In Python, the list data structure stores elements in sequential order. We can use the String replace() method to replace a specified string with another specified string. However, we cannot apply the replace() method to a list. If you try to use the replace() method on a list, you will raise the error “AttributeError: ‘list’ object has no attribute ‘replace’”.
This tutorial will go into detail on the error definition. We will go through an example that causes the error and how to solve it.
Table of contents
- AttributeError: ‘list’ object has no attribute ‘replace’
- Python replace() Syntax
- Example #1: Using replace() on a List of Strings
- Solution
- Example #2: Using split() then replace()
- Solution
- Summary
AttributeError: ‘list’ object has no attribute ‘replace’
AttributeError occurs in a Python program when we try to access an attribute (method or property) that does not exist for a particular object. The part “‘list’ object has no attribute ‘replace’” tells us that the list object we are handling does not have the replace attribute. We will raise this error if we try to call the replace() method on a list object. replace() is a string method that replaces a specified string with another specified string.
Python replace() Syntax
The syntax for the String method replace() is as follows:
string.replace(oldvalue, newvalue, count)Parameters:
- oldvalue: Required. The string value to search for within string
- newvalue: Required. The string value to replace the old value
- count: Optional. A number specifying how many times to replace the old value with the new value. The default is all occurrences
Let’s look at an example of calling the replace() method to remove leading white space from a string:
str_ = "the cat is on the table"
str_ = str.replace("cat", "dog")
print(str_)the dog is on the tableNow we will see what happens if we try to use the replace() method on a list:
a_list = ["the cat is on the table"]
a_list = a_list.replace("cat", "dog")
print(a_list)---------------------------------------------------------------------------
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
1 a_list = ["the cat is on the table"]
2
----≻ 3 a_list = a_list.replace("cat", "dog")
4
5 print(a_list)
AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'replace'The Python interpreter throws the Attribute error because the list object does not have replace() as an attribute.
Example #1: Using replace() on a List of Strings
Let’s look at an example list of strings containing descriptions of different cars. We want to use the replace() method to replace the phrase “car” with “bike”. Let’s look at the code:
lst = ["car one is red", "car two is blue", "car three is green"]
lst = lst.replace('car', 'bike')
print(lst)Let’s run the code to get the result:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
----≻ 1 lst = lst.replace('car', 'bike')
AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'replace'We can only call the replace() method on string objects. If we try to call replace() on a list, we will raise the AttributeError.
Solution
We can use list comprehension to iterate over each string and call the replace() method. Let’s look at the revised code:
lst = ["car one is red", "car two is blue", "car three is green"]
lst_repl = [i.replace('car', 'bike') for i in lst]
print(lst_repl)List comprehension provides a concise, Pythonic way of accessing elements in a list and generating a new list based on a specified condition. In the above code, we create a new list of strings and replace every occurrence of “car” in each string with “bike”. Let’s run the code to get the result:
['bike one is red', 'bike two is blue', 'bike three is green']Example #2: Using split() then replace()
A common source of the error is the use of the split() method on a string prior to using replace(). The split() method returns a list of strings, not a string. Therefore if you want to perform any string operations you will have to iterate over the items in the list. Let’s look at an example:
particles_str = "electron,proton,muon,cheese"We have a string that stores four names separated by commas. Three of the names are correct particle names and the last one “cheese” is not. We want to split the string using the comma separator and then replace the name “cheese” with “neutron”. Let’s look at the implementation that will raise an AttributeError:
particles = str_.split(",")
particles = particles.replace("cheese", "neutron")Let’s run the code to see the result:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
----≻ 1 particles = particles.replace("cheese", "neutron")
AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'replace'The error occurs because particles is a list object, not a string object:
print(particles)['electron', 'proton', 'muon', 'cheese']Solution
We need to iterate over the items in the particles list and call the replace() method on each string to solve this error. Let’s look at the revised code:
particles = [i.replace("cheese","neutron") for i in particles]
print(particles)In the above code, we create a new list of strings and replace every occurrence of “cheese” in each string with “neutron”. Let’s run the code to get the result:
['electron', 'proton', 'muon', 'neutron']Summary
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial! The error “AttributeError: ‘list’ object has no attribute ‘replace’” occurs when you try to use the replace() function to replace a string with another string on a list of strings.
The replace() function is suitable for string type objects. If you want to use the replace() method, ensure that you iterate over the items in the list of strings and call the replace method on each item. You can use list comprehension to access the items in the list.
