Given an array of n integers. The task is to print the duplicates in the given array. If there are no duplicates then print -1.
Examples:
Input: {2, 10,10, 100, 2, 10, 11,2,11,2}
Output: 2 10 11
Input: {5, 40, 1, 40, 100000, 1, 5, 1}
Output: 5 40 1
Note: The duplicate elements can be printed in any order.
Simple Approach: The idea is to use nested loop and for each element check if the element is present in the array more than once or not. If present, then store it in a Hash-map. Otherwise, continue checking other elements.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void findDuplicates(int arr[], int len)
{
bool ifPresent = false;
vector<int> al;
for(int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < len; j++)
{
if (arr[i] == arr[j])
{
auto it = std::find(al.begin(),
al.end(), arr[i]);
if (it != al.end())
{
break;
}
else
{
al.push_back(arr[i]);
ifPresent = true;
}
}
}
}
if (ifPresent == true)
{
cout << "[" << al[0] << ", ";
for(int i = 1; i < al.size() - 1; i++)
{
cout << al[i] << ", ";
}
cout << al[al.size() - 1] << "]";
}
else
{
cout << "No duplicates present in arrays";
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 40, 12,
5, 6, 5, 12, 11 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
findDuplicates(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class GFG {
static void findDuplicates(
int arr[], int len)
{
boolean ifPresent = false;
ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
if (arr[i] == arr[j]) {
if (al.contains(arr[i])) {
break;
}
else {
al.add(arr[i]);
ifPresent = true;
}
}
}
}
if (ifPresent == true) {
System.out.print(al + " ");
}
else {
System.out.print(
"No duplicates present in arrays");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 40, 12, 5, 6, 5, 12, 11 };
int n = arr.length;
findDuplicates(arr, n);
}
}
Python3
def findDuplicates(arr, Len):
ifPresent = False
a1 = []
for i in range(Len - 1):
for j in range(i + 1, Len):
if (arr[i] == arr[j]):
if arr[i] in a1:
break
else:
a1.append(arr[i])
ifPresent = True
if (ifPresent):
print(a1, end = " ")
else:
print("No duplicates present in arrays")
arr = [ 12, 11, 40, 12, 5, 6, 5, 12, 11 ]
n = len(arr)
findDuplicates(arr, n)
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static void findDuplicates(int[] arr, int len)
{
bool ifPresent = false;
List<int> al = new List<int>();
for(int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < len; j++)
{
if (arr[i] == arr[j])
{
if (al.Contains(arr[i]))
{
break;
}
else
{
al.Add(arr[i]);
ifPresent = true;
}
}
}
}
if (ifPresent == true)
{
Console.Write("[" + al[0] + ", ");
for(int i = 1; i < al.Count - 1; i++)
{
Console.Write(al[i] + ", ");
}
Console.Write(al[al.Count - 1] + "]");
}
else
{
Console.Write("No duplicates present in arrays");
}
}
static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 12, 11, 40, 12,
5, 6, 5, 12, 11 };
int n = arr.Length;
findDuplicates(arr, n);
}
}
Javascript
<script>
function findDuplicates(arr, len) {
let ifPresent = false;
let al = new Array();
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
if (arr[i] == arr[j]) {
if (al.includes(arr[i])) {
break;
}
else {
al.push(arr[i]);
ifPresent = true;
}
}
}
}
if (ifPresent == true) {
document.write(`[${al}]`);
}
else {
document.write("No duplicates present in arrays");
