Tall Arrays
Calculate with arrays that have more rows than fit in memory.
This function fully supports tall arrays. For
more information, see Tall Arrays.
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
GPU Code Generation
Generate CUDA® code for NVIDIA® GPUs using GPU Coder™.
Thread-Based Environment
Run code in the background using MATLAB® backgroundPool or accelerate code with Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool.
GPU Arrays
Accelerate code by running on a graphics processing unit (GPU) using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
This function fully supports GPU arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Distributed Arrays
Partition large arrays across the combined memory of your cluster using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
“Высокие” массивы
Осуществление вычислений с массивами, которые содержат больше строк, чем помещается в памяти.
Генерация кода C/C++
Генерация кода C и C++ с помощью MATLAB® Coder™.
Генерация кода графического процессора
Сгенерируйте код CUDA® для NVIDIA® графические процессоры с помощью GPU Coder™.
Основанная на потоке среда
Запустите код в фоновом режиме с помощью MATLAB® backgroundPool или ускорьте код с Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool.
Массивы графического процессора
Ускорьте код путем работы графического процессора (GPU) с помощью Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
Эта функция полностью поддерживает массивы графического процессора. Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите функции MATLAB Запуска на графическом процессоре (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Распределенные массивы
Большие массивы раздела через объединенную память о вашем кластере с помощью Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
Introduction to Absolute Value Matlab
Absolute value of a number gives us its distance form 0 on the number line. Absolute value does not consider the direction in which the number lies, and so absolute values are never negative. For vectors, absolute value is the magnitude of the vector. The absolute value for complex number is given by distance of the number from the origin in a complex plane. In Matlab, we use ‘absolute function’ to get the absolute value of any number or vector.
Syntax of Absolute Value Function in Matlab:
X = abs (S)
Description:
- X = abs (S): It is used to get the absolute value for every element in the input S.
- If the input array S has complex elements, then abs (S) function will return ‘complex magnitude’.
Examples of Absolute Value Matlab
Given below are the codes to calculate the absolute value in Matlab using ‘abs (S) function’:
Example #1
In this example, we will take a simple scalar and will find its absolute value using abs (S) function.
We will follow the following 2 steps:
- Take a scalar.
- Pass it as an argument to the absolute value function.
Code:
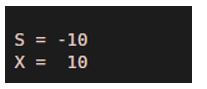
S = -10
[Initializing the scalar ‘S’]
X = abs (S)
[Passing the scalar as an input to the absolute function]
[Please note that, we can directly pass the scalar value as input to the abs function like, abs (-10)]
[Mathematically, the absolute value of -10 is 10]
Input:
S = -10
X = abs (S)
Output:
As we can see in the output, we have obtained absolute value of our input scalar as 10, which is same as expected by us.
Let us now see how the code for absolute value looks like in Matlab if we want to compute absolute value of a complex number.
[Please note that, mathematically, the complex magnitude or absolute value of a complex number (a + ib) is given by square root of (a^2 + b^2)].
Example #2
In this example, we will take a complex number and will find its absolute value using abs (S) function.
We will follow the following 2 steps:
- Take a complex number.
- Pass it as an argument to the absolute value function.
Code:
S = 6 + 8i
[Initializing the complex number ‘S’]
X = abs (S)
[Passing the complex number as an input to the absolute function]
[Please note that, we can directly pass the complex value as input to the abs function like, abs (6 + 8i)]
[Mathematically, the absolute value of (6 + 8i) is 10]
Input:
S = 6 + 8i
X = abs (S)
Output:
As we can see in the output, we have obtained absolute value of our input complex number as 10, which is same as expected by us.
Let us now see how the code for absolute value looks like in Matlab if we want to compute absolute value for vectors.
Example #3
In this example, we will take an array of vectors and will find its absolute value using abs (S) function.
We will follow the following 2 steps:
- Create the input array.
- Pass it as an argument to the absolute value function.
