I’m assuming that you’re looking for the server used by the W32Time service to perform time sync on domain-member computers.
In a stock Active Directory deployment the only computer configured with a time server explicitly will be computer holding the PDC Emulator FSMO role in the forest root domain. All domain controllers in the forest root domain synchronize time with the PDC Emulator FSMO role-holder. All PDC Emulator FSMO role-holders in child domains synchronize their time with domain controllers in their parent domain (including, potentially, the PDF Emulator FSMO role-holder in the forest root domain). All domain member computers synchronize time with domain controller computers in their respective domains.
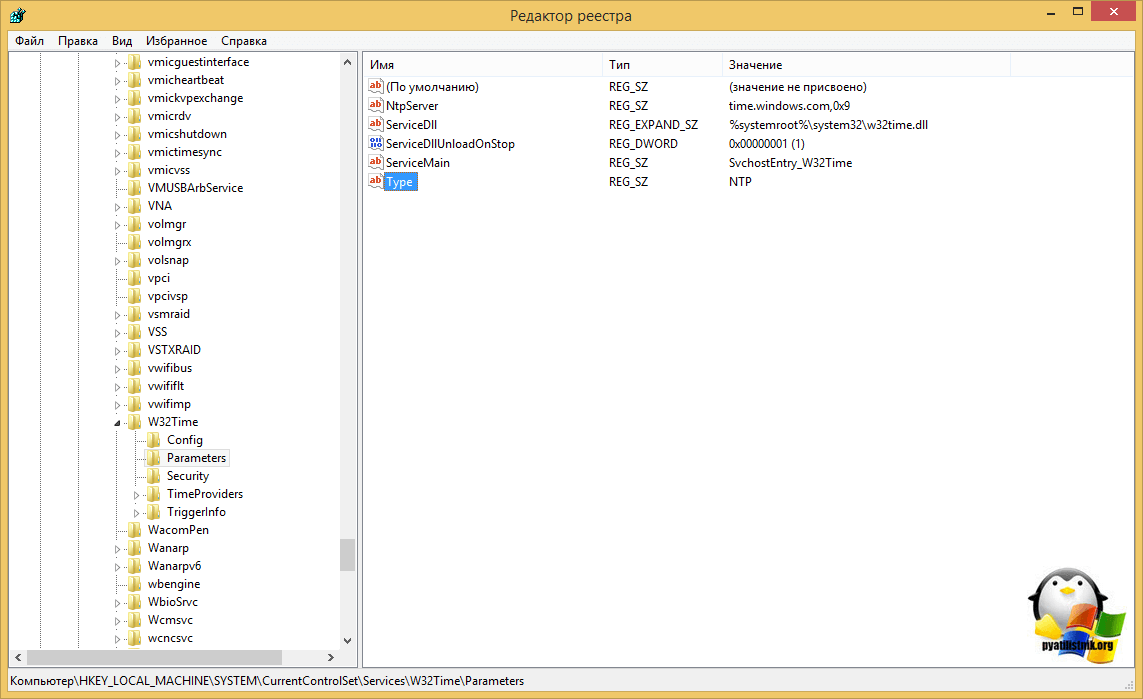
To determine if a domain member is configured for domain time sync, examine the REG_SZ value at HKLMSystemCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParametersType. If it is set to “Nt5DS” then the computer is synchronizing time with the Active Directory time hierarchy. If it’s configured with the value “NTP” then the comptuer is synchronizing time with the NTP server specified in the NtpServer REG_SZ value in the same registry key.
The low-level details of the time synchronization protocol are available in this article: How Windows Time Service Works
Beware that not every domain controller (the KDC’s, as James directs you in finding via DNS in his post) may be running a time service. In a stock AD deployment every domain controller will be, but some deployments may use virtualized domain controllers that have the W32Time service disabled (to facilitate hypervisor-based time synchronization) and, as such, you would probably do well to implement functionality as described by the “How Windows Time Service Works” article if you’re developing a piece of software that needs to synchronize time in the same manner that a domain member computer would.
Сохранить все ПК
синхронизация, обновление времени в Интернете поможет вам справиться с этим. И делать
что вам нужно сначала найти NTP (сетевой протокол времени).
Командная строка Windows доставит вас туда. А также
если вы не знаете, с чего начать, не волнуйтесь.
В этом посте
вы узнаете, что вам нужно, как найти NTP-сервер для домена.
Зарегистрируйтесь и начните
Если вы не
зарегистрированный Windows Time Service пока что, приведенные ниже команды покажут вам, как это сделать
Это. Вам также нужно запустить службу, прежде чем вы сможете синхронизировать время вашего компьютера
с вашим NTP-сервером.
Сначала нужно
Запустите командную строку. Выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».
Затем введите
Следующая команда для регистрации вашей системы: w32tm
/регистр
Как только вы нажмете
введите, вы узнаете, если регистрация прошла успешно.
Теперь начнем
с помощью этой команды: sc start
w32time
W32tm / запрос
Теперь, когда
Служба времени Windows зарегистрирована и работает, вы можете получить информацию от
Это. Вы можете сделать это, набрав следующее: w32tm / query и сопоставив его со следующими параметрами.
/положение дел
Это покажет
у вас статус службы времени Windows.
/положение дел
/подробный
Это установит
подробный режим, чтобы показать вам больше информации.
/источник
Это покажет
Вы источник времени.
/ конфигурации
Это покажет
вы конфигурация и настройки во время выполнения.
/ сверстники
Это покажет
список людей, использующих вашу систему.
w32tm
/ ресинхронизации
Вы также можете использовать
Командная строка для повторной синхронизации
часы как можно скорее.
Вот
обсуждение каждого параметра этой команды:
/ Компьютер:
Это позволяет вам
укажите компьютер, который будет синхронизирован. Если вы оставите это поле пустым,
темой будет локальный компьютер.
/Нет, подождите
Это позволяет вам
исключить время ожидания для повторной синхронизации. Это означает, что вы не будете
придется ждать завершения процесса, прежде чем результаты будут возвращены.
/мягкий
Это позволяет вам
повторно синхронизировать часы, используя существующие ошибки. Конечно, это не сделает вас
хорошо. Но вы можете обратиться к информации, которую он предоставляет для совместимости.
w32tm
/ конфигурации
Используйте эту команду
настроить вашу систему.
Давайте посмотрим на его
компоненты:
/ Manualpeerlist:
Это позволяет вам установить
список пэров. Это список IP-адресов.
Вы можете оставить это
пусто и по умолчанию будет установлено значение ,
/Обновить
Это позволяет вам
уведомить службу о новых изменениях, которые должны вступить в силу.
/ Localclockdispersion:
Это настраивает
Точность внутренних часов.
/ Надежность:
Это позволяет вам
указать, является ли система надежным источником времени.
