узнать длину строки двумерного массива? int arr = {{1,2,3}, 7 |
|
I2um1 Злой няш 2136 / 1505 / 565 Регистрация: 05.04.2010 Сообщений: 2,881 |
||||
|
08.02.2012, 22:28 |
2 |
|||
|
У меня код выше дает ошибку компиляции.
1 |
|
n971030 188 / 120 / 4 Регистрация: 23.01.2010 Сообщений: 1,320 |
||||
|
08.02.2012, 22:33 [ТС] |
3 |
|||
|
У меня код выше дает ошибку компиляции.
int b = value.Length;
0 |
|
Злой няш 2136 / 1505 / 565 Регистрация: 05.04.2010 Сообщений: 2,881 |
|
|
08.02.2012, 22:38 |
4 |
|
как определить кол-во символов в строке типа стринги Этот код это и делает.
1 |
|
Сtrl 144 / 134 / 8 Регистрация: 19.07.2011 Сообщений: 184 |
||||
|
08.02.2012, 22:39 |
5 |
|||
5 |
|
188 / 120 / 4 Регистрация: 23.01.2010 Сообщений: 1,320 |
|
|
08.02.2012, 22:41 [ТС] |
6 |
|
Этот код это и делает. СОРИ ЗА ТУПОСТЬ СРАЗУ ПРОСТО НЕ СРАБОТАЛО А ВЕДЬ ЗНАЛ!! НО ВСЕРАВНО СПАСИБО
1 |
|
EdwardTeach 0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 31.01.2017 Сообщений: 8 |
||||
|
13.11.2018, 14:08 |
7 |
|||
0 |
|
maxim0192 0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 10.04.2016 Сообщений: 14 Записей в блоге: 3 |
||||
|
24.12.2021, 20:17 |
8 |
|||
|
Мой метод определения длины строки.
0 |
Содержание
- 1. Какие характерные особенности типа string в языке C#?
- 2. Способы создания экземпляра s типа string
- 3. Как в переменную типа string занести значение строки? Операция присваивания =
- 4. Как определить, равны ли две строки типа string между собой? Операция сравнения ==
- 5. Как сравнить две строки типа string в лексикографическом порядке? Метод CompareTo()
- 6. Как соединить две строки типа string? Метод Concat(), операция +
- 7.Как скопировать одну строку типа string в другую? Метод Copy(), оператор присваивания =
- 8. Вставка подстроки начиная из заданного индекса. Метод Insert()
- 9. Поиск и получение индекса первого вхождения подстроки в данную строку. Метод IndexOf()
- 10. Поиск и получение индекса последнего вхождения подстроки в данную строку функцией LastIndexOf()
- 11. Как определить длину строки типа string? Свойство Length
- 12. Создание строки заданной ширины. Методы PadLeft() и PadRight()
- 13. Удаление заданного количества символов из строки. Метод Remove()
- 14. Замена символов в строке. Метод Replace()
- 15. Как в строке выделить подстроку. Метод Substring()
- 16. Преобразование числовой строки типа string в целое число. Метод Parse()
- 17. Преобразование целого числа в строку. Метод ToString()
- 18. Преобразование строки string в число с плавающей запятой (вещественное число)
- 19. Преобразование числа с плавающей запятой в string
- 20. Перевод значения переменной логического типа bool в строку string
- 21. Постоянство строк. Как в строке типа string заменить символ в заданной позиции: s[index] = c
Поиск на других ресурсах:
1. Какие характерные особенности типа string в языке C#?
В языке C# встроенный тип данных string поддерживает символьные строки в кодировке Unicode. Для строк типа string можно выделить следующие особенности:
- любая переменная типа string представляет собой объект класса System.String;
- тип string относится к ссылочным типам а не типам-значениям;
- строки типа string размещаются в «куче» (heap);
- к строкам типа string можно применять разнообразные методы, свойства и операции;
- строку типа string можно создавать с использованием оператора new и без использования этого оператора путем присваивания =;
- содержимое объекта типа string изменить нельзя.
