Крутящий
момент на рабочем валу машины определяется
по формуле
,
где
Т
– крутящий момент, Нм;
Р
– мощность, кВт;
n
–
частота вращения, мин-1.
Переходя
от рабочего вала машины к следующему
валу привода (например к тихоходному
валу редуктора), крутящий момент
определится
,
где
Ттр
– крутящий момент на тихоходном валу
редуктора; Тм
– крутящий момент на рабочем валу
машины; uп
– передаточное число передачи от
рабочего вала машины к тихоходному валу
редуктора;
–
КПД передачи.
Определяем
крутящие моменты на валах
Проверка:
Определяем
частоты вращения валов привода
и
угловые скорости валов
Раздел 2. Выбор материалов и определение допускаемых напряжений
2.1 Выбор материалов и термообработки шестерен
В
производственных условиях при
проектировании и изготовлении редукторов
выбор материалов и назначение термической
обработки производится на базе опыта
конструкторов и технологов. Рекомендации
по применению марок стали для изготовления
различных деталей приведены в работе
[1].
В
курсовом проектировании при выборе
марок стали и термической обработки
для шестерен и колес можно руководствоваться
табл.4.
Для
лучшей приработки зубьев твердость
шестерни рекомендуется назначать больше
твердости колеса для прямозубых передач
на 10-15
единиц по шкале НВ.
Для косозубых передач твердость шестерни
должна быть еще больше на 50-70НВ
(для улучшения несущей способности
передачи).
Для
передач, к размерам которых не предъявляют
высоких требований, следует применять
дешевые марки сталей типа 40,
40Х.
Для колес открытых передач большого
диаметра (D500
мм)
применить стальное литье (35Л,
40Л, 45Л, 40ГЛ,
термообработка – нормализация, улучшение)
в паре с кованной шестерней из стали
соответствующей марки.
Таблица
4
Предпочтительные
марки сталей
|
Термическая |
Твердость |
Диаметр |
||||
|
любой |
315 |
200 |
125 |
80 |
||
|
Ширина |
||||||
|
любой |
200 |
125 |
80 |
50 |
||
|
Нормализация, |
НВ
НВ
НВ |
45 – – |
45 35ХМ – |
45 45Х 35ХМ |
45 45 40Х |
45 45 45 |
|
Объемная |
НRC |
– |
– |
35ХМ |
35ХМ |
35ХМ |
|
Поверхностная |
НRC |
– |
– |
35ХМ |
35ХМ |
35ХМ |
|
ТВЧ |
НRC |
– |
– |
50ХМ |
50ХМ |
50ХМ |
|
Цементация |
НRC |
– |
– |
20ХН2М |
20ХН2М |
20ХН2М |
|
Нитроцементация |
НRC |
– |
– |
25ХГТ |
25ХГТ |
25ХГТ |
|
Азотирование |
НRC |
– |
– |
40ХН2МА |
40ХН2МА |
40ХН2МА |
|
В |
По
рекомендациям [1] принимаем следующие
марки сталей: для шестерни сталь 35ХМ
твердостью 35-45
HRC
(объемная закалка);
для колеса сталь 40Х
твердостью 270-300
НВ (улучшение).
Средние твердости зубьев шестерни и
колеса определятся
По
графику 1 находим
Рис.1.
График соотношения твердостей, выраженных
в единицах HB
и HRC.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Download Article
Download Article
You likely know that if you push or pull on an object (exert force), it will move a distance. The distance it moves depends on how heavy the object is and how much force you apply. However, if the object is fixed at some point (called the “rotational point” or “axis”), and you push or pull on the object at some distance from that point, the object will instead rotate around that axis. The magnitude of that rotation is torque (τ), expressed in newton-meters (N∙m). The most basic way to calculate torque is to multiply the Newtons of force exerted by the meters of distance from the axis. There’s also a rotational version of this formula for 3-dimensional objects that uses the moment of inertia and angular acceleration. Calculating torque is a physics concept requiring an understanding of algebra, geometry, and trigonometry.[1]
-
1
Find the length of the moment arm. The distance from the axis or rotational point to the point where force is applied is called the moment arm. This distance is typically expressed in meters (m).[2]
- Since torque is a rotational force, this distance is also a radius. For this reason, you’ll sometimes see it represented with an “r” in the basic torque equation.
