В данной публикации мы рассмотрим, каким образом можно посчитать объем прямого кругового конуса и разберем примеры решения задач.
-
Формула вычисления объема
- 1. Через площадь основания и высоту
- 2. Через радиус основания и высоту
-
Примеры задач
Формула вычисления объема
1. Через площадь основания и высоту
Объем (V) конуса равняется одной третьей произведения его высоты на площадь основания:
![]()

2. Через радиус основания и высоту
Как мы знаем, основанием конуса является круг, площадь которого вычисляется по формуле: S = πR2.
Следовательно, формулу для вычисления объема конуса можно представить в виде:
![]()
Т.е. объем конуса равняется одной третьей произведения его высоты на число π и на радиус основания в квадрате.
Примечание: в расчетах значение числа π округляется до 3,14.
Формула для нахождения объема усеченного конуса представлена в отдельной публикации.
Примеры задач
Задание 1
Найдите объем конуса, если известна площадь его основания – 50,24 см2, а также, высота – 9 см.
Решение:
Применим первую формулу, подставив в нее заданные значения:
![]()
Задание 2
Высота конуса равна 7 см, а его радиус – 3 см. Найдите объем фигуры.
Решение:
Воспользовавшись второй, более расширенной, формулой получаем:![]()

{V=dfrac {1}{3} pi r^2 h}
Конус – это трехмерная фигура, в основании которой лежит круг. Чтобы найти объем конуса достаточно знать два параметра – высоту (h) и радиус основания (r).
Содержание:
- калькулятор объема конуса
- формула объема конуса через высоту и радиус
- формула объема конуса через площадь основания и высоту
- формула объёма усеченного конуса
- примеры задач
Если мы сравним формулу объема конуса с формулой объема цилиндра, то мы увидим, что объем конуса в 3 раза меньше объема цилиндра с той же высотой и радиусом основания.
Наш калькулятор может рассчитать объем конуса через радиус основания и высоту, площадь основания и высоту, а также объем усеченного конуса через его высоту и радиусы нижнего и верхнего оснований.
Кроме того объем конуса можено найти, подставив значения в формулы, приведенные ниже.
Формула объёма конуса через радиус и высоту
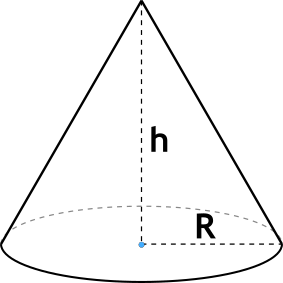
{V=frac {1}{3} pi r^2 h}
r – радиус основания конуса,
h – высота конуса
Формула объёма конуса через площадь основания и высоту
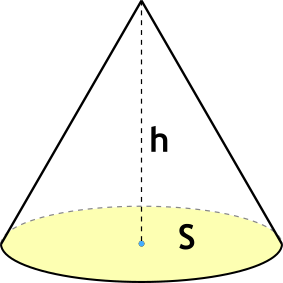
{V=frac {1}{3} S h}
S – площадь основания конуса,
h – высота конуса
Формула объёма усеченного конуса
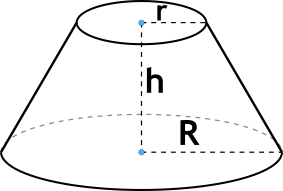
{V=frac {1}{3} pi h(r^2 + r R + R^2)}
h – высота усеченного конуса,
r – радиус меньшего основания усеченного конуса,
R – радиус большего основания усеченного конуса.
Примеры задач на нахождение объема конуса
Задача 1
Найдем объем конуса, высота которого 30см, а радиус основания 20см.
Решение
Подставим эти значения в формулу и произведем расчет:
V=dfrac {1}{3} pi r^2 h = dfrac {1}{3} cdot pi cdot 20^2 cdot 30 = dfrac {1}{3} cdot pi cdot 12000 = 400 pi : см^3 approx 12 566,37 : см^3
Ответ: {400 pi : см^3 approx 12 566,37 : см^3}
Проверить результат можно с помощью калькулятора .
Задача 2
Найдем объем конуса с высотой 3 см и диаметром основания 8 см².
Решение
Подставим эти значения в формулу и произведем расчет:
V=dfrac {1}{3} S h = dfrac {1}{3} cdot 8 cdot 3 = dfrac {1}{3} cdot 24 = 8 : см^3
Ответ: 8 см³
Воспользуемся калькулятором для проверки результата.
Задача 3
