При необходимости вычислить объем правильной шестиугольной призмы достаточно знать сторону ее грани
(ребро) a и высоту h. Формула вычисления объема следующая (объем любой призмы равен площади ее
основания, умноженной на высоту, в данном случае берется площадь основания правильного
шестиугольника):
V = (3 * a² / 2) * h * √3
где a — сторона его граней (ребро), h — высота.
Цифр после
запятой:
Результат в:
Пример. Вычислим объем шестигранного простого карандаша типа 7 длиной 177 мм (это
высота призмы h) со стороной грани a = 4,5 мм. V = (3 * 4,5² / 2) * 177 * √3 =9312 (мм³) = 9,312 см³.
Призма – это многогранник, две грани которого являются равными многоугольниками, лежащими в
параллельных плоскостях (эти грани называются основаниями), а остальные грани (называемые боковыми
гранями) являются параллелограммами, у которых стороны общие со сторонами многоугольников. Если у
призмы боковые ребра перпендикулярны плоскости основания, она называется прямой призмой. Все боковые
ребра призмы параллельны и равны по длине. Длина бокового ребра прямой призмы – это ее высота. Если
при этом у прямой призмы основания представляют собой правильные многоугольники, призма называется
правильной. У правильной призмы боковые грани представляют собой равные прямоугольники.
У правильной шестиугольной призмы (другое название – правильная шестигранная призма) основания –
правильные шестиугольники. Примерами правильной шестиугольной призмы являются новый незаточенный
шестигранный карандаш, шестигранная головка болта, башни некоторых средневековых замков, смотревшие
в поле 3 или 4 сторонами.
Объем правильной шестиугольной призмы
У правильной шестиугольной призмы в основании лежит правильный шестиугольник.

Объем правильной шестиугольной призмы
Объем правильной шестиугольной призмы равен произведению площади правильного шестиугольника лежащего в основании на высоту призмы.
[ V = frac{3sqrt{3}}{2}a^{2} h ]
Вычислить, найти объем правильной шестиугольной призмы
| a (сторона правильного шестиугольника) |
| h (высота призмы) |
Вычислить
нажмите кнопку для расчета
Объем правильной шестиугольной призмы |
стр. 362 |
|---|
Определение объемов геометрических тел является одной из важных задач пространственной геометрии. В данной статье рассматривается вопрос, что такое призма с шестиугольным основанием, а также приводится формула объема правильной шестиугольной призмы.
Определение призмы
С точки зрения геометрии призмой называется фигура в пространстве, которая образована двумя одинаковыми многоугольниками, расположенными в параллельных плоскостях. А также несколькими параллелограммами, которые эти многоугольники соединяют в единую фигуру.
В трехмерном пространстве призму произвольной формы можно получить, если взять любой многоугольник и отрезок. Причем последний плоскости многоугольника принадлежать не будет. Тогда, располагая этот отрезок от каждой вершины многоугольника, можно получить параллельный перенос последнего в другую плоскость. Образованная таким способом фигура будет призмой.
Чтобы иметь наглядное представление о рассматриваемом классе фигур, приведем рисунок четырехугольной призмы.

Многие знают эту фигуру под названием параллелепипеда. Видно, что два одинаковых многоугольника призмы представляют собой квадраты. Их называют основаниями фигуры. Остальные четыре ее стороны – прямоугольники, то есть это частный случай параллелограммов.
Шестиугольная призма: определение и виды
Прежде чем приводить формулу, как определяется объем шестиугольной правильной призмы, необходимо четко понять, о какой фигуре пойдет речь. Шестиугольная призма имеет в основаниях шестиугольник. То есть, плоский многоугольник с шестью сторонами, углов столько же. Боковые стороны фигуры так же, как и для любой призмы, в общем случае являются параллелограммами. Сразу отметим, что шестиугольное основание может быть представлено как правильным, так и неправильным шестиугольником.
Расстояние между основаниями фигуры – это ее высота. Далее мы будем обозначать ее буквой h. Геометрически высота h представляет собой отрезок, перпендикулярный обоим основаниям. Если этот перпендикуляр:
- опущен с геометрического центра одного из оснований;
- пересекает второе основание также в геометрическом центре.
Фигура в этом случае называется прямой. В любом другом случае призма будет косоугольной или наклонной. Разницу между этими видами шестиугольной призмы можно увидеть с первого взгляда.
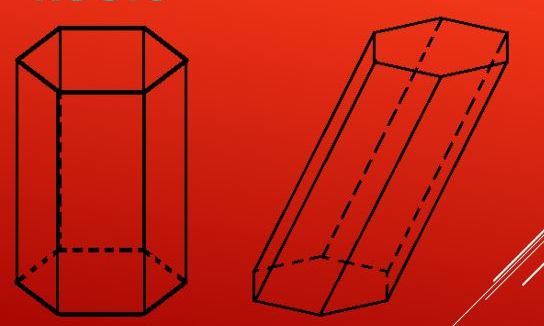
Прямая шестиугольная призма – это фигура, имеющая в основании правильные шестиугольники. При этом она является прямой. Рассмотрим подробнее ее свойства.
Элементы правильной шестиугольной призмы
Чтобы понять, как вычислить объем правильной шестиугольной призмы (формула приведена ниже в статье), необходимо также разобраться, из каких элементов состоит фигура, а также какими свойствами она обладает. Чтобы было легче анализировать фигуру, покажем ее на рисунке.