-
2
Work out the force being applied perpendicular to the moment arm. The force applied perpendicular to the moment arm produces the greatest torque. The simplest torque equation assumes the force is being applied perpendicular to the moment arm.[3]
- In torque problems, you’ll typically be given the magnitude force. However, if you have to work it out yourself, you’ll need to know the mass of the object and the acceleration of the object in m/s2. According to Newton’s Second Law, force is equal to mass times acceleration (
).
Advertisement
- In torque problems, you’ll typically be given the magnitude force. However, if you have to work it out yourself, you’ll need to know the mass of the object and the acceleration of the object in m/s2. According to Newton’s Second Law, force is equal to mass times acceleration (
-
3
Multiply the force times the distance to find the torque. The basic formula for torque is
, where torque is represented by the Greek letter tau (τ) and equals the force (F) times the distance (or radius, r). If you know the magnitude of the force (in Newtons) and the distance (in meters), you can solve for the torque, expressed in newton-meters (N∙m).[4]
- For example, suppose you have a force perpendicular to your object exerting 20 Newtons of force on the object 10 meters from the axis. The magnitude of the torque is 200 N∙m:
- For example, suppose you have a force perpendicular to your object exerting 20 Newtons of force on the object 10 meters from the axis. The magnitude of the torque is 200 N∙m:
-
4
Show the direction of the force with positive or negative torque. You now know the magnitude of the torque, but you don’t know if it’s positive or negative. This depends on the direction of the rotation. If the object is rotating counterclockwise, the torque is positive. If the object is rotating clockwise, the torque is negative.[5]
- For example, if the object is moving clockwise and the magnitude of the torque is 200 N∙m, you would express this as -200 N∙m of torque. No sign is necessary if the magnitude of the torque is positive.
- The value given for the magnitude of the torque remains the same. If a negative sign appears before the value, it simply means that the object in question is rotating clockwise.
-
5
Total individual torques around a given axis to find the net torque (Στ). It’s possible to have more than one force acting on an object at a different distance from the axis. If one force is pushing or pulling in the opposite direction of the other force, the object will rotate in the direction of the stronger torque. If the net torque is zero, you have a balanced system. If you’re given the net torque but not some other variable, such as the force, use basic algebraic principles to solve for the missing variable.[6]
Advertisement
-
1
Start with the distance of the radial vector. The radial vector is the line that extends from the axis or point of rotation. It could also be any object, such as a door or the minute-hand of a clock. The distance to measure for the purposes of calculating torque is the distance from the axis to the point where the force is applied to rotate the vector.[7]
- For most physics problems, this distance is measured in meters.
- In the torque equation, this distance is represented by “r” for radius or radial vector.
-
2
Work out the amount of force being applied. In most torque problems, this value will also be given to you. The amount of force is measured in Newtons and will be applied in a particular direction. However, rather than being perpendicular to the radial vector, the force is applied at an angle, giving you a radial vector.[8]
- If you’re not provided with the amount of force, you would multiply mass times acceleration to find the force, which means you would need to be given those values. You might also be given the torque and told to solve for the force.
- In the torque equation, force is represented by “F.”
-
3
Measure the angle made by the force vector and the radial vector. The angle you measure is the one to the right of the force vector. If the measurement isn’t provided for you, use a compass to measure the angle. If the force is being applied to the end of the radial vector, extend the radial vector out in a straight line to get your angle.[9]
- In the torque equation, this angle is represented by the Greek letter theta, “θ.” You’ll typically see it referred to as “angle θ” or “angle theta.”
-
4
Use your calculator to find the sine of the angle θ. In the torque equation, you multiply the distance of the radial vector and the amount of force with the sine of the angle you just measured. Put the angle measurement into your calculator, then press the “sin” button to get the sine of the angle.[10]
- If you were determining the sine of the angle by hand, you would need the measurements for the opposite side and the hypotenuse side of a right triangle. Since most torque problems don’t involve making exact measurements, however, you shouldn’t have to worry about this.