/ Largephaseoffset:
Это позволяет вам установить
разница во времени с вашим местным и сетевым временем.
w32tm
/ dumpreg
Получить
Информацию о ключе реестра вы также можете перейти в командную строку. Там введите следующее вместе с w32tm / dumpreg
/ Подраздел:
Это показывает вам
значения, связанные с вложенным ключом ключа по умолчанию.
/ Компьютер:
Это показывает вам
параметры реестра запросов для указанного компьютера.
w32tm
/ отладки
Командная строка также там, где вы можете
получить доступ к личному журналу вашего компьютера. Вот краткое обсуждение параметров
в этой категории.
/включить
или / отключить
Это позволяет вам включить или отключить личный журнал. Потому что вы хотите получить доступ к этому журналу,
Разрешение — это путь.
/файл:
Это позволяет вам
укажите название вашего файла. В приведенном ниже примере, скажем, название нашего
файл «ххх».
/размер:
Это позволяет вам
укажите размер вашего файла. То, что вы должны ввести здесь, это максимальное количество
oftes.в примере, размер нашего файла составляет 100 байт.
/ записи:
Это позволяет вам
перечислить значение для ваших записей. Допустимые числа для этого поля:
от 0 до 300. В данном примере значение равно 10.
Обновлено 12.11.2019
Добрый день уважаемые читатели и гости блога pyatilistnik.org, как много люди говорят о времени, что оно быстро или медленно бежит, и все понимают, что оно бесценно и важно. Так и в инфраструктуре Active Directory, она является одним из важнейших факторов, правильного функционирования домена. В домене все друг другу доверяют, и один раз авторизовавшись и получив все тикеты от Kerberos, пользователь ходит куда угодно, ограничиваясь лишь своими доступными правами. Так вот если у вас не будет точного времени на ваших рабочих станциях к контроллеру домена, то можете считать, что у вас начинаются серьезные проблемы, о которых мы поговорим ниже и рассмотрим как их устранить с помощью настройки NTP сервера в Windows.
Синхронизация времени в Active Directory
Среди компьютеров, участвующих в Active Directory работает следующая схема синхронизация времени.
- Контроллер корневого домена в лесу AD, которому принадлежит FSMО-роль эмулятора PDC (назовем его корневым PDC), является источником времени для всех остальных контроллеров этого домена.
- Контроллеры дочерних доменов синхронизируют время с вышестоящих по топологии AD контроллеров домена.
- Рядовые члены домена (сервера и рабочие станции) синхронизируют свое время с ближайшим к ним доступным контроллером домена, соблюдая топологию AD.
Корневой PDC может синхронизировать свое время как со внешним источником, так и с самим собой, последнее задано конфигурацией по умолчанию и является абсурдом, о чем периодически намекают ошибки в системном журнале.
Синхронизация клиентов корневого PDC может осуществятся как с его внутренних часов, так и с внешнего источника. В первом случае сервер времени корневого PDC объявляет себя как «надежный» (reliable).
