У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Объём (значения).
| Объём | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Размерность | L3 |
| Единицы измерения | |
| СИ | м3 |
| СГС | см3 |
Объём — количественная характеристика пространства, занимаемого телом или веществом. Объём тела определяется его формой и линейными размерами. Основное свойство объёма — аддитивность , то есть объём любого тела равен сумме объёмов его (непересекающихся) частей[1].
Единица объёма в СИ — кубический метр; от неё образуются производные единицы — кубический сантиметр, кубический дециметр (литр) и т. д. В разных странах для жидких и сыпучих веществ используются также различные внесистемные единицы объёма — галлон, баррель и др.
В формулах для обозначения объёма традиционно используется заглавная латинская буква V, являющаяся сокращением от лат. volume — «объём», «наполнение».
Слово «объём» также используют в переносном значении для обозначения общего количества или текущей величины. Например, «объём спроса», «объём памяти», «объём работ». В изобразительном искусстве объёмом называется иллюзорная передача пространственных характеристик изображаемого предмета художественными методами.
Вычисление объёма[править | править код]
На практике приблизительный объём тела, в том числе сложной формы, можно вычислить по закону Архимеда, погрузив это тело в жидкость: объём вытесненной жидкости будет равен объёму измеряемого тела.
Математически[править | править код]
Для объёмов тел простой формы имеются специальные формулы. Например, объём куба с ребром 

Объём тела сложной формы вычисляется разбиением этого тела на отдельные части простой формы и суммированием объёмов этих частей. В интегральном исчислении объёмы частей, из которых складывается объём всего тела, рассматриваются как бесконечно малые величины.
Сводка формул[править | править код]
| Форма тела | Формула для вычисления объёма | Обозначения |
|---|---|---|
| Куб | 
|

|
| Прямоугольный параллелепипед | 
|

|
| Призма
(B: площадь основания) |

|
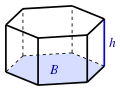
|
| Пирамида
(B: площадь основания) |

|

|
| Параллелепипед | 
|

|
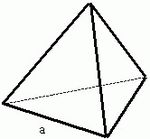
| Тетраэдр | 
|

|
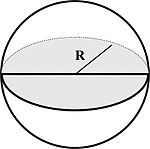
| Шар | 
|
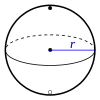
|
| Эллипсоид | 
|

|
| Прямой круговой цилиндр | 
|

|
| Конус | 
|
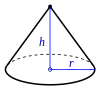
|
| Тело вращения | 
|

|
Через плотность[править | править код]
Зная массу (m) и среднюю плотность (ρ) тела, его объём рассчитывают по формуле: 
Единицы объёма жидкости[править | править код]
- 1 литр = 1 кубический дециметр = 1,76 пинты = 0,23 галлона
Русские[2][править | править код]
- Ведро = 12,3 литра
- Бочка = 40 вёдер = 492 литра
Английские[править | править код]
- 1 пинта = 0,568 литра
- 1 кварта (жидкостная) = 2 пинтам = 1,136 литра
- 1 галлон = 8 пинтам = 4,55 литра
- 1 галлон (амер.) = 3,785 литра
Античные[править | править код]
- Котила = 0,275 литра
Немецкие[править | править код]
- Шоппен
Древнееврейские[3][править | править код]
- Эйфа = 24,883 литра
- Гин = 1/6 эйфы = 4,147 литра
- Омер = 1/10 эйфы = 2,4883 литра
- Кав = 1/3 гина = 1,382 литра
Единицы объёма сыпучих веществ[править | править код]
Русские[править | править код]
- Четверик = 26,24 литра (1 пуд зерна)
- Гарнец = 3,28 литра
- Четверть = 1/4 ведра = 3,075 литра
- Штоф = 1/8 ведра = 1,54 литра
- Кружка = 1/10 ведра = 1,23 литра
- Бутылка (винная) = 1/16 ведра = 0,77 литра
- Бутылка (пивная) = 1/20 ведра = 0,61 литра
- Чарка = 1/10 кружки = 0,123 литра
- Шкалик (косушка) = 1/2 чарки = 0,0615 литра
Английские[править | править код]
- 1 бушель = 8 галлонов = 36,36872 литра
- 1 баррель = 163,65 литра
Прочие единицы[править | править код]
- 1 унция (англ.) = 2,841⋅10−5 м³
- 1 унция (амер.) = 2,957⋅10−5 м³
- 1 кубический дюйм = 1,63871⋅10−5 м³
- 1 кубический фут = 2,83168⋅10−2 м³
- 1 кубический ярд = 0,76455 м³
- 1 кубическая астрономическая единица =3,348⋅1024 км³
- 1 кубический световой год = 8,466⋅1038 км³
- 1 кубический парсек = 2,938⋅1040 км³
- 1 кубический килопарсек = 1 000 000 000 пк³ = 2,938⋅1049 км³
Примечания[править | править код]
- ↑ Математическая энциклопедия, 1982, с. 1149.
- ↑ Меры объёма в Древней Руси. Дата обращения: 17 ноября 2013. Архивировано 14 июля 2014 года.
- ↑ «ТЕГИЛАТ ГАШЕМ» — ISBN 965-310-008-4
Литература[править | править код]
- Объём // Математическая энциклопедия (в 5 томах). — М.: Советская Энциклопедия, 1982. — Т. 3.