Пример строки-литерала типа string:
"This is a text"
⇑
2. Способы создания экземпляра типа string
Как известно тип string есть псевдонимом класса System.String, который имеет несколько конструкторов. С помощью этих конструкторов можно создавать экземпляры класса string. Ниже приводится пример программы, в которой продемонстрировано создание экземпляров типа string разными способами.
using System; namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // Способы создания экземпляра типа string // 1. Создание и инициализация строки при объявлении string s1 = "Hello"; Console.WriteLine("s1 = {0}", s1); // 2. Создание строки из массива типа char[] char[] ArrayChar = { 'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o' }; string s2 = new string(ArrayChar); Console.WriteLine("s2 = {0}", s2); string s3 = new string(ArrayChar, 2, 3); // получить часть строки Console.WriteLine("s3 = {0}", s3); // 3. Создание строки с помощью перегруженного оператора присваивания = string s4; s4 = "Hello"; Console.WriteLine("s4 = {0}", s4); // 4. Создание строки из одного символа string s5 = new string('+', 10); // символ '+' - 10 раз Console.WriteLine("s5 = {0}", s5); // 5. Буквальные строки (verbatim strings) string s6; s6 = @"C:Programsabc.txt"; // это буквальная строка, перед строкой размещен @ Console.WriteLine("s6 = {0}", s6); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
Результат выполнения программы
s1 = Hello s2 = Hello s3 = llo s4 = Hello s5 = ++++++++++ s6 = C:Programsabc.txt
⇑
3. Как в переменную типа string занести значение строки? Операция присваивания =
Для этого нужно использовать оператор присваивания ‘=‘.
Вариант 1. Присваивание после описания.
string s; // описание переменной s = "This is a text"; // присваивание значения текста
Вариант 2. Присваивание во время описания (начальная инициализация).
string s = "This is a text"; // начальная инициализация
Вариант 3. Использование метода Copy().
s = string.Copy("This is a text"); // s = "This is a text"
⇑
4. Как определить, равны ли две строки типа string между собой? Операция сравнения ==
Две строки можно сравнивать обычным оператором сравнения «==«.
Фрагмент кода, который определяет равенство (неравенство) двух строк:
string s1 = "Hello!"; string s2 = "Hello!"; bool f_equal; if (s1 == s2) f_equal = true; else f_equal = false;
⇑
5. Как сравнить две строки типа string в лексикографическом порядке? Метод CompareTo()
В этом случае можно использовать метод CompareTo(). Метод возвращает -1, 0 или 1.
В приведенном примере видно результат работы метода.
string s1 = "abcd"; string s2 = "abcde"; int res; res = s1.CompareTo(s2); // res = -1, (s1<s2) res = s2.CompareTo(s1); // res = 1, (s2>s1) s2 = s1; // строки равны res = s1.CompareTo(s2); // res = 0, (s1==s2) res = s2.CompareTo(s1); // res = 0
⇑
6. Как соединить две строки типа string? Метод Concat(), операция +
Способ №1 — функция Concat().
string s1 = "Hello "; string s2 = "world!"; string s3; s3 = string.Concat(s1, s2); // s3 = "Hello world!"
Способ № 2 — использование оператора «+».
string s1 = "Hello "; string s2 = "world!"; string s3; s3 = s1 + s2; // s3 = "Hello world!"
⇑
7. Как скопировать одну строку типа string в другую? Метод Copy(), оператор присваивания =
Способ № 1 — оператор присваивания.
string s1 = "My string"; string s2; s2 = s1; // s2 = "My string"
Способ №2 — метод Copy().
string s1 = "My string"; string s2; s2 = string.Copy(s1); // s2 = "My string"
⇑
8. Вставка подстроки начиная из заданного индекса. Метод Insert()
Для вставки подстроки используется функция Insert(). Функция принимает два параметра. Первый параметр – позиция индекса в строке, из которой делается вставка (начинается с 0). Второй параметр – текст самой строки.
string s1 = "ABEF"; string s2; s2 = s1.Insert(2, "CD"); // s2 = "ABCDEF" s1 = "123"; s2 = s1.Insert(0, "555"); // s2 = "555123" // Ошибка! // Заданный аргумент находится за пределами допустимых значений. // s2 = s1.Insert(20, "33");
Если задать неверный индекс за пределами диапазона, то будет сгенерирована исключительная ситуация.
⇑
9. Поиск и получение индекса первого вхождения подстроки в данную строку. Метод IndexOf()
Эта операция реализуется функцией IndexOf(). Если найдена подстрока в строке, то функция возвращает позицию первого вхождения. В другом случае функция возвращает -1.