Далее я приведу оптимальную с моей точки зрения конфигурацию сервера времени корневого PDC, при которой сам корневой PDC периодически синхронизирует свое время от достоверного источника в интернете, а время обращающихся к нему клиентов синхронизирует со своими внутренними часами.
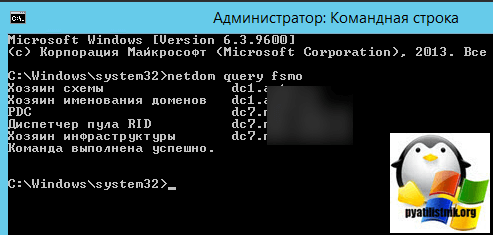
Для того, чтобы понять кто у вас в сети является NTP сервером из контроллеров домена, прочитайте вот эту статью, многие вопросы отпадут сами собой
Вводим netdom query fsmo. В моем примере, роль PDC и NTP сервера, принадлежит контроллеру dc7
Конфигурация NTP-сервера на корневом PDC
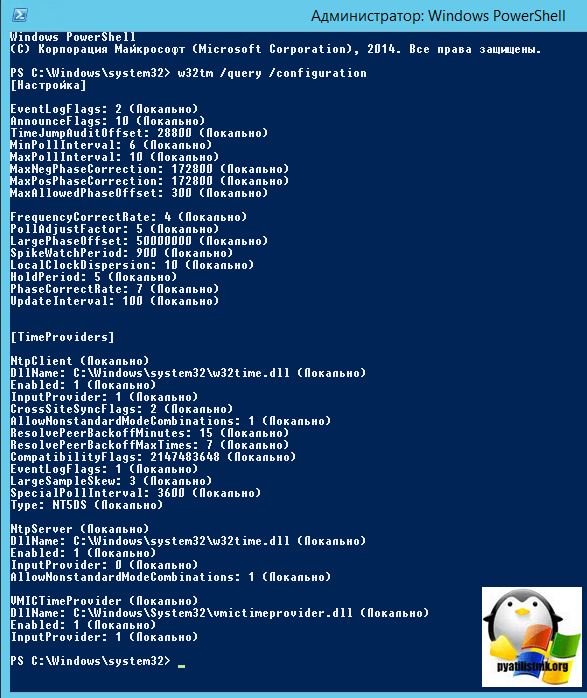
Конфигурирование сервера времени в Windows (NTP-сервера) может осуществляться как с помощью утилиты командной строки w32tm, так и через реестр. Где возможно, я приведу оба варианта. Но в начале посмотрите полностью ваши настройки на компьютере, делается это командой:
w32tm /query /configuration
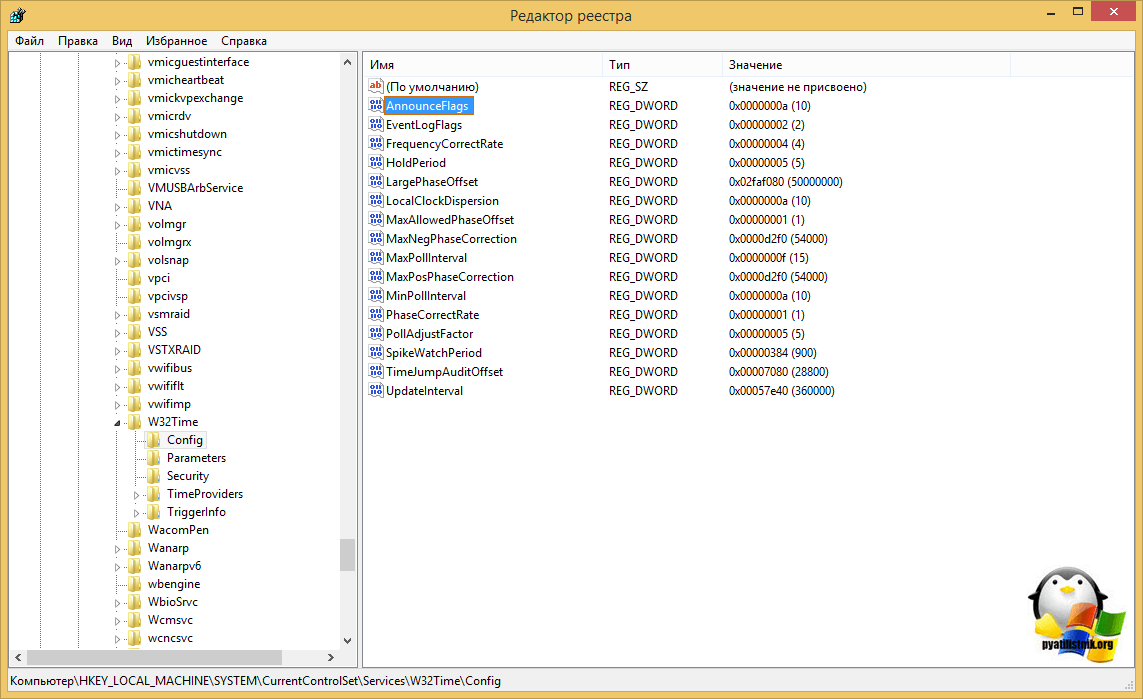
EventLogFlags: 2 (Локально)
AnnounceFlags: 10 (Локально)
TimeJumpAuditOffset: 28800 (Локально)
MinPollInterval: 6 (Локально)
MaxPollInterval: 10 (Локально)
MaxNegPhaseCorrection: 172800 (Локально)
MaxPosPhaseCorrection: 172800 (Локально)
MaxAllowedPhaseOffset: 300 (Локально)FrequencyCorrectRate: 4 (Локально)
PollAdjustFactor: 5 (Локально)
LargePhaseOffset: 50000000 (Локально)
SpikeWatchPeriod: 900 (Локально)
LocalClockDispersion: 10 (Локально)
HoldPeriod: 5 (Локально)
PhaseCorrectRate: 7 (Локально)
UpdateInterval: 100 (Локально)[TimeProviders]
NtpClient (Локально)
DllName: C:Windowssystem32w32time.dll (Локально)
Enabled: 1 (Локально)
InputProvider: 1 (Локально)
CrossSiteSyncFlags: 2 (Локально)
AllowNonstandardModeCombinations: 1 (Локально)
ResolvePeerBackoffMinutes: 15 (Локально)
ResolvePeerBackoffMaxTimes: 7 (Локально)
CompatibilityFlags: 2147483648 (Локально)
EventLogFlags: 1 (Локально)
LargeSampleSkew: 3 (Локально)
SpecialPollInterval: 3600 (Локально)
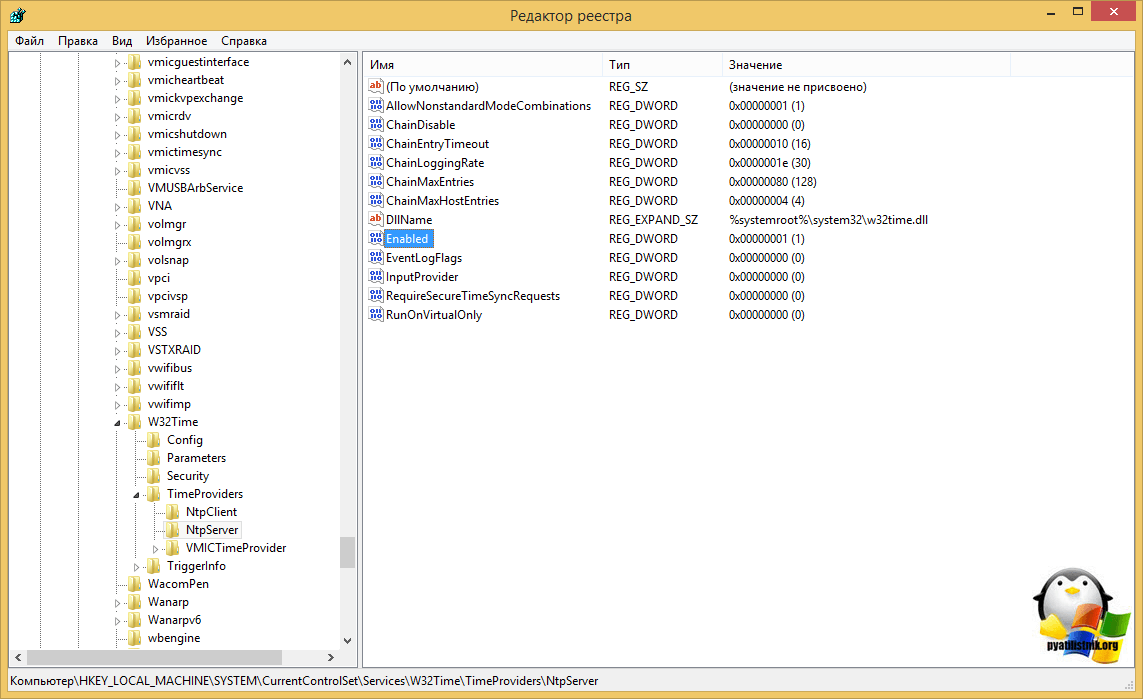
Type: NT5DS (Локально)NtpServer (Локально)
DllName: C:Windowssystem32w32time.dll (Локально)
Enabled: 1 (Локально)
InputProvider: 0 (Локально)
AllowNonstandardModeCombinations: 1 (Локально)VMICTimeProvider (Локально)
DllName: C:WindowsSystem32vmictimeprovider.dll (Локально)
Enabled: 1 (Локально)
InputProvider: 1 (Локально)
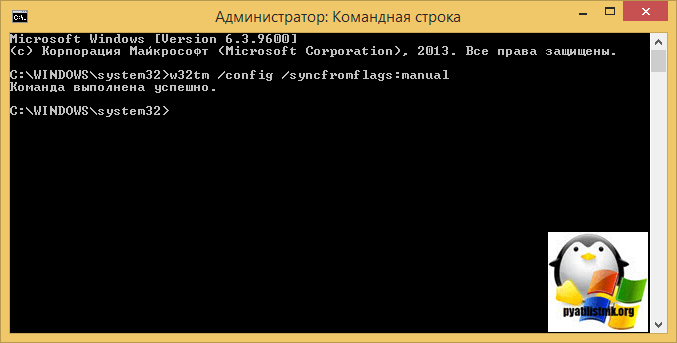
Включение синхронизации внутренних часов с внешним источником
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParameters]
"Type"="NTP"w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual
Объявление NTP-сервера в качестве надежного
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeConfig]
"AnnounceFlags"=dword:0000000aw32tm /config /reliable:yes
Включение NTP-сервера
