While using … HAVING COUNT(*) = ( …MAX().. ) works:
- Within the query, it needs almost the same sub-query twice.
- For most databases, it needs a 2nd level sub-query as MAX( COUNT(*) )
is not supported.
While using TOP / LIMIT / RANK etc works:
- It uses SQL extensions for a specific database.
Also, using TOP / LIMIT of 1 will only give one row – what if there are two or more doctors with the same maximum number of patients?
I would break the problem into steps:
Get target field(s) and associated count
SELECT docName, COUNT( patient ) AS countX
FROM doctor
GROUP BY docName
Using the above as a ‘statement scoped view’, use this to get the max count row(s)
WITH x AS
(
SELECT docName, COUNT( patient ) AS countX
FROM doctor
GROUP BY docName
)
SELECT x.docName, x.countX
FROM x
WHERE x.countX = ( SELECT MAX( countX ) FROM x )
The WITH clause, which defines a ‘statement scoped view’, effectively gives named sub-queries that can be re-used within the same query.
While this solution, using statement scoped views, is longer, it is:
- Easier to test
- Self documenting
- Extendable
It is easier to test as parts of the query can be run standalone.
It is self documenting as the query directly reflects the requirement
ie the statement scoped view lists the target field(s) and associated count.
It is extendable as if other conditions or fields are required, this can be easily added to the statement scoped view.
eg in this case, the table stucture should be changed to include a doctor-id as a primary key field and this should be part of the results.
Last update on August 19 2022 21:51:36 (UTC/GMT +8 hours)
MAX() with Count function
In this part, you will see the usage of SQL COUNT() along with the SQL MAX().
Example:
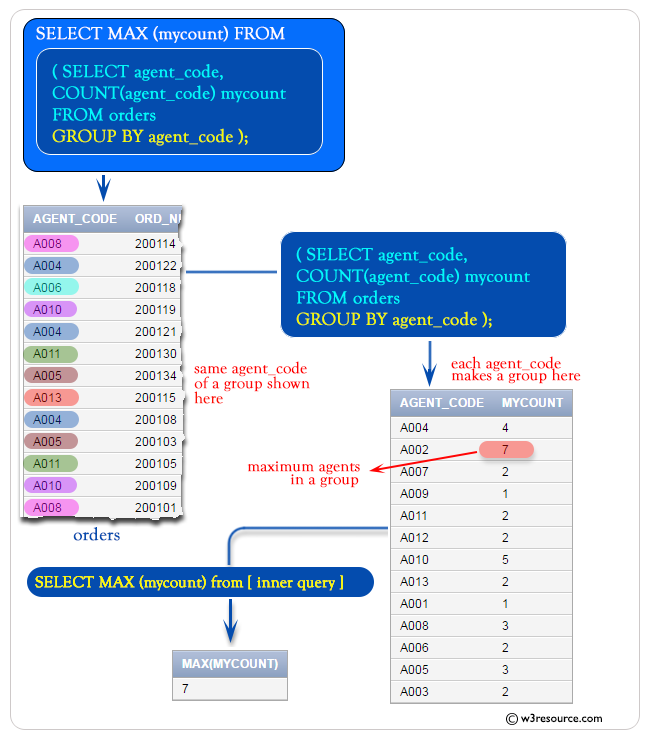
To get the maximum number of agents as column alias ‘mycount’ from the ‘orders’ table with the following condition –
1. ‘agent_code’ should be in a group,
the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT MAX (mycount)
FROM (SELECT agent_code,COUNT(agent_code) mycount
FROM orders
GROUP BY agent_code);Sample table: orders
Output:
MAX(MYCOUNT)
------------
7
Pictorial Presentation :
SQL MAX() and COUNT() with HAVING
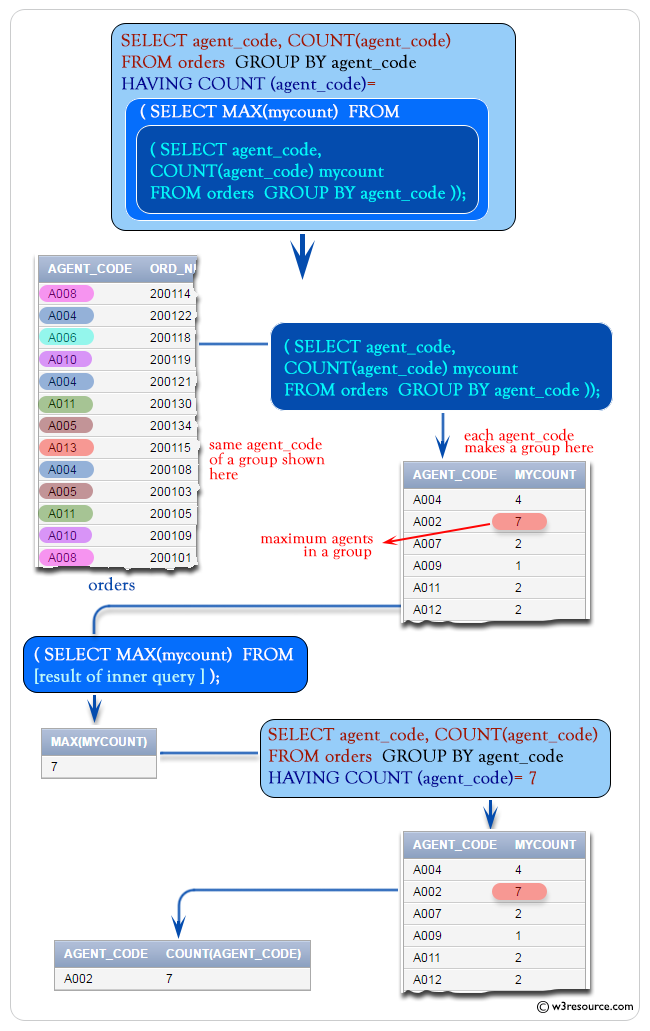
To get data of ‘agent_code’, and number of agents for each group of ‘agent_code’ from the orders table with the following conditions –