Главными ее элементами являются грани, ребра и вершины. Количества этих элементов подчиняется теореме Эйлера. Если обозначить Р – число ребер, В – количество вершин и Г – граней, тогда можно записать равенство:
Р = Г + В – 2.
Проверим его. Число граней рассматриваемой фигуры равно 8. Две из них – это правильные шестиугольники. Шесть граней представляет собой прямоугольники, это видно из рисунка. Число вершин составляет 12. Действительно, 6 вершин принадлежат одному основанию, и 6 другому. Согласно формуле, число ребер должно равняться 18, что является справедливым. 12 ребер лежат в основаниях и 6 образуют параллельные друг другу стороны прямоугольников.
Переходя к получению формулы объема правильной шестиугольной призмы, следует остановить свое внимание на одном важном свойстве этой фигуры: прямоугольники, образующие боковую поверхность, равны между собой и перпендикулярны обоим основаниям. Это приводит к двум важным следствиям:
- Высота фигуры равна длине ее бокового ребра.
- Любое сечение боковой поверхности пирамиды, выполненное с помощью секущей плоскости, которая параллельна основаниям, является правильным шестиугольником, равным этим основаниям.
Площадь шестиугольника
Можно интуитивно догадаться, что эта площадь основания фигуры появится в формуле объема правильной призмы шестиугольной. Поэтому в данном пункте статьи найдем эту площадь. Правильный шестиугольник, разделенный на 6 одинаковых треугольников, вершины которых пересекаются в его геометрическом центре, показан ниже:
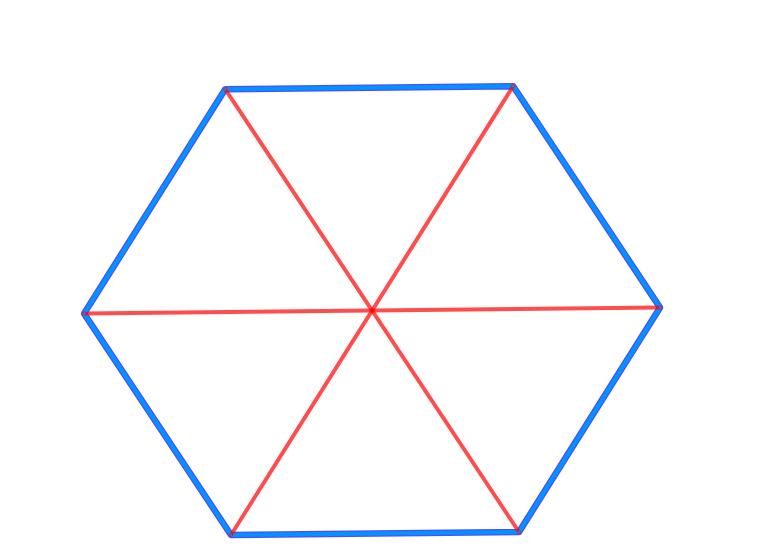
Каждый из этих треугольников является равносторонним. Доказать это не очень сложно. Поскольку вся окружность имеет 360o, то углы треугольников вблизи геометрического центра шестиугольника равны 360o/6=60o. Расстояния от геометрического центра до вершин шестиугольника являются одинаковыми.
Последнее означает, что все 6 треугольников будут равнобедренными. Поскольку один из углов равнобедренных треугольников равен 60o, значит, два остальных угла тоже равны по 60o. ((180o-60o)/2) – треугольники равносторонние.
Обозначим длину стороны шестиугольника буквой a. Тогда площадь одного треугольника будет равна:
S1 = 1/2*√3/2*a*a = √3/4*a2.
Формула получена на основании стандартного выражения для площади треугольника. Тогда площадь S6 для шестиугольника будет:
S6 = 6*S1 = 6*√3/4*a2 = 3*√3/2*a2.
Формула определения объема правильной шестиугольной призмы
Чтобы записать формулу для объема рассматриваемой фигуры, следует учесть приведенную выше информацию. Для произвольной призмы объем пространства, ограниченный ее гранями, вычисляется так:
V = h*So.
То есть, V равен произведению площади основания So на высоту h. Поскольку мы знаем, что высота h равна длине бокового ребра b для шестиугольной правильной призмы, а площадь ее основания соответствует S6, то формула объема правильной шестиугольной призмы примет вид:
V6 = 3*√3/2*a2*b.
Пример решения геометрической задачи
Дана шестиугольная правильная призма. Известно, что она вписана в цилиндр радиусом 10 см. Высота призмы в два раза больше стороны ее основания. Необходимо найти объем фигуры.