NTP-сервер по умолчанию включен на всех контроллерах домена, однако его можно включить и на рядовых серверах.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeTimeProvidersNtpServer]
"Enabled"=dword:00000001
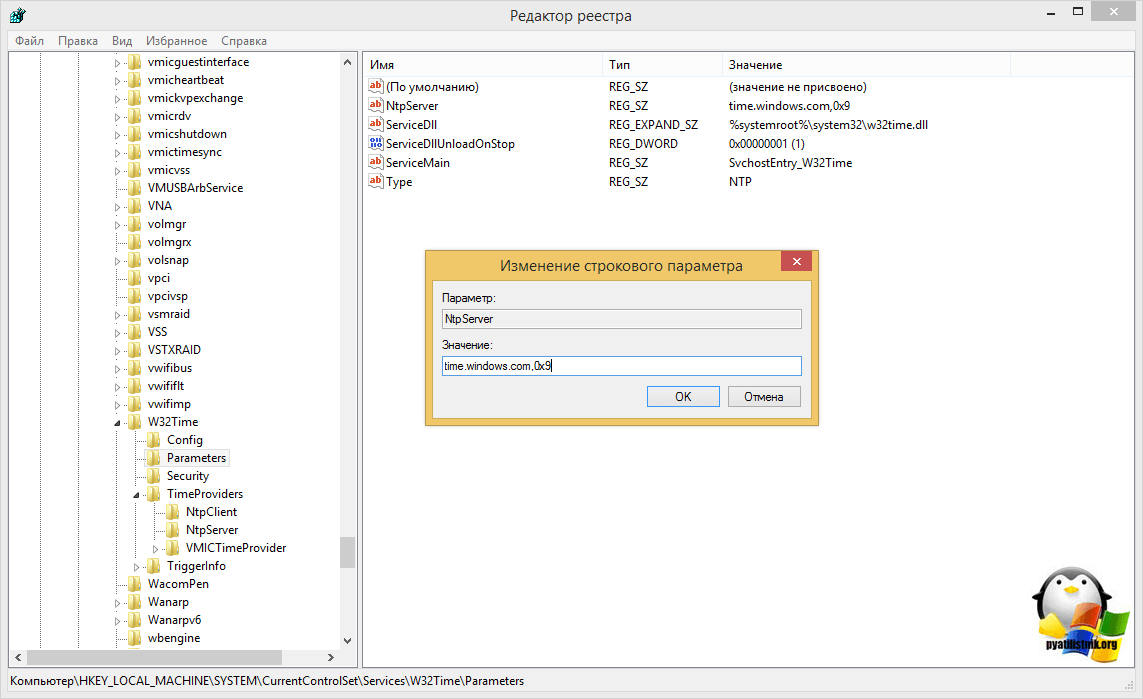
Задание списка внешних источников для синхронизации
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParameters]
"NtpServer"="time.nist.gov,0x8 ntp1.imvp.ru,0x8 ntp2.imvp.ru,0x8 time.windows.com,0x8 ru.pool.ntp.org,0x8"w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:"time.nist.gov,0x8 ntp1.imvp.ru,0x8 ntp2.imvp.ru,0x8 time.windows.com,0x8 ru.pool.ntp.org,0x8"
Флаг 0×8 на конце означает, что синхронизация должна происходить в режиме клиента NTP, через предложенные этим сервером интервалы времени. Для того, чтобы задать свой интервал синхронизации, необходимо использовать флаг 0×1.
Задание интервала синхронизации с внешним источником
Время в секундах между опросами источника синхронизации, по умолчанию 900с = 15мин. Работает только для источников, помеченных флагом 0×1.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeTimeProvidersNtpClient]
"SpecialPollInterval"=dword:00000384
Установка минимальной положительной и отрицательной коррекции
Максимальная положительная и отрицательная коррекция времени (разница между внутренними часами и источником синхронизации) в секундах, при превышении которой синхронизация не происходит. Рекомендую значение 0xFFFFFFFF, при котором коррекция сможет производиться всегда.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeConfig]
"MaxPosPhaseCorrection"=dword:FFFFFFFF
"MaxNegPhaseCorrection"=dword:FFFFFFFF
Все необходимое одной строкой
w32tm.exe /config /manualpeerlist:"time.nist.gov,0x8 ntp1.imvp.ru,0x8 ntp2.imvp.ru,0x8 time.windows.com,0x8 pool.ntp.org,0x8" /syncfromflags:manual /reliable:yes /update
Полезные команды
- Применение внесенных в конфигурацию службы времени изменений
w32tm /config /update - Принудительная синхронизация от источника
w32tm /resync /rediscover - Отображение состояния синхронизации контроллеров домена в домене
w32tm /monitor - Отображение текущих источников синхронизации и их статуса
w32tm /query /peers
Настройка NTP сервера и клиента групповой политикой
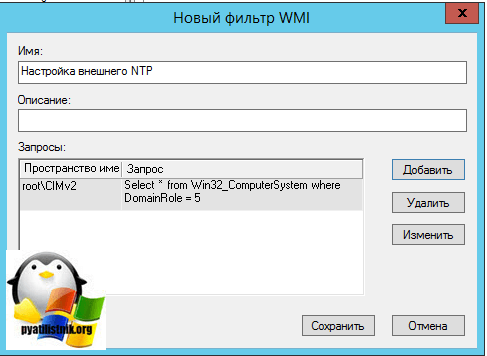
Раз уж у нас с вами домен Active Directory, то глупо не использовать групповые политики, для массовой настройки серверов и рабочих станций, я покажу как настроить ваш NTP сервер в windows и клиента. Открываем оснастку “Редактор групповых политик”. Перед тем как настроить наш NTP сервер в Windows, нам необходимо создать WMI фильтр, который будет применять политику, только к серверу мастера PDC.
Вводим имя запроса, пространство имен, будет иметь значение “rootCIMv2” и запрос “Select * from Win32_ComputerSystem where DomainRole = 5”. Сохраняем его.
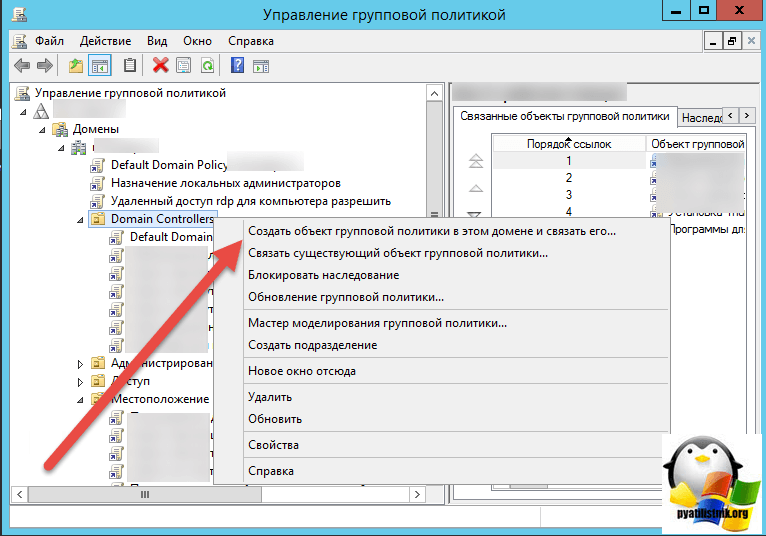
Затем вы создаете политику на контейнере Domain Controllers.
