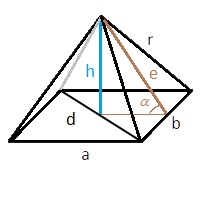В данной публикации мы рассмотрим, как можно вычислить площадь поверхности различных видов правильных пирамид: треугольной, четырехугольной и шестиугольной.
Правильная пирамида – это пирамида, вершина которой проецируется в центр основания, являющегося правильным многоугольником.
-
Формула площади правильной пирамиды
- 1. Общая формула
-
2. Площадь правильной треугольной пирамиды
- 3. Площадь правильной четырехугольной пирамиды
- 4. Площадь правильной шестиугольной пирамиды
Формула площади правильной пирамиды
1. Общая формула
Площадь (S) полной поверхности пирамиды равняется сумме площади ее боковой поверхности и основания.
Sполн. = Sбок. + Sосн.
Боковой гранью правильной пирамиды является равнобедренный треугольник.
Площадь треугольника вычисляется по формулам:
1. Через длину основания (a) и высоту (h):
2. Через основание (a) и боковую сторону (b):
Формула площади основания правильной пирамиды зависит от вида многогранника. Далее мы рассмотрим самые популярные варианты.
2. Площадь правильной треугольной пирамиды
Основание: равносторонний треугольник.
L (апофема) – перпендикулярная линия, опущенная из вершины пирамиды на ребро основания. Т.е. апофема пирамиды является высотой (h) ее боковой грани.
3. Площадь правильной четырехугольной пирамиды
Основание: квадрат.
| Площадь | Формула |
| основание | Sосн. = a2 |
| боковая поверхность | Sбок. = 2aL |
 |
|
| полная | Sполн. = a2 + 2aL |
 |
microexcel.ru
4. Площадь правильной шестиугольной пирамиды
Основание: правильный шестиугольник
Пирамида — это многогранник, в основании которого лежит многоугольник, а грани его являются треугольниками.
Онлайн-калькулятор площади поверхности пирамиды
Стоит остановиться на определении некоторых составляющих пирамиды.
У нее, как и у других многогранников, есть ребра. Они сходятся к одной точке, которая называется вершиной пирамиды. В ее основании может лежать произвольный многоугольник. Гранью называется геометрическая фигура, образованная одной из сторон основания и двумя ближайшими ребрами. В нашем случае это треугольник. Высотой пирамиды называется расстояние от плоскости, в которой лежит ее основание, до вершины многогранника. Для правильной пирамиды существует еще понятие апофемы – это перпендикуляр, опущенный из вершины пирамиды к её основанию.
Виды пирамид
Существуют 3 вида пирамид:
- Прямоугольная — та, у которой какое-либо ребро образует прямой угол с основанием.
- Правильная — у нее основание – правильная геометрическая фигура, а вершина самого многоугольника является проекцией центра основания.
- Тетраэдр — пирамида, составленная из треугольников. Причем каждый из них может быть принят за основание.
Формула площади поверхности пирамиды
Для нахождения полной площади поверхности пирамиды нужно сложить площадь боковой поверхности и площадь основания.
Самой простой является случай правильной пирамиды, поэтому нею мы и займемся. Вычислим полную площадь поверхности такой пирамиды. Площадь боковой поверхности равна:
Sбок=12⋅l⋅pS_{text{бок}}=frac{1}{2}cdot lcdot p
ll — апофема пирамиды;
pp — периметр основания пирамиды.
Полная площадь поверхности пирамиды:
S=Sбок+SоснS=S_{text{бок}}+S_{text{осн}}
SбокS_{text{бок}} — площадь боковой поверхности пирамиды;
SоснS_{text{осн}} — площадь основания пирамиды.
Пример решения задачи.
Найти полную площадь треугольной пирамиды, если её апофема равна 8 (см.), а в основании лежит равносторонний треугольник со стороной 3 (см.)