Найдите объем усеченного конуса радиусы оснований которого равны 1 см и 2 см, а высота равна 3 см.
Решение
Подставим высоту и радиусы оснований в формулу и произведем расчет:
V=dfrac {1}{3} pi h(r^2 + r R + R^2) = dfrac {1}{3} pi cdot 3 cdot (1^2 + 1 cdot 2 + 2^2) = dfrac {1}{3} pi cdot 3 cdot (1 + 2 + 4) = dfrac {1}{3} pi cdot 3 cdot 7 = dfrac {1}{3} pi cdot 21 = 7 pi : см^3 approx 21,99115 : см^3
Ответ: {7 pi : см^3 approx 21,99115 : см^3}
Проверим полученный ответ.
Конус – это тело в пространстве, образованное путем вращения прямоугольного треугольника вокруг одного из его катетов.
Онлайн-калькулятор объема конуса
Конус – это тело, образованное совокупностью всех лучей, исходящих из точки пространства и пересекающих плоскость.
Точка, из которой лучи исходят, получила название вершины конуса. В случае, когда основанием конуса является многоугольник, он превращается в пирамиду.
Рассмотрим некоторые важные понятия.
Образующей конуса называется отрезок, который соединяет любую точку границы основания конуса, с его вершиной.
Высотой конуса является перпендикуляр, который опущен из вершины к основанию тела.
Конус бывает нескольких типов:
Прямой, если его основание – одна из таких фигур, как эллипс или круг. Обязательным условием является проецирование вершины конуса в центр основания.
Косой – у него центр фигуры, которая находится в основании, не совпадает с проекцией вершины на это самое основание.
Круговой – отталкиваясь от названия, понятно, что в его основании лежит круг.
Усеченный – область конуса, лежащая между основанием и сечением плоскости, которая параллельна основанию и пересекает данный конус.
Формула объема прямого конуса
Объем прямого конуса можно рассчитать по следующей формуле:
V=13⋅Sосн⋅hV=frac{1}{3}cdot S_{text{осн}}cdot h
где SоснS_{text{осн}} – площадь основания конуса;
hh – высота конуса.
Рассмотрим несколько примеров.
Найдите объем конуса, если его образующая ll равна 5см5text {см}, а радиус основания RR, которым является круг, равен 3 см3text{ см}.
Решение
l=5l=5
R=3R=3
Сперва найдем высоту конуса hh. Включим его в прямоугольный треугольник, гипотенузой которого является образующая. По теореме Пифагора:
l2=h2+R2l^2=h^2+R^2
Отсюда, hh:
h=l2−R2h=sqrt{l^2-R^2}
h=52−32h=sqrt{5^2-3^2}
h=25−9h=sqrt{25-9}
h=16h=sqrt{16}
h=4h=4
Затем находим площадь основания конуса. Это площадь круга радиуса RR:
Sосн=π⋅R2=π⋅32≈28.26S_{text{осн}}=picdot R^2=picdot3^2approx28.26
Последние вычисления — нахождение объема конуса по формуле:
V=13⋅Sосн⋅h≈13⋅28.26⋅4≈37.68 см3V=frac{1}{3}cdot S_{text{осн}}cdot happroxfrac{1}{3}cdot 28.26cdot 4approx37.68text{ см}^3
Ответ: 37.68 см3.37.68text{ см}^3.
Известен диаметр круга DD лежащего в основании конуса, равен он 8 см8text{ см}. Высота конуса равна 9 см9text{ см}. Найдите его объем.
Решение
D=8D=8
h=9h=9
Найдем радиус RR круга через его диаметр:
R=12⋅D=82=4R=frac{1}{2}cdot D=frac{8}{2}=4
Площадь этого круга и есть основание нашего конуса:
Sосн=π⋅R2=π⋅42≈50.24S_{text{осн}}=picdot R^2=picdot4^2approx50.24
Сам объем равен:
V=13⋅Sосн⋅h≈13⋅50.24⋅9≈150.72 см3V=frac{1}{3}cdot S_{text{осн}}cdot happroxfrac{1}{3}cdot 50.24cdot 9approx150.72text{ см}^3
Ответ: 150.72 см3.150.72text{ см}^3.
Вам нужно решить задачу по алгебре? Наши эксперты помогут вам!
Тест на тему “Объем конуса”
Чтобы найти объем конуса необходимо произвести дополнительные построения.