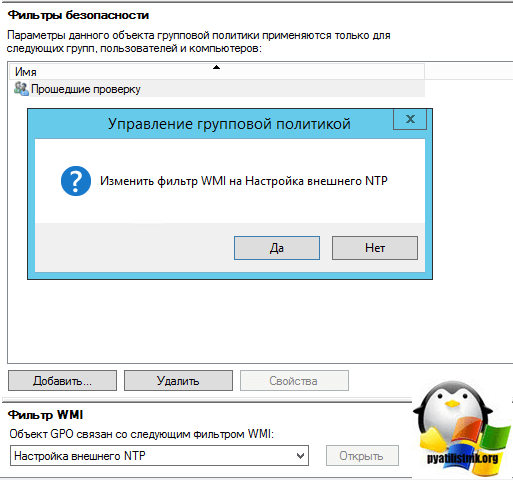
В самом низу политики применяете ваш созданный WMI фильтр.
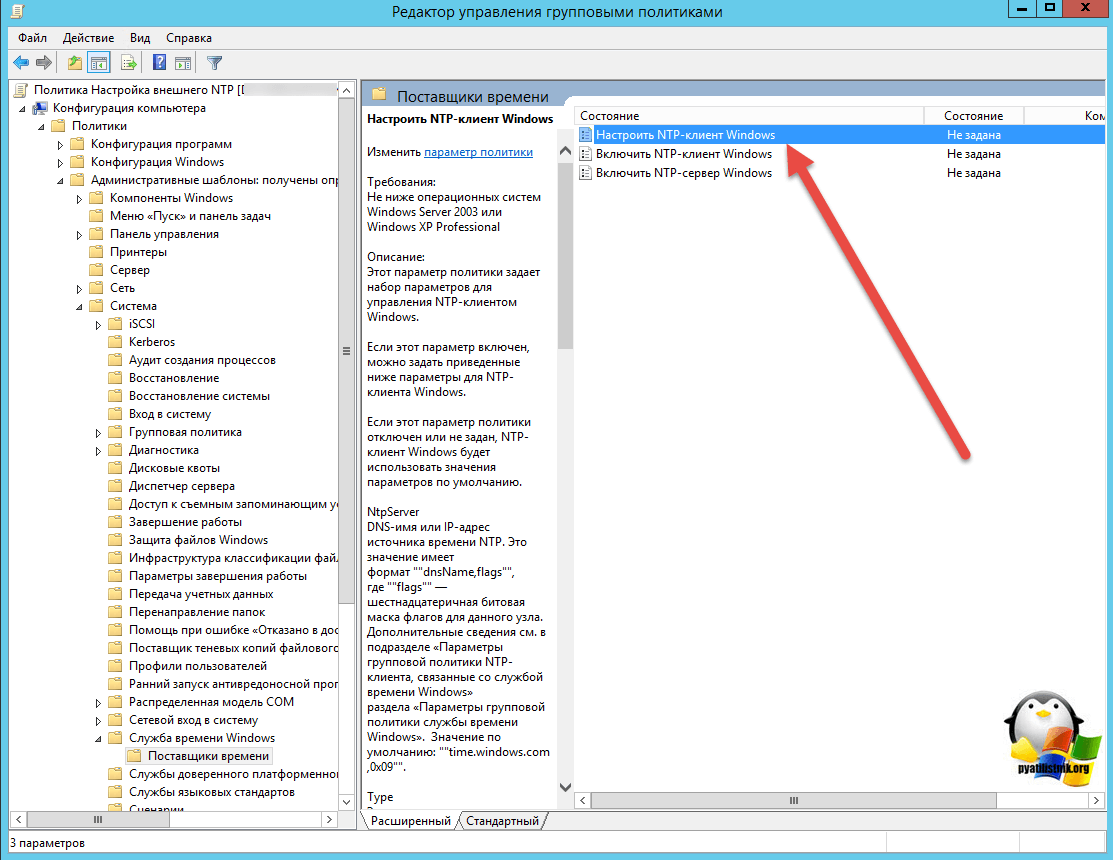
Переходим в ветку: Конфигурация компьютера > Политики > Административные шаблоны > Система > Служба времени Windows > Поставщики времени.
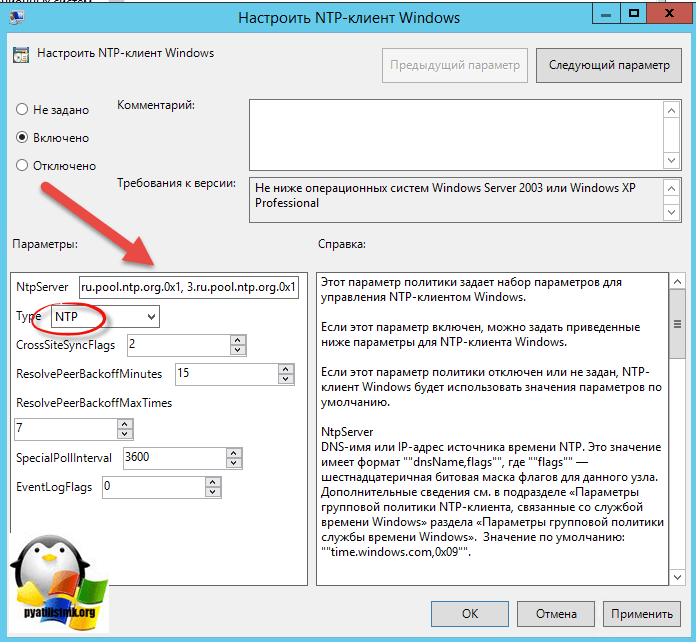
Тут открываем политику “Настроить NTP-клиент Windows”. Задаем параметры
- NtpServer: 0.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1 1.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1 2.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1 3.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1
- Type: NTP
- CrossSiteSyncFlags: 2. Двойка означает, если этот параметр равен 2 (Все), можно использовать любого участника синхронизации. Это значение игнорируется, если не задано значение NT5DS. Значение по умолчанию: 2 (десятичное) (0x02 (шестнадцатеричное))
- ResolvePeerBackoffMinutes: 15. Это значение, выраженное в минутах, определяет интервал ожидания службы W32time перед попыткой разрешения DNS-имени в случае неудачи. Значение по умолчанию: 15 минут
- Resolve Peer BAckoffMaxTimes: 7. Это значение определяет число попыток разрешения DNS-имени, предпринимаемых службой W32time перед перезапуском процесса обнаружения. При каждом неудачном разрешении DNS-имени интервал ожидания перед следующей попыткой удваивается. Значение по умолчанию: семь попыток.