‘agent_code’ for a group will be equal to the result of an outer query [SELECT MAX(agent_code)…….] with following condition –
the outer query produce the maximum number of agents mentioned as
‘mycount’ from an inner query [SELECT agent_code,
COUNT(agent_code) mycount FROM orders GROUP BY agent_code]
with following condition –
the inner query produced the data ‘agent_code’ number of agents as
column alias ‘mycount’ from the ‘orders’ table with the following
condition –
‘agent_code’ should be in a group,
the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT agent_code, COUNT(agent_code)
FROM orders GROUP BY agent_code
HAVING COUNT (agent_code)=(
SELECT MAX(mycount)
FROM (
SELECT agent_code, COUNT(agent_code) mycount
FROM orders
GROUP BY agent_code));Sample table: orders
Output:
AGENT_CODE COUNT(AGENT_CODE) ---------- ----------------- A002 7
Note: Outputs of the said SQL statement shown here is taken by using Oracle Database 10g Express Edition
Here is a slide presentation of all aggregate functions.
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
Previous: Max Date
Next: Min function
SQL: Tips of the Day
Get top 1 row of each group:
;WITH cte AS
(
SELECT *,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY DocumentID ORDER BY DateCreated DESC) AS rn
FROM DocumentStatusLogs
)
SELECT *
FROM cte
WHERE rn = 1
Ref: https://bit.ly/390IEAj
We are closing our Disqus commenting system for some maintenanace issues. You may write to us at reach[at]yahoo[dot]com or visit us
at Facebook
This question is old, but was referenced in a new question on dba.SE. I feel the best solutions haven’t been provided. Plus, there are new, faster options.
Question in the title
Can I do a
max(count(*))in SQL?
Yes, you can achieve that by nesting an aggregate function in a window function:
SELECT m.yr
, count(*) AS movie_count
, max(count(*)) OVER () AS max_ct
FROM casting c
JOIN movie m ON c.movieid = m.id
WHERE c.actorid = (SELECT id FROM actor WHERE name = 'John Travolta')
GROUP BY m.yr
ORDER BY count(*) DESC;
db<>fiddle here
That’s standard SQL. Postgres introduced it with version 8.4 (released 2009-07-01, before this question was asked. Other RDBMS should be capable of the same.
Consider the sequence of events in a SELECT query:
- Best way to get result count before LIMIT was applied
Possible downside: window functions do not aggregate rows. You get all rows left after the aggregate step. Useful in some queries, but not ideal for this one.