Построим вписанную в конус правильную n-угольную пирамиду и опишем вокруг данного конуса правильную n-угольную пирамиду.
Вписанная пирамида содержится в конусе. Из этого следует, что ее объем не больше объема конуса.
Описанная пирамида содержит конус, а это значит, что ее объем не меньше объема конуса.
Впишем в основание вписанной пирамиды окружность.
Если радиус вписанного правильного n-угольника равен R, то радиус вписанной в него окружности будет равен:


Объем вписанной пирамиды вычисляется по формуле: 
где S – основание пирамиды.
Площадь данного круга вычисляется по формуле: 
Площадь основания вписанной пирамиды не меньше площади круга, содержащегося в ней
Поэтому утверждение, что объем вписанной в конус пирамиды не меньше  верно.
верно.
А следовательно, мы может утверждать, что объем конуса, содержащий эту пирамиду будет больше или равен 
V≥
Теперь опишем окружность вокруг основания описанной вокруг конуса пирамиды.
Радиус этой окружности будет равен: 
Площадь данного круга вычисляется по формуле: 
Основание описанной пирамиды содержится в круге описанном вокруг него. Поэтому площадь основания пирамиды не больше 
Поэтому утверждение,что объем описанной пирамиды не больше  верно.
верно.
А следовательно, мы может утверждать, что объем конуса, содержащий в эту пирамиду будет меньше или равен 

Два полученных неравенства равны при любом n. Если  то
то 
Тогда из первого неравенства следует, что V≥
Из второго неравенства 
Отсюда следует, что

Объем конуса равен одной трети произведения радиуса на высоту.
![]() Пример расчета объема конуса
Пример расчета объема конуса
Найти объем конуса, если его радиус основания равен 3 см, а образующая 5 см.
Объем конуса вычисляется по формуле:

Для того, чтобы воспользоваться данной формулой необходимо найти высоту конуса. Образующая конуса, его высота и радиус основания образуют прямоугольный треугольник. Воспользовавшись теоремой Пифагора имеем:

Отсюда:

Подставим значение радиуса и высоты в формулу объема конуса.
Имеем:

Volume of a cone can be described as the space occupied by the cone or it is the capacity of the cone. Cone is a 3-D object having a circular flat base and a pointed top called an apex or vertex.
A cone is a solid three-dimensional geometric object with a circular base and a sharp edge at the top known as the apex. It is a form with a curving top and a round base. A cone has one face, one vertex, and no edges. Its slant height is the length of the line segment from the peak of the cone to any point on the circle of the cone’s base.
Volume of the Cone is the total space occupied by the cone in 3-D space. Let’s learn more about the volume of the cone its derivation and others in this article.
What is the Volume of a Cone?
A cone’s volume is defined as the amount of space or capacity it fills. The volume of a cone is measured in cubic units such as cm3, m3, in3, and so on. By rotating a triangle around any of its vertices, a cone can be produced. Volume of a cone can also be measured in litres.

Volume of a Cone Formula
A cone is a solid three-dimensional form having a circular base. It’s got a curved surface. The perpendicular height is the distance from the base to the vertex. A cone may be divided into two types: right circular cones and oblique cones. The vertex of the right circular cone is vertically above the centre of the base, but the vertex of the oblique cone is not vertically above the centre of the base.
The formula for the volume of a cone is given:
V =
where,
r is the radius of the cone,
h is the height of the cone,
π is constant with value 22/7 or 3.14Also, the relationship between the cone’s volume and slant height by applying Pythagoras’ theorem to it is given by,
h2 + r2 = L2
h = √(L2 – r2)
Hence, the volume of cone in terms of its slant height is given by,
V =
where,
r is the radius of the cone,
L is the slant height of the cone,
π is constant with value 22/7 or 3.14
Click here for, Surface area of a Cone
Volume of a Cone Derivation
Suppose we have a cone with a circular base whose radius is r and height is h.

