поделиться знаниями или
запомнить страничку
- Все категории
-
экономические
43,658 -
гуманитарные
33,653 -
юридические
17,917 -
школьный раздел
611,962 -
разное
16,905
Популярное на сайте:
Как быстро выучить стихотворение наизусть? Запоминание стихов является стандартным заданием во многих школах.
Как научится читать по диагонали? Скорость чтения зависит от скорости восприятия каждого отдельного слова в тексте.
Как быстро и эффективно исправить почерк? Люди часто предполагают, что каллиграфия и почерк являются синонимами, но это не так.
Как научится говорить грамотно и правильно? Общение на хорошем, уверенном и естественном русском языке является достижимой целью.
This article is about the mobility for electrons and holes in metals and semiconductors. For the general concept, see Electrical mobility.
In solid-state physics, the electron mobility characterises how quickly an electron can move through a metal or semiconductor when pulled by an electric field. There is an analogous quantity for holes, called hole mobility. The term carrier mobility refers in general to both electron and hole mobility.
Electron and hole mobility are special cases of electrical mobility of charged particles in a fluid under an applied electric field.
When an electric field E is applied across a piece of material, the electrons respond by moving with an average velocity called the drift velocity, 
Electron mobility is almost always specified in units of cm2/(V⋅s). This is different from the SI unit of mobility, m2/(V⋅s). They are related by 1 m2/(V⋅s) = 104 cm2/(V⋅s).
Conductivity is proportional to the product of mobility and carrier concentration. For example, the same conductivity could come from a small number of electrons with high mobility for each, or a large number of electrons with a small mobility for each. For semiconductors, the behavior of transistors and other devices can be very different depending on whether there are many electrons with low mobility or few electrons with high mobility. Therefore mobility is a very important parameter for semiconductor materials. Almost always, higher mobility leads to better device performance, with other things equal.
Semiconductor mobility depends on the impurity concentrations (including donor and acceptor concentrations), defect concentration, temperature, and electron and hole concentrations. It also depends on the electric field, particularly at high fields when velocity saturation occurs. It can be determined by the Hall effect, or inferred from transistor behavior.
Introduction[edit]
Drift velocity in an electric field[edit]
Without any applied electric field, in a solid, electrons and holes move around randomly. Therefore, on average there will be no overall motion of charge carriers in any particular direction over time.
However, when an electric field is applied, each electron or hole is accelerated by the electric field. If the electron were in a vacuum, it would be accelerated to ever-increasing velocity (called ballistic transport). However, in a solid, the electron repeatedly scatters off crystal defects, phonons, impurities, etc., so that it loses some energy and changes direction. The final result is that the electron moves with a finite average velocity, called the drift velocity. This net electron motion is usually much slower than the normally occurring random motion.
The two charge carriers, electrons and holes, will typically have different drift velocities for the same electric field.
Quasi-ballistic transport is possible in solids if the electrons are accelerated across a very small distance (as small as the mean free path), or for a very short time (as short as the mean free time). In these cases, drift velocity and mobility are not meaningful.
Definition and units[edit]
The electron mobility is defined by the equation:
where:
- E is the magnitude of the electric field applied to a material,
- vd is the magnitude of the electron drift velocity (in other words, the electron drift speed) caused by the electric field, and
- µe is the electron mobility.
The hole mobility is defined by a similar equation:
Both electron and hole mobilities are positive by definition.
Usually, the electron drift velocity in a material is directly proportional to the electric field, which means that the electron mobility is a constant (independent of the electric field). When this is not true (for example, in very large electric fields), mobility depends on the electric field.
The SI unit of velocity is m/s, and the SI unit of electric field is V/m. Therefore the SI unit of mobility is (m/s)/(V/m) = m2/(V⋅s). However, mobility is much more commonly expressed in cm2/(V⋅s) = 10−4 m2/(V⋅s).
Mobility is usually a strong function of material impurities and temperature, and is determined empirically. Mobility values are typically presented in table or chart form. Mobility is also different for electrons and holes in a given material.
Derivation[edit]
Starting with Newton’s Second Law:
where:
- a is the acceleration between collisions.
- F is the electric force exerted by the electric field, and
is the effective mass of an electron.
Since the force on the electron is −eE:
This is the acceleration on the electron between collisions. The drift velocity is therefore:
where 
Since we only care about how the drift velocity changes with the electric field, we lump the loose terms together to get
where
Similarly, for holes we have
where
Note that both electron mobility and hole mobility are positive. A minus sign is added for electron drift velocity to account for the minus charge.
Relation to current density[edit]
The drift current density resulting from an electric field can be calculated from the drift velocity. Consider a sample with cross-sectional area A, length l and an electron concentration of n. The current carried by each electron must be 
Using the expression for 
A similar set of equations applies to the holes, (noting that the charge on a hole is positive). Therefore the current density due to holes is given by
where p is the hole concentration and 
The total current density is the sum of the electron and hole components:
Relation to conductivity[edit]
We have previously derived the relationship between electron mobility and current density
Now Ohm’s Law can be written in the form
where 
which can be factorised to
Relation to electron diffusion[edit]
In a region where n and p vary with distance, a diffusion current is superimposed on that due to conductivity. This diffusion current is governed by Fick’s Law:
where:
- F is flux.
- De is the diffusion coefficient or diffusivity
is the concentration gradient of electrons
The diffusion coefficient for a charge carrier is related to its mobility by the Einstein relation:
where:
- kB is the Boltzmann constant
- T is the absolute temperature
- e is the electric charge of an electron
Examples[edit]
Typical electron mobility at room temperature (300 K) in metals like gold, copper and silver is 30–50 cm2/ (V⋅s). Carrier mobility in semiconductors is doping dependent. In silicon (Si) the electron mobility is of the order of 1,000, in germanium around 4,000, and in gallium arsenide up to 10,000 cm2/ (V⋅s). Hole mobilities are generally lower and range from around 100 cm2/ (V⋅s) in gallium arsenide, to 450 in silicon, and 2,000 in germanium.[1]
Very high mobility has been found in several ultrapure low-dimensional systems, such as two-dimensional electron gases (2DEG) (35,000,000 cm2/(V⋅s) at low temperature),[2] carbon nanotubes (100,000 cm2/(V⋅s) at room temperature)[3] and freestanding graphene (200,000 cm2/ V⋅s at low temperature).[4] Organic semiconductors (polymer, oligomer) developed thus far have carrier mobilities below 50 cm2/(V⋅s), and typically below 1, with well performing materials measured below 10.[5]
| Material | Electron mobility | Hole mobility |
|---|---|---|
| AlGaAs/GaAs heterostructures | 35,000,000[2] | |
| Freestanding Graphene | 200,000[4] | |
| Carbon nanotubes | 79,000[6][7] | |
| Cubic boron arsenide (c-BAs) | 1,600[8] | |
| Crystalline silicon | 1,400[1] | 450[1] |
| Polycrystalline silicon | 100 | |
| Metals (Al, Au, Cu, Ag) | 10-50 | |
| 2D Material (MoS2) | 10-50 | |
| Organics | 8.6[9] | 43[10] |
| Amorphous silicon | ~1[11] |
Electric field dependence and velocity saturation[edit]
At low fields, the drift velocity vd is proportional to the electric field E, so mobility μ is constant. This value of μ is called the low-field mobility.
As the electric field is increased, however, the carrier velocity increases sublinearly and asymptotically towards a maximum possible value, called the saturation velocity vsat. For example, the value of vsat is on the order of 1×107 cm/s for both electrons and holes in Si. It is on the order of 6×106 cm/s for Ge. This velocity is a characteristic of the material and a strong function of doping or impurity levels and temperature. It is one of the key material and semiconductor device properties that determine a device such as a transistor’s ultimate limit of speed of response and frequency.
This velocity saturation phenomenon results from a process called optical phonon scattering. At high fields, carriers are accelerated enough to gain sufficient kinetic energy between collisions to emit an optical phonon, and they do so very quickly, before being accelerated once again. The velocity that the electron reaches before emitting a phonon is:
where ωphonon(opt.) is the optical-phonon angular frequency and m* the carrier effective mass in the direction of the electric field. The value of Ephonon (opt.) is 0.063 eV for Si and 0.034 eV for GaAs and Ge. The saturation velocity is only one-half of vemit, because the electron starts at zero velocity and accelerates up to vemit in each cycle.[12] (This is a somewhat oversimplified description.[12])
Velocity saturation is not the only possible high-field behavior. Another is the Gunn effect, where a sufficiently high electric field can cause intervalley electron transfer, which reduces drift velocity. This is unusual; increasing the electric field almost always increases the drift velocity, or else leaves it unchanged. The result is negative differential resistance.
In the regime of velocity saturation (or other high-field effects), mobility is a strong function of electric field. This means that mobility is a somewhat less useful concept, compared to simply discussing drift velocity directly.
Relation between scattering and mobility[edit]
Recall that by definition, mobility is dependent on the drift velocity. The main factor determining drift velocity (other than effective mass) is scattering time, i.e. how long the carrier is ballistically accelerated by the electric field until it scatters (collides) with something that changes its direction and/or energy. The most important sources of scattering in typical semiconductor materials, discussed below, are ionized impurity scattering and acoustic phonon scattering (also called lattice scattering). In some cases other sources of scattering may be important, such as neutral impurity scattering, optical phonon scattering, surface scattering, and defect scattering.[13]
Elastic scattering means that energy is (almost) conserved during the scattering event. Some elastic scattering processes are scattering from acoustic phonons, impurity scattering, piezoelectric scattering, etc. In acoustic phonon scattering, electrons scatter from state k to k’, while emitting or absorbing a phonon of wave vector q. This phenomenon is usually modeled by assuming that lattice vibrations cause small shifts in energy bands. The additional potential causing the scattering process is generated by the deviations of bands due to these small transitions from frozen lattice positions.[14]
Ionized impurity scattering[edit]
Semiconductors are doped with donors and/or acceptors, which are typically ionized, and are thus charged. The Coulombic forces will deflect an electron or hole approaching the ionized impurity. This is known as ionized impurity scattering. The amount of deflection depends on the speed of the carrier and its proximity to the ion. The more heavily a material is doped, the higher the probability that a carrier will collide with an ion in a given time, and the smaller the mean free time between collisions, and the smaller the mobility. When determining the strength of these interactions due to the long-range nature of the Coulomb potential, other impurities and free carriers cause the range of interaction with the carriers to reduce significantly compared to bare Coulomb interaction.
If these scatterers are near the interface, the complexity of the problem increases due to the existence of crystal defects and disorders. Charge trapping centers that scatter free carriers form in many cases due to defects associated with dangling bonds. Scattering happens because after trapping a charge, the defect becomes charged and therefore starts interacting with free carriers. If scattered carriers are in the inversion layer at the interface, the reduced dimensionality of the carriers makes the case differ from the case of bulk impurity scattering as carriers move only in two dimensions. Interfacial roughness also causes short-range scattering limiting the mobility of quasi-two-dimensional electrons at the interface.[14]
Lattice (phonon) scattering[edit]
At any temperature above absolute zero, the vibrating atoms create pressure (acoustic) waves in the crystal, which are termed phonons. Like electrons, phonons can be considered to be particles. A phonon can interact (collide) with an electron (or hole) and scatter it. At higher temperature, there are more phonons, and thus increased electron scattering, which tends to reduce mobility.
Piezoelectric scattering[edit]
Piezoelectric effect can occur only in compound semiconductor due to their polar nature. It is small in most semiconductors but may lead to local electric fields that cause scattering of carriers by deflecting them, this effect is important mainly at low temperatures where other scattering mechanisms are weak. These electric fields arise from the distortion of the basic unit cell as strain is applied in certain directions in the lattice.[14]
Surface roughness scattering[edit]
Surface roughness scattering caused by interfacial disorder is short range scattering limiting the mobility of quasi-two-dimensional electrons at the interface. From high-resolution transmission electron micrographs, it has been determined that the interface is not abrupt on the atomic level, but actual position of the interfacial plane varies one or two atomic layers along the surface. These variations are random and cause fluctuations of the energy levels at the interface, which then causes scattering.[14]
Alloy scattering[edit]
In compound (alloy) semiconductors, which many thermoelectric materials are, scattering caused by the perturbation of crystal potential due to the random positioning of substituting atom species in a relevant sublattice is known as alloy scattering. This can only happen in ternary or higher alloys as their crystal structure forms by randomly replacing some atoms in one of the sublattices (sublattice) of the crystal structure. Generally, this phenomenon is quite weak but in certain materials or circumstances, it can become dominant effect limiting conductivity. In bulk materials, interface scattering is usually ignored.[14][15][16][17][18]
Inelastic scattering[edit]
During inelastic scattering processes, significant energy exchange happens. As with elastic phonon scattering also in the inelastic case, the potential arises from energy band deformations caused by atomic vibrations. Optical phonons causing inelastic scattering usually have the energy in the range 30-50 meV, for comparison energies of acoustic phonon are typically less than 1 meV but some might have energy in order of 10 meV. There is significant change in carrier energy during the scattering process. Optical or high-energy acoustic phonons can also cause intervalley or interband scattering, which means that scattering is not limited within single valley.[14]
Electron–electron scattering[edit]
Due to the Pauli exclusion principle, electrons can be considered as non-interacting if their density does not exceed the value 1016~1017 cm−3 or electric field value 103 V/cm. However, significantly above these limits electron–electron scattering starts to dominate. Long range and nonlinearity of the Coulomb potential governing interactions between electrons make these interactions difficult to deal with.[14][15][16]
Relation between mobility and scattering time[edit]
A simple model gives the approximate relation between scattering time (average time between scattering events) and mobility. It is assumed that after each scattering event, the carrier’s motion is randomized, so it has zero average velocity. After that, it accelerates uniformly in the electric field, until it scatters again. The resulting average drift mobility is:[19]
where q is the elementary charge, m* is the carrier effective mass, and τ is the average scattering time.
If the effective mass is anisotropic (direction-dependent), m* is the effective mass in the direction of the electric field.
Matthiessen’s rule[edit]
Normally, more than one source of scattering is present, for example both impurities and lattice phonons. It is normally a very good approximation to combine their influences using “Matthiessen’s Rule” (developed from work by Augustus Matthiessen in 1864):
where µ is the actual mobility, 

