Каноническое уравнение гиперболы по двум точкам
| Две точки с координатами |
|
Первая координата |
|
Вторая координата |
| Каноническое уравнение гиперболы |
| Большая полуось гиперболы |
| Малая/мнимая полуось гиперболы |
| Эксцентриситет гиперболы |
| Фокальный параметр |
| Фокальное расстояние |
| Перицентрическое расстояние |
Уравнение гиперболы в каноническом виде имеет вот такой вид.
Так же как и при расчете уравнения эллипса по двум точкам, мы можем по двум точкам однозначно построить гиперболу, выраженную через вышеуказанную формулу.
Используя универсальный калькулятор расчет кривой второго порядка на плоскости по точкам, мы легко определим значения 
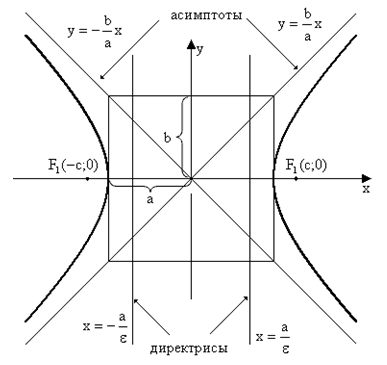
Кроме этого, зная эти параметры можно рассчитать следующее:
Большая полуось 
Фокальное расстояние 
Мнимая полуось 
Связь между тремя параметрами выражена в одной формуле
Эксцентриситет – коэффициент, численно равный, отношению фокусного расстояния к большой полуоси гиперболы
Фокальный параметр –расстояние от фокуса до гиперболы вдоль прямой, параллельной оси ординат
Прицельный параметр – расстояние от фокуса до асимптоты. Численно равен малой полуоси гиперболы.
Перицентрическое расстояние –расстояние от фокуса до ближайшей вершины гиперболы
Примеры задач
Cоставить каноническое уравнение гиперболы по двум точкам
Вводим данные в поля ввода. Можем писать как выражение, учитвая что квадратный корень обозначается sqrt, а можем сначала получить численные значения и подставить уже окончательные результаты.
В результате получим
| Каноническое уравнение гиперболы |
 |
| Большая полуось гиперболы |
|
4.47213595499958 |
| Малая/мнимая полуось гиперболы |
|
3.4641016147913444 |
| Эксцентриситет гиперболы |
|
1.1661903789073205 |
| Фокальный параметр |
|
1.79999999928 |
| Фокальное расстояние |
|
5.830951894536603 |
| Перицентрическое расстояние |
|
0.8309518945366023 |
Есть небольшая погрешность в вычислениях, вместо 2.9999999999 должно быть 3. Но думаю, что клиенты отнесутся с снисхождением, к одной десяти миллионной погрешности.
Удачных расчетов!
| bold{mathrm{Basic}} | bold{alphabetagamma} | bold{mathrm{ABGamma}} | bold{sincos} | bold{gedivrightarrow} | bold{overline{x}spacemathbb{C}forall} | bold{sumspaceintspaceproduct} | bold{begin{pmatrix}square&square\square&squareend{pmatrix}} | bold{H_{2}O} | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|

Subscribe to verify your answer
Subscribe
Sign in to save notes
Sign in
Number Line

Examples
-
frac{y^2}{25}-frac{x^2}{9}=1
-
center:frac{(x+3)^2}{25}-frac{(y-4)^2}{9}=1
-
axis:-frac{(y-3)^2}{25}+frac{(x+2)^2}{9}=1
-
foci:4x^2-9y^2-48x-72y+108=0
-
vertices:x^2-y^2=1
-
eccentricity:x^2-y^2=1
-
asymptotes:x^2-y^2=1
- Show More
Description
Calculate Hyperbola center, axis, foci, vertices, eccentricity and asymptotes step-by-step
hyperbola-equation-calculator
en
Related Symbolab blog posts
Practice, practice, practice
Math can be an intimidating subject. Each new topic we learn has symbols and problems we have never seen. The unknowing…
Read More
Enter a problem
Save to Notebook!
Sign in

Господин Экзамен
Другие калькуляторы
- График неявной функции
- Поверхность, заданная уравнением
Канонический вид/
Уравнение гиперболы
Каноническое уравнение гиперболы
⚟
График:
x: [,
]
y: [,
]
z: [,
]
Качество:
(Кол-во точек на оси)
Тип построения:
© Господин Экзамен
This calculator will find either the equation of the hyperbola from the given parameters or the center, foci, vertices, co-vertices, (semi)major axis length, (semi)minor axis length, latera recta, length of the latera recta (focal width), focal parameter, eccentricity, linear eccentricity (focal distance), directrices, asymptotes, x-intercepts, y-intercepts, domain, and range of the entered hyperbola. Also, it will graph the hyperbola. Steps are available.