Generally, check the type of object you are using before you call the replace() method.
For further reading on AttributeErrors involving the list object, go to the article:
- How to Solve Python AttributeError: ‘list’ object has no attribute ‘split’.
- How to Solve Python AttributeError: ‘list’ object has no attribute ‘lower’.
- How to Solve Python AttributeError: ‘list’ object has no attribute ‘get’.
To learn more about Python for data science and machine learning, go to the online courses page on Python for the most comprehensive courses available.
Have fun and happy researching!
I am trying to remove the character ‘ from my string by doing the following
kickoff = tree.xpath('//*[@id="page"]/div[1]/div/main/div/article/div/div[1]/section[2]/p[1]/b[1]/text()')
kickoff = kickoff.replace("'", "")
This gives me the error AttributeError: ‘list’ object has no attribute ‘replace’
Coming from a php background I am unsure what the correct way to do this is?
falsetru
354k63 gold badges718 silver badges631 bronze badges
asked Apr 15, 2016 at 9:03
2
xpath method returns a list, you need to iterate items.
kickoff = [item.replace("'", "") for item in kickoff]
answered Apr 15, 2016 at 9:05
falsetrufalsetru
354k63 gold badges718 silver badges631 bronze badges
2
kickoff = tree.xpath('//*[@id="page"]/div[1]/div/main/div/article/div/div[1]/section[2]/p[1]/b[1]/text()')
This code is returning list not a string.Replace function will not work on list.
[i.replace("'", "") for i in kickoff ]
answered Apr 15, 2016 at 9:06
Himanshu duaHimanshu dua
2,4861 gold badge19 silver badges27 bronze badges
This worked for me:
kickoff = str(tree.xpath('//*[@id="page"]/div[1]/div/main/div/article/div/div[1]/section[2]/p[1]/b[1]/text()'))
kickoff = kickoff.replace("'", "")
This error is caused because the xpath returns in a list. Lists don’t have the replace attribute. So by putting str before it, you convert it to a string which the code can handle. I hope this helped!
answered Mar 28, 2019 at 3:29
In this guide, we will explore the common error of the ‘List’ object attribute error in Python when trying to use the replace method with lists. We will learn how to identify the issue, understand its root cause, and provide a step-by-step solution to solve this problem.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the ‘List’ Object AttributeError
- Step-by-Step Solution to Solve the ‘Replace’ Issue
- FAQs
Understanding the ‘List’ Object AttributeError
Before diving into the solution, let’s first understand the error message itself. When you encounter the following error message in Python:
AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'replace'
This means that you are trying to use the replace method, which is a string method, on a list object. The replace method is designed to work with strings, not lists. Therefore, Python raises an AttributeError, indicating that the ‘list’ object has no attribute called ‘replace.’
To fix this issue, we need to use appropriate list methods or convert the list elements to strings before using the replace method.
Step-by-Step Solution to Solve the ‘Replace’ Issue
Let’s go through a step-by-step solution to fix the ‘List’ object AttributeError.
Step 1: Identify the problematic code
First, identify the part of your code that is causing the issue. Look for the line of code where you are trying to use the replace method on a list object.
For example:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
my_list.replace('apple', 'grape')
Step 2: Convert the list elements to strings
Since the replace method works with strings, you need to convert the list elements to strings before using the replace method. You can use a list comprehension to achieve this:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
my_list = [str(item) for item in my_list]
Step 3: Use the appropriate list method or loop
Now that the list elements are strings, you can use the replace method within a loop or list comprehension to replace the desired elements in the list.
Here’s an example using a for loop:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
new_list = []
for item in my_list:
new_item = item.replace('apple', 'grape')
new_list.append(new_item)
print(new_list)
Alternatively, you can use a list comprehension to achieve the same result:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
new_list = [item.replace('apple', 'grape') for item in my_list]
print(new_list)
FAQs
1. Can I use the replace method with other data types besides strings?
No, the replace method is specific to strings. If you want to use a similar method with other data types, you need to find an appropriate method or function for that data type.
2. What other common methods are available for lists in Python?
Some common list methods in Python include append(), extend(), insert(), remove(), pop(), count(), and sort(). You can find more information about these methods in the Python documentation.
