17 авг. 2022 г.
читать 1 мин
Вы можете использовать функцию median() , чтобы найти медиану одного или нескольких столбцов в кадре данных pandas:
#find median value in specific column
df['column1']. median ()
#find median value in several columns
df[['column1', 'column2']]. median ()
#find median value in every numeric column
df.median ()
В следующих примерах показано, как использовать эту функцию на практике со следующими пандами DataFrame:
#create DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'player': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H'],
'points': [25, pd.NA , 15, 14, 19, 23, 25, 29],
'assists': [5, 7, 7, 9, 12, 9, 9, 4],
'rebounds': [11, 8, 10, 6, 6, 5, 9, 12]})
#view DataFrame
df
player points assists rebounds
0 A 25 5 11
1 B NA 7 8
2 C 15 7 10
3 D 14 9 6
4 E 19 12 6
5 F 23 9 5
6 G 25 9 9
7 H 29 4 12
Пример 1: найти медиану одного столбца
В следующем коде показано, как найти медианное значение одного столбца в кадре данных pandas:
#find median value of *points* column
df['points']. median ()
23.0
Среднее значение в столбце очков равно 23 .
Обратите внимание, что по умолчанию функция median() игнорирует любые отсутствующие значения при вычислении медианы.
Пример 2: найти медиану нескольких столбцов
В следующем коде показано, как найти медианное значение нескольких столбцов в кадре данных pandas:
#find median value of *points* and *rebounds* columns
df[['points', 'rebounds']]. median ()
points 23.0
rebounds 8.5
dtype: float64
Пример 3. Найдите медиану всех числовых столбцов
В следующем коде показано, как найти медианное значение всех числовых столбцов в кадре данных pandas:
#find median value of all numeric columns
df.median ()
points 23.0
assists 8.0
rebounds 8.5
dtype: float64
Дополнительные ресурсы
Как рассчитать среднее значение столбцов в Pandas
Как рассчитать сумму столбцов в Pandas
Как найти максимальное значение столбцов в Pandas
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Python is a great language for doing data analysis, primarily because of the fantastic ecosystem of data-centric python packages. Pandas is one of those packages and makes importing and analyzing data much easier.
Pandas dataframe.median() function return the median of the values for the requested axis
If the method is applied on a pandas series object, then the method returns a scalar value which is the median value of all the observations in the dataframe. If the method is applied on a pandas dataframe object, then the method returns a pandas series object which contains the median of the values over the specified axis.
Syntax:DataFrame.median(axis=None, skipna=None, level=None, numeric_only=None, **kwargs)
Parameters :
axis : Align object with threshold along the given axis.
skipna : Exclude NA/null values when computing the result
level : If the axis is a MultiIndex (hierarchical), count along a particular level, collapsing into a Series
numeric_only : Include only float, int, boolean columns. If None, will attempt to use everything, then use only numeric data. Not implemented for Series.Returns : median : Series or DataFrame (if level specified)
Example #1: Use median() function to find the median of all the observations over the index axis.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[12, 4, 5, 44, 1],
"B":[5, 2, 54, 3, 2],
"C":[20, 16, 7, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, 17, 2, 6]})
df
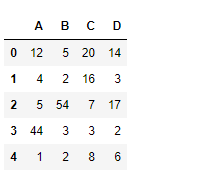
Lets use the dataframe.median() function to find the median over the index axis
Output :

Example #2: Use median() function on a dataframe which has Na values. Also find the median over the column axis.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[12, 4, 5, None, 1],
"B":[7, 2, 54, 3, None],
"C":[20, 16, 11, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, None, 2, 6]})
df

Lets implement the median function.
df.median(axis = 1, skipna = True)
Output :
Last Updated :
24 Nov, 2018
Like Article
Save Article
You can use the median() function to find the median of one or more columns in a pandas DataFrame:
#find median value in specific column
df['column1'].median()
#find median value in several columns
df[['column1', 'column2']].median()
#find median value in every numeric column
df.median()
The following examples show how to use this function in practice with the following pandas DataFrame:
#create DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'player': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H'],
'points': [25, pd.NA, 15, 14, 19, 23, 25, 29],
'assists': [5, 7, 7, 9, 12, 9, 9, 4],
'rebounds': [11, 8, 10, 6, 6, 5, 9, 12]})
#view DataFrame
df
player points assists rebounds
0 A 25 5 11
1 B NA 7 8
2 C 15 7 10
3 D 14 9 6
4 E 19 12 6
5 F 23 9 5
6 G 25 9 9
7 H 29 4 12
Example 1: Find Median of a Single Column
The following code shows how to find the median value of a single column in a pandas DataFrame:
#find median value of points column
df['points'].median()
23.0
The median value in the points column is 23.