Related calculators:
Parabola Calculator,
Circle Calculator,
Ellipse Calculator,
Conic Section Calculator
Your Input
Find the center, foci, vertices, co-vertices, major axis length, semi-major axis length, minor axis length, semi-minor axis length, latera recta, length of the latera recta (focal width), focal parameter, eccentricity, linear eccentricity (focal distance), directrices, asymptotes, x-intercepts, y-intercepts, domain, and range of the hyperbola $$$x^{2} – 4 y^{2} = 36$$$.
Solution
The equation of a hyperbola is $$$frac{left(x – hright)^{2}}{a^{2}} – frac{left(y – kright)^{2}}{b^{2}} = 1$$$, where $$$left(h, kright)$$$ is the center, $$$a$$$ and $$$b$$$ are the lengths of the semi-major and the semi-minor axes.
Our hyperbola in this form is $$$frac{left(x – 0right)^{2}}{36} – frac{left(y – 0right)^{2}}{9} = 1$$$.
Thus, $$$h = 0$$$, $$$k = 0$$$, $$$a = 6$$$, $$$b = 3$$$.
The standard form is $$$frac{x^{2}}{6^{2}} – frac{y^{2}}{3^{2}} = 1$$$.
The vertex form is $$$frac{x^{2}}{36} – frac{y^{2}}{9} = 1$$$.
The general form is $$$x^{2} – 4 y^{2} – 36 = 0$$$.
The linear eccentricity (focal distance) is $$$c = sqrt{a^{2} + b^{2}} = 3 sqrt{5}$$$.
The eccentricity is $$$e = frac{c}{a} = frac{sqrt{5}}{2}$$$.
The first focus is $$$left(h – c, kright) = left(- 3 sqrt{5}, 0right)$$$.
The second focus is $$$left(h + c, kright) = left(3 sqrt{5}, 0right)$$$.
The first vertex is $$$left(h – a, kright) = left(-6, 0right)$$$.
The second vertex is $$$left(h + a, kright) = left(6, 0right)$$$.
The first co-vertex is $$$left(h, k – bright) = left(0, -3right)$$$.
The second co-vertex is $$$left(h, k + bright) = left(0, 3right)$$$.
The length of the major axis is $$$2 a = 12$$$.
The length of the minor axis is $$$2 b = 6$$$.
The focal parameter is the distance between the focus and the directrix: $$$frac{b^{2}}{c} = frac{3 sqrt{5}}{5}$$$.
The latera recta are the lines parallel to the minor axis that pass through the foci.
The first latus rectum is $$$x = – 3 sqrt{5}$$$.
The second latus rectum is $$$x = 3 sqrt{5}$$$.
The endpoints of the first latus rectum can be found by solving the system $$$begin{cases} x^{2} – 4 y^{2} – 36 = 0 \ x = – 3 sqrt{5} end{cases}$$$ (for steps, see system of equations calculator).
The endpoints of the first latus rectum are $$$left(- 3 sqrt{5}, – frac{3}{2}right)$$$, $$$left(- 3 sqrt{5}, frac{3}{2}right)$$$.
The endpoints of the second latus rectum can be found by solving the system $$$begin{cases} x^{2} – 4 y^{2} – 36 = 0 \ x = 3 sqrt{5} end{cases}$$$ (for steps, see system of equations calculator).
The endpoints of the second latus rectum are $$$left(3 sqrt{5}, – frac{3}{2}right)$$$, $$$left(3 sqrt{5}, frac{3}{2}right)$$$.
The length of the latera recta (focal width) is $$$frac{2 b^{2}}{a} = 3$$$.
The first directrix is $$$x = h – frac{a^{2}}{c} = – frac{12 sqrt{5}}{5}$$$.
The second directrix is $$$x = h + frac{a^{2}}{c} = frac{12 sqrt{5}}{5}$$$.
The first asymptote is $$$y = – frac{b}{a} left(x – hright) + k = – frac{x}{2}$$$.
The second asymptote is $$$y = frac{b}{a} left(x – hright) + k = frac{x}{2}$$$.
The x-intercepts can be found by setting $$$y = 0$$$ in the equation and solving for $$$x$$$ (for steps, see intercepts calculator).
x-intercepts: $$$left(-6, 0right)$$$, $$$left(6, 0right)$$$
The y-intercepts can be found by setting $$$x = 0$$$ in the equation and solving for $$$y$$$: (for steps, see intercepts calculator).
Since there are no real solutions, there are no y-intercepts.