We know that the volume of a cone is equal to one-third of the volume of a cylinder having the same base radius and height.
So, the volume becomes,
V = 1/3 x Circular Base area x Height
= 1/3 x πr2 x h
= πr2h/3
This derives the formula for the volume of a cone.
How to Find the Volume of a Cone?
Let’s consider an example to determine the volume of a cone.
Example: Determine the volume of a cone if the radius of its circular base is 3 cm and the height is 5 cm.
Step 1: Note the radius of the circular base (r) and the height of the cone (h).
Here, the radius is 3 cm and the height is 5 cm.
Step 2: Calculate the area of the circular base = πr2. Substitute the value of r and π in the given equation,
i.e., 3.14 × (3)2 = 28.26 cm2.
Step 3: We know that the volume of a cone is (1/3) × (area of the circular base) × height of the cone.
Then, substitute the values in the equation = (1/3) × 28.26 × 5 = 47.1 cm3.
Step 4: Hence, the volume of the given cone is 47.1 cm3.
Using the steps discussed above the volume of a cone can be calculated.
Volume of Frustum of Cone
The frustum is the sliced part of a cone, and the volume of the frustum of the cone is the amount of liquid any frustum can hold. So for calculating the volume, we need to find the difference in the volumes of the two cones.
Know more on Frustum of Cone
Volume of Frustum of Cone Formula
The formula for finding the volume of the frustum of a cone is given by subtracting the volume of two cones.
Study the given figure for finding the volume of the frustum.