- Объём // Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона : в 86 т. (82 т. и 4 доп.). — СПб., 1890—1907.
Ссылки[править | править код]
- Формулы объёма и программы для расчета объёма. Дата обращения: 26 ноября 2020. Архивировано 24 ноября 2020 года.
Загрузить PDF
Загрузить PDF
Объем фигуры представляет собой занимаемое этой фигурой трехмерное пространство.[1]
Представьте себе объем как количество жидкости (или воздуха, или песка), которым можно заполнить данную фигуру. Объем измеряется в кубических единицах (мм3, см3, м3).[2]
Эта статья расскажет вам, как вычислять объем шести трехмерных фигур. Вы можете заметить, что многие формулы для вычисления объема схожи, что упрощает их запоминание.
-
1
Куб – это трехмерная фигура, которая имеет шесть одинаковых квадратных граней, то есть все ее стороны (ребра) равны.[3]
- Например, игральная кость – это куб.
-
2
Формула нахождения объема куба: V = s3, где V – объем, а s – длина ребра.
- Возведение в куб аналогично следующему умножению: s3 = s * s * s
-
3
Найдите длину стороны (ребра) куба. Она будет дана в задаче или вам нужно измерить ее (линейкой или рулеткой). Так как ребра куба равны, измеряйте любое ребро.
- Если вы не уверены, что ваша фигура является кубом, измерьте каждую сторону, чтобы убедиться, что они равны. Если они не равны, перейдите к следующему разделу.
-
4
Подставьте длину ребра куба в формулу V = s3. Например, если ребро куба равно 5 см, напишите формулу следующим образом: V = 53 = 5 * 5 * 5 = 125 см3 – это объем куба.
-
5
К ответу обязательно припишите соответствующие единицы измерения. В приведенном примере ребро куба измерялась в сантиметрах, поэтому объем будет измеряться в кубических сантиметрах. Если, например, сторона куба равна 3 см, то V = 33 = 27см3.
Реклама
-
1
Прямоугольный параллелепипед или прямоугольная призма – это трехмерная фигура с шестью гранями, каждая из которых является прямоугольником (вспомните коробку из под обуви). [4]
- Куб – это частный случай прямоугольного параллелепипеда, у которого все ребра равны.
-
2
Формула нахождения объема прямоугольного параллелепипеда или прямоугольной призмы: V = l*w*h, где V = объем, l = длина, w = ширина, h = высота.[5]
-
3
Длина прямоугольного параллелепипеда – это самое длинное ребро верхней или нижней грани, то есть грани, на которой стоит параллелепипед (нижняя грань) или параллельной ей грани (верхняя грань). Длина будет дана в задаче или вам нужно измерить ее (линейкой или рулеткой).
- Пример: длина прямоугольного параллелепипеда равна 4 см, то есть l = 4 см.
- Не беспокойтесь о том, какие ребра выбрать в качестве длины, ширины и высоты. В любом случае в итоге вы получите правильный ответ (только измерьте три ребра, перпендикулярные друг другу).
-
4
Ширина прямоугольного параллелепипеда – это самое короткое ребро верхней или нижней грани, то есть грани, на которой стоит параллелепипед (нижняя грань) или параллельной ей грани (верхняя грань). Ширина будет дана в задаче или вам нужно измерить ее (линейкой или рулеткой).
- Пример: ширина прямоугольного параллелепипеда равна 3 см, то есть w = 3 см.
- Если вы измеряете ребра параллелепипеда линейкой или рулеткой, не забудьте измерить их в одинаковых единицах измерения. Не измеряйте одно ребро в миллиметрах, а другое в сантиметрах.
-
5
Высота прямоугольного параллелепипеда – это расстояние между его нижней и верхней гранями. Высота будет дана в задаче или вам нужно измерить ее (линейкой или рулеткой).
- Пример: высота прямоугольного параллелепипеда равна 6 см, то есть h = 6 см.
-
6
Подставьте найденные значения в формулу V = l*w*h.
- В нашем примере l = 4, w = 3 и h = 6. Поэтому V = 4*3*6 = 72.
-
7
К ответу обязательно припишите соответствующие единицы измерения. В приведенном примере ребра измерялись в сантиметрах, поэтому объем будет измеряться в кубических сантиметрах: 72 см3.
- Если в прямоугольной призме l = 2 см, w = 4 см, h = 8 см, то V = 2*4*8 = 64 см3
Реклама
-
1
Цилиндр – это трехмерная фигура, ограниченная цилиндрической поверхностью и двумя параллельными плоскостями, пересекающими ее.[6]
- Например, банка или батарейка АА имеют форму цилиндра.
-
2
Формула нахождения объема цилиндра: V = πr2h, где V – объем, h – высота, r – радиус основания и πr2 – площадь основания цилиндра.
- В некоторых задачах ответ требуется представить с пи, а в некоторых вместо пи подставить 3,14.
- Формула для нахождения объема цилиндра на самом деле очень похожа на формулу вычисления объема прямоугольной призмы, то есть вы перемножаете высоту и площадь основания. В прямоугольной призме площадь основания равна l*w, а в цилиндре она равна πr2.
-
3
Найдите радиус основания. Он, скорее всего, дан в задаче. Если дан диаметр, разделите его на 2, чтобы найти радиус (d = 2r).