Matthiessen’s rule can also be stated in terms of the scattering time:
where τ is the true average scattering time and τimpurities is the scattering time if there was impurity scattering but no other source of scattering, etc.
Matthiessen’s rule is an approximation and is not universally valid. This rule is not valid if the factors affecting the mobility depend on each other, because individual scattering probabilities cannot be summed unless they are independent of each other.[18] The average free time of flight of a carrier and therefore the relaxation time is inversely proportional to the scattering probability.[14][15][17] For example, lattice scattering alters the average electron velocity (in the electric-field direction), which in turn alters the tendency to scatter off impurities. There are more complicated formulas that attempt to take these effects into account.[20]
Temperature dependence of mobility[edit]
| Si | Ge | GaAs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrons | ∝T −2.4 | ∝T −1.7 | ∝T −1.0 |
| Holes | ∝T −2.2 | ∝T −2.3 | ∝T −2.1 |
With increasing temperature, phonon concentration increases and causes increased scattering. Thus lattice scattering lowers the carrier mobility more and more at higher temperature. Theoretical calculations reveal that the mobility in non-polar semiconductors, such as silicon and germanium, is dominated by acoustic phonon interaction. The resulting mobility is expected to be proportional to T −3/2, while the mobility due to optical phonon scattering only is expected to be proportional to T −1/2. Experimentally, values of the temperature dependence of the mobility in Si, Ge and GaAs are listed in table.[21]
As 