Решение
l=8l=8
a=3a=3
Найдем периметр основания. Так как в основании лежит равносторонний треугольник со стороной aa, то его периметр pp (сумма всех его сторон):
p=a+a+a=3⋅a=3⋅3=9p=a+a+a=3cdot a=3cdot 3=9
Тогда боковая площадь пирамиды:
Sбок=12⋅l⋅p=12⋅8⋅9=36S_{text{бок}}=frac{1}{2}cdot lcdot p=frac{1}{2}cdot 8cdot 9=36 (см. кв.)
Теперь найдем площадь основания пирамиды, то есть площадь треугольника. В нашем случае треугольник равносторонний и его площадь можно вычислить по формуле:
Sосн=3⋅a24S_{text{осн}}=frac{sqrt{3}cdot a^2}{4}
aa — сторона треугольника.
Получаем:
Sосн=3⋅a24=3⋅324≈3.9S_{text{осн}}=frac{sqrt{3}cdot a^2}{4}=frac{sqrt{3}cdot 3^2}{4}approx3.9 (см. кв.)
Полная площадь:
S=Sбок+Sосн≈36+3.9=39.9S=S_{text{бок}}+S_{text{осн}}approx36+3.9=39.9 (см. кв.)
Ответ: 39.9 см. кв.
Еще один пример, немного сложнее.
Основанием пирамиды является квадрат с площадью 36 (см. кв.). Апофема многогранника в 3 раза больше стороны основания aa. Найти полную площадь поверхности данной фигуры.
Решение
Sквад=36S_{text{квад}}=36
l=3⋅al=3cdot a
Найдем сторону основания, то есть сторону квадрата. Его площадь и длина стороны связанны:
Sквад=a2S_{text{квад}}=a^2
36=a236=a^2
a=6a=6
Найдем периметр основания пирамиды (то есть, периметр квадрата):
p=a+a+a+a=4⋅a=4⋅6=24p=a+a+a+a=4cdot a=4cdot 6=24
Найдем длину апофемы:
l=3⋅a=3⋅6=18l=3cdot a=3cdot 6=18
В нашем случае:
Sквад=SоснS_{text{квад}}=S_{text{осн}}
Осталось найти только площадь боковой поверхности. По формуле:
Sбок=12⋅l⋅p=12⋅18⋅24=216S_{text{бок}}=frac{1}{2}cdot lcdot p=frac{1}{2}cdot 18cdot 24=216 (см. кв.)
Полная площадь:
S=Sбок+Sосн=216+36=252S=S_{text{бок}}+S_{text{осн}}=216+36=252 (см. кв.)
Ответ: 252 см. кв.
Возникают трудности с тем, чтобы найти площадь поверхности пирамиды? У нас вы можете заказать контрольную работу по геометрии!
Формулы для расчета приведены под калькулятором.
Площадь четырехугольной пирамиды
Угол наклона граней в градусах (α)
Точность вычисления
Знаков после запятой: 2
Четырехугольная пирамида
В формулах ниже будем использовать следующие обозначения:
a – длина первой стороны основания
b – длина второй стороны основания (для квадрата будет равна первой)
h – высота пирамиды
r – ребро пирамиды
d – диагональ основания
e – высота треугольника, образованного боковой гранью, т.е. высота, опущенная из вершины пирамиды на ее сторону
α – угол наклона грани пирамиды (угол между высотой треугольника боковой грани и плоскостью основания)
Во всех случаях площадь основания вычисляется тривиально – перемножением длин сторон основания. Ниже рассмотрим нахождение площадей боковых граней для разных случаев.
Площадь поверхности пирамиды через высоту
-
Находим высоту треугольника, образованного боковой гранью. Используем теорему Пифагора на прямоугольном треугольнике, образованном высотой пирамиды, высотой треугольника боковой грани, и проекцией высоты треугольника на плоскость основания. Длина проекции очевидно равна половине длины противоположной стороны. Таким образом, высота треугольника, опущенная на сторону a
высота треугольника, опущенная на сторону b
-
Находим площади боковых граней, по формуле площади равнобедренного треугольника
- Общая площадь боковых граней
Площадь поверхности пирамиды через угол наклона
Расчет через один угол наклона возможен, только если в основании пирамиды лежит квадрат (иначе пришлось бы задавать два угла). Соответственно, сторона a равна стороне b, и все грани одинаковые.