-
4
Если радиус не дан, измерьте его. Для этого измерьте основание цилиндра при помощи линейки или рулетки. Измеряйте основание в его самой широкой части (то есть измерьте диаметр основания), а затем разделите полученное значение на 2, чтобы найти радиус.
- Другой вариант – измерьте длину окружности цилиндра (то есть измерьте обхват цилиндра) при помощи рулетки, а затем найдите радиус по формуле r = с/2π, где с – обхват (длина окружности) цилиндра (2π = 6,28).
- Например, если обхват цилиндра равен 8 см, то радиус будет равен 1,27 см.
- Если вам нужно точное измерение, вы можете использовать оба метода, чтобы убедиться, что значения радиуса совпадают (нахождение радиуса через длину окружности является более точным методом).
-
5
Вычислите площадь круглого основания. Для этого подставьте радиус в формулу πr2.
- Если радиус основания равен 4 см, то площадь основания равна π42.
- 42 = 4 * 4 = 16. 16*π = 16*3,14 = 50,24 см2
- Если дан диаметр основания, то помните, что d = 2r. Вам нужно разделить диаметр пополам, чтобы найти радиус.
-
6
Найдите высоту цилиндра. Это расстояние между двумя круглыми основаниями. Высота будет дана в задаче или вам нужно измерить ее (линейкой или рулеткой).
-
7
Умножьте площадь основания на высоту цилиндра, чтобы найти его объем. Или же просто подставьте значения соответствующих величин в формулу V = πr2h. В нашем примере, когда радиус основания равен 4 см, а высота равна 10 см:
- V = π4210
- π42 = 50,24
- 50,24 * 10 = 502,4
- V = 502,4
-
8
К ответу обязательно припишите соответствующие единицы измерения. В приведенном примере все величины измерялась в сантиметрах, поэтому объем будет измеряться в кубических сантиметрах: 502,4 см3.
Реклама
-
1
Пирамида – это трехмерная фигура, в основании которой лежит многоугольник, а грани являются треугольниками, имеющими общую вершину. [7]
Правильная пирамида – это трехмерная фигура, в основании которой лежит правильный многоугольник (с равными сторонами), а вершина проецируется в центр основания.[8]
- Обычно мы представляем пирамиду, имеющую квадратное основание, но в основании пирамиды может лежать многоугольник с 5, 6 или даже со 100 сторонами!
- Пирамида с круглым основанием называется конусом, который будет обсуждаться в следующем разделе.
-
2
Формула нахождения объема правильной пирамиды: V = 1/3bh, где b – площадь основания пирамиды, h – высота пирамиды (перпендикуляр, соединяющий основание и вершину пирамиды).
- Эта формула для вычисления объема пирамиды одинаково годна как для правильных пирамид (в которых вершина проецируется в центр основания), так и для наклонных (в которых вершина не проецируется в центр основания).
-
3
Вычислите площадь основания. Формула будет зависеть от фигуры, лежащей в основании пирамиды. В нашем примере в основании пирамиды лежит квадрат со стороной 6 см. Площадь квадрата равна s2, где s – сторона квадрата. Таким образом, в нашем примере площадь основания пирамиды равна 62 = 36 см2
- Площадь треугольника равна 1/2bh, где h – высота треугольника, b – сторона, к которой проведена высота.
- Площадь любого правильного многоугольника можно вычислить по формуле: А = 1/2ра, где А – площадь, р – периметр фигуры, а – апофема (отрезок, соединяющий центр фигуры с серединой любой стороны фигуры). Для получения дополнительной информации о нахождении площади многоугольников прочитайте эту статью.[9]
-
4
Найдите высоту пирамиды. Высота будет дана в задаче. В нашем примере высота пирамиды равна 10 см.
-
5
Умножьте площадь основания пирамиды на ее высоту, а затем разделите полученный результат на 3, чтобы найти объем пирамиды. Формула для вычисления объема пирамиды: V = 1/3bh. В нашем примере площадь основания равна 36, а высота равна 10, поэтому объем: 36*10*1/3 = 120.
- Если, например, дана пирамида с пятиугольным основанием площадью 26, а высота пирамиды равна 8, то объем пирамиды: 1/3*26*8 = 69,33.
-
6
К ответу обязательно припишите соответствующие единицы измерения. В приведенном примере все величины измерялась в сантиметрах, поэтому объем будет измеряться в кубических сантиметрах: 120 см3.
Реклама
-
1
Конус – это трехмерная фигура, которая имеет круглое основание и одну вершину. Или конус – это особый случай пирамиды с круглым основанием.[10]
- Если вершина конуса находится непосредственно над центром круглого основания, то конус называется прямым; в противном случае конус называется наклонным. Но формула для вычисления объема конуса одинаковая для обоих типов конуса.
-
2
Формула для вычисления объема конуса: V = 1/3πr2h, где r – радиус круглого основания, h – высота конуса.
- b = πr2 – это площадь круглого основания конуса. Таким образом, формулу для вычисления объема конуса можно записать так: V = 1/3bh, что совпадает с формулой нахождения объема пирамиды!
-
3
Вычислите площадь круглого основания. Радиус должен быть дан в задаче. Если дан диаметр основания, то помните, что d = 2r. Вам нужно разделить диаметр пополам, чтобы найти радиус. Для вычисления площади круглого основания подставьте радиус в формулу πr2.
- Например, радиус круглого основания конуса равен 3 см. Тогда площадь этого основания равна π32.