For scattering from acoustic phonons, for temperatures well above Debye temperature, the estimated cross section Σph is determined from the square of the average vibrational amplitude of a phonon to be proportional to T. The scattering from charged defects (ionized donors or acceptors) leads to the cross section 
The temperature dependencies of these two scattering mechanism in semiconductors can be determined by combining formulas for τ, Σ and 


The effect of ionized impurity scattering, however, decreases with increasing temperature because the average thermal speeds of the carriers are increased.[13] Thus, the carriers spend less time near an ionized impurity as they pass and the scattering effect of the ions is thus reduced.
These two effects operate simultaneously on the carriers through Matthiessen’s rule. At lower temperatures, ionized impurity scattering dominates, while at higher temperatures, phonon scattering dominates, and the actual mobility reaches a maximum at an intermediate temperature.
Disordered Semiconductors[edit]

While in crystalline materials electrons can be described by wavefunctions extended over the entire solid,[22] this is not the case in systems with appreciable structural disorder, such as polycrystalline or amorphous semiconductors. Anderson suggested that beyond a critical value of structural disorder,[23] electron states would be localized. Localized states are described as being confined to finite region of real space, normalizable, and not contributing to transport. Extended states are spread over the extent of the material, not normalizable, and contribute to transport. Unlike crystalline semiconductors, mobility generally increases with temperature in disordered semiconductors.
Multiple trapping and release[edit]
Mott later developed[24] the concept of a mobility edge. This is an energy 

Energy band diagram depicting electron transport under multiple trapping and release.
where 



Variable Range Hopping[edit]
At low temperature, or in system with a large degree of structural disorder (such as fully amorphous systems), electrons cannot access delocalized states. In such a system, electrons can only travel by tunnelling for one site to another, in a process called variable range hopping. In the original theory of variable range hopping, as developed by Mott and Davis,[26] the probability 




Here 

where 


Measurement of semiconductor mobility[edit]
Hall mobility[edit]

Hall effect measurement setup for holes

Hall effect measurement setup for electrons
Carrier mobility is most commonly measured using the Hall effect. The result of the measurement is called the “Hall mobility” (meaning “mobility inferred from a Hall-effect measurement”).
Consider a semiconductor sample with a rectangular cross section as shown in the figures, a current is flowing in the x-direction and a magnetic field is applied in the z-direction. The resulting Lorentz force will accelerate the electrons (n-type materials) or holes (p-type materials) in the (−y) direction, according to the right hand rule and set up an electric field ξy. As a result there is a voltage across the sample, which can be measured with a high-impedance voltmeter. This voltage, VH, is called the Hall voltage. VH is negative for n-type material and positive for p-type material.
Mathematically, the Lorentz force acting on a charge q is given by
For electrons:
For holes:
In steady state this force is balanced by the force set up by the Hall voltage, so that there is no net force on the carriers in the y direction. For electrons,
For electrons, the field points in the −y direction, and for holes, it points in the +y direction.
The electron current I is given by 
where RHn is the Hall coefficient for electron, and is defined as
Since 
Similarly, for holes
From the Hall coefficient, we can obtain the carrier mobility as follows:
Similarly,
Here the value of VHp (Hall voltage), t (sample thickness), I (current) and B (magnetic field) can be measured directly, and the conductivities σn or σp are either known or can be obtained from measuring the resistivity.
Field-effect mobility[edit]
The mobility can also be measured using a field-effect transistor (FET). The result of the measurement is called the “field-effect mobility” (meaning “mobility inferred from a field-effect measurement”).
The measurement can work in two ways: From saturation-mode measurements, or linear-region measurements.[28] (See MOSFET for a description of the different modes or regions of operation.)
Using saturation mode[edit]
In this technique,[28] for each fixed gate voltage VGS, the drain-source voltage VDS is increased until the current ID saturates. Next, the square root of this saturated current is plotted against the gate voltage, and the slope msat is measured. Then the mobility is:
where L and W are the length and width of the channel and Ci is the gate insulator capacitance per unit area. This equation comes from the approximate equation for a MOSFET in saturation mode:
where Vth is the threshold voltage. This approximation ignores the Early effect (channel length modulation), among other things. In practice, this technique may underestimate the true mobility.[29]
Using the linear region[edit]
In this technique,[28] the transistor is operated in the linear region (or “ohmic mode”), where VDS is small and 
This equation comes from the approximate equation for a MOSFET in the linear region:
In practice, this technique may overestimate the true mobility, because if VDS is not small enough and VG is not large enough, the MOSFET may not stay in the linear region.[29]
Optical mobility[edit]
Electron mobility may be determined from non-contact laser photo-reflectance technique measurements. A series of photo-reflectance measurements are made as the sample is stepped through focus. The electron diffusion length and recombination time are determined by a regressive fit to the data. Then the Einstein relation is used to calculate the mobility.[30][31]
Terahertz mobility[edit]
Electron mobility can be calculated from time-resolved terahertz probe measurement.[32][33] Femtosecond laser pulses excite the semiconductor and the resulting photoconductivity is measured using a terahertz probe, which detects changes in the terahertz electric field.
Time resolved microwave conductivity (TRMC)[edit]
A proxy for charge carrier mobility can be evaluated using time-resolved microwave conductivity (TRMC).[35] A pulsed optical laser is used to create electrons and holes in a semiconductor, which are then detected as an increase in photoconductance. With knowledge of the sample absorbance, dimensions, and incident laser fluence, the parameter 