Чтобы найти требуемую величину, необходимо знать длину стороны и бокового ребра. При рассмотрении правильного шестиугольника было показано, что его геометрический центр расположен в середине описанной вокруг него окружности. Радиус последней равен расстоянию от центра до любой из вершин. То есть он равен длине стороны шестиугольника. Эти рассуждения приводят к следующим результатам:
a = r = 10 см;
b = h = 2*a = 20 см.
Подставляя эти данные в формулу объема правильной шестиугольной призмы, получим ответ: V6≈5196 см3 или около 5,2 литра.
Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 18 апреля 2020 года; проверки требует 1 правка.
Шестиугольная призма — призма с шестиугольным основанием. У этого многогранника 8 граней, 18 рёбер и 12 вершин[1].
До заточки многие карандаши имеют форму длинной шестиугольной призмы[2].
Полуправильный (или однородный) многогранник[править | править код]
Если все боковые грани одинаковые, шестиугольная призма является полуправильным многогранником, более обще, однородным многогранником и четвёртой призмой в бесконечном множестве призм, образованных прямоугольными боковыми сторонами и двумя правильными основаниями. Призму можно рассматривать как усечённый[en] шестигранный осоэдр, представленный символом Шлефли t{2,6}. С другой стороны, его можно рассматривать как прямое произведение правильного шестиугольника на отрезок, которое представляется как {6}×{}. Двойственным многогранником шестиугольной призмы является шестиугольная бипирамида[en].
Группой симметрии прямой шестиугольной призмы является D6h с порядком 24, а группой вращений является D6 с порядком 12.
Объём[править | править код]
Как и у большинства призм, объём правильной шестигранной призмы можно найти умножением площади основания (с длиной стороны 


Симметрия[править | править код]
Топология однородной шестиугольной призмы могут иметь геометрические вариации с низкой симметрией:
| Симметрия | D6h, [2,6], (*622) | C6v, [6], (*66) | D3h, [2,3], (*322) | D3d, [2+,6], (2*3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Конструкция | {6}×{}, |
t{3}×{}, |
s2{2,6}, |
||
| Рисунок | 
|

|

|
|
|
| Нарушение | 
|

|
|

|
Как часть пространственных мозаик[править | править код]
Шестигранная призма присутствует как ячейка в четырёх призматических однородных выпуклых сотах[en] в трёхмерном пространстве:
Шестигранные призмы существуют также в качестве трёхмерных граней четырёхмерных однородных многогранников[en]:
| Усечённая тетраэдральная призма[en] |
Усечённая октаэдральная призма[en] |
Усечённая кубоктаэдрическая призма[en] |
Усечённая икосаэдрическая призма[en] |
Усечённая икосододекаэдрическая призма[en] |

|
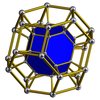
|
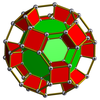
|
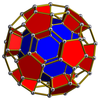
|