- π32 = π(3*3) = 9π.
- = 28,27 см2
-
4
Найдите высоту конуса. Это перпендикуляр, опущенный из вершины к основанию пирамиды. В нашем примере высота конуса равна 5 см.
-
5
Перемножьте высоту конуса и площадь основания. В нашем примере площадь основания равна 28,27 см2, а высота равна 5 см, поэтому bh = 28,27 * 5 = 141,35.
-
6
Теперь умножьте полученный результат на 1/3 (или просто разделите его на 3), чтобы найти объем конуса. В описанном выше шаге вы нашли объем цилиндра, а объем конуса всегда в 3 раза меньше объема цилиндра.
- В нашем примере: 141,35 * 1/3 = 47,12 – это объем конуса.
- Или: 1/3π325 = 47,12
-
7
К ответу обязательно припишите соответствующие единицы измерения. В приведенном примере все величины измерялась в сантиметрах, поэтому объем будет измеряться в кубических сантиметрах: 47,12 см3.
Реклама
-
1
Шар – это идеально круглая трехмерная фигура, каждая точка поверхности которой равноудалена от одной точки (центра шара). [11]
-
2
Формула для вычисления объема шара: V = 4/3πr3, где r – радиус шара.[12]
-
3
Найдите радиус шара. Радиус должен быть дан в задаче. Если дан диаметр шара, то помните, что d = 2r. Вам нужно разделить диаметр пополам, чтобы найти радиус. Например, радиус шара равен 3 см.
-
4
Если радиус не дан, вычислите его. Для этого измерьте длину окружности шара (например, теннисного мяча) в его самой широкой части при помощи веревки, нити или другого подобного предмета. Затем измерьте длину веревки, чтобы найти длину окружности. Разделите полученное значение на 2π (или на 6,28), чтобы вычислить радиус шара.
- Например, если вы измерили мяч и нашли, что длина его окружности равна 18 см, разделите это число на 6,28 и получите, что радиус мяча равен 2,87 см.
- Проделайте 3 измерения окружности шара, а затем усредните полученные значения (для этого сложите их и сумму разделите на 3), чтобы убедиться, что вы получили значение, близкое к истинному.
- Например, в результате трех измерений длины окружности вы получили следующие результаты: 18 см, 17,75 см, 18,2 см. Сложите эти значения: 18 + 17,5 + 18,2 = 53,95, а затем разделите их на 3: 53,95/3 = 17,98. Используйте это среднее значение в расчетах объема шара.
-
5
Возведите радиус в куб (r3). То есть r3 = r*r*r. В нашем примере r = 3, поэтому r3 = 3 * 3 * 3 = 27.
-
6
Теперь умножьте полученный результат на 4/3. Вы можете использовать калькулятор или выполнить умножение вручную, а затем упростить дробь. В нашем примере: 27*4/3 = 108/3 = 36.
-
7
Умножьте полученный результат на π (3,14), чтобы найти объем шара.
- В нашем примере: 36*3,14 = 113,09.
-
8
К ответу обязательно припишите соответствующие единицы измерения. В приведенном примере все величины измерялась в сантиметрах, поэтому объем будет измеряться в кубических сантиметрах: 113,09 см3.
Реклама
Об этой статье
Эту страницу просматривали 74 216 раз.
Была ли эта статья полезной?
Download Article
Download Article
The volume of a shape is the measure of how much three-dimensional space that shape takes up.[1]
You can also think of the volume of a shape as how much water (or air, or sand, etc.) the shape could hold if it was filled completely. Common units of volume include cubic centimeters (cm3), cubic meters (m3), cubic inches (in3), and cubic feet (ft3).[2]
This article will teach you how to calculate the volume of six different three-dimensional shapes that are commonly found on math tests, including cubes, spheres, and cones. You might notice that a lot of the volume formulas share similarities that can make them easier to remember. See if you can spot them along the way!
-
1
Recognize a cube. A cube is a three-dimensional shape that has six identical square faces.[3]
In other words, it is a box shape with equal sides all around.- A 6-sided die is a good example of a cube you might find in your house. Sugar cubes, and children’s letter blocks are also usually cubes.
-
2
Learn the formula for the volume of a cube. Since all of the side lengths of a cube are the same, the formula for the volume of a cube is really easy. It is V = s3 where V stands for volume, and s is the length of the sides of the cube.[4]
- To find s3, simply multiply s by itself 3 times: s3 = s * s * s
Advertisement
-
3
Find the length of one side of the cube. Depending on your assignment, the cube will either be labeled with this information, or you may have to measure the side length with a ruler. Remember that since it is a cube, all of the side lengths should be equal so it doesn’t matter which one you measure.
- If you are not 100% sure that your shape is a cube, measure each of the sides to determine if they are equal. If they are not, you will need to use the method below for Calculating the Volume of a Rectangular Solid.
-
4
Plug the side length into the formula V = s3 and calculate. For example, if you find that the length of the sides of your cube is 5 inches, then you should write the formula out as follows: V = (5 in)3. 5 in * 5 in * 5 in = 125 in3, the volume of our cube!
- Make sure all of the lengths are in the same unit before multiplying them.[5]
- Make sure all of the lengths are in the same unit before multiplying them.[5]
-
5
Be sure to state your answer in cubic units.[6]
In the above example, the side length of our cube was measured in inches, so the volume was given in cubic inches. If the side length of the cube had been 3 centimeters, for example, the volume would be V = (3 cm)3, or V = 27cm3.
