Марьюшка
17 апреля, 01:19
-
-
Викторинка
17 апреля, 02:52
-1
sin7 п/6=sin (6 п/6 + п/6) = sin (п + п/6) (попадаем в 3 ю четвертерьть, поэтому sin<0 отрицателный)
-sinп/6=-1/2
- Комментировать
- Жалоба
- Ссылка
Найди верный ответ на вопрос ✅ «Вычислить с помощью формул приведения: sin 7 п/6 …» по предмету 📙 Математика, а если ответа нет или никто не дал верного ответа, то воспользуйся поиском и попробуй найти ответ среди похожих вопросов.
Искать другие ответы
Новые вопросы по математике
Главная » Математика » Вычислить с помощью формул приведения: sin 7 п/6
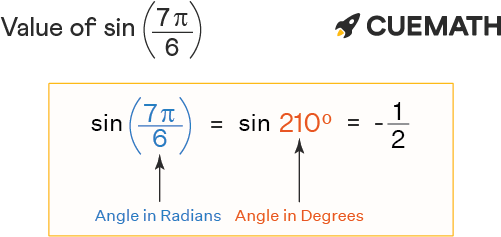
The value of sin 7pi/6 is -0.5. Sin 7pi/6 radians in degrees is written as sin ((7π/6) × 180°/π), i.e., sin (210°). In this article, we will discuss the methods to find the value of sin 7pi/6 with examples.
- Sin 7pi/6: -(1/2)
- Sin 7pi/6 in decimal: -0.5
- Sin (-7pi/6): 0.5 or 1/2
- Sin 7pi/6 in degrees: sin (210°)
What is the Value of Sin 7pi/6?
The value of sin 7pi/6 in decimal is -0.5. Sin 7pi/6 can also be expressed using the equivalent of the given angle (7pi/6) in degrees (210°).
We know, using radian to degree conversion, θ in degrees = θ in radians × (180°/pi)
⇒ 7pi/6 radians = 7pi/6 × (180°/pi) = 210° or 210 degrees
∴ sin 7pi/6 = sin 7π/6 = sin(210°) = -(1/2) or -0.5
Explanation:
For sin 7pi/6, the angle 7pi/6 lies between pi and 3pi/2 (Third Quadrant). Since sine function is negative in the third quadrant, thus sin 7pi/6 value = -(1/2) or -0.5
Since the sine function is a periodic function, we can represent sin 7pi/6 as, sin 7pi/6 = sin(7pi/6 + n × 2pi), n ∈ Z.
⇒ sin 7pi/6 = sin 19pi/6 = sin 31pi/6 , and so on.
Note: Since, sine is an odd function, the value of sin(-7pi/6) = -sin(7pi/6).
Methods to Find Value of Sin 7pi/6
The sine function is negative in the 3rd quadrant. The value of sin 7pi/6 is given as -0.5. We can find the value of sin 7pi/6 by:
- Using Unit Circle
- Using Trigonometric Functions
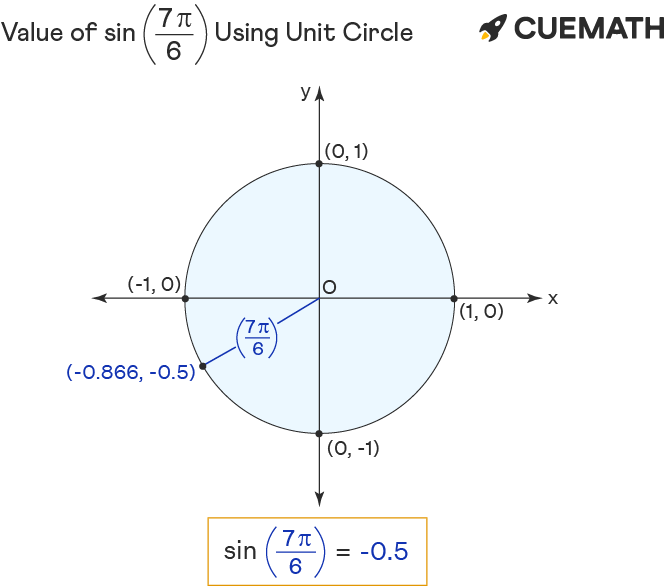
Sin 7pi/6 Using Unit Circle
To find the value of sin 7π/6 using the unit circle:
- Rotate ‘r’ anticlockwise to form 7pi/6 angle with the positive x-axis.
- The sin of 7pi/6 equals the y-coordinate(-0.5) of the point of intersection (-0.866, -0.5) of unit circle and r.
Hence the value of sin 7pi/6 = y = -0.5
Sin 7pi/6 in Terms of Trigonometric Functions
Using trigonometry formulas, we can represent the sin 7pi/6 as:
- ± √(1-cos²(7pi/6))
- ± tan(7pi/6)/√(1 + tan²(7pi/6))
- ± 1/√(1 + cot²(7pi/6))
- ± √(sec²(7pi/6) – 1)/sec(7pi/6)
- 1/cosec(7pi/6)
Note: Since 7pi/6 lies in the 3rd Quadrant, the final value of sin 7pi/6 will be negative.
We can use trigonometric identities to represent sin 7pi/6 as,
- sin(pi – 7pi/6) = sin(-pi/6)
- -sin(pi + 7pi/6) = -sin 13pi/6
- cos(pi/2 – 7pi/6) = cos(-2pi/3)
- -cos(pi/2 + 7pi/6) = -cos 5pi/3
☛ Also Check:
- cos pi/3
- cos 5pi/3
- cos pi/4
- cos pi/6
- cot pi
- tan pi/8