}
}
let arr = [12, 11, 40, 12, 5, 6, 5, 12, 11];
let n = arr.length;
findDuplicates(arr, n);
</script>
Time Complexity: O(N2)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Efficient Approach: Use unordered_map for hashing. Count frequency of occurrence of each element and the elements with frequency more than 1 is printed. unordered_map is used as range of integers is not known. For Python, Use Dictionary to store number as key and it’s frequency as value. Dictionary can be used as range of integers is not known.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
usingnamespacestd;
voidprintDuplicates(intarr[],intn)
{
unordered_map<int,int> freq;
for(inti=0; i<n; i++)
freq[arr[i]]++;
booldup =false;
unordered_map<int,int>:: iterator itr;
for(itr=freq.begin(); itr!=freq.end(); itr++)
{
if(itr->second > 1)
{
cout << itr->first <<" ";
dup =true;
}
}
if(dup ==false)
cout <<"-1";
}
intmain()
{
intarr[] = {12, 11, 40, 12, 5, 6, 5, 12, 11};
intn =sizeof(arr) /sizeof(arr[0]);
printDuplicates(arr, n);
return0;
}Java
importjava.util.HashMap;
importjava.util.Map;
importjava.util.Map.Entry;
publicclassFindDuplicatedInArray
{
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args)
{
intarr[] = {12,11,40,12,5,6,5,12,11};
intn = arr.length;
printDuplicates(arr, n);
}
privatestaticvoidprintDuplicates(int[] arr,intn)
{
Map<Integer,Integer> map =newHashMap<>();
intcount =0;
booleandup =false;
for(inti =0; i < n; i++){
if(map.containsKey(arr[i])){
count = map.get(arr[i]);
map.put(arr[i], count +1);
}
else{
map.put(arr[i],1);
}
}
for(Entry<Integer,Integer> entry : map.entrySet())
{
if(entry.getValue() >1){
System.out.print(entry.getKey()+" ");
dup =true;
}
}
if(!dup){
System.out.println("-1");
}
}
}Python3
defprintDuplicates(arr):
dict={}
foreleinarr:
try:
dict[ele]+=1
except:
dict[ele]=1
foritemindict:
if(dict[item] >1):
(item, end=" ")
("n")
if__name__=="__main__":
list=[12,11,40,12,
5,6,5,12,11]
printDuplicates(list)C#
usingSystem;
usingSystem.Collections.Generic;
classGFG
{
staticvoidprintDuplicates(int[] arr,intn)
{
Dictionary<int,
int> map =newDictionary<int,
int>();
intcount = 0;
booldup =false;
for(inti = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(map.ContainsKey(arr[i]))
{
count = map[arr[i]];
map[arr[i]]++;
}
else
map.Add(arr[i], 1);
}
foreach(KeyValuePair<int,
int> entryinmap)
{
if(entry.Value > 1)
Console.Write(entry.Key +" ");
dup =true;
}
if(!dup)
Console.WriteLine("-1");
}
publicstaticvoidMain(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 12, 11, 40, 12,
5, 6, 5, 12, 11 };
intn = arr.Length;
printDuplicates(arr, n);
}
}Javascript
<script>
functionprintDuplicates(arr, n)
{
varfreq =newMap();
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(freq.has(arr[i]))
{
freq.set(arr[i], freq.get(arr[i]) + 1);
}
else
{
freq.set(arr[i], 1);
}
}
vardup =false;
for(let [key, value] of freq)
{
if(value > 1)
{
document.write(key +" ");
dup =true;
}
}
if(dup ==false)
document.write("-1");
}
vararr = [ 12, 11, 40, 12,
5, 6, 5, 12, 11 ];
varn = arr.length;
printDuplicates(arr, n);
</script>
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Another Efficient Approach(Space optimization):
- First we will sort the array for binary search function.