Advertisement
-
1
Recognize a rectangular solid. A rectangular solid, also known as a rectangular prism, is a three-dimensional shape with six sides that are all rectangles.[7]
In other words, a rectangular solid is simply a three-dimensional rectangle, or box shape.- A cube is really just a special rectangular solid in which the sides of all of the rectangles are equal.
-
2
Learn the formula for calculating the volume of a rectangular solid. The formula for the volume of a rectangular solid is Volume = length * width * height, or V = lwh.
-
3
Find the length of the rectangular solid. The length is the longest side of the rectangular solid that is parallel to the ground or surface it is resting on. The length may be given in a diagram, or you may need to measure it with a ruler or tape measure.
- Example: The length of this rectangular solid is 4 inches, so l = 4 in.
- Don’t worry too much about which side is the length, which is the width, etc. As long as you end up with three different measurements, the math will come out the same regardless of how your arrange the terms.
-
4
Find the width of the rectangular solid. The width of the rectangular solid is the measurement of the shorter side of the solid, parallel to the ground or surface the shape is resting on. Again, look for a label on the diagram indicating the width, or measure your shape with a ruler or tape measure.
- Example: The width of this rectangular solid is 3 inches, so w = 3 in.
- If you are measuring the rectangular solid with a ruler or tape measure, remember to take and record all measurements in the same units. Don’t measure one side in inches another in centimeters; all measurements must use the same unit!
-
5
Find the height of the rectangular solid. This height is the distance from the ground or surface the rectangular solid is resting on to the top of the rectangular solid. Locate the information in your diagram, or measure the height using a ruler or tape measure.
- Example: The height of this rectangular solid is 6 inches, so h = 6 in.
-
6
Plug the dimensions of the rectangular solid into the volume formula and calculate. Remember that V = lwh.
- In our example, l = 4, w = 3, and h = 6. Therefore, V = 4 * 3 * 6, or 72.
-
7
Be sure to express your answer in cubic units. Since our example rectangle was measured in inches, the volume should be written as 72 cubic inches, or 72 in3.
- If the measurements of our rectangular solid were: length = 2 cm, width = 4 cm, and height = 8 cm, the Volume would be 2 cm * 4 cm * 8 cm, or 64cm3.
Advertisement
-
1
Learn to identify a cylinder. A cylinder is a three-dimensional shape that has two identical flat ends that are circular in shape, and a single curved side that connects them.[8]
- A can is a good example of a cylinder, so is a AA or AAA battery.
-
2
Memorize the formula for the volume of a cylinder. To calculate the volume of a cylinder, you must know its height and the radius of the circular base (the distance from the center of the circle to its edge) at the top and bottom. The formula is V = πr2h, where V is the Volume, r is the radius of the circular base, h is the height, and π is the constant pi.
- In some geometry problems the answer will be given in terms of pi, but in most cases it is sufficient to round pi to 3.14. Check with your instructor to find out what she would prefer.
- The formula for finding the volume of a cylinder is actually very similar to that for a rectangular solid: you are simply multiplying the height of the shape by the surface area of its base. In a rectangular solid, that surface area is l * w, for the cylinder it is πr2, the area of a circle with radius r.
-
3
Find the radius of the base.[9]
If it is given in the diagram, simply use that number. If the diameter is given instead of the radius, you simply need to divide the value by 2 to get the radius (d = 2r). -
4
Measure the object if the radius is not given. Be aware that getting precise measurement of a circular solid can be a bit tricky. One option is to measure the base of the cylinder across the top with a ruler or tape measure. Do your best to measure the width of the cylinder at its widest part, and divide that measurement by 2 to find the radius.
- Another option is to measure the circumference of the cylinder (the distance around it) using a tape measure or a length of string that you can mark and then measure with a ruler. Then plug the measurement into the formula: C (circumference) = 2πr. Divide the circumference by 2π (6.28) and that will give you the radius.
- For example, if the circumference you measured was 8 inches, the radius would be 1.27in.
- If you need a really precise measurement, you might use both methods to make sure that your measurements are similar. If they are not, double check them. The circumference method will usually yield more accurate results.
-
5
Calculate the area of the circular base.[10]
Plug the radius of the base into the formula πr2. Then multiply the radius by itself one time, and then multiply the product by π. For example:- If the radius of the circle is equal to 4 inches, the area of the base will be A = π42.
- 42 = 4 * 4, or 16. 16 * π (3.14) = 50.24 in2
- If the diameter of the base is given instead of the radius, remember that d = 2r. You simply need to divide the diameter in half to find the radius.
-
6
Find the height of the cylinder.[11]
This is simply the distance between the two circular bases, or the distance from the surface the cylinder is resting on to its top. Find the label in your diagram that indicates the height of the cylinder, or measure the height with a ruler or tape measure. -
7
Multiply the area of the base times the height of the cylinder to find the volume.[12]
Or you can save a step and simply plug the values for the cylinder’s dimensions into the formula V = πr2h. For our example cylinder with radius 4 inches and height 10 inches:- V = π4210
- π42 = 50.24
- 50.24 * 10 = 502.4
- V = 502.4
-
8
Remember to state your answer in cubic units. Our example cylinder was measured in inches, so the volume must be expressed in cubic inches: V = 502.4in3. If our cylinder had been measured in centimeters, the volume would be expressed in cubic centimeters (cm3).