-
5
Multiply the distance, force, and sine to find the torque. The full formula for torque when you have angled force is
. The result is expressed in newton-meters (N∙m).[11]
- For example, suppose you have a radial vector 10 meters long. You’re told that 20 Newtons of force is being applied to that radial vector at a 70° angle. You would find that the torque is 188 N∙m:
- For example, suppose you have a radial vector 10 meters long. You’re told that 20 Newtons of force is being applied to that radial vector at a 70° angle. You would find that the torque is 188 N∙m:
Advertisement
-
1
Find the moment of inertia. The amount of torque required to move an object with angular acceleration depends on the distribution of the object’s mass, or its moment of inertia, expressed in kg∙m2. When the moment of inertia isn’t provided, you can also look it up online for common objects.[12]
-
2
Determine the angular acceleration. If you’re trying to find torque, the angular acceleration will typically be given to you. This is the amount, in radians/s2, that the object’s velocity is changing as it rotates.[13]
- Remember that the angular acceleration can be zero if the object is moving at a constant speed and is neither speeding up nor slowing down.
-
3
Multiply the moment of inertia by the angular acceleration to find the torque. The full formula for torque using the moment of inertia and the angular acceleration is
, where “τ” stands for torque, “I” stands for the moment of inertia, and “α” stands for the angular acceleration. If you’re trying to find torque, simply multiply the moment of inertia and the angular acceleration to get your result. As with other equations, if you’re trying to find one of the other values, you can re-order the equation using common algebraic principles.[14]
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
What is the formula to find the torque from the weight?
Tiagoroth
Community Answer
Torque is measured in Newton meters and is calculated by N·m = (kg*m²)/s². Manipulating the formula to find mass, we get kg = (N·m*s²)/m².
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
The equation for torque is very similar to the equation for work (the physical force required for an object to move). However, with work, the force is parallel to the distance, whereas, with torque, the force is perpendicular to the distance vector.[15]
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
-
Calculating torque requires knowledge of advanced algebraic concepts, geometry, and trigonometry. If you’re not strong in these areas, you might want to refresh your knowledge before you attempt torque calculations.
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
To calculate torque, start multiplying the mass of the object exerting force by the acceleration due to gravity, which is 9.81. When the force is clockwise, its torque is negative, and when it’s moving counterclockwise, it’s positive. If more than one force is present, add up all the torques to get the net torque of the combined forces. For tips on how to calculate torque using angular acceleration, read on!
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 205,854 times.
Did this article help you?
расчет крутящего момента на валу (мощность и обороты)
Крутящий момент М (Нм), который требуется передать гидравлическому насосу от двигателя может быть вычислен с использованием следующих параметров:
1. Скорость вращения вала насоса n, для электродвигателей переменного тока это обычно – 960, 1370, 1450 или 2850 оборотов в минуту
2. Мощность N (кВт), это может находиться в пределах от 0.25 до 55 кВт
Затем нажмите «M», чтобы вычислить.