- we will find index at which arr[i] occur first time lower_bound
- Then , we will find index at which arr[i] occur last time upper_bound
- Then check if diff=(last_index-first_index+1)>1
- If diff >1 means it occurs more than once and print
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void printDuplicates(int arr[], int n)
{
sort(arr,arr+n);
cout<<"[";
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ;i++)
{
int first_index = lower_bound(arr,arr+n,arr[i])- arr;
int last_index = upper_bound(arr,arr+n,arr[i])- arr-1;
int occur_time = last_index-first_index+1;
if(occur_time > 1 )
{ i=last_index;
cout<<arr[i]<<", "; }
} cout<<"]";
}
int main()
{ int arr[] = {12, 11, 40, 12, 5, 6, 5, 12, 11};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printDuplicates(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Python3
def printDuplicates(arr, n):
arr.sort()
print("[", end="")
i = 0
while i < n:
first_index = arr.index(arr[i])
last_index = n - arr[::-1].index(arr[i]) - 1
occur_time = last_index - first_index + 1
if occur_time > 1:
i = last_index
print(arr[i], end=", ")
i += 1
print("]")
arr = [12, 11, 40, 12, 5, 6, 5, 12, 11]
n = len(arr)
printDuplicates(arr, n)
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static int lowerBound(int[] arr, int target)
{
int lo = 0, hi = arr.length - 1;
int ans = -1;
while (lo <= hi) {
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
if (arr[mid] >= target) {
ans = mid;
hi = mid - 1;
}
else {
lo = mid + 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
public static int upperBound(int[] arr, int target)
{
int lo = 0, hi = arr.length - 1;
int ans = -1;
while (lo <= hi) {
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
if (arr[mid] <= target) {
ans = mid;
lo = mid + 1;
}
else {
hi = mid - 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
static void printDuplicates(int[] arr, int n)
{
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int firstIndex = lowerBound(arr, arr[i]);
int lastIndex = upperBound(arr, arr[i]);
int occurTime = lastIndex - firstIndex
+ 1;
if (occurTime
> 1) {
i = lastIndex;
System.out.print(arr[i] + ", ");
}
}
System.out.println("]");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 12, 11, 40, 12, 5, 6, 5, 12, 11 };
int n = arr.length;
printDuplicates(arr, n);
}
}
Javascript
function printDuplicates(arr, n) {
arr.sort();
console.log("[");
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
let first_index = arr.indexOf(arr[i]);
let last_index = arr.lastIndexOf(arr[i]);
let occur_time = last_index - first_index + 1;
if (occur_time > 1) {
i = last_index;
console.log(arr[i] + ", ");
}
}
console.log("]");
}
let arr = [12, 11, 40, 12, 5, 6, 5, 12, 11];
let n = arr.length;
printDuplicates(arr, n);
C#
using System;
class MainClass {
static void printDuplicates(int[] arr, int n) {
Array.Sort(arr);
Console.Write("[");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int first_index = Array.IndexOf(arr, arr[i]);
int last_index = Array.LastIndexOf(arr, arr[i]);
int occur_time = last_index - first_index + 1;
if (occur_time > 1) {
i = last_index;
Console.Write(arr[i] + ", ");
}
}
Console.Write("]");
}
static void Main() {
int[] arr = {12, 11, 40, 12, 5, 6, 5, 12, 11};
int n = arr.Length;
printDuplicates(arr, n);
}
}
Time Complexity: O(n*log2n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Related Post :
Print All Distinct Elements of a given integer array
Find duplicates in O(n) time and O(1) extra space | Set 1
Duplicates in an array in O(n) and by using O(1) extra space | Set-2
Print all the duplicates in the input string
This article is contributed by Ayush Jauhari. If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using write.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Last Updated :
18 Apr, 2023
Like Article
Save Article
Дан массив с числами. Проверьте, есть ли в нём два одинаковых числа подряд.
Если есть – выведите ‘да’, а если нет – выведите ‘нет’
Моё решение такое:
var arr = [3, 1, 1, 12];
for (var i = 0; i > arr.length; i++) {
for (var j = i + 1; j > arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i] === arr[j]) {
alert('yes')
} else {
alert('no')
}
}Но ничего не выводит alert. В чём проблема?
![]()
Bharatha
5,2561 золотой знак18 серебряных знаков36 бронзовых знаков
задан 6 июн 2018 в 9:09
1
Проблема в том, что ты делаешь вывод для каждого числа в массиве. В случае нахождения подходящей пары надо прекращать проверку. А для неподходящих пар вообще ничего делать не надо.
function check(a) {
for (var q=1; q<a.length; ++q) {
if (a[q] === a[q-1]) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
console.log(check([3, 1, 1, 12]) ? "Да" : "Нет");ответ дан 6 июн 2018 в 9:26
Qwertiy♦Qwertiy
120k24 золотых знака121 серебряный знак291 бронзовый знак
[3, 1, 1, 12].reduce((a, b) => (typeof a === 'number' && typeof b === 'number' && a === b ? console.info('Yes') : null, b), null);ответ дан 6 июн 2018 в 9:15
3
Можно воспользоваться функцией Array.prototype.some
// Дословно:
// Существует ли элемент(не являющийся первым) равный предыдущему?
const hasSeqEq = arr => arr.some((el, i, arr) => i!=0 && el===arr[i-1]);
console.log(hasSeqEq([5, 1, 5, 2])); // false
console.log(hasSeqEq([5, 1, 5, 2, 2, 7])); // trueПреимущество some перед reduce заключается в том, что, если будет найдено совпадение, результат будет получен сразу же, не завершая прохода всего массива.