Advertisement
-
1
Understand what a regular pyramid is. A pyramid is a three-dimensional shape with a polygon for a base, and lateral faces that taper at an apex (the point of the pyramid).[13]
A regular pyramid is a pyramid in which the base of the pyramid is a regular polygon, meaning that all of the sides of the polygon are equal in length, and all of the angles are equal in measure.[14]
- We most commonly imagine a pyramid as having a square base, and sides that taper up to a single point, but the base of a pyramid can actually have 5, 6, or even 100 sides!
- A pyramid with a circular base is called a cone, which will be discussed in the next method.
-
2
Learn the formula for the volume of a regular pyramid. The formula for the volume of a regular pyramid is V = 1/3bh, where b is the area of the base of the pyramid (the polygon at the bottom) and h is the height of the pyramid, or the vertical distance from the base to the apex (point).
- The volume formula is the same for right pyramids, in which the apex is directly above the center of the base, and for oblique pyramids, in which the apex is not centered.
-
3
Calculate the area of the base. The formula for this will depend on the number of sides the base of the pyramid has. In the pyramid in our diagram, the base is a square with sides that are 6 inches in length. Remember that the formula for the area of a square is A = s2 where s is the length of the sides. So for this pyramid, the area of the base is (6 in) 2, or 36in2.
- The formula for the area of a triangle is: A = 1/2bh, where b is the base of the triangle and h is the height.
- It is possible to find the area of any regular polygon using the formula A = 1/2pa, where A is the area, p is the perimeter of the shape, and a is the apothem, or distance from the center of the shape to the midpoint of any of its sides. This is a pretty involved calculation that goes beyond the scope of this article, but check out Calculate the Area of a Polygon for some great instructions on how to use it. Or you can make your life easy and search for a Regular Polygon Calculator online.[15]
-
4
Find the height of the pyramid. In most cases, this will be indicated in the diagram. In our example, the height of the pyramid is 10 inches.
-
5
Multiply the area of the base of the pyramid by its height, and divide by 3 to find the volume. Remember that the formula for the volume is V = 1/3bh. In our example pyramid, that had a base with area 36 and height 10, the volume is: 36 * 10 * 1/3, or 120.
- If we had a different pyramid, with a pentagonal base with area 26, and height of 8, the volume would be: 1/3 * 26 * 8 = 69.33.
-
6
Remember to express your answer in cubic units. The measurements of our example pyramid were given in inches, so its volume must be expressed in cubic inches, 120in. If our pyramid had been measured in meters, the volume would be expressed in cubic meters (m3) instead.3
Advertisement
-
1
Learn the properties of a cone. A cone is a 3-dimesional solid that has a circular base and a single vertex (the point of the cone). Another way to think of this is that a cone is a special pyramid that has a circular base.[16]
- If the vertex of the cone is directly above the center of the circular base, the cone is called a “right cone”. If it is not directly over the center, the cone is called an “oblique cone.” Fortunately, the formula for calculating the area of a cone is the same whether it is right or oblique.
-
2
Know the formula for calculating the volume of a cone. The formula is V = 1/3πr2h, where r is the radius of the circular base of the cone, h is the height of the cone, and π is the constant pi, which can be rounded to 3.14.
- The πr2 part of the formula refers to the area of the circular base of the cone. The formula for the volume of the cone is thus 1/3bh, just like the formula for the volume of a pyramid in the method above!
-
3
Calculate the area of the circular base of the cone. To do this, you need to know the radius of the base, which should be listed in your diagram. If you are instead given the diameter of the circular base, simply divide that number by 2, since the diameter is simply 2 times the radios (d = 2r). Then plug the radius into the formula A = πr2 to calculate the area.
- In the example in the diagram, the radius of the circular base of the cone is 3 inches. When we plug that into the formula we get: A = π32.
- 32 = 3 *3, or 0, so A = 9π.
- A = 28.27in2
-
4
Find the height of the cone. This is the vertical distance between the base of the cone, and its apex. In our example, the height of the cone is 5 inches.
-
5
Multiply the height of the cone by the area of the base. In our example, the area of the base is 28.27in2 and the height is 5in, so bh = 28.27 * 5 = 141.35.
-
6
Now multiply the result by 1/3 (or simply divide by 3) to find the volume of the cone. In the above step, we actually calculated the volume of the cylinder that would be formed if the walls of the cone extended straight up to another circle, instead of slanting in to a single point. Dividing by 3 gives us the volume of just the cone itself.
- In our example, 141.35 * 1/3 = 47.12, the volume of our cone.
- To restate it, 1/3π325 = 47.12
-
7
Remember to express your answer in cubic units. Our cone was measured in inches, so its volume must be expressed in cubic inches: 47.12in3.
Advertisement
-
1
Spot a sphere. A sphere is a perfectly round three-dimensional object, in which every point on the surface is an equal distance from the center. In other words, a sphere is a ball-shaped object.[17]
-
2
Learn the formula for the volume of a sphere. The formula for the volume of a sphere is V = 4/3πr3 (stated: “four-thirds times pi r-cubed”) where r is the radius of the sphere, and π is the constant pi (3.14).[18]
-
3
Find the radius of the sphere. If the radius is given in the diagram, then finding r is simply a matter of locating it. If the diameter is given, you must divide this number by 2 to find the radius. For example, the radius of the sphere in the diagram is 3 inches.