Doping concentration dependence in heavily-doped silicon[edit]
The charge carriers in semiconductors are electrons and holes. Their numbers are controlled by the concentrations of impurity elements, i.e. doping concentration. Thus doping concentration has great influence on carrier mobility.
While there is considerable scatter in the experimental data, for noncompensated material (no counter doping) for heavily doped substrates (i.e. 
where N is the doping concentration (either ND or NA), and Nref and α are fitting parameters. At room temperature, the above equation becomes:
Majority carriers:[37]
Minority carriers:[38]
These equations apply only to silicon, and only under low field.
See also[edit]
- Speed of electricity
References[edit]
- ^ a b c “NSM Archive – Physical Properties of Semiconductors”. www.matprop.ru. Retrieved 2020-07-25.
- ^ a b Umansky, V.; Heiblum, M.; Levinson, Y.; Smet, J.; Nübler, J.; Dolev, M. (2009). “MBE growth of ultra-low disorder 2DEG with mobility exceeding 35×106 cm2 V−1 s−1”. Journal of Crystal Growth. 311 (7): 1658–1661. Bibcode:2009JCrGr.311.1658U. doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2008.09.151.
- ^ Dürkop, T.; Getty, S. A.; Cobas, Enrique; Fuhrer, M. S. (2004). “Extraordinary Mobility in Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes”. Nano Letters. 4 (1): 35. Bibcode:2004NanoL…4…35D. doi:10.1021/nl034841q. S2CID 45010238.
- ^ a b Bolotin, K; Sikes, K; Jiang, Z; Klima, M; Fudenberg, G; Hone, J; Kim, P; Stormer, H (2008). “Ultrahigh electron mobility in suspended graphene”. Solid State Communications. 146 (9): 351–355. arXiv:0802.2389. Bibcode:2008SSCom.146..351B. doi:10.1016/j.ssc.2008.02.024. S2CID 118392999.
- ^ Nawrocki, Robert (2016). “300‐nm Imperceptible, Ultraflexible, and Biocompatible e‐Skin Fit with Tactile Sensors and Organic Transistors”. Advanced Electronic Materials. 2 (4): 1500452. doi:10.1002/aelm.201500452. S2CID 138355533.
- ^ Dürkop, T.; Getty, S. A.; Cobas, Enrique; Fuhrer, M. S. (2004). “Extraordinary Mobility in Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes”. Nano Letters. 4 (1): 35–39. Bibcode:2004NanoL…4…35D. doi:10.1021/nl034841q. S2CID 45010238.
- ^ Snow, E. S.; Campbell, P. M.; Ancona, M. G.; Novak, J. P. (2005). “High-mobility carbon-nanotube thin-film transistors on a polymeric substrate”. Applied Physics Letters. 86 (3): 033105. Bibcode:2005ApPhL..86c3105S. doi:10.1063/1.1854721. ISSN 0003-6951. Archived from the original on September 24, 2017.
- ^ Shin, Jungwoo; Gamage, Geethal Amila; Ding, Zhiwei; Chen, Ke; Tian, Fei; Qian, Xin; Zhou, Jiawei; Lee, Hwijong; Zhou, Jianshi; Shi, Li; Nguyen, Thanh; Han, Fei; Li, Mingda; Broido, David; Schmidt, Aaron; Ren, Zhifeng; Chen, Gang (2022). “High ambipolar mobility in cubic boron arsenide”. Science. 377 (6604): 437–440. Bibcode:2022Sci…377..437S. doi:10.1126/science.abn4290. PMID 35862526. S2CID 250952849.
- ^ He, Tao; Stolte, Matthias; Würthner, Frank (2013-12-23). “Air‐Stable n‐Channel Organic Single Crystal Field‐Effect Transistors Based on Microribbons of Core‐Chlorinated Naphthalene Diimide”. Advanced Materials. 25 (48): 6951–6955. Bibcode:2013AdM….25.6951H. doi:10.1002/adma.201303392. PMID 24105872.
- ^ Yuan, Yongbo (2014). “Ultra-high mobility transparent organic thin film transistors grown by an off-centre spin-coating method”. Nature Communications. 5: 3005. Bibcode:2014NatCo…5.3005Y. doi:10.1038/ncomms4005. PMID 24398476.
- ^ Heremans, Paul (2015). “Mechanical and Electronic Properties of Thin‐Film Transistors on Plastic, and Their Integration in Flexible Electronic Applications”. Advanced Materials. 28 (22): 4266–4282. doi:10.1002/adma.201504360. PMID 26707947. S2CID 25457390.
- ^ a b Vladimir Vasilʹevich Mitin; Vi︠a︡cheslav Aleksandrovich Kochelap; Michael A. Stroscio (1999). Quantum heterostructures: microelectronics and optoelectronics. Cambridge University Press. pp. 307–9. ISBN 978-0-521-63635-3. Retrieved 2 March 2011.
- ^ a b Singh (2008). Electronic Devices And Integrated Circuits. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. pp. 77–. ISBN 978-81-203-3192-1. Retrieved 1 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Ferry, David K. Semiconductor transport. London: Taylor & Francis, 2000. ISBN 0-7484-0865-7 (hbk.), ISBN 0-7484-0866-5 (pbk.)
- ^ a b c d Ibach, Harald. ; Luth, Hans. Solid-state physics : an introduction to principles of materials science / Harald Ibach, Hans Luth. New York: Springer, 2009. -(Advanced texts in physics) ISBN 978-3-540-93803-3
- ^ a b Bulusu, A. (2008). “Review of electronic transport models for thermoelectric materials”. Superlattices and Microstructures. 44 (1): 1–36. Bibcode:2008SuMi…44….1B. doi:10.1016/j.spmi.2008.02.008..
- ^ a b c Bhattacharya, Pallab. Semiconductor optoelectronic devices / Pallab Bhattacharya. Upper Saddle River (NJ): Prentice-Hall, 1997. ISBN 0-13-495656-7 (nid.)
- ^ a b Y. Takeda and T.P. Pearsall, “Failure of Mattheissen’s Rule in the Calculation of Carrier Mobility and Alloy Scattering Effects in Ga0.47In0.53As”, Electronics Lett. 17, 573-574 (1981).
- ^ Peter Y. Yu; Manuel Cardona (30 May 2010). Fundamentals of Semiconductors: Physics and Materials Properties. Springer. pp. 205–. ISBN 978-3-642-00709-5. Retrieved 1 March 2011.
- ^ Antonio Luque; Steven Hegedus (9 June 2003). Handbook of photovoltaic science and engineering. John Wiley and Sons. p. 79, eq. 3.58. ISBN 978-0-471-49196-5. Retrieved 2 March 2011. weblink (subscription only)
- ^ a b Chapter 2: Semiconductor Fundamentals. Online textbook by B. Van Zeghbroeck]
- ^ Hook, J. R.; Hall, H. E. (1991-09-05). Solid State Physics. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-92804-1.
- ^ Anderson, P. W. (1958-03-01). “Absence of Diffusion in Certain Random Lattices”. Physical Review. 109 (5): 1492–1505. Bibcode:1958PhRv..109.1492A. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.109.1492.
- ^ Mott, N. F. (1967-01-01). “Electrons in disordered structures”. Advances in Physics. 16 (61): 49–144. Bibcode:1967AdPhy..16…49M. doi:10.1080/00018736700101265. ISSN 0001-8732.
- ^ Brotherton, S. D. (2013). Introduction to Thin Film Transistors: Physics and Technology of TFTs. Springer International Publishing. p. 143. ISBN 978-3-319-00001-5.
- ^ a b Electronic Processes in Non-Crystalline Materials. Oxford Classic Texts in the Physical Sciences. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press. 2012-03-24. ISBN 978-0-19-964533-6.
- ^ Emin, David (1974-02-11). “Phonon-Assisted Jump Rate in Noncrystalline Solids”. Physical Review Letters. 32 (6): 303–307. Bibcode:1974PhRvL..32..303E. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.32.303.
- ^ a b c Constance Rost-Bietsch (August 2005). Ambipolar and Light-Emitting Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Cuvillier Verlag. pp. 17–. ISBN 978-3-86537-535-3. Retrieved 1 March 2011.. This reference mistakenly leaves out a factor of 1/VDS in eqn (2.11). The correct version of that equation can be found, e.g., in Stassen, A. F.; De Boer, R. W. I.; Iosad, N. N.; Morpurgo, A. F. (2004). “Influence of the gate dielectric on the mobility of rubrene single-crystal field-effect transistors”. Applied Physics Letters. 85 (17): 3899–3901. arXiv:cond-mat/0407293. Bibcode:2004ApPhL..85.3899S. doi:10.1063/1.1812368. S2CID 119532427.
- ^ a b Constance Rost-Bietsch (August 2005). Ambipolar and Light-Emitting Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Cuvillier Verlag. pp. 19–. ISBN 978-3-86537-535-3. Retrieved 20 April 2011. “Extracting the field-effect mobility directly from the linear region of the output characteristic may yield larger values for the field-effect mobility than the actual one, since the drain current is linear only for very small VDS and large VG. In contrast, extracting the field-effect mobility from the saturated region might yield rather conservative values for the field-effect mobility, since the drain-current dependence from the gate-voltage becomes sub-quadratic for large VG as well as for small VDS.”
- ^ W. Chism, “Precise Optical Measurement of Carrier Mobilities Using Z-scanning Laser Photoreflectance,” arXiv:1711.01138 [physics:ins-det], Oct. 2017.
- ^ W. Chism, “Z-scanning Laser Photoreflectance as a Tool for Characterization of Electronic Transport Properties,” arXiv:1808.01897 [cond-mat:mes-hall], Aug. 2018.
- ^ Ulbricht, Ronald; Hendry, Euan; Shan, Jie; Heinz, Tony F.; Bonn, Mischa (2011). “Carrier dynamics in semiconductors studied with time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy” (PDF). Reviews of Modern Physics. 83 (2): 543–586. Bibcode:2011RvMP…83..543U. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.83.543. hdl:10871/15671. ISSN 0034-6861.
- ^ Lloyd-Hughes, James; Jeon, Tae-In (2012). “A Review of the Terahertz Conductivity of Bulk and Nano-Materials”. Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves. 33 (9): 871–925. Bibcode:2012JIMTW..33..871L. doi:10.1007/s10762-012-9905-y. ISSN 1866-6892. S2CID 13849900.
- ^ Savenije, Tom J.; Ferguson, Andrew J.; Kopidakis, Nikos; Rumbles, Garry (2013-11-21). “Revealing the Dynamics of Charge Carriers in Polymer:Fullerene Blends Using Photoinduced Time-Resolved Microwave Conductivity”. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 117 (46): 24085–24103. doi:10.1021/jp406706u. ISSN 1932-7447.
- ^ B. L. Anderson and R. L. Anderson, “Fundamentals of Semiconductor Devices, ” Mc Graw Hill, 2005
- ^ Caughey, D.M.; Thomas, R.E. (1967). “Carrier mobilities in silicon empirically related to doping and field”. Proceedings of the IEEE. 55 (12): 2192–2193. doi:10.1109/PROC.1967.6123.
- ^ Del Alamo, J (1985). “Measuring and modeling minority carrier transport in heavily doped silicon”. Solid-State Electronics. 28 (1): 47–54. Bibcode:1985SSEle..28…47D. doi:10.1016/0038-1101(85)90209-6.
External links[edit]
- semiconductor glossary entry for electron mobility
- Resistivity and Mobility Calculator from the BYU Cleanroom
- Online lecture- Mobility from an atomistic point of view
Найдем
скорость дрейфа
![]() электронов металла в электрическом
электронов металла в электрическом
полеЕ.
За
время свободного пробега t
с нулевой начальной скоростью электрон
в электрическом поле Е
набирает скорость
![]() ,
,
где ускорение![]() .
.
В результате столкновения упорядоченная
скорость теряется, тогда средняя скорость
![]() .
.
Время
свободного пробега меняется от
столкновения к столкновению. Пусть
электрон испытывает последовательно
N
столкновений с временами свободного
пробега t1,
t2,…,
tN
и средними скоростями
![]() ,
,
тогда скорость дрейфа
 .
.
Поделив
числитель и знаменатель на число
столкновений N,
и полагая
![]() ,
,
получаем
 .
.
Для
распределения (П.1.23)
![]()
используем
![]() ,
,
![]() .
.
Находим
![]() ,
,
(П.1.24)
где
подвижность
электронов
![]() .
.
Скорость
дрейфа пропорциональна электрическому
полю и среднему времени
свободного пробега электрона.
В поле напряженностью
![]() получаем
получаем![]() .
.
Пример 4
Для
вакуумного диода получим средний ток
термоэмиссии, дисперсию и относительную
флуктуацию тока.