ES5:
// Дословно:
// Существует ли элемент(не являющийся первым) равный предыдущему?
function hasSeqEq(arr) {
return arr.some(function(el, i, arr) {
return i != 0 && el === arr[i - 1];
});
}
console.log(hasSeqEq([5, 1, 5, 2])); // false
console.log(hasSeqEq([5, 1, 5, 2, 2, 7])); // trueответ дан 6 июн 2018 в 9:32
![]()
vp_arthvp_arth
27.1k2 золотых знака45 серебряных знаков76 бронзовых знаков
11
function f(arr) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr.indexOf(arr[i]) !== arr.lastIndexOf(arr[i])) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 4, 8];
console.log(f(arr))
ответ дан 17 ноя 2020 в 18:47
KrovorgenKrovorgen
7684 серебряных знака16 бронзовых знаков
Проблема в том, что вы написали неправильное условие выхода из цикла.
i > arr.length – возвращает false на первой же проверке и цикл заканчивается не сделав ни одной итерации.
var arr = [3, 1, 1, 12];
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
for (var j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++){
if (arr[i] === arr[j]){
alert('yes')
} else {
alert('no');
}
}
}ответ дан 6 июн 2018 в 9:12
DarthDarth
13k2 золотых знака25 серебряных знаков56 бронзовых знаков
В этом посте мы обсудим, как найти все дубликаты в массиве в JavaScript.
1. Использование Array.prototype.indexOf() функция
Идея состоит в том, чтобы сравнить индекс всех элементов в массиве с индексом их первого появления. Если оба индекса не совпадают ни для одного элемента в массиве, можно сказать, что текущий элемент дублируется. Чтобы вернуть новый массив с дубликатами, используйте filter() метод.
В следующем примере кода показано, как реализовать это с помощью indexOf() метод:
|
const arr = [ 5, 3, 4, 2, 3, 7, 5, 6 ]; const findDuplicates = arr => arr.filter((item, index) => arr.indexOf(item) !== index) const duplicates = findDuplicates(arr); console.log(duplicates); /* результат: [ 3, 5 ] */ |
Скачать Выполнить код
Приведенное выше решение может привести к дублированию значений на выходе. Чтобы справиться с этим, вы можете преобразовать результат в Set, в котором хранятся уникальные значения.
|
function findDuplicates(arr) { const filtered = arr.filter((item, index) => arr.indexOf(item) !== index); return [...new Set(filtered)] } const arr = [ 5, 3, 4, 2, 3, 7, 5, 6 ]; const duplicates = findDuplicates(arr); console.log(duplicates); /* результат: [ 3, 5 ] */ |
Скачать Выполнить код
2. Использование Set.prototype.has() функция
Кроме того, для повышения производительности вы можете использовать ES6. Установить структуру данных для эффективной фильтрации массива.
Следующее решение находит и возвращает дубликаты, используя has() метод. Это работает, потому что каждое значение в наборе должно быть уникальным.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
function findDuplicates(arr) { const distinct = new Set(arr); // для повышения производительности const filtered = arr.filter(item => { // удаляем элемент из набора при первой же встрече if (distinct.has(item)) { distinct.delete(item); } // возвращаем элемент при последующих встречах else { return item; } }); return [...new Set(filtered)] } const arr = [ 5, 3, 4, 2, 3, 7, 5, 6 ]; const duplicates = findDuplicates(arr); console.log(duplicates); /* результат: [ 3, 5 ] */ |
Скачать Выполнить код
Это все о поиске всех дубликатов в массиве в JavaScript.
Спасибо за чтение.
Пожалуйста, используйте наш онлайн-компилятор размещать код в комментариях, используя C, C++, Java, Python, JavaScript, C#, PHP и многие другие популярные языки программирования.
Как мы? Порекомендуйте нас своим друзьям и помогите нам расти. Удачного кодирования 🙂
#статьи
- 23 янв 2023
-
0
Задача: проверить массив на дубликаты
Решаем задачи, которые дают программистам на собеседованиях в IT-компаниях. Сегодня ищем в массиве повторяющиеся элементы.