Функция имеет перегруженные варианты реализации.
string s = "Hello world!"; int index; index = s.IndexOf("wor"); // index = 6 index = s.IndexOf("abc"); // index = -1 // другой вариант функции IndexOf() index = s.IndexOf("wor", 7); // index = -1 - поиск из позиции 7 index = s.IndexOf("wor", 0); // index = 6 - поиск из позиции 0 // поиск идет от заданного индекса (3) // и проверяется заданное количество символов (5) index = s.IndexOf("wo", 3, 5); // index = 6
⇑
10. Поиск и получение индекса последнего вхождения подстроки в данную строку функцией LastIndexOf().
Функция имеет несколько перегруженных реализаций. Нумерация индекса последнего вхождения начинается с 0.
string s = "bestprog.net"; int index; index = s.LastIndexOf("prog"); // index = 4
⇑
11. Как определить длину строки типа string? Свойство Length
Для определения длины строки (количество символов) типа string используется свойство Length.
string s = "bestprog.net"; int len; len = s.Length; // len = 12 s = ""; // len = 0
⇑
12. Создание строки заданной ширины. Функции PadLeft() и PadRight()
Функции PadLeft() и PadRight() используются для создания форматированной строки, в которой позиции справа или слева заполняются пробелами.
string s1 = "abc"; string s2; s2 = s1.PadLeft(5); // s2 = " abc" s2 = s1.PadLeft(2); // s2 = "abc" s2 = s1.PadLeft(9); // s2 = " abc" // ошибка "Non-negative number required." // "Нужно неотъемлемое число // s2 = s1.PadLeft(-2); s2 = s1.PadRight(2); // s2 = "abc" s2 = s1.PadRight(8); // s2 = "abc "
⇑
13. Удаление заданного количества символов из строки. Функция Remove()
Функция Remove() имеет две реализации. В первой реализации функция имеет два параметра. Во второй – один параметр.
Пример 1. Реализация функции Remove() с двумя параметрами.
string s1 = "0123456789"; string s2; s2 = s1.Remove(3, 2); // s2 = "01256789"
В данном примере функция Remove() получает два параметра. Первый параметр – позиция, из которой делается удаление. Второй параметр – количество удаленных символов.
Пример 2. Реализация с одним параметром.
string s1 = "0123456789"; string s2; s2 = s1.Remove(4); // s2 = "0123"
В этом примере функция получает один параметр. Этот параметр определяет позицию из которой будет осуществлено удаление символов до конца строки.
Если указать
s2 = s1.Remove(0);
то будет удалена вся строка.
Пример 3. Если нужно удалить последний символ в строке, то нужно написать такой код.
string s1 = "This is a text!"; string s2; int len; len = s1.Length; s2 = s1.Remove(len-1); // s2 = "This is a text"
⇑
14. Замена символов в строке. Функция Replace()
Функция Replace() имеет два варианта реализации.
Первый вариант оперирует строками типа string. Второй вариант оперирует типом char.
Пример 1. Использование функции Replace() для замены одной строки на другую.
string s1 = "0123456789"; string s2; s2 = s1.Replace("012", "ABC"); // s2 = "ABC3456789"
Пример 2. Использование функции Replace() для замены символа ‘0’ на символ ‘A’.
string s1 = "0123456789"; string s2; s2 = s1.Replace('0', 'A'); // s2 = "A123456789"
⇑
15. Как в строке выделить подстроку. Функция Substring()
Функция Substring() имеет две реализации.
Вариант 1. Выделение подстроки с заданной позиции до конца строки.
string s1 = "Automobile"; string s2; s2 = s1.Substring(4); // s2 = "mobile
Вариант 2. Выделение подстроки с заданной позиции (параметр 1) в заданном количестве символов (параметр 2).
string s1 = "Automobile"; string s2; s2 = s1.Substring(0, 4); // s2 = "Auto"
⇑
16. Преобразование числовой строки типа string в целое число. Функция Parse()
Функция Parse() разрешает переводить строку, которая состоит из цифр, в целое число. Такая функция полезна если нужно получить число, которое было введено из клавиатуры и получено в виде строки. Например, ввод из элемента управления типа TextBox.
// string => int string s = "389"; int i; i = int.Parse(s); i = int.Parse("-29"); // i = -29
⇑
17. Преобразование целого числа в строку. Функция ToString()
Функция ToString() переводит целое число в его строчное представление. Например, такая функция полезная, если нужно вывести целое число на форму в элементе управления Label.