Вакуумный
диод и ВАХ
Электроны,
испущенные нагретым катодом, перемещаются
в вакууме напряжением, приложенным
между катодом и анодом. Количество
испущенных электронов за единицу времени
зависит от температуры и площади катода.
Считаем их постоянными. В режиме насыщения
между катодом и анодом отсутствует
объемный заряд. Все электроны, испущенные
катодом, приходят к аноду, ток достигает
максимума и называется током
насыщения
![]() .
.
Электроны подходят к аноду случайным
образом, независимо друг от друга,
возникают импульсы тока, называемыедробовым
шумом.
Такой импульсный шум образуют дробинки,
сыплющиеся на лист металла. Дробовой
шум
создается
случайными независимыми движениями
зарядов в транспортных процессах –
при испускании электронов термокатодом,
при прохождении зарядов через p–n-переход.
Если
напряжение меньше напряжения насыщения
![]() ,
,
то движение электронов оказывается
настолько медленным, что из катода
испускается новый электрон до поглощения
первого анодом. В результате электроны
затормаживаются, накапливаются, и вблизи
анода образуется электронное облако.
С ним взаимодействуют электроны по пути
к аноду, их движения перестают быть
независимыми. В результате дробовой
шум сглаживается и уменьшается.
В
режиме насыщения флуктуация числа
электронов проводимости создает
флуктуацию тока, регистрируемого
гальванометром G.
Минимальное время Т,
необходимое для измерения, по порядку
величины равно времени затухания
колебаний указателя и для баллистического
гальванометра составляет несколько
секунд. Продолжительность испускания
электрона
![]() ,
,
тогда число
интервалов испускания за время регистрации
сигнала
![]() .
.
Вероятность
p
испускания электрона за время τ
пропорциональна площади катода и мала
![]() .
.
Поэтому применимо распределение
Пуассона. Из (1.15) и (1.18б) получаем среднее
число электронов, испускаемых за времяТ,
и их дисперсию
![]() ,
,
![]() .
.
Находим
прошедший средний заряд
![]() ,
,
средний
ток
![]() ,
,
дисперсию
заряда и тока
![]() ,
,
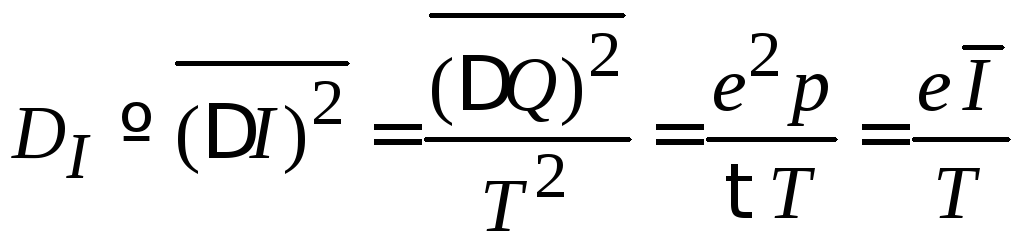 ,
,
(П.1.18)
относительная
флуктуация тока
 .
.
(П.1.19)
Относительная
флуктуация тока увеличивается при
уменьшении среднего тока и времени
измерения
Т.
Малость вероятности
![]() ограничивает средний ток
ограничивает средний ток![]() .
.
При![]() находим
находим![]() .
.
Дробовой
шум вакуумного диода исследовал Шоттки
в 1918 г.