-
4
Measure the sphere if the radius is not given. If you need to measure a spherical object (like a tennis ball) to find the radius, first find a piece of string large enough to wrap around the object. Then wrap the string around the object at its widest point and mark the points where the string overlaps itself. Then measure the string with a ruler to find the circumference. Divide that value by 2π, or 6.28, and that will give you the radius of the sphere.
- For example, if you measure a ball and find its circumference is 18 inches, divide that number by 6.28 and you will find that the radius is 2.87in.
- Measuring a spherical object can be a little tricky, so you might want to take 3 different measurements, and then average them together (add the three measurements together, then divide by 3) to make sure you have the most accurate value possible.
- For example, if your three circumference measurements were 18 inches, 17.75 inches, and 18.2 inches, you would add those three values together (18 + 17.5 + 18.2 = 53.95) and divide that value by 3 (53.95/3 = 17.98). Use this average value in your volume calculations.
-
5
Cube the radius to find r3. Cubing a number simply means multiplying the number by itself 3 times, so r3 = r * r * r. In our example, r = 3, so r3 = 3 * 3 * 3, or 27.
-
6
Now multiply your answer by 4/3. You can either use your calculator, or do the multiplication by hand and then simplify the fraction. In our example, multiplying 27 by 4/3 = 108/3, or 36.
-
7
Multiply the result by π to find the volume of the sphere. The last step in calculating the volume is simply to multiply the result so far by π. Rounding π to two digits is usually sufficient for most math problems (unless your teacher specified otherwise,) so multiply by 3.14 and you have your answer.
- In our example, 36 * 3.14 = 113.09.
-
8
Express your answer in cubic units. In our example, the measurement of the radius of the sphere was in inches, so our answer is actually V = 113.09 cubic inches (113.09 in3).
Advertisement
Worksheet and Practice Problems
Add New Question
-
Question
How do you find the volume of a box?
Grace Imson, MA
Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco
Grace Imson is a math teacher with over 40 years of teaching experience. Grace is currently a math instructor at the City College of San Francisco and was previously in the Math Department at Saint Louis University. She has taught math at the elementary, middle, high school, and college levels. She has an MA in Education, specializing in Administration and Supervision from Saint Louis University.
Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco
Expert Answer
Support wikiHow by
unlocking this expert answer.The volume of a box is equal to the product of the three dimensions of the box. You would multiply the length, the width, and the height of the box to find its volume. Make sure the dimensions have the same unit. Some tricky questions give different units for each dimension.
-
Question
How would you find the volume of a water tank?
Grace Imson, MA
Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco
Grace Imson is a math teacher with over 40 years of teaching experience. Grace is currently a math instructor at the City College of San Francisco and was previously in the Math Department at Saint Louis University. She has taught math at the elementary, middle, high school, and college levels. She has an MA in Education, specializing in Administration and Supervision from Saint Louis University.
Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco
Expert Answer
Support wikiHow by
unlocking this expert answer.Assuming the tank is a cylinder, you’ll need the radius or diameter of one of the circular bases as well as the height of the tank. Calculate the area of the circle using πr² (if you have the diameter, divide it in half to get the radius). Then, just multiply the area of the circular base by the height of the tank to find its volume.
-
Question
How do I calculate the volume of compound shapes?
If the compound shapes are made up of basic geometric solids, then you can try dissecting them into their simpler parts. Their volumes will be additive.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Things You’ll Need
- Writing utensil
- Paper
- Calculator (optional)
- Ruler (optional)
References
- ↑ https://www.nist.gov/pml/owm/si-units-volume
- ↑ http://www.mathsisfun.com/measure/us-standard-volume.html
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/definitions/cube.html
- ↑ Grace Imson, MA. Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco. Expert Interview. 1 November 2019.
- ↑ Grace Imson, MA. Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco. Expert Interview. 1 November 2019.
- ↑ Grace Imson, MA. Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco. Expert Interview. 1 November 2019.
- ↑ http://www.algebralab.org/lessons/lesson.aspx?file=Geometry_3Dprisms.xml
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/definitions/cylinder.html
- ↑ Grace Imson, MA. Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco. Expert Interview. 1 November 2019.
- ↑ Grace Imson, MA. Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco. Expert Interview. 1 November 2019.
- ↑ Grace Imson, MA. Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco. Expert Interview. 1 November 2019.
- ↑ Grace Imson, MA. Math Instructor, City College of San Francisco. Expert Interview. 1 November 2019.
- ↑ http://www.mathwords.com/p/pyramid.htm
- ↑ http://www.mathwords.com/r/regular_pyramid.htm
- ↑ http://www.calculatorsoup.com/calculators/geometry-plane/polygon.php
- ↑ http://www.mathopenref.com/cone.html
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/definitions/sphere.html
- ↑ https://www.splashlearn.com/math-vocabulary/geometry/volume
About This Article
Article SummaryX
To calculate volume with a cube, use the formula v = s^3, where s is the length of the sides of the cube. To calculate the volume of a cylinder, use the formula v = hπr^2, where r is the radius of the base, h is the height, and π is pi. If you’re trying to find the volume of a rectangular prism, use the formula v = lwh, where l is the length, w is the width, and h is the height. If you need to learn how to calculate the volume of a sphere or pyramid, keep reading the article!
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 1,413,544 times.