To get one row with the highest count, you can use ORDER BY ct DESC FETCH FIRST 1 ROW ONLY:
SELECT c.yr, count(*) AS ct
FROM actor a
JOIN casting c ON c.actorid = a.id
WHERE a.name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY c.yr
ORDER BY ct DESC
FETCH FIRST 1 ROW ONLY;
Using only basic SQL features, available in any halfway decent RDBMS. Most popular RDBMS (also) support alternative syntax for FETCH FIRST with LIMIT, TOP or ROWNUM. See:
- SQL select elements where sum of field is less than N
Or you can get one row per group with the highest count with DISTINCT ON (only Postgres):
- Select first row in each GROUP BY group?
Actual Question
I need to get the rows for which
count(*)is max.
There may be more than one row with the highest count.
SQL Server has had the feature WITH TIES for some time – with non-standard syntax:
SELECT TOP 1 WITH TIES
m.yr, count(*) AS movie_count
FROM casting c
JOIN movie m ON c.movieid = m.id
WHERE c.actorid = (SELECT id FROM actor WHERE name = 'John Travolta')
GROUP BY m.yr
ORDER BY count(*) DESC; -- can't sort by year for this
db<>fiddle here
PostgreSQL 13 added WITH TIES with standard SQL syntax:
SELECT m.yr, count(*) AS movie_count
FROM casting c
JOIN movie m ON c.movieid = m.id
WHERE c.actorid = (SELECT id FROM actor WHERE name = 'John Travolta')
GROUP BY m.yr
ORDER BY count(*) DESC -- can't sort by year for this
FETCH FIRST 1 ROWS WITH TIES;
db<>fiddle here
This should be the fastest possible query. Further reading:
-
Get top row(s) with highest value, with ties
-
PostgreSQL equivalent for TOP n WITH TIES: LIMIT “with ties”?
To sort results by additional criteria (or for older versions of Postgres or other RDBMS without WITH TIES), use the window function rank() in a subquery:
SELECT yr, movie_count
FROM (
SELECT m.yr, count(*) AS movie_count
, rank() OVER (ORDER BY count(*) DESC) AS rnk
FROM casting c
JOIN movie m ON c.movieid = m.id
WHERE c.actorid = (SELECT id FROM actor WHERE name = 'John Travolta')
GROUP BY m.yr
) sub
WHERE rnk = 1
ORDER BY yr; -- optionally sort by year
All major RDBMS support window functions nowadays.
Здесь мой код:
select yr,count(*) from movie
join casting on casting.movieid=movie.id
join actor on casting.actorid = actor.id
where actor.name = 'John Travolta'
group by yr
Здесь вопрос
Какими были самые долгие годы для “Джона Траволты”. Покажите количество фильмов, которые он сделал за каждый год.
Здесь структура таблицы:
movie(id, title, yr, score, votes, director)
actor(id, name)
casting(movieid, actorid, ord)
Это результат, который я получаю:
yr count(*)
1976 1
1977 1
1978 1
1981 1
1994 1
etcetc
Мне нужно получить строки, для которых count(*) max.
Как это сделать?
Ответ 1
Использование:
SELECT m.yr,
COUNT(*) AS num_movies
FROM MOVIE m
JOIN CASTING c ON c.movieid = m.id
JOIN ACTOR a ON a.id = c.actorid
AND a.name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY m.yr
ORDER BY num_movies DESC, m.yr DESC
Заказ num_movies DESC будет содержать самые высокие значения в верхней части набора результатов. Если многолетний период имеет одинаковый счет, m.yr поместит последний год вверху… до следующего значения num_movies.