Вальтер
Герман Шоттки (1886–1976)
Дисперсия
тока дробового шума в двухмерном
электронном газе при низкой температуре
в магнитном поле в режиме квантового
эффекта Холла измерена в 1997 г. Из формулы
дисперсии тока (П.1.18)
![]() получена эффективная величина переносимого
получена эффективная величина переносимого
заряда![]() .
.
Такой эффект Холла называется дробным.
Соседние файлы в папке СГФ лекции
- #
- #
- #
Подвижность. Дрейф
носителей заряда
Если в полупроводнике создано электрическое поле величины Е, то помимо хаотического появляется
направленное перемещение носителей заряда, называемое дрейфом. Скорость дрейфа,
vдр,
– это скорость, направленная вдоль вектора напряженности электрического поля,
усредненная по всем носителям заряда одного знака (электронами или дырками).
Оценить среднюю скорость дрейфа можно исходя из формулы vдр=a tп, где а
– ускорение, приобретаемое электроном между столкновениями. Среднее ускорение
электрона можно рассчитать, используя второй закон Ньютона
![]() ,
,
где qE=F – сила, действующая на
электрон со стороны поля.
Подставив это выражение в формулу для скорости дрейфа, получаем
![]() . (3.1)
. (3.1)
В формуле (3.1) величина ![]() называется подвижностью
называется подвижностью
носителей заряда. Таким образом, подвижность носителей заряда обратно
пропорциональна эффективной массе носителей m и прямо пропорциональна
времени свободного пробега tп.
Поскольку скорость дрейфа vдр=μЕ,
то значение подвижности можно рассчитать по формуле
![]() , м2/В·с. (3.2)
, м2/В·с. (3.2)
Иначе говоря, подвижность носителей заряда – это скорость дрейфа,
приобретаемая свободными носителями в электрическом поле напряженности Е=1 В/м.
Оценка величины подвижности электрона
μ в кристаллической решетке по формуле (3.1)
дает следующее значение:
![]() м2/В·с.
м2/В·с.
Поскольку в полупроводниках существуют два вида носителей
заряда с различными эффективными массами, то различают подвижность электронов
mn и подвижность дырок
mp. Подвижность
электронов в кремнии по различным данным составляет (0,14…0,19) м2/(В×с),
а в арсениде галлия – (0,93…1,1) м2/(В×с). Подвижность дырок оказывается
значительно меньшей и равной (0,04…0,05) м2/(В×с) для
кремния и германия и 0,045 м2/(В×с) для арсенида галлия, что объясняется
меньшим временем свободного пробега дырок в этих полупроводниковых материалах.
Температурная зависимость величины подвижности носителей заряда в
полупроводниках определяется механизмами рассеяния носителей заряда.
В слабых электрических полях дрейфовая скорость значительно меньше
средней скорости теплового хаотического движения. Длина свободного пробега
определяется в основном рассеянием
свободных носителей на колеблющихся атомах полупроводника (фононах) и ионизированных атомах примесей. Фононное рассеяние преобладает при малых концентрациях примесей
(1020…1023 м-3), в этом случае длина свободного
пробега, следовательно и подвижность, уменьшаются с
ростом температуры (рис. 3.1, а).
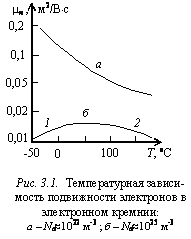 Подвижность
Подвижность
носителей заряда в полупроводнике становится значительно меньшей при высокой
концентрации примесей, 1024…1025 м-3. В
этом случае при сравнительно низких температурах преобладает рассеяние
носителей заряда на примесях, находящихся в ионизированном или нейтральном
состоянии. При нагреве полупроводника вследствие увеличения тепловой
скорости электронов и уменьшения их времени взаимодействия с ионами,
подвижность носителей заряда mи растет с температурой по закону mи~T3/2/Nи, где Nи – концентрация ионизированных
примесей (доноров или акцепторов). При высоких температурах преобладает рассеяние
носителей заряда на тепловых колебаниях атомов или ионов кристаллической
решетки полупроводника. При этом подвижность mт уменьшается с ростом
температуры по закону mт ~T -3/2.
График зависимости m=f(T) в сильно легированом
полупроводнике представлен на рис. 3.1, б.
Видно, что температурная зависимость подвижности носителей заряда в примесном полупроводнике состоит из двух участков.
Участок 1 характерен для низких
температур, когда преобладает рассеяние на ионизированных примесях; на
участке 2 подвижность носителей
уменьшается вследствие рассеяния на тепловых колебаниях атомов и ионов.
Результирующая подвижность m определяется с помощью соотношения
![]() . (3.3)
. (3.3)
Подвижность и дрейфовая скорость
носителей заряда зависят не только от температуры, но и от напряженности
электрического поля в полупроводнике.
В слабых электрических полях vдр<<vт,
тогда полная средняя скорость ![]() не зависит от напряженности поля Е и подвижность m=mo постоянна. Дополнительная,
не зависит от напряженности поля Е и подвижность m=mo постоянна. Дополнительная,
приобретаемая электронами на длине свободного пробега, энергия много меньше kT, она теряется при рассеянии
на возбуждение низкочастотных акустических фононов (п. 1.5.7).
С ростом напряженности электрического поля скорость дрейфа электронов
возрастает (рис. 3.2), приобретаемая электронами энергия увеличивается и начинает
превышать потери при рассеянии, поскольку энергия возбуждаемых акустических
фононов по-прежнему мала по сравнению с kT. Это вытекает из условия сохранения
импульса – импульс возбуждаемого фонона должен быть равен изменению импульса
электрона. Однако импульс акустического фонона pфон=![]() = =(h/vфон)fфон с энергией Wфон
= =(h/vфон)fфон с энергией Wфон![]() kT значительно превышает импульс электрона из-за невысокой скорости
kT значительно превышает импульс электрона из-за невысокой скорости
фонона vфон![]() 5·103 м/с и энергия электрона не может быть
5·103 м/с и энергия электрона не может быть
передана фононам с такой энергией.
Вследствие увеличения средней скорости электронов уменьшается время свободного
пробега tп электрона
между двумя столкновениями и, согласно соотношению (3.1), подвижность
уменьшается. Известно, что подвижность
снижается на 10%, когда напряженность электрического поля достигает критического
значения Eкр=1,4vфон/m0, где m0
– значение подвижности в слабом электрическом поле. Таким образом, значение
критического поля обратно пропорционально величине подвижности носителей заряда
в конкретном полупроводниковом материале. В кремнии для электронов Eкр=7,5·104 В/м, а для дырок Eкр=2·105 В/м при Т=300 К. Следовательно, в кремнии
величина критического поля для дырок примерно в 2,5 раза выше, чем для
электронов, характеризующихся более высокой подвижностью.
Величина подвижности носителей
заряда, в свою очередь, зависит от напряженности электрического поля. При E>>vфон/m0
подвижность уменьшается с ростом напряженности поля Е по закону m~1/![]() , а дрейфовая скорость увеличивается: vдр~
, а дрейфовая скорость увеличивается: vдр~![]() .
.
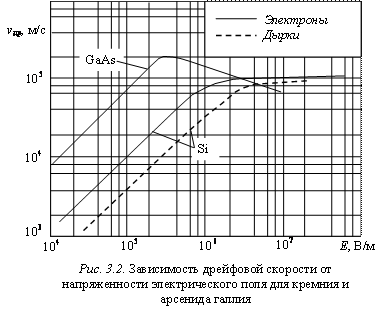
В сильных электрических полях (Е=106…107 В/м), когда скорость дрейфа приближается к средней тепловой
скорости, средняя энергия электронов становится достаточной для возбуждения
оптических фононов. В отличие от акустических оптические фононы при
сравнительно небольших импульсах того же порядка что и у электрона, обладают
большими энергиями (2…3)kТ при Т=300 K. В процессе рассеяния электроны отдают почти всю
свою кинетическую энергию на образование фононов, поскольку как только она
достигает величины Wфон. опт, возбуждается фонон и энергия электрона снижается. В этих условиях
время свободного пробега tп и подвижность обратно пропорциональны напряженности электрического
поля: m~1/Е, а дрейфовая скорость перестает
зависеть от Е и достигает предельного
значения – скорости насыщения vнас. В кремнии при Т=300 К для электронов vнас=105 м/c, а для
дырок vнас=8×104 м/c.
Скорость
насыщения vнас является важнейшим электрофизическим
параметром полупроводника. При Т=300 К она имеет значение близкое к тепловой скорости, однако в
отличие от последней vнас
может уменьшаться с ростом температуры. Например, в кремнии n-типа в диапазоне температур от минус 50 до +120 оС скорость насыщения vнас уменьшается в
диапазоне (1,1…0,8)×105,
а тепловая скорость vт
– возрастает в диапазоне (1,7…2)×105
м/с.
Для кремния и германия зависимость дрейфовой скорости от напряженности
электрического поля может быть аппроксимирована формулой
![]() ,
,
(3.4)
где m0 –
значение подвижности в слабом электрическом поле.
Таким образом, дрейфовая скорость в
полупроводниках возрастает с ростом напряженности электрического поля, достигая
своего максимального значения – скорости насыщения, близкого к тепловой
скорости.
Зависимость подвижности носителей заряда
(электронов или дырок) от напряженности электрического поля в кремнии аппроксимируется выражением
![]() . (3.5)
. (3.5)
Подвижность носителей заряда в средних и
сильных электрических полях уменьшается с ростом напряженности электрического
поля.
Дрейфовый ток
Создание в однородном полупроводнике электрического поля с
напряженностью E, в результате
подключения внешнего источника ЭДС или тока, приводит к появлению дрейфа
носителей тока (электронов и дырок).
Поскольку знаки зарядов электронов и дырок противоположны, то носители
дрейфуют со скоростью vдр в
противоположных направлениях в соответствии с силами, действующими со стороны электрического
поля. Поэтому соответствующие дрейфовые токи складываются, как показано на рис.
3.3.