// int => string string s; int i; i = 230; s = i.ToString(); // s = "230"
⇑
18. Преобразование строки string в число с плавающей запятой (вещественное число)
При преобразовании строки в соответствующее вещественное число, важно учитывать кодировку символов.
Если у вас установлена операционная система с кирилличной кодировкой и настроены соответствующие региональные стандарты, тогда символ ‘.’ может быть заменен на символ ‘,’. Это связано с тем, что в странах, которые используют кириллицу как разделитель между целой и дробной частями, есть символ ‘,’ (запятая). А в англоязычных странах разделителем целой и дробовой частей есть символ ‘.’ (точка).
Символ-разделитель целой и дробной частей можно изменить в региональных настройках Windows.
Поэтому, в ОС Windows с кириллическим кодированием по умолчанию, следующий код вызовет исключительную ситуацию FormatException с сообщением: «Input string was not in a correct format» (Исходная строка имеет неверный формат).
double x; string s; s = "9.83"; // генерируется исключительная ситуация FormatException // с сообщением "Input string was not in a correct format." x = double.Parse(s);
Ниже приведен правильный вариант для ОС с кирилличной кодировкой:
// string => double double x; string s; s = "9,83"; x = double.Parse(s);
⇑
19. Преобразование числа с плавающей запятой в string.
// double => string double x; string s; x = -39.038; s = x.ToString(); // s = "-39,038"
⇑
20. Перевод значения переменной логического типа bool в строку string
// string => bool bool b; string s; s = "true"; b = bool.Parse(s); // b = True
Если ввести неправильное значение в строку s, то генерируется исключительная ситуация с сообщением:
"String was not recognized as a valid Boolean"
⇑
21. Постоянство строк. Как в строке типа string заменить символ в заданной позиции: s[index] = c
В языке C# тип string имеет одну особенность. Доступ к отдельному символу строки осуществляется в режиме чтения. Непосредственно изменить значение символа в строке не получится. Это означает, что строки есть постоянными (константными).
Нижеследующий фрагмент кода
string s = "Hello world!"; s[6] = 'W'; // ошибка!!! - символ можно только прочитать char c; c = s[6]; // c = 'w' - так работает
в строке
s[6] = 'W';
вызовет ошибку компилятора
Property or indexer 'string.this[int]' cannot be assigned to -- it is read only
Значит, значение символа в заданной позиции строки типа string можно только прочитать.
Чтобы решить эту задачу можно использовать (как пример) один из предложенных способов.
Способ 1. Использование методов Substring() и String(). При использовании этого способа нужно выполнять проверку значения индекса на корректность. Если значение индекса выходит за пределы размерности строки, то возникнет исключительная ситуация.
// Как в строке заменить символ в заданной позиции: s[index]=c // Способ 1. Использование методов Substring(), ToString(). // Входные данные: string s = "Hello world!"; // исходная строка int index = 0; // индекс в строке, где нужно сделать замену (начинается с 0) char c = '+'; // символ замены // Проверка значения index на корректность if ((index >= 0) && (index < s.Length)) s = s.Substring(0, index) + c.ToString() + s.Substring(index + 1);
Способ 2. Использование оператора цикла.
// Способ 2. Использование цикла и дополнительной строки. // Если значение index некорректно, то исходная строка не изменяется // Исходные данные: string s = "Hello world!"; // исходная строка int index = 5; // индекс замены (нумеруется с 0) char c = '+'; // символ замены string s2 = ""; // дополнительная строка for (int i = 0; i < s.Length; i++) if (i != index) s2 += s[i]; else s2 += c; s = s2;
Способ 3. Использование методов Remove() и Insert(). В этом случае также нужно проверять индекс замены на корректность.
// Способ 3. Методы Insert(), Remove() // Исходные данные: string s = "Hello world!"; // исходная строка int index = 5; // индекс в строке, где нужно сделать замену (нумеруется с 0) char c = '+'; // символ замены // Здесь нужно делать проверку на корректность значения pos, // если index некорректен, то сгенерируется исключение if ((index >= 0) && (index < s.Length)) { s = s.Remove(index, 1); s = s.Insert(index, c.ToString()); }

 Как узнать длину строки
Как узнать длину строки