Нет, вы не можете группировать агрегированные функции друг над другом в том же предложении SELECT. Внутренний агрегат должен выполняться в подзапросе. IE:
SELECT MAX(y.num)
FROM (SELECT COUNT(*) AS num
FROM TABLE x) y
Ответ 2
Просто закажите count(*) desc, и вы получите наивысший результат (если вы объедините его с limit 1)
Ответ 3
SELECT * from
(
SELECT yr as YEAR, COUNT(title) as TCOUNT
FROM actor
JOIN casting ON actor.id = casting.actorid
JOIN movie ON casting.movieid = movie.id
WHERE name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY yr
order by TCOUNT desc
) res
where rownum < 2
Ответ 4
с этого сайта – http://sqlzoo.net/3.htm
2 возможных решения:
с TOP 1 a ORDER BY… DESC:
SELECT yr, COUNT(title)
FROM actor
JOIN casting ON actor.id=actorid
JOIN movie ON movie.id=movieid
WHERE name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY yr
HAVING count(title)=(SELECT TOP 1 COUNT(title)
FROM casting
JOIN movie ON movieid=movie.id
JOIN actor ON actor.id=actorid
WHERE name='John Travolta'
GROUP BY yr
ORDER BY count(title) desc)
с MAX:
SELECT yr, COUNT(title)
FROM actor
JOIN casting ON actor.id=actorid
JOIN movie ON movie.id=movieid
WHERE name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY yr
HAVING
count(title)=
(SELECT MAX(A.CNT)
FROM (SELECT COUNT(title) AS CNT FROM actor
JOIN casting ON actor.id=actorid
JOIN movie ON movie.id=movieid
WHERE name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY (yr)) AS A)
Ответ 5
Использование max с лимитом даст вам только первую строку, но если есть две или более строк с одинаковым количеством максимальных фильмов, вы можете пропустить некоторые данные. Ниже приведен способ сделать это, если у вас есть функция rank().
SELECT
total_final.yr,
total_final.num_movies
FROM
( SELECT
total.yr,
total.num_movies,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY num_movies desc) rnk
FROM (
SELECT
m.yr,
COUNT(*) AS num_movies
FROM MOVIE m
JOIN CASTING c ON c.movieid = m.id
JOIN ACTOR a ON a.id = c.actorid
WHERE a.name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY m.yr
) AS total
) AS total_final
WHERE rnk = 1
Ответ 6
Следующий код дает вам ответ. Он по существу реализует MAX (COUNT (*)), используя ALL. Преимущество состоит в том, что он использует очень простые команды и операции.
SELECT yr, COUNT(title)
FROM actor
JOIN casting ON actor.id = casting.actorid
JOIN movie ON casting.movieid = movie.id
WHERE name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY yr HAVING COUNT(title) >= ALL
(SELECT COUNT(title)
FROM actor
JOIN casting ON actor.id = casting.actorid
JOIN movie ON casting.movieid = movie.id
WHERE name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY yr)
Ответ 7
В зависимости от используемой базы данных…
select yr, count(*) num from ...
order by num desc
Большая часть моего опыта в Sybase, который использует какой-то другой синтаксис, чем другие БД. Но в этом случае вы назовете свой столбец count, чтобы вы могли сортировать его по убыванию. Вы можете сделать еще один шаг и ограничить результаты до первых 10 строк (чтобы найти его 10 самых загруженных лет).
Ответ 8
select top 1 yr,count(*) from movie
join casting on casting.movieid=movie.id
join actor on casting.actorid = actor.id
where actor.name = 'John Travolta'
group by yr order by 2 desc
Ответ 9
Этот вопрос старый, но был указан в новом вопросе на dba.SE. Я чувствую, что лучшие решения не были предоставлены, но я добавляю еще один.
Прежде всего, при условии ссылочной целостности (как правило, с ограничениями внешних ключей), вам не нужно вообще присоединяться к таблице movie. Этот мертвый груз в вашем запросе. Все ответы пока не указывают на это.
Можно ли сделать
max(count(*))в SQL?
Чтобы ответить на вопрос в заголовке: Да, в Postgres 8.4 (выпущен 2009-07-01, перед тем, как этот вопрос был задан) или позже, вы можете добиться этого, вложив агрегированную функцию в функция окна:
SELECT c.yr, count(*) AS ct, max(count(*)) OVER () AS max_ct
FROM actor a
JOIN casting c ON c.actorid = a.id
WHERE a.name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY c.yr;
Рассмотрим последовательность событий в запросе SELECT:
- Лучший способ получить результат до применения LIMIT
(возможный) недостаток: функции окна не группируют строки. Вы получаете все строки, оставшиеся после совокупного шага. Полезно в некоторых запросах, но не идеально для этого.