Answer
Standard form/equation: $$$frac{x^{2}}{6^{2}} – frac{y^{2}}{3^{2}} = 1$$$A.
Vertex form/equation: $$$frac{x^{2}}{36} – frac{y^{2}}{9} = 1$$$A.
General form/equation: $$$x^{2} – 4 y^{2} – 36 = 0$$$A.
First focus-directrix form/equation: $$$left(x + 3 sqrt{5}right)^{2} + y^{2} = frac{5 left(x + frac{12 sqrt{5}}{5}right)^{2}}{4}$$$A.
Second focus-directrix form/equation: $$$left(x – 3 sqrt{5}right)^{2} + y^{2} = frac{5 left(x – frac{12 sqrt{5}}{5}right)^{2}}{4}$$$A.
Graph: see the graphing calculator.
Center: $$$left(0, 0right)$$$A.
First focus: $$$left(- 3 sqrt{5}, 0right)approx left(-6.708203932499369, 0right)$$$A.
Second focus: $$$left(3 sqrt{5}, 0right)approx left(6.708203932499369, 0right)$$$A.
First vertex: $$$left(-6, 0right)$$$A.
Second vertex: $$$left(6, 0right)$$$A.
First co-vertex: $$$left(0, -3right)$$$A.
Second co-vertex: $$$left(0, 3right)$$$A.
Major (transverse) axis length: $$$12$$$A.
Semi-major axis length: $$$6$$$A.
Minor (conjugate) axis length: $$$6$$$A.
Semi-minor axis length: $$$3$$$A.
First latus rectum: $$$x = – 3 sqrt{5}approx -6.708203932499369$$$A.
Second latus rectum: $$$x = 3 sqrt{5}approx 6.708203932499369$$$A.
Endpoints of the first latus rectum: $$$left(- 3 sqrt{5}, – frac{3}{2}right)approx left(-6.708203932499369, -1.5right)$$$, $$$left(- 3 sqrt{5}, frac{3}{2}right)approx left(-6.708203932499369, 1.5right)$$$A.
Endpoints of the second latus rectum: $$$left(3 sqrt{5}, – frac{3}{2}right)approx left(6.708203932499369, -1.5right)$$$, $$$left(3 sqrt{5}, frac{3}{2}right)approx left(6.708203932499369, 1.5right)$$$A.
Length of the latera recta (focal width): $$$3$$$A.
Focal parameter: $$$frac{3 sqrt{5}}{5}approx 1.341640786499874$$$A.
Eccentricity: $$$frac{sqrt{5}}{2}approx 1.118033988749895$$$A.
Linear eccentricity (focal distance): $$$3 sqrt{5}approx 6.708203932499369$$$A.
First directrix: $$$x = – frac{12 sqrt{5}}{5}approx -5.366563145999495$$$A.
Second directrix: $$$x = frac{12 sqrt{5}}{5}approx 5.366563145999495$$$A.
First asymptote: $$$y = – frac{x}{2} = – 0.5 x$$$A.
Second asymptote: $$$y = frac{x}{2} = 0.5 x$$$A.
x-intercepts: $$$left(-6, 0right)$$$, $$$left(6, 0right)$$$A.
y-intercepts: no y-intercepts.
Domain: $$$left(-infty, -6right] cup left[6, inftyright)$$$A.
Range: $$$left(-infty, inftyright)$$$A.
Как составить каноническое уравнение гиперболы зная координаты двух точек?
Rodion Bokiy
Знаток
(362),
закрыт
12 лет назад
Как составить каноническое уравнение гиперболы зная координаты двух точек?
Координаты:
A(корень из 80; 3) B (4 корня из 6; 3 корня из 2)
Заранее спасибо!
Удачник
Высший разум
(141068)
12 лет назад
Каноническое уравнение гиперболы
x^2/a^2 – y^2/b^2 = 1
Подставляем координаты точек и получаем 2 уравнения с неизвестными а и b.
{ 80/a^2 – 9/b^2 = 1
{ 16*6/a^2 – 9*2/b^2 = 1
{ 80/a^2 – 9/b^2 = 1
{ 96/a^2 – 18/b^2 = 1
{ 80b^2 – 9a^2 = a^2*b^2
{ 96b^2 – 18a^2 = a^2*b^2
{ -160b^2 + 18a^2 = -2a^2*b^2
{ 96b^2 – 18a^2 = a^2*b^2
-64b^2 = -a^2*b^2
a^2 = 64, a = 8
80b^2 – 9*64 = 64b^2
16b^2 = 9*64
b^2 = 9*4 = 36
b = 6
Ответ: Уравнение гиперболы x^2/64 – y^2/36 = 1



)
;M_2(-2sqrt{5}:3))