Если вы хотите купить расчет крутящего момента на валу (мощность и обороты) , вы можете:
Ещё из раздела расчет гидропривода
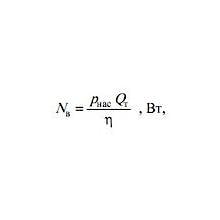
Этот калькулятор позволяет Вам вычислить три параметра, важные для проектирования гидравлической станции: – скорость потока Q (л/мин); – мощность N (кВт); – давление P (бар). Чтобы вычислить потребную мощность N (кВт) , Вы должны ввести следующие …
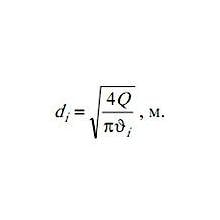
Для правильного расчета должно быть известно назначение трубопровода: всасывающая магистраль, напорная или сливная. Справочник по допустимой скорости жидкости в пределах этих типов магистралей приведен ниже. Расчетная скорость жидкости (м/с) должна …

Если известны геометрические размеры цилиндра, то можно вычислить площади поршня и объемы полостей цилиндра. Если известно давление гидравлической системы, то дополнительно можно вычислить усилие при выдвижении и втягивании штока. Мощность и …
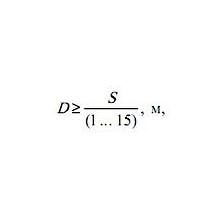
Здесь Вы можете вычислить геометрический размер цилиндра, зная необходимое усилие и рабочее давление гидроситемы. Общее усилие (Fst), Кг Количество цилиндров Давление ( P ), бар Диаметр поршня цилиндра ( fi ), мм Длина хода ( L ), мм Время …
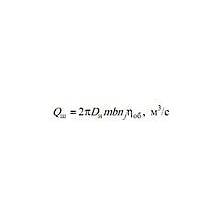
Этот калькулятор позволяет Вам вычислить или подачу Q (л/мин) или объем насоса Vg (cm3). Чтобы вычислить подачу насоса Q (l/min) , Вы должны ввести следующие данные: 1. Скорость вращения вала насоса n, для электродвигателей переменного тока это …
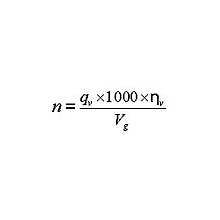
Для того чтобы вычислить количество оборотов гидромотора n (rpm), Вы должны знать следующие параметры 1) Подача насоса Q (л/мин), которая подается к гидромотору 2) коэффициент объемных потерь (КПД) , для гидромоторов он находится в диапазоне …
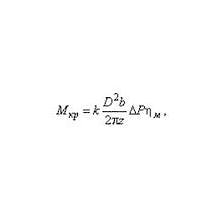
Крутящий момент на валу гидромотора М (кгм) может быть вычислен с использованием следующих параметров: 1. Давление P (бар). 2. Коэффициент объемных потерь, для гидромоторов он находится в диапазоне 0.85-0.95. 3. Объем гидромотора Vg, задается в …
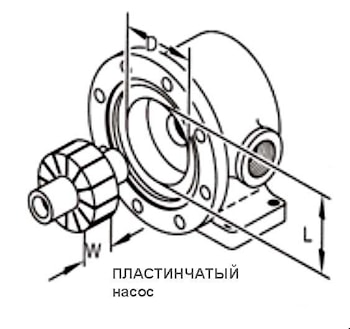
Этот калькулятор позволяет вычислить объемную подачу пластинчатого насоса за один оборот по геометрическим размерам. Тип Ширина ( W ), Диаметр ( D ), Длина ( L ) …
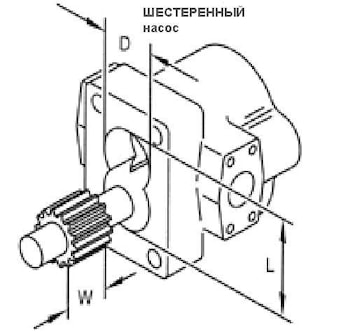
Данный калькулятор позволяет вычислить объемную подачу шестеренного насоса по его геометрическим размерам. Для этого необходимо замерить 3 размера в сантиметрах, в результате вычисления получается подача насоса с см3 за один оборот. Можно измерять в …
§3. ОПРЕДЕЛЕНИЕ ВРАЩАЮЩИХ МОМЕНТОВ НА ВАЛАХ
Случай 1 (см. рис. 1.1).
Момент на приводном валу (Н · м)

где Ft — окружная сила, Н, на барабане или
тяговых звездочках; D6 и D3B —
диаметр барабана, м, делительный диаметр тяговых звездочек, м. Момент на
тихоходном валу редуктора (Н · м)
где ип
и ηπ —
передаточное число и КПД цепной или ременной передачи, расположенной после
редуктора; ηοπ — КПД опор
приводного вала. При отсутствии такой передачи в схеме привода
где ηΜ — КПД
муфты, соединяющей вал редуктора и приводной вал. Момент на промежуточном валу
редуктора (Н · м)
где η3Τ — КПД зубчатой передачи тихоходной ступени. Момент на
быстроходном валу редуктора (Н · м)
гДе
Лз.б — КПД зубчатой
передачи быстроходной ступени. Для одноступенчатой передачи
Случай 2
(см. рис. 1.2). Момент Гвых приведен в задании. Момент на тихоходной
ступени Тт=Тъых.