FAQs on Sin 7pi/6
What is Sin 7pi/6?
Sin 7pi/6 is the value of sine trigonometric function for an angle equal to 7pi/6 radians. The value of sin 7pi/6 is -(1/2) or -0.5.
How to Find the Value of Sin 7pi/6?
The value of sin 7pi/6 can be calculated by constructing an angle of 7π/6 radians with the x-axis, and then finding the coordinates of the corresponding point (-0.866, -0.5) on the unit circle. The value of sin 7pi/6 is equal to the y-coordinate (-0.5). ∴ sin 7pi/6 = -0.5.
How to Find Sin 7pi/6 in Terms of Other Trigonometric Functions?
Using trigonometry formula, the value of sin 7π/6 can be given in terms of other trigonometric functions as:
- ± √(1-cos²(7pi/6))
- ± tan(7pi/6)/√(1 + tan²(7pi/6))
- ± 1/√(1 + cot²(7pi/6))
- ± √(sec²(7pi/6) – 1)/sec(7pi/6)
- 1/cosec(7pi/6)
☛ Also check: trigonometry table
What is the Value of Sin 7pi/6 in Terms of Cosec 7pi/6?
Since the cosecant function is the reciprocal of the sine function, we can write sin 7pi/6 as 1/cosec(7pi/6). The value of cosec 7pi/6 is equal to -2.
What is the Value of Sin 7pi/6 in Terms of Tan 7pi/6?
We know, using trig identities, we can write sin 7pi/6 as -tan(7pi/6)/√(1 + tan²(7pi/6)). Here, the value of tan 7pi/6 is equal to 0.577350.
| bold{mathrm{Basic}} | bold{alphabetagamma} | bold{mathrm{ABGamma}} | bold{sincos} | bold{gedivrightarrow} | bold{overline{x}spacemathbb{C}forall} | bold{sumspaceintspaceproduct} | bold{begin{pmatrix}square&square\square&squareend{pmatrix}} | bold{H_{2}O} | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Subscribe to verify your answer
Subscribe
Sign in to save notes
Sign in
Number Line
Examples
-
x^{2}-x-6=0
-
-x+3gt 2x+1
-
line:(1,:2),:(3,:1)
-
f(x)=x^3
-
prove:tan^2(x)-sin^2(x)=tan^2(x)sin^2(x)
-
frac{d}{dx}(frac{3x+9}{2-x})
-
(sin^2(theta))’
-
sin(120)
-
lim _{xto 0}(xln (x))
-
int e^xcos (x)dx
-
int_{0}^{pi}sin(x)dx
-
sum_{n=0}^{infty}frac{3}{2^n}
- Show More
Description
Solve problems from Pre Algebra to Calculus step-by-step
step-by-step
sin(frac{7π}{6})
en
Related Symbolab blog posts
Practice Makes Perfect
Learning math takes practice, lots of practice. Just like running, it takes practice and dedication. If you want…
Read More
Enter a problem
Save to Notebook!
Sign in
В статье мы рассмотрим, как найти значения:
(cosfrac{π}{6}), (sin(-frac{7π}{3})), (cosfrac{3π}{4}), (sin(-frac{27π}{2}))
и других тригонометрических выражений без тригонометрической таблицы.
Для начала внимательно прочтите статью о числовой окружности. Вы должны научиться находить точки на окружности в числах с Пи.
Уже умеете? Тогда два ключевых утверждения:
Например, пусть нам нужно найти синус и косинус числа (frac{π}{6}). Обозначим на числовой окружности точку со значением (frac{π}{6}).
Если построить все точно и крупно, то можно убедиться, что абсцисса этой точки будет равна (0,866…) , что соответствует числу (frac{sqrt{3}}{2}) , а ордината равна (0,5), то есть (frac{1}{2}).