|
| Усечённая внутрь 5-ячейка[en] |
Рёберно усечённая 5-ячейка[en] |
Усечённая внутрь 16-ячейка[en] |
Рёберно усечённый гиперкуб[en] |
|

|
|
|

|
|
| Усечённая внутрь 24-ячейка[en] |
Рёберно усечённая 24-ячейка[en] |
Усечённая внутрь 600-ячейка[en] |
Рёберно усечённая 120-ячейка[en] |
|

|

|

|

|
Связанные многогранники и мозаики[править | править код]
| Симметрия: [6,2], (*622) | [6,2]+, (622) | [6,2+], (2*3) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|

|

|

|

|
|

|
||
| {6,2} | t{6,2} | r{6,2} | t{2,6} | {2,6} | rr{2,6} | tr{6,2}[en] | sr{6,2} | s{2,6} |
| Двойственные им многогранники | ||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| V62 | V122 | V62 | V4.4.6[en] | V26 | V4.4.6[en] | V4.4.12 | V3.3.3.6[en] | V3.3.3.3 |
Этот многогранник можно считать членом последовательности однородных многогранников с угловой фигурой (4.6.2p) и диаграммой Коксетера — Дынкина ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . Для p < 6 членами последовательности являются усечённые во всех углах многогранники (зоноэдры), и они показаны ниже как сферические мозаики. Для p > 6 они являются мозаиками гиперболической плоскости начиная с усечённой трисемиугольной мозаики[en].
. Для p < 6 членами последовательности являются усечённые во всех углах многогранники (зоноэдры), и они показаны ниже как сферические мозаики. Для p > 6 они являются мозаиками гиперболической плоскости начиная с усечённой трисемиугольной мозаики[en].
| Симметрия *n32[en] n,3[en] |
Сферическая | Евклидова | Компактная гиперболическая | Паракомп. | Некомпактная гиперболическая | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *232 [2,3] |
*332 [3,3] |
*432 [4,3] |
*532 [5,3] |
*632 [6,3] |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3] |
*∞32 [∞,3] |
[12i,3] |
[9i,3] |
[6i,3] |
[3i,3] |
|
| Фигуры | 
|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|
|

|
|
| Конфигурация | 4.6.4 | 4.6.6 | 4.6.8 | 4.6.10 | 4.6.12[en] | 4.6.14[en] | 4.6.16[en] | 4.6.∞[en] | 4.6.24i | 4.6.18i | 4.6.12i | 4.6.6i |
| Двойственная | 
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Конфигурация грани | V4.6.4[en] | V4.6.6 | V4.6.8[en] | V4.6.10 | V4.6.12[en] | V4.6.14[en] | V4.6.16[en] | V4.6.∞ | V4.6.24i | V4.6.18i | V4.6.12i | V4.6.6i |
См. также[править | править код]
| Многоугольник | 
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Мозаика | ||||||||||||
| Конфигурация | 3.4.4 | 4.4.4 | 5.4.4 | 6.4.4 | 7.4.4 | 8.4.4 | 9.4.4 | 10.4.4 | 11.4.4 | 12.4.4 | 17.4.4 | ∞.4.4 |
Примечания[править | править код]
- ↑ 1 2 Anthony Pugh. Polyhedra: A Visual Approach. — University of California Press, 1976. — С. 21, 27, 62. — ISBN 9780520030565.
- ↑ Audrey Simpson. Core Mathematics for Cambridge IGCSE. — Cambridge University Press, 2011. — С. 266–267. — ISBN 9780521727921.
- ↑ Carolyn C. Wheater. Geometry. — Career Press, 2007. — С. 236–237. — ISBN 9781564149367.
Ссылки[править | править код]
- Uniform Honeycombs in 3-Space Модели в формате VRML
- The Uniform Polyhedra
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
- Prisms and antiprisms
- Weisstein, Eric W. Hexagonal prism (англ.) на сайте Wolfram MathWorld.
- Hexagonal Prism Interactive Model — Просмотр призм в браузере
A hexagonal prism is a three-dimensional geometric structure with two hexagonal bases connected by six rectangular faces. It is a polyhedron with eight faces, twelve vertices, and eighteen edges. It is also known as an octahedron as it has eight faces; two of the eight faces are hexagons, which are the bases of the prism, and the other six faces are rectangles, which are the lateral (or) side faces of the prism. The top and bottom faces of the hexagonal prism are in the shape of a hexagon and are congruent with each other.