Моменты на промежуточном и быстроходном валах определяют по
формулам (1.17), (1.18), (1.19).
Случай 3 (см.
рис. 1.2). Мощность электродвигателя Рэ
(кВт) приведена в задании. Частота вращения вала электродвигателя пэ (об/мин) определена в § 1. Момент на валу
электродвигателя (Н · м)
Момент на быстроходном валу передачи (Н · м)
где ип и
ηπ—передаточное
число и КПД ременной (цепной) передачи, расположенной между электродвигателем и
редуктором (коробкой передач).
Если
в схеме привода отсутствует такая передача, момент на быстроходном валу
где ηΜ — КПД
муфты, соединяющей валы электродвигателя и редуктора (коробки передач).
Момент на промежуточном валу передачи (Н · м)
где иБ и
η3Β
— передаточное число и КПД быстроходной ступени.
Момент на тихоходном валу передачи (Н · м)
где η3Τ —
КПД тихоходной ступени передачи.
ГЛАВА 2 РАСЧЕТЫ ПЕРЕДАЧ
Расчеты
при курсовом проектировании должны выполняться с использованием вычислительной
техники. Эффективно выполнение расчетов на программируемых микрокалькуляторах
«Электроника» МК-52; МК-72; МК-61 и других типов. Для этих калькуляторов можно
составить программы расчета и хранить их в памяти калькулятора.
Расчет крутящего момента на валу
Расчет крутящего момента на валу электродвигателя
Крутящий момент напрямую зависит от мощности и числа оборотов двигателя в минуту.
- M = P х 9550 / N;
Где:
- P – это мощность двигателя в киловаттах (кВт);
- N – обороты вала в минуту;
- 9550=1000*60/(2*ПИ);
Расчет крутящего момента на валу онлайн
Мощность на валу двигателя, кВт:
Частота вращения вала двигателя, об/мин:
Крутящий момент:
Популярные сообщения из этого блога
Найти тангенс фи , если известен косинус фи
Калькулятор коэффициент мощности cos fi в tg fi Как найти тангенс фи, если известен косинус фи формула: tg φ = (√(1-cos²φ))/cos φ Калькулятор онлайн – косинус в тангенс cos φ: tg φ: Поделиться в соц сетях: Найти синус φ, если известен тангенс φ Найти косинус φ, если известен тангенс φ
Индекс Руфье калькулятор
Проба Руфье калькулятор онлайн. Первые упоминания теста относиться к 1950 году. Именно в это время мы находим первое упоминание доктора Диксона о “Использование сердечного индекса Руфье в медико-спортивном контроле”. Проба Руфье – представляет собой нагрузочный комплекс, предназначенный для оценки работоспособности сердца при физической нагрузке. Индекс Руфье для школьников и студентов. У испытуемого, находящегося в положении лежа на спине в течение 5 мин, определяют число пульсаций за 15 сек (P1); После чего в течение 45 сек испытуемый выполняет 30 приседаний. После окончания нагрузки испытуемый ложится, и у него вновь подсчитывается число пульсаций за первые 15 с (Р2); И в завершении за последние 15 сек первой минуты периода восстановления (Р3); Оценку работоспособности сердца производят по формуле: Индекс Руфье = (4(P1+P2+P3)-200)/10; Индекс Руфье для спортсменов Измеряют пульс в положении сидя (Р1); Спортсмен выполняет 30 глубоких приседаний в
Найти косинус фи (cos φ), через тангенс фи (tg φ)
tg фи=… чему равен cos фи? Как перевести тангенс в косинус формула: cos(a)=(+-)1/sqrt(1+(tg(a))^2) Косинус через тангенс, перевести tg в cos, калькулятор – онлайн tg φ: cos φ: ± Поделиться в соц сетях:





