3. How can I replace an element in a list without using the replace method?
You can use the list’s index to replace an element directly. For example:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
my_list[0] = 'grape'
print(my_list)
4. How do I find the index of an element in a list?
You can use the index() method to find the index of an element in a list. For example:
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
index = my_list.index('banana')
print(index)
5. Can I use the replace method to replace multiple occurrences of a substring in a string?
Yes, you can use the replace method to replace all occurrences of a substring in a string. By default, the replace method replaces all occurrences of the specified substring. If you want to limit the number of replacements, you can pass an additional argument to the method. For example:
my_string = "apple banana apple orange apple"
new_string = my_string.replace("apple", "grape", 2)
print(new_string)
This will replace the first two occurrences of “apple” with “grape.”
- Python List Methods (Official Documentation)
- Python String Methods (Official Documentation)
- List Comprehensions in Python (Real Python)
AttributeError: list object has no attribute replace error occurs because of invoking replace() function with list object in the place of str type object. There are many methods or attributes which is being supported with str type of object like split(), lower(), and strip(). But all these attribute are not defined in the list type of object. Invoking different attribute with the different objects will always be through Attributeerrors.
Well, In this article we will fix the AttributeError related to replace() function with the list. Along with we will understand the generic ways to fix attributeError related to list object.
Firstly let’s replicate this error. Then we will understand the solution.
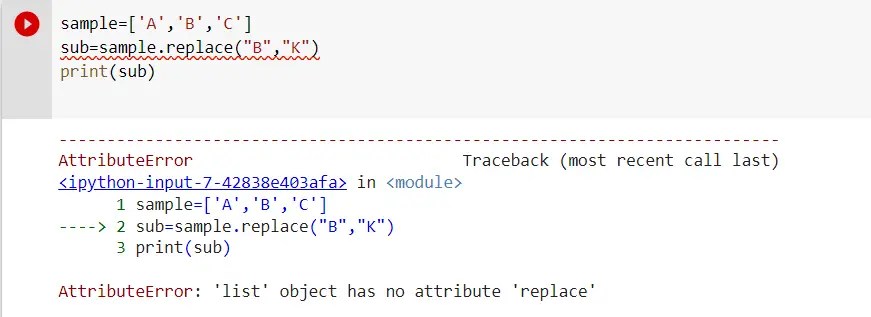
Here we want to replace the element “B” with “K”. But the piece of code is throwing the attributeError because the list object does not contain replace as a member element in the class. Now let’s understand with the help of the above example how we can fix up this error.
Solution 1: Accessing the element as an str object –
Here we access the individual element as str and there apply this replace function. Let’s understand with the above example. Here the sub-element of the list are strings –
sample=['A','B','C']
sub=sample[1].replace("B","K")
print(sub)Solution 2: Converting the list to str object –
In the above approach, we take out one element and then convert the same into str object. But here we will convert the complete object into str object and then invoke replace function.
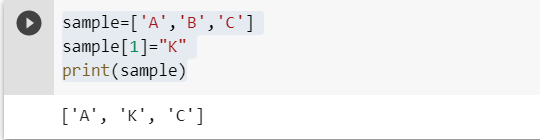
Solution 3 : Use assignment in the place of replace[Mostly Adapted ]-
Since list is a mutable type object hence we can use the assignment operator to replace individual elements in the list.
sample=['A','B','C']
sample[1]="K"
print(sample)Thanks
DSL Team
Join our list
Subscribe to our mailing list and get interesting stuff and updates to your email inbox.
We respect your privacy and take protecting it seriously
Thank you for signup. A Confirmation Email has been sent to your Email Address.
Something went wrong.
I try to replace a text in csv read with some data dictionary, but I got an Error.
import csv
dataset = open('../sentimenprabowo.csv', 'r')
sentiment = csv.reader(dataset, delimiter=',')
newDok = open('../sentimenprabowopreproses.csv', 'w')
save = csv.writer(newDok)
data= open("convertcsv.json", "r")
APPOSTOPHES=data.read()
new_sentence = []
for row in sentiment:
print(row)
for candidate_replacement in APPOSTOPHES:
if candidate_replacement in row:
#print(candidate_replacement)
row = row.replace(candidate_replacement, APPOSTOPHES[candidate_replacement])
new_sentence.append(row)
rfrm = "".join(new_sentence)
print(rfrm)
I hope this can be replace all the text in my csv who same text with data dictionary (correction spelling).
but the result is error:
File "readdata.py", line 45, in <module>
row = row.replace(candidate_replacement, APPOSTOPHES[candidate_replacement])
AttributeError: 'list' object has no attribute 'replace'
help me please…
this is my convertcsv.json file:
{"@":"di","ababil":"abg labil","abis":"habis","acc":"accord","ad":"ada","adlah":"adalah"}