There are two kinds of hexagonal prisms, namely, a regular hexagonal prism and an irregular hexagonal prism.
- A regular hexagonal prism is a prism that has two hexagonal bases whose all sides are of the same length. In a regular hexagonal prism, the angles also measure the same.
- An irregular hexagonal prism is a prism that has two irregular hexagonal bases. All the sides of the base do not have the same length, and the measures of each angle are different.
Surface Area of a Hexagonal Prism
The total area that is covered by the surfaces of a hexagonal prism is referred to as its surface area. The surface area of a prism is measured in terms of square units such as sq. m, sq. cm, sq. in, etc. A hexagonal prism has two types of areas just like other three-dimensional shapes: lateral surface area (LSA) and total surface area (TSA).
Let us consider a hexagonal prism that has an apothem length “a”, a base length “s”, and a height “h”. We know that the general formula to calculate the lateral surface area of a prism is the product of its base and height. So, the lateral surface area of the prism of a hexagonal prism is determined by calculating the product of the perimeter of the base of the hexagonal prism and its height.
The formula to determine the lateral surface area of the hexagonal prism is equal to the sum of the areas of its six rectangular faces. Thus,
Lateral surface area of hexagonal prism (LSA) = 6sh sq. units.
Where “s” is the length of the base edge, and
“h” is the height of the prism.

The formula to determine the surface area of a hexagonal prism is given as follows:
Total Surface Area, TSA = 2×(Area of hexagonal base) + 6×(Area of rectangular faces) = 6s(a + h).
Total surface area of the hexagonal prism (TSA) = 6s(a + h) sq. units.
Where “a” is the apothem length,
“s” is the length of the base edge, and
“h” is the height of the prism.
The formula to determine the surface area of a hexagonal prism in the case of a regular hexagonal prism, TSA = 6sh + 3√3s2.
Total surface area of the hexagonal prism (TSA) = 6sh + 3√3s2 sq. units.
Where “s” is the length of the base edge, and
“h” is the height of the prism.
Volume of a Hexagonal Prism
The volume of a hexagonal prism is the amount of space enclosed by it in three-dimensional space. It is also referred to as the amount of substance that it can hold, which is the capacity of a hexagonal prism. The formula for the volume of a hexagonal prism is equivalent to the product of its base area and height, which is measured in terms of cubic units such as cm3, m3, in3, etc.
The formula for finding the volume of a hexagonal prism is given as follows,
Volume of the Hexagonal Prism (V) = Base area × height