Code:
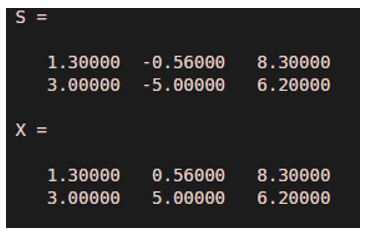
S = [1.3 -0.56 8.3; 3 -5 6.2]
[Initializing the input array ‘S’]
X = abs (S)
[Passing the array as an input to the absolute function]
[Mathematically, the absolute value of [1.3 -0.56 8.3; 3 -5 6.2] is [1.3000 0.5600 8.3000; 3.0000 5.0000 6.2000]
Input:
S = [1.3 -0.56 8.3; 3 -5 6.2]
X = abs (S)
Output:
As we can see in the output, we have obtained absolute value of our input array of vectors as expected by us.
Let us now see how the code for absolute value looks like in Matlab if we want to compute absolute value for an array of complex numbers.
Example #4
In this example, we will take an array of complex numbers and will find its absolute value using abs (S) function.
We will follow the following 2 steps:
- Create an array of complex number.
- Pass it as an argument to the absolute value function.
Code:
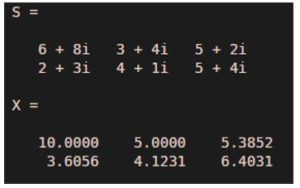
S = [6+8i 3+4i 5+2i; 2+3i 4+1i 5+4i]
[Creating the array of complex numbers]
X = abs (S)
[Passing the array as an input to the absolute function]
[abs (S) will find the absolute value of every element of the array]
Input:
S = [6+8i 3+4i 5+2i; 2+3i 4+1i 5+4i]
X = abs (S)
Output:
As we can see in the output, we have obtained absolute value of our input array of complex numbers as expected by us.
Conclusion
Absolute value function can be used in Matlab to get the absolute value of any scalar or vector. We can also use the same function to get the complex magnitude of complex numbers.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Absolute Value Matlab. Here we discuss the introduction to Absolute Value Matlab along with examples respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
- Magnitude Matlab
- Matlab fopen
- Matlab Plot Multiple Lines
- MATLAB Unique
MatLab содержит в себе
все распространенные математические функции, которые доступны по их имени при
реализации алгоритмов. Например, функция sqrt() позволяет
вычислять квадрат числа и может быть использована в программе следующим
образом:
x = 2;
y = 4;
d = sqrt(x^2+y^2); %вычисление
евклидового расстояния
Аналогичным
образом вызываются и все другие математические функции, представленные в табл.
1.2.
Таблица
1.2. Основные математические функции MatLab
|
sqrt(x) |
вычисление |
|
exp(x) |
возведение |
|
pow2(x) |
возведение |
|
log(x) |
вычисление |
|
log10(x) |
вычисление |
|
log2(x) |
вычисление |
|
sin(x) |
синус |
|
cos(x) |
косинус |
|
tan(x) |
тангенс |
|
cot(x) |
котангенс |
|
asin(x) |
арксинус |
|
acos(x) |
арккосинус |
|
atan(x) |
арктангенс |
|
pi |
число |
|
round(x) |
округление |
|
fix(x) |
усечение |
|
floor(x) |
округление |
|
ceil(x) |
округление |
|
mod(x) |
остаток |
|
sign(x) |
знак |
|
factor(x) |
разложение |
|
isprime(x) |
истинно, |
|
rand |
генерация |
|
randn |
генерация |
|
abs(x) |
вычисление |
Почти все элементарные функции допускают
вычисления и с комплексными аргументами. Например:
res = sin(2+3i)*atan(4i)/(1
— 6i); % res = -1.8009 — 1.9190i
или
exp(i*x) = cos(x)+i*sin(x);
abs
Absolute value and complex magnitude
Syntax
-
Y = abs(X)
Description
abs(X) returns an array
Y such that each element of Y is the absolute value of the corresponding element of X.
If X is complex, abs(X) returns the complex modulus (magnitude), which is the same as
-
sqrt(real(X).^2 + imag(X).^2)
Examples
-
abs(-5) ans = 5 abs(3+4i) ans = 5
See Also
angle, sign, unwrap
 |
zip | acos |  |