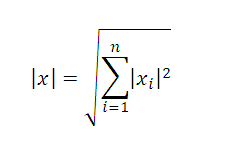Онлайн калькулятор для нахождения длины (нормы) вектора.
Найти нормированный вектор, норма вектора – длина вектора на линейном пространстве.
Построить вектор в двухмерном и трехмерном пространстве.
Скачать калькулятор
Рейтинг: 3.1 (Голосов 15)
×
Пожалуйста напишите с чем связна такая низкая оценка:
×
Для установки калькулятора на iPhone – просто добавьте страницу
«На главный экран»
Для установки калькулятора на Android – просто добавьте страницу
«На главный экран»
Сообщить об ошибке
Смотрите также
| Действия с векторами | Cкалярное произведение | Векторное произведение | Длина, модуль вектора | Угол между векторами |
| Векторный калькулятор | Сложение и вычитание | Разложить вектор по базису | Сумма векторов | Середина отрезка |
Норма вектораФормулы, примеры, калькулятор нормы вектора Определение 1. Норма вектора ( эвклидова норма, модуль вектора, длина вектора) x=(x1,x2, …xn) Пример 1. Найти норму вектора a = (5,-2,7) Решение. Подставляем координаты вектора, получаем норму вектора Как нормировать векторНормированный вектор – это единичный вектор по направлению. То есть, сохраняется информация только о направлении вектора: Для того чтобы получить нормированный вектор, необходимо каждую координату исходного вектора разделить на норму вектора. Пример 2. Нормировать вектор a = (5,-2,7) Решение. Подставляем координаты вектора, получаем нормированный вектор Проверить правильность вычисления нормы вектора, а также найти нормированный вектор можно с помощью калькулятора. |
Категория: Аналитическая геометрия | Просмотров: 12351 | | Теги: вектор | Рейтинг: 0.0/0 |
Unit Converter
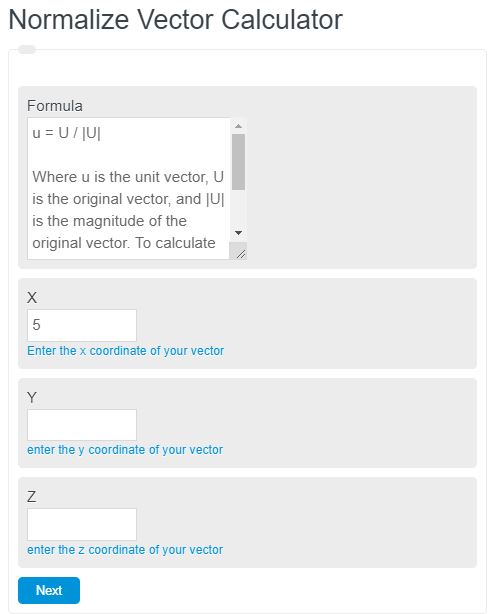
Enter any vector into the normalize vector calculator. The calculator will normalize this vector and display the unit vector.
- Vector Subtraction Calculator
- Vector Magnitude Calculator
- Unit Vector Calculator
- Resultant Vector Calculator
Normalizing a Vector Formula
The following formula is used to normalize a vector.
u = U / |U|
|U| = Square Root ( X^2 + Y^2+Z^2)
- Where U is the original vector
- |U| is the magnitude of the vector
- u is the unit vector
Normalize Vector Definition
A vector normalization is a process of finding the unit vector of a given vector.
How to normalize a vector?
How to normalize a vector?
- First, calculate the magnitude of the original vector
Using the formula above, calculate the magnitude of the original vector.
- Next, divide each component of the vector by the magnitude.
For example, for a vector x,y,z, divide x by the magnitude, y by the magnitude, and z by the magnitude. The results of those divisions are your unit vector values.
Example Problem:
In the following example, a vector of (5,6,10) is given.
First, the magnitude of the vector must bed calculated. Using the formula above:
|U| = sqrt( 5^2 + 6^2+10^2)
|U| = 12. 688
Next, divide each individual component of the vector by the magnitude to normalize the vector.
X = 5 / 12.688 = .394
Y = 6 / 12.688 = .472
Z = 10 / 12.688 = .788
So the final normalized vector would be (.394,.472,.788).
FAQ
What is normalizing a vector?
Normalizing a vector is the process of turning a vector into its unit vector. This process involves dividing a vector by its magnitude. The result is a vector with the same direction, but with a magnitude of 1.
Why would you normalize a vector?
Normalizing a vector can simply problems. For example, if you want to multiply two vectors A and B, you can actually multiply their unit vectors to get the direction, then multiply that answer by the magnitudes to get the resulting vector of A * B.

-
Customer Voice
-
Questionnaire
-
FAQ
-
Vector norm
| [0-0] / 0 | Disp-Num |
|
The message is not registered.

Thank you for your questionnaire.
Sending completion
To improve this ‘Vector norm Calculator’, please fill in questionnaire.
- Age
- Under 20 years old20 years old level
30 years old level40 years old level
50 years old level60 years old level or over
- Occupation
- Elementary school/ Junior high-school student
High-school/ University/ Grad studentA homemakerAn office worker / A public employee
Self-employed peopleAn engineerA teacher / A researcherA retired personOthers
- Useful?
- VeryUseful
A little Not at All
- Purpose of use?
- Comment/Request (Click here to report a bug).Bug report (Click here to report questionnaire.)
Calculation bug(Please enter information such as specific input values, calculation result, correct result, and reference materials (URL and documents).)
Text bug(Please enter information such as wrong and correct texts)
Your feedback and comments may be posted as customer voice.
- The hyperlink to [Vector norm]
Enter a vector to find the unit vector in the same direction.
Unit Vector:
Unit Vector:
Magnitude
Steps to Solve
Use the Unit Vector Formula
â = a / |a|
Step One: Solve the Magnitude
|a| = x² + y² + z²
Substitute Values and Solve
Enter vector coordinates above to see the solution here
Step Two: Divide by the Magnitude
Divide each vector component by the magnitude.
Substitute Values and Solve
Enter vector coordinates above to see the solution here
Learn how we calculated this below
scroll down
On this page:
-
Unit Vector Calculator
-
How to Find a Unit Vector
-
Unit Vector Formula
-
How to Use the Unit Vector Formula
How to Find a Unit Vector
A unit vector is a vector with a length, or magnitude, of 1. You can scale a vector to a unit vector by reducing its length to 1 without changing its direction.
This is often referred to as vector normalization.
Unit Vector Formula
To normalize a vector to a unit vector, use the following formula:
û = u / |u|
Thus, the unit vector û of vector u is equal to each component of vector u divided by its magnitude |u|.
How to Use the Unit Vector Formula
The first step to scale a vector to a unit vector is to find the vector’s magnitude. You can use the magnitude formula to find it.
|u|= x² + y² + z²
The magnitude |u| of vector u is equal to the square root of the sum of the square of each of the vector’s components x, y, and z.
Then, divide each component of vector u by the magnitude |u|. The resulting components form the unit vector.
For example, given a vector (3, 5, 8), let’s find the unit vector.
Start by solving the magnitude.
|u|= 3² + 5² + 8²
|u|= 9 + 25 + 64
|u|= 98
Then, divide each vector coordinate by the magnitude 98.
xû = 3 / √98 = 0.303
yû = 5 / √98 = 0.505
zû = 8 / √98 = 0.808
So, the unit vector û is (0.303, 0.505, 0.808).
û = (0.303, 0.505, 0.808)