Значит, что (cos(frac{π}{6}) = frac{sqrt{3}}{2}), а (sin(frac{π}{6}) =frac{1}{2}).
Аналогично и для любой другой точки: значение абсциссы совпадает со значением косинуса, а ординаты – синуса. Поэтому:
В тригонометрии ось абсцисс часто называют «ось косинусов», а ординат – «ось синусов».
И обычно на них не наносят значения в десятичных ((0,1); (0,2); (0,3) и т.д.), а сразу отмечают стандартные значения для синуса и косинуса: (frac{1}{2} =0,5); (frac{sqrt{2}}{2} ≈0,707); (frac{sqrt{3}}{2}≈0,866), причем, как со знаком плюс, так и минус. Почему стандартные значения синуса и косинуса именно (frac{1}{2}),(frac{sqrt{2}}{2}) и (frac{sqrt{3}}{2}) вы можете узнать из этого видео.
Как находить значения синуса и косинуса без таблицы, а только с помощью круга?
Алгоритм прост:
- Начертите круг и оси косинусов и синусов.
- Отметьте на круге число, синус и косинус которого надо найти. Если с этим возникают проблемы, прочитайте здесь о том, как расставлять числа на числовой окружности.
- Найдите координаты точки, используя картинку ниже.

Пример. Найдите синус и косинус для числа (-frac{7π}{6}).
Решение:(-frac{7π}{6}=-frac{6π}{6}-frac{π}{6}=-π-frac{π}{6}) , то есть, чтобы отметить на окружности точку (-frac{7π}{6}) сначала находим число (-π) и от него в отрицательную сторону откладываем дугу длиной (frac{π}{6}).

Отмечаем число, синус и косинус которого надо найти:

Получается, что (sin(-frac{7π}{6})=frac{1}{2}), (cos(-frac{7π}{6})=-frac{sqrt{3}}{2}).
Пример. Вычислите (sinfrac{5π}{2}) и (cosfrac{5π}{2}).
Решение: (frac{5π}{2}=frac{4π+π}{2}=frac{4π}{2}+frac{π}{2}=2π+frac{π}{2}).

Точка (frac{5π}{2}) совпадает с (1) на оси синусов, значит (sinfrac{5π}{2}=1). А если провести перпендикуляр из точки (frac{5π}{2}) до оси косинусов, то можно убедиться, что он попадет в (0). Поэтому (cosfrac{5π}{2}=0).

И тут некоторые из вас подумали: «с кругом, на котором подписаны числа, каждый дурак сможет посчитать, а что делать, когда его под рукой нет? Что делать на ЕГЭ?» Ответ прост – нарисуйте круг сами! Для этого вам будет нужно понять логику расположения чисел на осях (подробнее об этом читайте в статье «Как запомнить тригонометрический круг»).
Пример. Найдите а) (sinfrac{3π}{2}), б) (cosfrac{3π}{4}), в) (sin(-frac{π}{3})) .
Решение: а) Чертим круг, оси и отмечаем число (frac{3π}{2}). Обращаем внимание на ось синусов и понимаем, что точка совпала с (-1), получается (sinfrac{3π}{2}=-1).
б) (frac{3π}{4}=frac{4π}{4}-frac{π}{4}=π-frac{π}{4}) – отмечаем число на круге. Проводим перпендикуляр до оси косинусов и вспоминаем, что точки со знаменателем (4) находятся посередине. Мы еще попали и в отрицательную часть оси косинусов, получается (cosfrac{3π}{4}=-frac{sqrt{2}}{2}).
в) (-frac{π}{3}) – отмечаем число на круге. Видим, что перпендикуляр к оси синусов попал в точку близкую к (-1), значит (sin(-frac{π}{3})=-frac{sqrt{3}}{2}).

Как видите не обязательно рисовать, очень красивую или очень большую окружность – вы можете определить нужное вам значение, быстро набросав круг. И ничего не надо учить!
Если вы хотите еще примеров с вычислением синусов и косинусов без тригонометрической таблицы, то прочтите эту статью.
Пример (ЕГЭ). Найдите значение выражения (frac{8}{sin(-frac{27π}{4}) cos(frac{31π}{4})}) .
Решение. (-frac{27π}{4}=-frac{28π}{4}+frac{π}{4}=-7π+frac{π}{4}).
(frac{31π}{4}=frac{32π}{4}-frac{π}{4}=8π-frac{π}{4}).

(sin(-frac{27π}{4})=-frac{sqrt{2}}{2}), (cos(frac{31π}{4})=frac{sqrt{2}}{2}).
(frac{8}{sin(-frac{27π}{4}) cos(frac{31π}{4})})(=) (frac{ 8}{-frac{sqrt{2}}{2}cdotfrac{sqrt{2}}{2}})(=-8:frac{2}{4}=-8cdotfrac{2}{1}=-16).
Ответ: (-16).
Смотрите также:
Как найти синус и косинус углов в градусах без тригонометрической таблицы?
Из градусов в радианы и наборот
Тригонометрическая таблица с кругом
Почему в тригонометрической таблице такие числа?
Для тех кто хочет закрепить знания:
Задание на вычисление синусов, косинусов, тангенсов и котангенсов