Иллюстрация: Polina Vari для Skillbox Media

Любитель научной фантастики и технологического прогресса. Хорошо сочетает в себе заумного технаря и утончённого гуманитария. Пишет про IT и радуется этому.

Условие. Дан массив целых чисел — nums. Необходимо написать функцию, которая возвращает true, если в этом массиве хотя бы одно число повторяется дважды. Если же все элементы уникальны, функция должна вернуть false.
Ввод: nums = [1,2,3,1] Вывод: true
Ввод: nums = [1,2,3,4] Вывод: false
Ввод: nums = [1,1,1,3,3,4,3,2,4,2] Вывод: true
Решить эту задачу самостоятельно и на разных языках программирования можно на LeetCode. Наше решение взято из телеграм-канала Сергея Cracking code interview.
Решение
При решении подобных задач важно выбрать подходящий тип данных. Здесь мы исходим из такой логики: «повторяется дважды» → значит, ищем дубликаты. Следовательно, выбираем множество (set).
Мы создадим пустое множество и будем обходить весь массив, просто проверяя, находится ли элемент во множестве:
- если он ещё не находится — добавляем его;
- если элемент уже там — значит, мы встретили повторяющийся элемент и просто возвращаем true.
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) { Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); for (int i : nums) { if (set.contains(i)) { return true; } else { set.add(i); } } return false; }
Результаты
Временная сложность: O(n) — так как в самом плохом случае мы проходимся по всему массиву.
Ёмкостная сложность: O(1) — нам нужно заранее определённое количество места в памяти.

Научитесь: Профессия Java-разработчик
Узнать больше
Иногда возникает необходимость найти дубликаты в массиве. В данной статье мы расскажем, как это сделать двумя способами.
Задача
Итак, у нас есть массив. Это может быть массив любых объектов или примитивов. Для примера возьмём массив строк:
String[] animals = {"cat", "dog", "cow", "sheep", "cat", "dog"};
Теперь попробуем найти дублирующиеся строки в этом массиве.
Поиск дубликатов перебором
Сначала объявим вспомогательную коллекцию для хранения дубликатов – HashSet:
Set<T> duplicates = new HashSet<>();
Каждый раз, находя дубликат в массиве, мы будет его класть в данный HashSet.
Далее мы будем проходить по элементам массива, используя два цикла. В первом цикле мы извлекаем элемент массива и поочерёдно сравниваем его с остальными элементами массива, используя второй цикл:
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
T e1 = a[i];
if (e1 == null) continue; // игнорируем null
// сравниваем каждый элемент со всеми остальными
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) {
if (i == j) continue; // не проверяем элемент с собой же
T e2 = a[j];
if (e1.equals(e2)) {
// дубликат найден, сохраним его
duplicates.add(e2);
}
}
}
И в конце возвратим найденные дубликаты:
return new ArrayList<>(duplicates);
Проверка
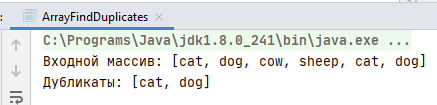
Проверим нашу программу:
String[] animals = {"cat", "dog", "cow", "sheep", "cat", "dog"};
System.out.println("Входной массив: " + Arrays.toString(animals));
System.out.println("Дубликаты: " + getDuplicatesWithIteration(animals));
Исходный код
package ru.javalessons.arrays;
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayFindDuplicates {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] animals = {"cat", "dog", "cow", "sheep", "cat", "dog"};
System.out.println("Входной массив: " + Arrays.toString(animals));
System.out.println("Дубликаты: " + getDuplicatesWithIteration(animals));
}
public static <T> List<T> getDuplicatesWithIteration(T[] a) {
Set<T> duplicates = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
T e1 = a[i];
if (e1 == null) continue; // игнорируем null
// сравниваем каждый элемент со всеми остальными
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) {
if (i == j) continue; // не проверяем элемент с собой же
T e2 = a[j];
if (e1.equals(e2)) {
// дубликат найден, сохраним его
duplicates.add(e2);
}
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(duplicates);
}
}
Заключение
На данном примере мы разобрали, как находить дубликаты в массиве. Это может быть массив любых объектов.