From the above figure, we have,
The total height H’ = H+h
The total slant height L = l1 +l2
The radius of the cone = r and the radius of the sliced cone = r’
Now the volume of the bigger cone = 1/3 π r2 H’ = 1/3 π r2 (H+h)
Volume of the smaller cone = 1/3 π(r’)2h. The volume of the frustum can be calculated by the difference between the two cones, i.e.
Volume of Frustum = 1/3 π r2 H’ -1/3 π(r’)2h
= 1/3π r2 (H+h) – 1/3 π(r’)2h
= 1/3 π [ r2 (H+h) – (r’)2 h ] ………(1)
Using the properties of similar triangles in Δ QPS and Δ QAB. we have,
r/ r’ = H+h / h
H+h = (rh)/r’
Substituting the value of H+h in the formula for the volume of frustum we get,
Volume of frustum = 1/3 π [r2 (rh/r’) – (r’)2 h]
= 1/3 π [r3h/r’ – (r’)2 h]
= 1/3 π h (r3/r – (r’)2)
= 1/3 π h [{r3 – (r’)3} / r]
Volume of Frustum of Cone = 1/3 π h [{r3 – (r’)3} / r]
where,
r is the radius of the lower base of the frustum of cone,
r’ is the radius of the upper base of the frustum of cone,
h is the height of the smaller cone,
π is constant with value 22/7 or 3.14
Volume of Cone with Height and Radius
The volume of the cone if its height(h) and radius(r) are given is calculated using the formula,
V = (1/3)πr2h cubic units
Volume of Cone with Height and Diameter
As we know,
r = d/2
where,
r is the radius of the base of the cone
d is the diameter of the base of the cone
The volume of the cone if its height(h) and diameter(d) are given is calculated using the formula,
V = (1/12)πd2h cubic units
Volume of Cone with Slant Height
For a cone with height ‘h’ and radius ‘r’ the slant height ‘L’ of the cone is given by the formula,
h2 + r2 = L2
h = √(L2 – r2)
Then the volume of the cone in terms of slant height is,
V = (1/3)πr2h
V = (1/3)πr2√(L2 – r2)
where,
r is the radius of the cone
L is the Slant Height
Volume of a cone (If Radius and Height are doubled)
Suppose,
Radius of the cone (r) = 2r
Height of the Cone (h) = 2h
Then the volume of a cone is given as,
Volume of a cone = (1/3)π(2r)2(2h) cubic units
V = (⅓)π(4r2)(2h)
V = (8/3)πr2h
Thus, volume of a cone becomes 8 times the original volume i.e. V = (8/3)πr2h, when its radius and height are doubled.
Volume of a cone (If Radius and Height are Halved)
Suppose,
Radius of the cone (r) = r/2
Height of the Cone (h) = h/2
Then the volume of a cone is given as,
Volume of a cone = (1/3)π(r/2)2(h/2) cubic units
V = (⅓)π(r2/4)(h/2)
V = (1/24)πr2h
Thus, volume of a cone becomes 1/8 times the original volume i.e. V = (1/24)πr2h, when its radius and height are halved.
Related Resources
- Surface Area of a Cone
- Volume of Sphere
Solved Example on Volume of a Cone
Example 1. Find the volume of a cone for a radius of 7 cm and height of 14 cm.
Solution:
We have, r = 7 and h = 14.
Volume of cone = 1/3 πr2h
= (1/3) (22/7) (7) (7) (14)
= (1/3) (7) (7) (2)
= 32.66 cm3
Example 2. Find the volume of a cone for a radius of 5 cm and height of 9 cm.
Solution:
We have, r = 5 and h = 9.
Volume of cone = 1/3 πr2h
= (1/3) (3.14) (5) (5) (9)
= (3.14) (5) (5) (3)
= 235.49 cm3
Example 3. Find the volume of a cone for a radius of 7 cm and height of 12 cm.
Solution:
We have, r = 7 and h = 12.
Volume of cone = 1/3 πr2h
= (1/3) (22/7) (7) (7) (12)
= (22) (7) (4)
= 616 cm3
Example 4. Find the volume of a cone for a radius of 8 cm and height of 15 cm.
Solution:
We have, r = 8 and h = 15.
Volume of cone = 1/3 πr2h
= (1/3) (22/7) (8) (8) (15)
= (1/3) (22/7) (8) (8) (5)
= 335.02 cm3
Example 5. Find the volume of a cone for a diameter of 24 cm and a slant height of 13 cm.
Solution:
We have, 2r = 24
r = 24/2
r = 12
Also, l = 13.
Volume of cone = 1/3 πr2 √(l2 – r2)
= (1/3) (22/7) (12) (12) (√(132 – 122)
= (1/3) (22/7) (12) (12) (5)
= 754.28 cm3
Example 6. Find the volume of a cone for a diameter of 16 cm and a slant height of 10 cm.
Solution:
We have, 2r = 16
r = 16/2
r = 8
Also, l = 10.
Volume of cone = 1/3 πr2 √(l2 – r2)
= (1/3) (22/7) (8) (8) (√(102 – 82)
= (1/3) (22/7) (8) (8) (6)
= 402.048 cm3
Example 7. Find the volume of a cone for the height of 8 cm and the slant height of 17 cm.
Solution:
We have h = 8 and l = 10.
Find the value of r.
r = √(l2 – h2)
= √(172 – 82)
= √(289 – 64)
= 15
Volume of cone = 1/3 πr2h
= (1/3) (22/7) (15) (15) (8)
= (1/3) (22/7) (5) (15) (8)
= 1884.6 cm3
FAQs on Volume of a Cone
Q1: What is volume of a cone?
Answer:
Volume of a cone is defined as the total capacity of the liquid a cone can hold in 3-dimension. It is the total space occupied by the cone.
Q2: Why cone volume is 1/3 of a cylinder?
Answer:
Experimentally it is clear that a cylinder can hold three times the volume of liquid as compared to a cone of similar dimensions. Thus, the volume of a cone is 1/3 of a cylinder
Q3: How to find volume of a cone with slant height?
Answer:
The volume of the cone if its slant height is given is calculated using the formula,
V = (1/3)πr2√(L2 – r2)
where,
r is the radius of the cone
L is the Slant Height
Q4: What is the formula for the total surface area of a cone?
Answer:
Total surface area of a cone is given by the formula
TSA of Cone = πr(l + r) square units
where,
r is the radius of the circular base
l is the slant height of the cone
Q5: What is the formula for the volume of a cone?
Answer:
Volume of a cone is given by the formula
Volume of Cone = ⅓ πr2 h cubic units
where,
r is the radius of the circular base
h is the height of the cone
Q6: What is the relation between the Volume of the cylinder and the volume of a cone with similar dimensions?
Answer:
- Volume of a cylinder = πr2h
- Volume of a cone = 1/3πr2h
Thus from the above formulas it is clear that one-third of the volume of a cylinder is equal to the volume of a cone, having the same radius and height.
Q7: What is the formula for the slant height of a cone?
Answer:
The slant height(l) of a cone is calculated using the formula,
l = √(h2 + r2)
where,
h is the height of the cone
r is the radius of the circular base
Q8: How to find the volume of a cone, if the height and diameter of the cone are given?
Answer:
We know that,
Volume of a Cone = (1/3)πr2h cubic units
where
r is radius and h is heightSince,
(radius)r = (diameter)d/2The volume of a cone becomes
V = (1/3)π(d/2)2h cubic units
V = (1/12)πd2h cubic units
Hence, this formula for the volume of a cone if its height(h) and diameter(d) are given.