Чтобы получить одну строку с наивысшим счетчиком, вы можете использовать ORDER BY ct LIMIT 1 как @wolph hinted:
SELECT c.yr, count(*) AS ct
FROM actor a
JOIN casting c ON c.actorid = a.id
WHERE a.name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY c.yr
ORDER BY ct DESC
LIMIT 1;
Использование только базовых функций SQL, доступных в любой половине допустимой РСУБД – реализация LIMIT различается:
- Элементы выбора SQL, где сумма поля меньше N
Или вы можете получить одну строку на группу с наивысшим счетчиком с помощью DISTINCT ON (только Postgres):
- Выберите первую строку в каждой группе GROUP BY?
Ответ
Но вы просили:
… строки, для которых count (*) max.
Возможно, более одного. Наиболее элегантным решением является функция окна rank() в подзапросе. Ryan предоставил запрос, но это может быть проще (подробности в моем ответе выше):
SELECT yr, ct
FROM (
SELECT c.yr, count(*) AS ct, rank() OVER (ORDER BY count(*) DESC) AS rnk
FROM actor a
JOIN casting c ON c.actorid = a.id
WHERE a.name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY c.yr
) sub
WHERE rnk = 1;
В настоящее время все основные функции поддержки RDBMS поддерживаются. За исключением MySQL и forks (MariaDB, похоже, их реализовала наконец в версии 10.2).
Ответ 10
Благодаря последнему ответу
SELECT yr, COUNT(title)
FROM actor
JOIN casting ON actor.id = casting.actorid
JOIN movie ON casting.movieid = movie.id
WHERE name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY yr HAVING COUNT(title) >= ALL
(SELECT COUNT(title)
FROM actor
JOIN casting ON actor.id = casting.actorid
JOIN movie ON casting.movieid = movie.id
WHERE name = 'John Travolta'
GROUP BY yr)
У меня была такая же проблема, мне нужно было знать только те записи, которые их счетчик соответствует максимальному счету. (это может быть одна или несколько записей)
Мне нужно узнать больше о “ALL clause”, и это именно то простое решение, которое я искал.
Ответ 11
create view sal as
select yr,count(*) as ct from
(select title,yr from movie m, actor a, casting c
where a.name='JOHN'
and a.id=c.actorid
and c.movieid=m.id)group by yr
—– СМОТРЕТЬ СМОТРЕТЬ —–
select yr from sal
where ct =(select max(ct) from sal)
Ю.Р.
2013
|
4aineg 0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 07.08.2008 Сообщений: 23 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
1 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
18.11.2008, 20:16. Показов 21746. Ответов 2 Метки нет (Все метки)
подскажите пожалуйста как найти самый покупаемый товар
сама таблица ContGoods
0 |
|
Programming Эксперт 94731 / 64177 / 26122 Регистрация: 12.04.2006 Сообщений: 116,782 |
18.11.2008, 20:16 |
|
Ответы с готовыми решениями: Выбрать MAX из COUNT SELECT… Запрос max(count() с группировкой по годам Есть таблица res, в ней 3 столбца birth_date, res_name, sex.
10, 20, 50 Найти max значение в каждой группе… 2 |
|
Green 1922 / 427 / 41 Регистрация: 12.07.2007 Сообщений: 2,062 |
||||
|
19.11.2008, 03:23 |
2 |
|||
|
за достоверность не ручаюсь, но возможно так
0 |
|
artyuri |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
26.11.2008, 20:13 |
3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
запрос:
работает на sql server2000 пример:
результат:
Добавлено через 54 минуты 5 секунд
(проверено – работает) |
|
IT_Exp Эксперт 87844 / 49110 / 22898 Регистрация: 17.06.2006 Сообщений: 92,604 |
26.11.2008, 20:13 |
|
Помогаю со студенческими работами здесь Sql MAX( COUNT) НУжно вытащить Имя города, Колличество Квартир, Цена за… Запрос MAX(COUNT(*) Запрос max из count
Искать еще темы с ответами Или воспользуйтесь поиском по форуму: 3 |

 Задача для курсовой: определить значение z=max(a, 2b)*max(2a-b,b), где max(x, y)-максимальные из чисел х и у
Задача для курсовой: определить значение z=max(a, 2b)*max(2a-b,b), где max(x, y)-максимальные из чисел х и у