Note that by default, the median() function ignores any missing values when calculating the median.
Example 2: Find Median of Multiple Columns
The following code shows how to find the median value of multiple columns in a pandas DataFrame:
#find median value of points and rebounds columns
df[['points', 'rebounds']].median()
points 23.0
rebounds 8.5
dtype: float64
Example 3: Find Median of All Numeric Columns
The following code shows how to find the median value of all numeric columns in a pandas DataFrame:
#find median value of all numeric columns
df.median()
points 23.0
assists 8.0
rebounds 8.5
dtype: float64
Additional Resources
How to Calculate the Mean of Columns in Pandas
How to Calculate the Sum of Columns in Pandas
How to Find the Max Value of Columns in Pandas
The median of a set of numbers represents the middle value if the numbers are arranged in sorted order. It is a measure of central tendency and is often preferred over the mean as it’s not much affected by the presence of outliers. In this tutorial, we will look at how to get the median of one or more columns in a pandas dataframe.
How to calculate the median of pandas column values?
You can use the pandas median() function or the pandas quantile() function to get the median of column values in a pandas dataframe. The following is the syntax:
# median of single column df['Col'].median() # median of single column with quantile() df['Col'].quantile(0.5) # median of all numerical columns in dataframe df.median() # median of all numerical columns in dataframe with quantile() df.quantile(0.5)
Let’s create a sample dataframe that we will be using throughout this tutorial to demonstrate the usage of the methods and syntax mentioned.
import pandas as pd
# create a dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({
'sepal_legth': [5.1, 4.9, 4.7, 4.6, 5.0, 5.4, 4.6, 5.0],
'sepal_width': [3.5, 3.0, 3.2, 3.1, 3.6, 3.9, 3.4, 3.4],
'petal_length': [1.4, 1.4, 1.3, 1.5, 1.4, 1.7, 1.4, 1.5],
'petal_width': [0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.4, 0.3, 0.2],
'sepices': ['setosa']*8
})
# display the dataframe
print(df)
Output:
sepal_legth sepal_width petal_length petal_width sepices 0 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa 1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa 2 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa 3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa 4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa 5 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 setosa 6 4.6 3.4 1.4 0.3 setosa 7 5.0 3.4 1.5 0.2 setosa
The sample dataframe is taken form a section of the Iris dataset. This sample has petal and sepal dimensions of eight data points of the “Setosa” species.
Median of a single column
First, let’s see how to get the median of a single dataframe column.
You can use the pandas series median() function to get the median of individual columns (which essentially are pandas series). For example, let’s get the median of the “sepal_length” column in the above dataframe.
# median of sepal_length column print(df['sepal_length'].median())
Output:
4.95
You see that we get the median of all values in the “sepal_length” column as the scaler value 4.95.
Median of a single column using quantile()
Additionally, you can also use pandas quantile() function which gives the nth percentile value. Median is the 50th percentile value. So, to get the median with the quantile() function, pass 0.5 as the argument.
# median of sepal_length column using quantile() print(df['sepal_length'].quantile(0.5))
Output:
4.95
Median of more than one column
Use the pandas dataframe median() function to get the median values for all the numerical columns in the dataframe. For example, let’s get the median of all the numerical columns in the dataframe “df”
# mean of multiple columns print(df.median())
Output:
sepal_length 4.95 sepal_width 3.40 petal_length 1.40 petal_width 0.20 dtype: float64
We get the result as a pandas series.
Median of more than one column using quantile()
Additionally, you can use the pandas dataframe quantile() function with an argument of 0.5 to get the median of all the numerical columns in a dataframe. Let’s use this function on the dataframe “df” created above.
# mean of multiple columns using quantile() print(df.quantile(0.5))
Output:
sepal_length 4.95 sepal_width 3.40 petal_length 1.40 petal_width 0.20 Name: 0.5, dtype: float64
You can see that we get the median of all the numerical columns present in the dataframe.