Плотность дрейфового тока jдр в собственном полупроводнике
складывается из плотностей токов электронов jn др
и дырок jp др и определяется из выражения
jдр= jn др+ jp др=(qnivn др+qpivp др)= qni(mn+mp)E, А/м2,
(3.6)
где q – заряды; ni=pi– концентрации; vn др и vp др –
скорости дрейфа; mn и mp – подвижности электронов и дырок.
В примесных полупроводниках общая
плотность дрейфового тока электронов и дырок
jдр= jn др+ jp др=q(nmn+pmp)E, А/м2, (3.7)
В рабочей области температур плотность дрейфового тока определяется,
преимущественно, основными носителями тока и рассчитывается по формулам jn др=qnnmnE
и jp др=qppmpE, где nn и pp –
концентрации основных носителей тока в электронном и дырочном полупроводниках.
Научная статья
на тему: “Экскурс:
скорость дрейфа электронов“
Если нажать
выключатель света, лампа загорится практически «сразу». Следовательно,
напряжение, первоначально приложенное только к концам проводов переключателя,
который все еще разомкнут, необходимо также приложить к лампе сразу после
включения переключателя.
Фактически,
электрические поля движутся со скоростью света. Вы можете представить это в
простом сравнении, как шланг, который уже полностью заполнен водой: если вы
добавляете воду с одного конца, она немедленно выливается из другого конца.
Однако для этого свежая вода не должна проходить через шланг.
Итак, как быстро
электроны движутся в проводнике? Оценка может быть сделана по так называемой
электронной плотности ![]() соответствующего материала проводника; это
соответствующего материала проводника; это
показывает, сколько свободных электронов находится в материале на единицу
пространства. Для меди, например, это значение составляет ![]() .
.
Каждый электрон
несет ровно один элементарный заряд ![]() . Следующее
. Следующее
относится к подвижному количеству заряда в секции лестницы:
![]()
Объем  сечения
сечения
проводника, в свою очередь, можно записать как произведение площади его
поперечного сечения ![]() и длины
и длины ![]() . Применимо следующее:
. Применимо следующее:
![]()
Электрический
ток  соответствует количеству заряда, который перемещается во времени, так
соответствует количеству заряда, который перемещается во времени, так
оно и есть  . Если кусок проводника во всех точках
. Если кусок проводника во всех точках
изготовлен из одного и того же материала и имеет постоянную площадь поперечного
сечения, то длина –  единственная переменная, которая изменяется
единственная переменная, которая изменяется
со временем. Однако изменение маршрута с течением времени – это не что иное,
как скорость; так что можно написать:

Скорость дрейфа  показывает, как быстро определенный объем электронов,
показывает, как быстро определенный объем электронов,
который можно представить, например, окрашенным, «проталкивает» проводник.
Решая приведенное выше уравнение для  , получаем:
, получаем:
(1) 
В дополнение к
естественным константам  и константам материала
и константам материала
это уравнение  содержит только площадь поперечного сечения
содержит только площадь поперечного сечения
 проводника
проводника
и протекающий ток  как легко измеримые величины.
как легко измеримые величины.
Пример:
● Какова скорость дрейфа электронов в обычной медной линии с
площадью поперечного сечения, ![A = unit [1.5] {мм ^ 2}](https://documents.infourok.ru/b85328ee-5cb1-4871-a14e-315d0ba6cf19/0/image005.gif) когда
когда ![I = unit [5.0] {A}](https://documents.infourok.ru/b85328ee-5cb1-4871-a14e-315d0ba6cf19/0/image005.gif) в цепи возникает ток ?
в цепи возникает ток ?
Для меди электронная плотность равна ![n _ { mathrm {Cu}} = unit [8.47 cdot 10 ^ {19}] { frac {1} {mm ^ 3}}](https://documents.infourok.ru/b85328ee-5cb1-4871-a14e-315d0ba6cf19/0/image005.gif) ;
;
таким образом, согласно формуле (1) для скорости
дрейфа получаем :
![v _ { mathrm {D}} = frac {I} {n cdot A cdot q _ { mathrm {e}}} = frac { unit [5,0] {A}} { unit [8,47 cdot 10 ^ {19}] { frac {1} {мм ^ 3}} cdot unit [1,5] {мм ^ 2} cdot unit [1,6022 cdot 10 ^ {- 19}] {C}} приблизительно unit [0,246] { frac {мм} {s}}](https://documents.infourok.ru/b85328ee-5cb1-4871-a14e-315d0ba6cf19/0/image005.gif)
Единство возникает из-за  .
.
Поэтому скорость
дрейфа электронов в металлическом проводнике очень мала по сравнению со
скоростью распространения электрического поля (скоростью света).
Примечания:
|
[1] |
Электропроводность металла |
|
[2] |
Чем более отчетливо |
|
[3] |
Прочно закрепленные атомные |


























![{displaystyle mu =mu _{0}exp left(-left[{frac {T_{0}}{T}}right]^{-1/(d+1)}right)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2ec6dbb01dae46490fe94780f7719b272fd5f4ad)


![{displaystyle {vec {F}}_{y}=(-q){vec {xi }}_{y}+(-q)[{vec {v}}_{n}times {vec {B}}_{z}]=0}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ddcbe1f951022700b2af8e0537cebaa8bc411b4f)

