- SpecilalPoolInterval: 3600. Это значение параметра NTP-клиента, выраженное в секундах, определяет частоту опроса настроенного вручную источника времени, который использует особый интервал опроса. Если для параметра NTPServer установлен флаг SpecialInterval, клиент использует значение, заданное как SpecialPollInterval, вместо значений MinPollInterval и MaxPollInterval, чтобы определить частоту опроса источника времени. Значение по умолчанию: 3600 секунд (1 час).
- EventLogFlags: 0
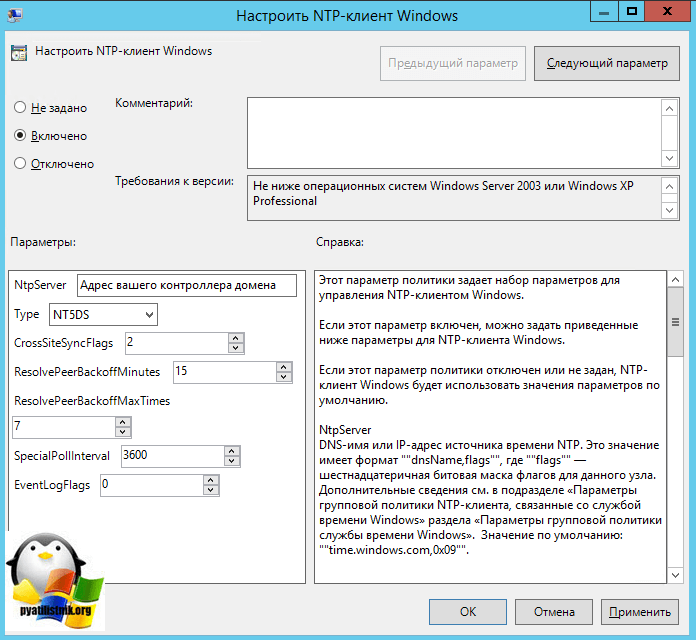
Делаем отдельную групповую политику для клиентских рабочих машин, вот с такими параметрами.
- NtpServer: Адрес вашего контроллера домена с ролью PDC.
- Type: NT5DS
- CrossSiteSyncFlags: 2
- ResolvePeerBackoffMinutes: 15
- Resolve Peer BAckoffMaxTimes: 7
- SpecilalPoolInterval: 3600
- EventLogFlags: 0
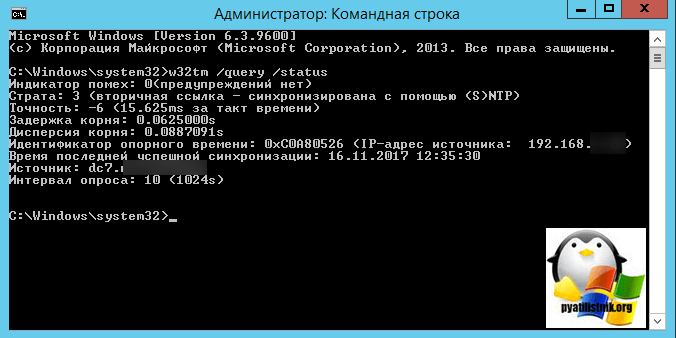
Далее идем на клиента и обновляем групповые политики gpupdate /force и вводим команду w32tm /query /status
Особенности виртуализированных контроллеров домена
Контроллеры домена, работающие в виртуализированной среде, требуют к себе особенного отношения.
- Средства синхронизации времени виртуальной машины и хостовой ОС должны быть выключены. Во всех адекватных системах виртуализации (Microsoft, vmWare и т. д.) присутствуют компоненты интеграции гостевой ОС с хостовой, которые значительно повышают производительность и управляемость гостевой системой. Среди этих компонентов всегда есть средство синхронизации времени гостевой ОС с хостовой, которое очень полезно для рядовых машин, но противопоказано для контроллеров домена. Потому как в этом случае весьма вероятен цикл, при котором контроллер домена и хостовая ОС будут синхронизировать друг друга. Последствия печальны.
- Для корневого PDC синхронизация с внешним источником должна быть настроена всегда. В виртуальной среде часы не настолько точны как в физической, потому как виртуальная машина работает с виртуальным процессором и прерываниями, для которых характерно как замедление, так и ускорение относительно «обычной» частоты. Если не настроить синхронизацию виртуализированного корневого PDC с внешним источником, время на всех компьютерах предприятия может убегать/отставать на пару часов в сутки. Не трудно представить неприятности, которые может принести такое поведение.
If you want to know how to properly configure your Active Directory environment, including Domain Controllers and domain computers, to have a reliable time service working correctly and synchronizing with an external time server, this post shows how to do that in a very easy way.
Why?
Active Directory can’t work correctly if the clock is not synchronized around domain controllers and member machines.
Some of the services that rely on the correct time configuration is Kerberos, which by default, computers that are more than 5 minutes out of sync will not authenticate to domain. Another example is replication, Active Directory uses time stamps to resolve replication conflicts, etc.
How Does it Work?
-
In Active Directory, we use the Windows Time service for clock synchronization: W32Time;
-
All member machines synchronizes with any domain controller;
-
In a domain, all domain controllers synchronize from the PDC Emulator of that domain;
-
The PDC Emulator of a domain should synchronize with any domain controller of the parent domain: using NTP;
-
The PDC Emulator of the root domain in a forest should synchronize with an external time server, which could be a router, another standalone server, an internet time server, etc.
You can have a better idea about this flow in the following picture:

time-configuration-AD
Said that, let’s set up the time service.
Configuration
From your PDC, open the prompt as administrator and type:
w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:yourNTPserver,0x8 /syncfromflags:manual /reliable:yes /update
w32tm /resync /rediscover
net stop w32time && net start w32time
Where “yourNTPserver” should be the address of the external NTP source you want set up, it could be a pool in the Internet or your internal NTP server.
Note the “,0x8” is part of the command and it will set the PDC to force sending client requests to the specified NTP server, and not other different type of requests like symmetric, which could cause PDC to do not receive correct NTP answers.
Also, should you wish to add more than one NTP server in the command above you should put them within quotes and separated by a space, like that:
w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:"yourNTPserver1,0x8 yourNTPserver2,0x8" /syncfromflags:manual /reliable:yes /update
Confirm if your server is properly configured:
w32tm /query /status
The output from command above should show the peers you configured, if not something is wrong, double check firewall and other settings, more troubleshooting details below.