-
Находим высоту треугольника, образованного боковой гранью, поделив длину проекции на плоскость основания на косинус угла наклона
-
Находим площадь боковой грани, по формуле площади равнобедренного треугольника
- Общую площадь боковых граней получаем, умножив площадь одной грани на 4.
Площадь поверхности пирамиды через длину ребра
Здесь есть ограничение: длина ребра должна быть больше чем половина диагонали основания (иначе это не пирамида)
-
Находим высоту треугольника, образованного боковой гранью. Используем теорему Пифагора на прямоугольном треугольнике, образованном ребром пирамиды, высотой треугольника боковой грани, и половиной стороны, на которую опущена высота. Таким образом, высота треугольника, опущенная на сторону a
высота треугольника, опущенная на сторону b
-
Находим площади боковых граней, по формуле площади равнобедренного треугольника
- Общая площадь боковых граней
Площадь прямоугольной пирамиды находится как сумма (S_{бок} ) и (S_{осн}):
(S_{пир}=)(S_{бок} )(+S_{осн})(=frac{1}{2}PS+b^2)
где (P-)периметр пирамиды;
(S-)апофема пирамиды;
P пирамиды :
Апофема пирамиды:
Сторона основания пирамиды:
Больше уроков и заданий по всем школьным предметам в онлайн-школе “Альфа”. Запишитесь на пробное занятие прямо сейчас!
Запишитесь на бесплатное тестирование знаний!
Нажимая кнопку “Записаться” принимаю условия Пользовательского соглашения и Политики конфиденциальности
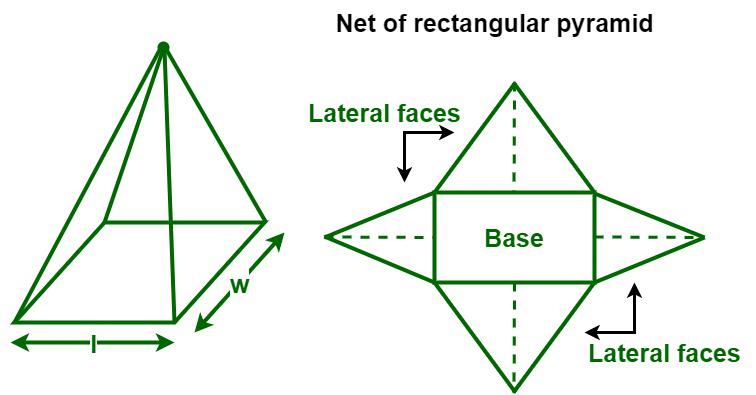
A rectangular pyramid is a three-dimensional object that has a rectangular base upon which are erected four triangular faces that meet at a common point called the apex. It has a total of five faces, i.e., a rectangular base, four triangular faces, five vertices, and eight edges. In a rectangular pyramid, all the triangular faces are congruent to the opposite face. A rectangular pyramid is classified into two types, i.e., a right rectangular pyramid and an oblique rectangular pyramid. A right rectangular pyramid is a rectangular pyramid that has its apex directly above the center of its base, whereas an oblique rectangular pyramid is a rectangular pyramid where the apex is not aligned right above the center of its base. The height of an oblique rectangular pyramid is the perpendicular line drawn from the apex to the base of the pyramid. In this article, we will discuss the surface area of a rectangular pyramid in detail.
Surface Area of a Rectangular Pyramid
Surface area is defined as the total region occupied by the surfaces of a three-dimensional figure, and it is measured in terms of square units such as cm2, m2, in2, ft2, etc. A rectangular pyramid has two types of surface areas, i.e., the lateral surface area and the total surface area.
Lateral Surface Area
The lateral surface area of a rectangular pyramid is equal to the sum of the areas of its four lateral faces (triangular faces). In a rectangular pyramid, the areas of the opposite triangular faces are the same. To find the surface area of a rectangular pyramid, we need to know the measures of the base length, base width, and slant height of the triangular face.