Note that you can also use the pandas describe() function to look at key statistics including the median values of the numerical columns in the dataframe.
# get dataframe statistics df.describe()
Output:
The median here is represented by the 50% value (that is, the value at the 50th percentile).
For more on the pandas dataframe median() function, refer to its documention.
With this, we come to the end of this tutorial. The code examples and results presented in this tutorial have been implemented in a Jupyter Notebook with a python (version 3.8.3) kernel having pandas version 1.0.5
Subscribe to our newsletter for more informative guides and tutorials.
We do not spam and you can opt out any time.
Tutorials on getting statistics for pandas dataframe values –
- Pandas – Get Mean of one or more Columns
- Pandas – Get Standard Deviation of one or more Columns
- Pandas – Get Median of One or More Columns
- Get correlation between columns of Pandas DataFrame
- Cumulative Sum of Column in Pandas DataFrame
- Pandas – Count Missing Values in Each Column
- Get Rolling Window estimates in Pandas
- Get the number of rows in a Pandas DataFrame
- Pandas – Count of Unique Values in Each Column
-

Piyush is a data professional passionate about using data to understand things better and make informed decisions. He has experience working as a Data Scientist in the consulting domain and holds an engineering degree from IIT Roorkee. His hobbies include watching cricket, reading, and working on side projects.
View all posts
In this tutorial, I’ll illustrate how to calculate the median value for a list or the columns of a pandas DataFrame in Python programming.
The page is structured as follows:
Let’s dive right in…
Example 1: Median of List Object
This example explains how to get the median value of a list object in Python.
First, we have to create an example list:
my_list = [1, 4, 3, 2, 1, 3, 7, 1, 4, 1] # Create example list print(my_list) # Print example list # [1, 4, 3, 2, 1, 3, 7, 1, 4, 1]
Furthermore, we have to load the NumPy library:
import numpy as np # Load NumPy library
Next, we can apply the median function of the NumPy library to our example list:
print(np.median(my_list)) # Get median of list # 2.5
As you can see based on the previous output, the median of our list is 2.5.
Example 2: Median of One Particular Column in pandas DataFrame
In Example 2, I’ll illustrate how to find the median value for the columns of a pandas DataFrame.
Let’s import pandas to Python:
import pandas as pd # Load pandas library
Next, let’s create an exemplifying pandas DataFrame:
data = pd.DataFrame({'x1':[6, 2, 7, 2, 1, 5, 3, 4, 2, 7, 5], # Create pandas DataFrame 'x2':range(0, 11), 'group':['A', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'B', 'A', 'A', 'C', 'C', 'B', 'A']}) print(data) # Print pandas DataFrame
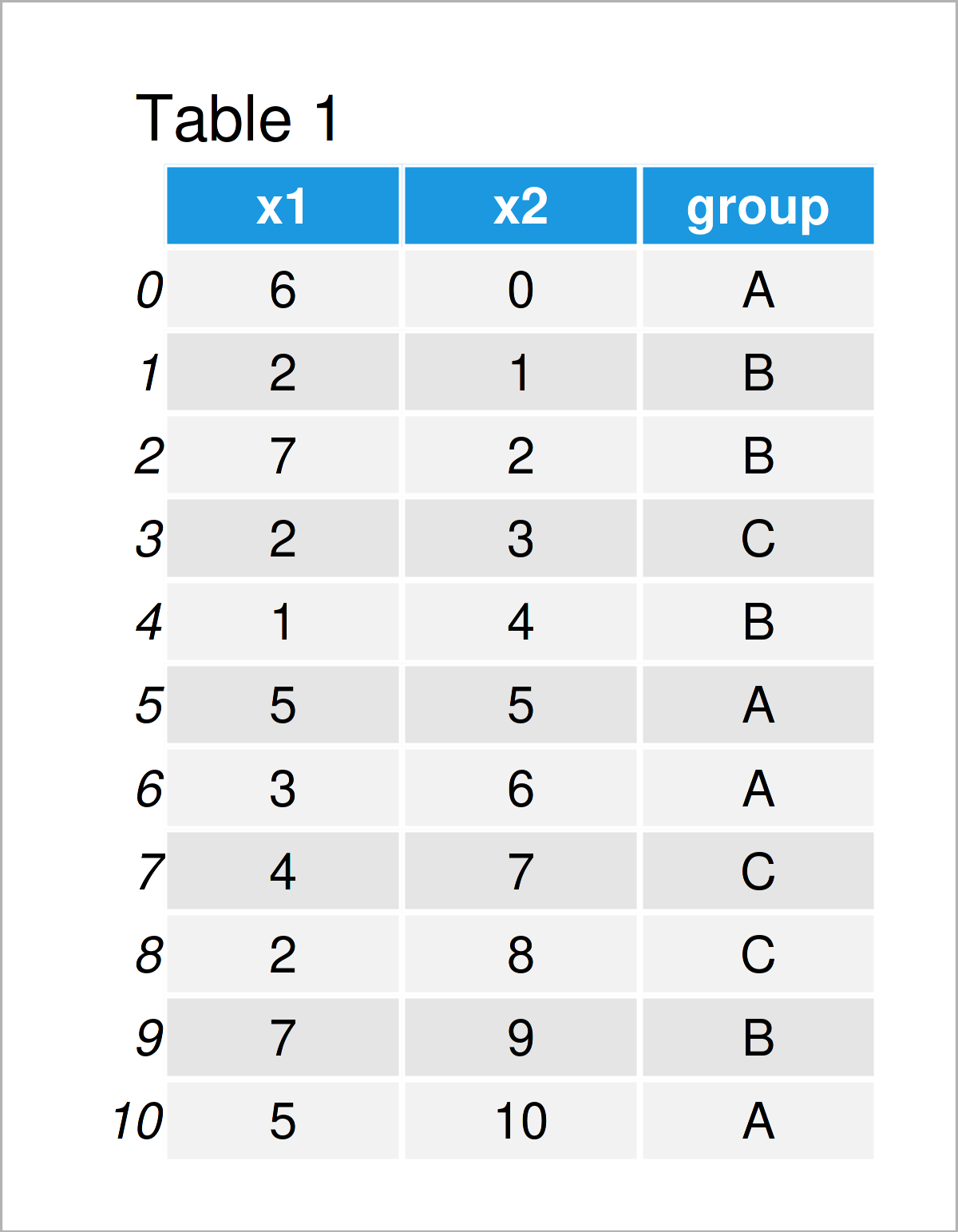
After running the previous Python programming code the pandas DataFrame you can see in Table 1 has been created. Our example data set contains two float columns and a group indicator.
Next, we can compute the median for one specific column (i.e. x1) as shown below:
print(data['x1'].median()) # Get median of one column # 4.0
The median of the column x1 is equal to 4.0.
Example 3: Median of All Columns in pandas DataFrame
This example demonstrates how to return the medians for all columns of our pandas DataFrame.
For this task, we can simply apply the median function to our entire data set:
print(data.median()) # Get median of all columns # x1 4.0 # x2 5.0 # dtype: float64
The median of the column x1 is 4.0 (as we already know from the previous example), and the median of the variable x2 is 5.0.
Example 4: Median of Rows in pandas DataFrame
We can also calculate the median of the rows of a pandas DataFrame in Python.
To accomplish this, we have to specify the axis argument within the median function to be equal to 1:
print(data.median(axis = 1)) # Get median of rows # 0 3.0 # 1 1.5 # 2 4.5 # 3 2.5 # 4 2.5 # 5 5.0 # 6 4.5 # 7 5.5 # 8 5.0 # 9 8.0 # 10 7.5 # dtype: float64
Example 5: Median by Group in pandas DataFrame
Example 5 shows how to calculate the median for each pandas DataFrame column by group.
For this, we have to use the groupby function in addition to the median function:
print(data.groupby('group').median()) # Get median by group # x1 x2 # group # A 5.0 5.5 # B 4.5 3.0 # C 2.0 7.0
The previous output shows the median values for all columns and groups in our data set.
Video & Further Resources
In case you need more info on the Python programming code of this article, I recommend watching the following video on my YouTube channel. I demonstrate the contents of this article in the video:
Besides that, you may want to read the related posts on my website:
- Calculate Median by Group in Python
- Get Median of Array with np.median Function of NumPy Library
- median Function of statistics Module
- Calculate Mean in Python
- Calculate Mode in Python
- Introduction to the pandas Library in Python
- Python Programming Overview
To summarize: At this point you should have learned how to compute the median value in the Python programming language. In case you have further comments or questions, please let me know in the comments.