Once the PDC was correctly configured, force all other DCs to rediscover the new time server by configuring it to Domain Hierarchy with the commands below:
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:DOMHIER /update
w32tm /resync /nowait
net stop w32time && net start w32time
Check settings after a minute, it should show your PDC/Time Server:
w32tm /query /status
Once the commands above were executed in all DCs, check the NTP settings for them with the command below:
w32tm /monitor
The correct and expected output should be the PDC/NTP with Stratum = 3 and all other DCs with Stratum = 4
Firewall
Set your internal firewall and your perimeter firewall to allow outgoing and incoming NTP traffic from/to your server on 123 UDP port.
Virtual Server?
Don’t forget, if your PDC is a virtual machine hosted on a Hyper-V server, you have to disable the time synchronization in your VM settings. To do that follow the instruction below:
1 – Open Hyper-V Manager.
2 – Select the Virtual Guest DC
3 – Click Settings.
4 – Click Integration services.
5 – Clear the Time Synchronization option.
6 – Exit Hyper-V Manager.
7 – Restart the server.
Screwed up configuration, what now?
Don’t worry, you can restore time service to its default value:
net stop w32time
w32tm /unregister
w32tm /register
Errors?
If you are facing Event ID errors 47, or if your configuration has the source configuration set as “Local CMOS Clock“, try:
1 – Do the above procedures again and be sure to set “,0x8” immediate after the NTP address without any spaces.
2 – Make sure you can reach your external NTP server through port UDP 123.
3 – Restart your server and try again.
4 – Make sure you don’t have any other NTP setting being applied on your domain through GPO.
5 – Make sure your current time is not as far as 1000 seconds from the real time.
6 – Make sure your server is set at the right zone time.
7 – You can also check for time advertisement on the PDC by running this command w32tm.exe /resync /rediscover /no_wait, then check for Event ID 139
8 – You can check the registry entries if the domain controller is using NTP (should be on PDC) or NT5DS (on non-PDC):Find the value of Type under:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParameters
References:
https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/nepapfe/2013/03/01/its-simple-time-configuration-in-active-directory/
https://kb.meinbergglobal.com/kb/time_sync/timekeeping_on_windows/configuring_w32time_as_ntp_client
For any doubts or suggestions, please leave a comment below.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Network Time Protocol (NTP)
- Active Directory Time Synchronization Architecture
- How to check the configuration from client side
- External Time Source
- Stratum Value
- Configure a reliable external time source for the Forest Root Domain PDC Emulator
- Remove the reliable external time source settings from the old PDC Emulator (If you are changing the PDC emulator)
- Post configuration checking
- A Note on Registry keys
- Designing a Time Service Policy
- How can we ensure that our systems are maintaining accurate time?
- Summary
- References
Introduction
In an Active Directory domain, it is very important for all clocks to be within 5 minutes of each other (by default) due to the implementation of the Kerberos protocol for authentication.
Also, Active Directory uses multi-master replication model between Domain Controllers. So it is important that changes made at a later actual time on one DC don’t get overwritten by similar changes on another DC, whose time is
set wrong thus making it look like the most recent change.
In this article, we would discuss the AD Time Synchronization architecture, how to configure an external time source and various other aspects of the Windows Time Service.
We also recommend checking this TechNet article, which gives a very good insight of the Windows Time Service:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc773013(WS.10).aspx
Network Time Protocol (NTP)
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is the default time synchronization protocol used by the Windows Time Service (WTS) in Windows servers and workstations.
NTP is implemented via UDP over port 123 and can operate in broadcast and multicast modes, or by direct queries.
Active Directory Time Synchronization Architecture
In Active Directory deployment, the only computer configured with a time server explicitly should be computer holding the PDC Emulator FSMO role in the forest root domain.
This is because the Forest root domain PDC emulator is the one and only one-time source for all the Domain Controllers, member servers and windows based workstations for the entire forest.
It is possible to override this configuration and bypass PDC emulator, but the default (and recommend) configuration is that all domain members should sync time with forest PDC emulator, directly or indirectly.
- All domain controllers in the forest root domain synchronize time with the PDC Emulator FSMO role-holder.
- All Domain Controllers in child Domains synchronize time with any Domain Controller with Parent Domain or with PDC Emulator of its own Domain.
- All PDC Emulator FSMO role-holders in child domains synchronize their time with domain controllers in their parent domain (including, potentially, the PDC Emulator FSMO role-holder in the forest root domain).
- All domain member computers (Servers / Workstations/ any other devices) synchronize time with domain controller computers in their respective domains.
Diagram Source: Microsoft
How to check the configuration from client side
To determine if a domain member is configured for domain time sync, examine the REG_SZ value at HKLMSystemCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParametersType.
- If it is set to “Nt5DS” then the computer is synchronizing time with the Active Directory time hierarchy.
- If it’s configured with the value “NTP” then the computer is synchronizing time with the NTP server specified in the NtpServer REG_SZ value in the same registry key.
External Time Source
Since PDC Emulator of the forest root domain is the main time source of the entire forest, it is important that the system clock of this computer is accurate.
To maintain the accuracy, the forest root domain PDC emulator must be configured to synchronize its time with an external time source which is reliable. Example: Windows Time Server or Google Time Server.
Stratum Value
The degree to which a computer’s time is accurate is called a
stratum.
- The most accurate time source on a network (such as a hardware clock) occupies the lowest stratum level, or stratum one.
This accurate time source is called a reference clock.
- An NTP server that acquires its time directly from a reference clock occupies a stratum that is one level higher than that of the reference clock.
- Resources that acquire time from the NTP server are two steps away from the reference clock, and therefore occupy a stratum that is two higher than the most accurate time source, and so on.
As a computer’s stratum number increases, the time on its system clock may become less accurate.
Therefore, the stratum level of any computer is an indicator of how closely that computer is synchronized with the most accurate time source.
So when you configure a new PDC emulator or move existing PDC emulator role to a different domain controller, please follow below steps for external time source configuration.
Old PDC Emulator: DC1.subhro.com
New PDC Emulator: DC2.subhro.com
External Time Sources: 1) time.windows.com 2) time.google.com
Configure a reliable external time source for the Forest Root Domain PDC Emulator
Note: If Forest PDC Emulator is a VM, make sure it is
not configured to Sync time with its host.
1. On the PDC Emulator, run the following command from command prompt (Admin Mode)
w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:”0.time.windows.com,0x1 1. time.google.com ,0X1″ /syncfromflags:manual /reliable:yes /update
2. Check and confirm the below registry value:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParametersType has “NTP” as the value
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParametersNtpServer
has the value “0.time.windows.com,0x1 1. time.google.com ,0X1”
Please note: Make sure the time server names are resolvable. Otherwise, please use IP address.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeConfigAnnounceFlags
has the value 0x5. This value indicates that this system is configured to sync with an external time source. If the value is 0XA, it means this system will not sync with any external time source but would sync with itself.