Reader Success Stories
-
“Thanks. I was doing science homework, and it said to find the volume of an object. I chose one shaped like a cake…” more
Did this article help you?
По какой формуле можно найти объем?
Анонимный вопрос
1 ноября 2018 · 65,7 K
Смотря что известно о теле, объем которого вы хотите вычислить.
- Зная массу и плотность V = m/ρ, где m – масса, а ρ – плотность
- Для геометрических фигур, например куб V = a^3 перемножить три стороны, а для цилиндра V = S*H площадь основания помножить на высоту
Для остальных фигур часто фигурирует площадь, которую тоже предстоит вычислить, например площадь круга S = 2πR^2
На практике можно использовать закон Архимеда, тело погруженное в жидкость вытеснет свой объем.
61,5 K
вообще не понимаю, за что минусовали ответ))
Комментировать ответ…Комментировать…
У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Объём (значения).
| Объём | |
 |
|
| Размерность | L3 |
|---|---|
| Единицы измерения | |
| СИ | м3 |
| СГС | см3 |
Примеры вычисления объёмов:
Куба с помощью перемножения трех сторон[1]
Пирамиды с помощью умножения площади основания пирамиды на её высоту и делению на три[1]
Конуса с помощью умножения площади основания на треть высоты[1]
Цилиндра с помощью перемножения площади на высоту[1]
Шара с помощью перемножения четырёх третьих числа Пи на радиус шара в кубе[1]
Тетраэдра с помощью произведения длины его ребра в кубе на корень из двух и деления полученного на двенадцать[1]
Объём — количественная характеристика пространства, занимаемого телом или веществом.
Объём тела или вместимость сосуда определяется его формой и линейными размерами. С понятием объёма тесно связано понятие вместимость, то есть объём внутреннего пространства сосуда, упаковочного ящика и т. п..
Единица измерения объёма в СИ — кубический метр; от неё образуются производные единицы, такие как кубический сантиметр, кубический дециметр (литр) и т. д. В разных странах для жидких и сыпучих веществ используются также различные внесистемные единицы объёма — галлон, баррель.
В формулах для обозначения объёма используется заглавная латинская буква V, являющаяся сокращением от лат. volume — «объём», «наполнение».
Слово «объём» также используют в переносном значении для обозначения общего количества или текущей величины. Например, «объём спроса», «объём памяти», «объём работ». В изобразительном искусстве объёмом называется иллюзорная передача пространственных характеристик изображаемого предмета художественными методами.
Содержание
- 1 Вычисление объёма
- 1.1 Математически
- 1.2 Через плотность
- 2 Единицы объёма жидкости
- 2.1 Английские
- 2.2 Античные
- 2.3 Древнееврейские[2]
- 2.4 Русские[3]
- 3 Единицы объёма сыпучих веществ
- 3.1 Английские
- 3.2 Русские
- 4 Прочие единицы
- 5 Примечания
- 6 Литература
- 7 Ссылки
Вычисление объёма
На практике приблизительный объём тела, в том числе сложной формы, можно вычислить погрузив это тело в жидкость. Объём вытесненной жидкости будет равен объёму измеряемого тела.
Математически
Для объёмов тел простой формы имеются специальные формулы. Например, объём куба с ребром 

Объём тела сложной формы вычисляется разбиением этого тела на отдельные части простой формы и суммированием объёмов этих частей. В интегральном исчислении объёмы частей, из которых складывается объём всего тела, рассматриваются как бесконечно малые величины.
Через плотность
Зная массу (m) и плотность (ρ) тела объём рассчитывается по формуле: 
Единицы объёма жидкости
- 1 л = 1,76 пинты = 0,23 галлона
Английские
- 1 пинта = 0,58 литра.
- 1 кварта = 2 пинты = 1,23 литра
- 1 галлон = 8 пинтам = 4,55 литра
- 1 галлон (амер.) = 3,785 литра
Античные
- Котила = 0,275 литра
Древнееврейские[2]
- Эйфа = 24,9 литра
- Гин = 1/6 эйфы = 4,15 литра
- Омер = 1/10 эйфы = 2,49 литра
- Кав = 1/3 гина = 1,38 литра
Русские[3]
- Бочка = 40 вёдер = 492 литра
- Ведро = 12,3 литра
Единицы объёма сыпучих веществ
Английские
- 1 бушель = 8 галлонов = 36,37 литра
- 1 баррель = 163,65 литра
Русские
- Четверик = 26,24 литра (1 пуд зерна)
- Гарнец = 3,28 литра
Прочие единицы
- 1 унция (англ.) = 2,841·10−5 м³
- 1 унция (амер.) = 2,957·10−5 м³
- 1 кубический дюйм = 1,64·10−5 м³
- 1 кубический фут = 2,83·10−2 м³
- 1 кубический ярд = 0,765 м³
- 1 кубическая астрономическая единица =3,348·1024 км³
- 1 кубический световой год = 8,466·1038 км³
- 1 кубический парсек = 2,938·1040 км³
- 1 кубический килопарсек = 1 000 000 000 пк³ = 2,938·1049 км³
Примечания
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 6 Вычисление объёма различных тел и пространств
- ↑ «ТЕГИЛАТ ГАШЕМ» — ISBN 965-310-008-4
- ↑ Меры объёма в Древней Руси
Литература
- Объем // Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона : в 86 т. (82 т. и 4 доп.). — СПб., 1890—1907.