Lateral Surface Area of a Pyramid (LSA) = Sum of Areas of the lateral surfaces (triangles) of the pyramid
Slant height of length face of the pyramid = √[h2 + (w/2)2]
Slant height of width face of the pyramid = √[h2 + (l/2)2]
We know that,
The area of a triangle = ½ × base × height
Area of the triangle that has a length as the base = ½ × l × {√[h2 + (l/2)2]}
Area of the triangle that has a width as the base = ½ × w × {√[h2 + (w/2)2}
Now, LSA = ½ × l × {√[h2 + (w/2)2]} + ½ × w × {√[h2 + (l/2)2} + ½ × l × {√[h2 + (w/2)2]} + ½ × w × {√[h2 + (l/2)2}
= 2 × {½ × l ×√[h2 + (w/2)2]} + 2 × {½ × w ×√[h2 + (l/2)2]}
= l√[h2 + (w/2)2] + w√[h2 + (l/2)2]
Lateral surface area of a rectangular pyramid = l√[h2 + (w/2)2] + w√[h2 + (l/2)2]
where,
“l” is the base length,
“w” is the base width, and
“h” is the height of the pyramid.
Total Surface Area
The total surface area of a rectangular pyramid is equal to the sum of the areas of its four lateral faces (triangular faces) and the area of its rectangular base. To determine the total surface area of a rectangular pyramid, we need to find the area of its rectangular base and its lateral surface area, i.e., the sum of the areas of its four triangular faces.
Total surface area of a pyramid (TSA) = Lateral surface area of the pyramid + Area of the base
Area of rectangular base = l × w
So, TSA = l√[h2 + (w/2)2] + w√[h2 + (l/2)2] + l × w
TSA of a Rectangular Pyramid = l√[h2 + (w/2)2] + w√[h2 + (l/2)2] + l × w
where,
“l” is the base length,
“w” is the base width, and
“h” is the height of the pyramid.
How to Calculate the Surface Area of a Rectangular Pyramid?
The surface area of a rectangular pyramid is calculated by converting the 3-D shape into its 2-D net. After opening the Rectangular pyramid, we get four triangles and one rectangle. To find its surface area follow these steps.
Steps used to calculate the surface area of a rectangular pyramid is:
Step 1: Find the area of the rectangular base. The area of the rectangle is calculated using its length and breadth.
Step 2: Find an area of the triangle faces. The area of a triangle is calculated using its base and height.
Step 3: Now for finding the required surface area the area of the rectangular base and the triangular face are added accordingly.
Step 4: The area obtained in Step 3 is the required area it is measured in unit2
Solved Examples on Surface Area of Rectangular Pyramid
Problem 1. Determine the lateral surface area of a rectangular pyramid if the base length is 10 inches and the base width is 8 inches, and the height of the pyramid is 12 inches.
Solution:
Given data,
Base length (l) = 16 inches
Base width (w) = 12 inches
The height of the pyramid (h) = 15 inches
We know that,
Lateral surface area of a rectangular pyramid = l√[h2 + (w/2)2] + w√[h2 + (l/2)2]
= 10 × √[122 + (8/2)2] + 8 × √[122 + (10/2)2]
= 10 × √(144 + 16) + 8 × √(144 + 25)
= 10 × √160 + 8 × √169
= 10 × 12.649 + 8 × 13
= 126.49 + 104 = 230.49 sq. in
Hence, the lateral surface area of the given rectangular pyramid is 230.49 sq. in.
Problem 2. Find the surface area of a rectangular pyramid if the base length is 8 cm and the base width is 6 cm, and the height of the pyramid is 10 cm.
Solution:
Given data,
Base length (l) = 8 cm
Base width (w) = 6 cm
The height of the pyramid (h) = 10 cm
We know that,
Total surface area of a rectangular pyramid = l√[h2 + (w/2)2] + w√[h2 + (l/2)2] + l × w
= (8 × √[102 + (6/2)2] + 6 × √[102 + (8/2)2] + 8 × 6
= 8 × √(100 + 9) + 6 × √(100 + 16) + 48
= 8 × √109 + 6 × √116 + 48
= 8 × 10.440 + 6 × 10.770 + 48
= 83.522 + 64.621 + 48 = 196.143 sq. cm
Hence, the surface area of the given rectangular pyramid is 196.143 sq. cm.