The formula for calculating the volume of a hexagonal prism when the length of the edge of the base and height of the prism is known is given as follows.
Volume of the Hexagonal Prism (V) = [(3√3)/2]s2h
Where “s” is the length of the base edge, and
“h” is the height of the prism.
The formula for calculating the volume of a hexagonal prism when the apothem length, length of the edge of the base, and height of the prism are known is given as follows.
Volume of the Hexagonal Prism (V) = 3ash
Where “a” is the apothem length,
“s” is the length of the base edge, and
“h” is the height of the prism.
Solved Example on Volume of a Hexagonal Prism
Example 1: Calculate the volume of a hexagonal prism with a base edge length of 15 cm and a height of 12 cm.
Solution:
Given data,
Length of the base edge (s) = 15 cm
The height of the prism (h) = 12 cm
We know that,
The volume of a hexagonal prism = [(3√3)/2]s2h
= (3/2) × (1.732) × (15)2 × 12
= 7,014.805 cu. cm
Hence, the volume of the hexagonal prism is 7,014.805 cu. cm.
Example 2: Determine the volume of the hexagonal prism if its height is 10 inches and its base area is given as 60 sq. in.
Solution:
Given data,
Base area = 60 sq. in
The height of the prism (h) = 10 inches
We know that
The volume of the hexagonal prism (V) = Base area × height
= 60 × 10 = 600 cu. in
Hence, the volume of the hexagonal prism is 600 cu. in.
Example 3: Calculate the volume of a hexagonal prism if its height is 13 cm, the length of each side of the base is 10 cm, and the apothem length is 8 cm.
Solution:
Given data,
Length of the base edge length (s) = 10 cm
Apothem length (a) = 8 cm
The height of the prism (h) = 13 cm
We know that
The volume of the hexagonal prism (V) = 3ash cubic units
= 3 × 8 × 10 × 13 = 3,120 cu. cm
Hence, the volume of the hexagonal prism is 3,120 cu. cm.
Example 4: Find the total surface area of a hexagonal prism if the length of each side of the base is 8 cm and the height is 10 cm.
Solution:
Given data,
Length of the base edge (s) = 8 cm
The height of the prism (h) = 10 cm
We know that,
The total surface area of the hexagonal prism = 6sh + 3√3s2
= 6 × 8 × 10 + 3√3 × (8)2
= 480 + 3√3 × 64
= 480 + 332.554 = 812.554 sq. cm
Thus, the total surface area of the hexagonal prism is 812.554 sq. cm.
Example 5: Determine the lateral surface area of a hexagonal prism with a base edge length of 12 cm and a height of 9 cm.
Solution:
Given data,
Length of the base edge length (s) = 12 cm
The height of the prism (h) = 9 cm
We know that,
The lateral surface area of a hexagonal prism = 6sh sq. units
LSA = 6 × 12 × 9
LSA = 648 sq. cm
Hence, the volume of the hexagonal prism is 648 sq. cm.
FAQs on Hexagonal Prism
Question 1: What is the Volume of a Hexagonal Prism?
Answer:
The volume of a hexagonal prism is the amount of space enclosed by it in three-dimensional space. It is also referred to as the amount of substance that it can hold, which is the capacity of a hexagonal prism. The formula for the volume of a hexagonal prism is equivalent to the product of its base area and height, which is measured in terms of cubic units such as cm3, m3, in3, etc.
The formula for finding the volume of a rectangular prism is given as follows,
The volume of the hexagonal prism (V) = Base area × height
Question 2: How to determine the Volume of a Hexagonal Prism?
Answer:
Follow the steps given below to determine the volume of a hexagonal prism:
Step 1: Calculate the base area of the prism using the appropriate formula.
Step 2: Note down the value of the height of the given hexagonal prism.
Step 3: Substitute the values of the given dimensions in the formula, V = [(3√3)/2]s2h
Step 4: Finally, write the final value in appropriate cubic units.
Question 3: How can we determine the Volume of a Hexagonal Prism when its Base Area and Height are given?
Answer:
We know that the general formula for calculating the volume of any prism is the product of its base area and its height. A hexagonal prism is a prism that has a hexagon as its base. So, we can also use the same formula for determining the volume of a hexagonal prism. As both the base area and the height of the hexagonal prism are given, the formula to determine the volume of a hexagonal prism is given as follows:
Volume of a hexagonal prism = Base Area × height.
Question 4: What will happen to the Volume of the Hexagonal Prism if its Height is reduced to Half?
Answer:
We know that the formula for calculating the volume of the hexagonal prism is V = 3abh. Where “a” is the apothem length, “s” is the length of the base edge, and “h” is the height of the prism. So, the volume of the prism is directly proportional to its height. So, if the height is reduced to half, the new height will become (h/2). So, the volume of the new hexagonal prism will be 3ab (h/2) = (1/2) (3abh) = V/2. Therefore, we can conclude the volume will also be reduced by half.
Question 5: What is meant by the Surface Area of a Hexagonal Prism?
Answer:
The total area that is covered by the surfaces of a hexagonal prism is referred to as its surface area. The surface area of a prism is measured in terms of square units such as sq. m, sq. cm, sq. in, etc. The formula to determine the surface area of a hexagonal prism is given as follows:
Total Surface Area, TSA = 2(Area of hexagon base) + 6(Area of rectangle faces) = 6s(a + h), where the “a” is apothem length of the prism, “s” is the length of the base edge, and “h” is the height of the prism.
The formula to determine the surface area of a hexagonal prism in the case of a regular hexagonal prism, TSA = 6sh + 3√3s2.
Question 6: How to determine the Lateral Surface Area of a Hexagonal Prism?
Answer:
Follow the steps mentioned below to determine the lateral surface area of the hexagonal prism:
- Step 1: Note down the values of the apothem length, base length, and height of the given hexagonal prism.
- Step 2: Substitute the given values in the formula of the lateral surface area of a hexagonal prism, LSA = 6sh.
- Step 3: Write the resulting value in square units.