3. Configure poll interval with external time source by modifying below registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeTimeProvidersNtpClientSpecialPollInterval
Put the value in seconds. For example, if you want to set the poll interval to 1 hour, put 3600 here.
4. Run the following commands in sequential order :
net stop w32time
net start w32time
5. If required, restart the new PDC emulator.
Remove the reliable external time source settings from the old PDC Emulator (If you are changing the PDC emulator)
1. Run the following command from command prompt of the old PDC Emulator :
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:domhier /reliable:no /update
2. Check and confirm the registry key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParametersType has “NT5DS” as the value
3. Run the following commands in sequential order :
net stop w32time
net start w32time
2. If required, restart the server.
Post configuration checking
1. Check the time configuration by running the command
w32tm /query /configuration
2. Check the time synchronization report by running the command
Click here to get the Powershell script, which will automate the Time Skew report for your domain, and will send the result in an email.
3. To compare the time synchronization of a server with an external time source use the following command
w32tm /stripchart /computer: time.windows.com
d: Internal delay (time difference between the UDP package received and UDP package sent on the server side.
O: Actual offset between the local time and the server time.
4. To check the time source of a server run this command
w32tm /query /status
5. To manually sync the time with time source, run this command
w32tm /resync
Few points to observe from the above output:
-
Root dispersion is the maximum clock time difference that was ever observed between the local clock and the root clock. As you can see, this value has been reduced to milliseconds after synchronization.
- Since the primary time source (time.windows.com) is not reachable, it has automatically switched to secondary time source (time.google.com).
- Stratum value was earlier 1, indicating that no external time source was configured and this PDC emulator was the root time source (which is not the recommended configuration, as explained earlier)
After running the first sync, the server detected the newly configured external time source and marked it as root (Stratum value 1). Therefore, the new value of the PDC emulator has been changed to one level up, which is 2.
A Note on Registry keys
There is an article on Technet which explains these registry values which we have used here.
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/w32time/2008/02/26/configuring-the-time-service-ntpserver-and-specialpollinterval/
Excerpts from that article
It is important to note that W32Time will only actively synchronize with one time source at a time, even though you are able to list more than one time source. The reason for this is simple: If your favorite time source goes down,
it would be good to have a backup, or possibly a list of backups.
W32Time configures the list of time sources through the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParametersNtpServer
The NtpServer key is a space-delimited list of time servers, either as DNS address or as IP addresses. Each server in the list can optionally have a set of flags, which are denoted as a hex value at the end of the address, separated
by a comma.
Now let’s take a look at the flags. We have 4 possible flags:
• 0x01 SpecialInterval
• 0x02 UseAsFallbackOnly
• 0x04 SymmatricActive
• 0x08 Client
For 99% of cases, we only care about the first two options, so that is where we will focus. If you use the SpecialInterval flag, then you need to also set the “SpecialPollInterval” key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeTimeProviders
NtpClientSpecialPollInterval
Normally, W32Time will poll (make a time request) on a floating interval, based on the quality of the time samples being returned by the time source. You can, however, specify a static interval that the time service will synchronize
on. This value is in seconds. For example, if you set an of 3600, the time service will synchronize every hour (60 minutes * 60 seconds).
The second flag is the UseAsFallbackOnly option. Setting this flag will tell the time service that you want to try every other time server specified before trying this one.
Designing a Time Service Policy
Configuring PDC Emulator and external time source is only one part of the time service configuration. There are still many other points which we need to consider. Some of the important points are described below.
1.
Force all windows systems to use Domain Controller as their time source
By default in Active Directory domain environment clients synchronize their time with domain controllers (option Nt5DS — synchronize time to domain hierarchy).
Typically, this behavior does not need to be reconfigured. However, if you want to ensure that the default behavior would not be overridden by someone on the client side, you can force a Group Policy to push the configuration.
a) Navigate to Computer Configuration->Policies->Administrative Templates->System->Windows Time Service->Time Providers. In the right pane, double-click “Enable Windows NTP Client”. Set it to “Enabled” and click OK.
b) Next, double-click “Configure Windows NTP Client”. Configure the options then append, 0x1 to the NtpServer field so that it reads yourdc.yourdomain.com,0x1)
2.
Disable Virtual Machine Time Sync from host
All modern hypervisors have the ability to provide time synchronization to guest machines through that hypervisor’s integration tools. If enabled, guest machines will draw time from the physical host they are running on.
In an Active Directory environment, it is recommended to disable Virtual Machine time sync with a host, to avoid potential conflict.
3. Enable DHCP Scope Option
If you would like to push NTP server settings to a non-windows device (Like IP Phone), use DHCP scope option 042. Do not use DHCP scope option 004 unless it is specifically mentioned in any documentation.
4.
Allow UDP Port 123 through Firewall
UDP port 123 should be unblocked by the firewalls, in both directions.
Also, remember NTP client sends UDP request from random port >1023 to port 123 on NTP server. It waits for a response on the same originating port. The firewall should be able to keep open originating port for UDP traffic from
NTP server.
5.
Configure Static Devices
There are few static devices (like few SAN, NAS devices) which do not support NTP server configuration over Group Policy or DHCP. For such devices, you need to configure the time sources statically, from the device console.
The downside is, if NTP server name would be changed, you have to change these settings manually.
How can we ensure that our systems are maintaining accurate time?
We recommend to follow below steps to ensure that all systems in an AD environment are maintaining accurate time.
a) Forest Root Domain PDC Emulator should sync its time with external NTP server on a regular basis.
To ensure that, follow these steps
1. Execute w32tm /query /status from the forest root domain PDC emulator. Validate the NTP server, last sync time, root desperation.
2. Compare the PDC emulator clock time with any world clock time and observe the difference in seconds. One such site is https://www.timeanddate.com/ , where you can view world clock with second value and can compare with your
PDC.
b) All other Domain Controllers should sync time with Forest Root Domain PDC emulator on a regular basis. The time difference between Domain Controllers should be less than 1 second in an entire forest.
To ensure that, configure a scheduled task, which would generate the Time Skew Report for all Domain Controllers and send it to your mailbox.
Click here for the script, which I have prepared for this purpose.
c) All other computers and workstations should sync with Domain Controllers at a regular interval.
Summary
In this article, we have gone through the time service architecture within an Active Directory Forest. We have also discussed how to configure external time source for Forest PDC Emulator, and how to ensure client systems will
follow the Active Directory Time Architecture.
Additionally, we have covered some best practices related to Time Service Configuration of virtual machines, Firewall Port Configuration and configuring non windows devices.
References
1. https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc773013(WS.10).aspx
2. https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/w32time/2008/02/26/configuring-the-time-service-ntpserver-and-specialpollinterval/