Problem 3. Find the total surface area of a rectangular pyramid if the base length is 12 cm and the base width is 10 cm, and the height of the pyramid is 15 cm.
Solution:
Given data,
Base length (l) = 12 cm
Base width (w) = 10 cm
The height of the pyramid (h) = 15 cm
We know that,
Total surface area of a rectangular pyramid = l√[h2 + (w/2)2] + w√[h2 + (l/2)2] + l × w
= (10 × √[152 + (12/2)2] + 12 × √[152 + (10/2)2] + 12 × 10
= 10 × √(225 + 36) + 12 × √(225 + 25) + 120
= 10 × √261 + 12 × √250 + 120
= 10 × 16.155 + 12 × 15.811 + 120
= 161.554 + 189.736 + 120 = 471.29 sq. cm
Hence, the surface area of the given rectangular pyramid is 471.29 sq. cm.
Problem 4. Determine the lateral surface area of a rectangular pyramid if the base length is 8 m and the base width is 4 m, and the height of the pyramid is 9 m.
Solution:
Given data,
Base length (l) = 8 m
Base width (w) = 4 m
The height of the pyramid (h) = 9 m
We know that,
Lateral surface area of a rectangular pyramid = l√[h2 + (w/2)2] + w√[h2 + (l/2)2]
= 8 × √[92 + (4/2)2] + 4 × √[92 + (8/2)2]
= 8 × √(81 + 4) + 4 × √(81 + 16)
= 8 × √85 + 4 × √97
= 8 × 9.219 + 4 × 9.849
= 73.756 + 39.395 = 113.151 sq. m
Hence, the lateral surface area of the given rectangular pyramid is 113.151 sq. m.
Problem 5. Find the surface area of a rectangular pyramid if the base length is 20 inches and the base width is 16 inches, and the height of the pyramid is 25 inches.
Solution:
Given data,
Base length (l) = 20 inches
Base width (w) = 16 inches
The height of the pyramid (h) = 25 inches
We know that,
Total surface area of a rectangular pyramid = l√[h2 + (w/2)2] + w√[h2 + (l/2)2] + l × w
= (20 × √[252 + (16/2)2] + 16 × √[252 + (20/2)2] + 20 × 16
= 20 × √(625 + 36) + 16 × √(625 + 100) + 320
= 20 × √689 + 16 × √250 + 320
= 20 × 26.249 + 16 × 26.925 + 320
= 524.976 + 430.813 + 320 = 1,275.789 sq. in
Hence, the surface area of the given rectangular pyramid is 1,275.789 sq. in.
FAQs on Surface Area of Rectangular Pyramid
Question 1: What is the definition of a rectangular pyramid?
Answer:
A rectangular pyramid is a three-dimensional geometric figure that has a rectangular base and four triangular faces that meet at a common vertex called the apex.
Question 2: What are the types of rectangular pyramids?
Answer:
There are two types of rectangular pyramids, namely, a right rectangular pyramid and an oblique rectangular pyramid.
Question 3: What is the formula to find the lateral surface area of a rectangular pyramid?
Answer:
The lateral surface area of a rectangular pyramid is equal to the sum of the areas of its four lateral faces (triangular faces), and the formula to calculate it is given below.
Lateral surface area of a rectangular pyramid = l√[h2 + (w/2)2] + w√[h2 + (l/2)2]
Where “l” is the base length,
“w” is the base width, and
“h” is the height of the pyramid.
Question 4: Define surface area.
Answer:
Surface area is defined as the total region occupied by the surfaces of a three-dimensional figure.
Question 5: What is the formula to find the total surface area of a rectangular pyramid?
Answer:
The total surface area of a rectangular pyramid is equal to the sum of the areas of its four lateral faces (triangular faces) and the area of its rectangular base, and the formula to calculate it is given below.
Total surface area of a rectangular pyramid = l√[h2 + (w/2)2] + w√[h2 + (l/2)2] + l × w
where,
“l” is the base length,
“w” is the base width,
“h” is the height of the pyramid.
Related Resources
- Surface Area of Pyramid
- Volume of Pyramid
- Square Pyramid