The theoretical answers from everyone else are all neat, but let’s be pragmatic. ActionScript provides the tools you need so that you don’t even have to write a loop in this case!
First, note that Math.min() and Math.max() can take any number of arguments. Also, it’s important to understand the apply() method available to Function objects. It allows you to pass arguments to the function using an Array. Let’s take advantage of both:
var myArray:Array = [2,3,3,4,2,2,5,6,7,2];
var maxValue:Number = Math.max.apply(null, myArray);
var minValue:Number = Math.min.apply(null, myArray);
Here’s the best part: the “loop” is actually run using native code (inside Flash Player), so it’s faster than searching for the minimum or maximum value using a pure ActionScript loop.
answered Jan 8, 2009 at 23:51
Josh TynjalaJosh Tynjala
5,2253 gold badges23 silver badges25 bronze badges
4
There isn’t any reliable way to get the minimum/maximum without testing every value. You don’t want to try a sort or anything like that, walking through the array is O(n), which is better than any sort algorithm can do in the general case.
answered Jan 8, 2009 at 16:00
Adam BellaireAdam Bellaire
107k19 gold badges148 silver badges163 bronze badges
If
- The array is not sorted
- Finding the min and max is done simultaneously
Then there is an algorithm that finds the min and max in 3n/2 number of comparisons. What one needs to do is process the elements of the array in pairs. The larger of the pair should be compared with the current max and the smaller of the pair should be compared with the current min. Also, one needs take special care if the array contains odd number of elements.
In c++ code (borrowing some code from Mehrdad).
struct MinMax{
int Min,Max;
}
MinMax FindMinMax(int[] array, int start, int end) {
MinMax min_max;
int index;
int n = end - start + 1;//n: the number of elements to be sorted, assuming n>0
if ( n%2 != 0 ){// if n is odd
min_max.Min = array[start];
min_max.Max = array[start];
index = start + 1;
}
else{// n is even
if ( array[start] < array[start+1] ){
min_max.Min = array[start];
min_max.Max = array[start+1];
}
else{
min_max.Min = array[start+1];
min_max.Max = array[start];
}
index = start + 2;
}
int big, small;
for ( int i = index; i < n-1; i = i+2 ){
if ( array[i] < array[i+1] ){ //one comparison
small = array[i];
big = array[i+1];
}
else{
small = array[i+1];
big = array[i];
}
if ( min_max.Min > small ){ //one comparison
min_max.Min = small;
}
if ( min_max.Max < big ){ //one comparison
min_max.Max = big;
}
}
return min_max;
}
It’s very easy to see that the number of comparisons it takes is 3n/2. The loop runs n/2 times and in each iteration 3 comparisons are performed. This is probably the optimum one can achieve. At this moment, I cannot point to a definite source of that. (But, I think I have seen a proof of that somewhere.)
The recursive solution given by Mehrdad above, probably also achieves this minimal number of comparisons (the last line needs to be changed). But with the same number of comparisons an iterative solution will always beat a recursive solution due to overhead in the function call as he mentioned. However, if one only cares about finding min and max of a few numbers (as Eric Belair does), no one will notice any difference in todays computer with any of the approaches above. For a large array, the difference could be significant.
Though this solution and the solution given by Matthew Brubaker has O(n) complexity, in practice one should carefully asses the hidden constants involved. The number of comparisons in his solution is 2n. The speedup gained with the solution with 3n/2 comparisons as opposed to 2n comparisons would be noticeable.
answered Jul 26, 2009 at 7:41
2
Unless the array is sorted, that’s the best you’re going to get. If it is sorted, just take the first and last elements.
Of course, if it’s not sorted, then sorting first and grabbing the first and last is guaranteed to be less efficient than just looping through once. Even the best sorting algorithms have to look at each element more than once (an average of O(log N) times for each element. That’s O(N*Log N) total. A simple scan once through is only O(N).
If you are wanting quick access to the largest element in a data structure, take a look at heaps for an efficient way to keep objects in some sort of order.
answered Jan 8, 2009 at 16:10
EclipseEclipse
44.6k20 gold badges112 silver badges170 bronze badges
9
You have to loop through the array, no other way to check all elements. Just one correction for the code – if all elements are negative, maxValue will be 0 at the end. You should initialize it with the minimum possible value for integer.
And if you are going to search the array many times it’s a good idea to sort it first, than searching is faster (binary search) and minimum and maximum elements are just the first and the last.
answered Jan 8, 2009 at 16:03
1
Depends on what you call “best.” From a theoretical point of view, you cannot solve the problem in less than O(n) in a deterministic Turing machine.
The naive algorithm is too loop and update min, max. However, a recursive solution will require less comparisons than naive algorithm, if you want to get min, max simultaneously (it isn’t necessarily faster due to function call overhead).
struct MinMax{
public int Min,Max;
}
MinMax FindMinMax(int[] array, int start, int end) {
if (start == end)
return new MinMax { Min = array[start], Max = array[start] };
if (start == end - 1)
return new MinMax { Min = Math.Min(array[start], array[end]), Max = Math.Max(array[start], array[end]) } ;
MinMax res1 = FindMinMax(array, start, (start + end)/2);
MinMax res2 = FindMinMax(array, (start+end)/2+1, end);
return new MinMax { Min = Math.Min(res1.Min, res2.Min), Max = Math.Max(res1.Max, res2.Max) } ;
}
The simplest solution would be to sort and get the first and last item, though it’s obviously not the fastest 😉
The best solution, performance-wise, to find the minimum or maximum is the naive algorithm you written (with a single loop).
answered Jan 8, 2009 at 16:06
![]()
Mehrdad AfshariMehrdad Afshari
412k90 gold badges850 silver badges788 bronze badges
9
Math.max() is actually as3 code compiled to AVM2 opcodes, and as such is not more “native” than any other as3 code. As a consequence, it is not necessarily the fastest implementation.
Actually, given that it works on Array type, it is slower than carefully written code usign Vector:
I did a quick benchmark comparison of several naive Vector and Array implementations of Math.max, using gskinner’s PerformanceTest (Vector and Array being filled with identical random Numbers).
The fastest Vector implementation appeared to be more than 3x faster than Math.max with recent AIR SDK/release player (flash player WIN 14,0,0,122 RELEASE, compiled with AIR SDK 14):
average 3.5 ms for 1,000,000 values, compared to Math.max() average of 11ms :
function max(values:Vector.<Number>):Number
{
var max:Number = Number.MIN_VALUE;
var length:uint = values.length;
for (var i:uint = 0; i < length ; ++i)
if (values[i] > max)
max = values[i];
return max;
}
Conclusion is that if you are concerned by performance, you should use Vector over Array anywhere you can in the first place, and not always rely on default implementations, especially when they force the use of Array
PS:same implementation with a for each() loop is 12x slower …!
answered Aug 27, 2014 at 13:47
jaubouxjauboux
8886 silver badges12 bronze badges
This depends on real world application requirements.
If your question is merely hypothetical, then the basics have already been explained. It is a typical search vs. sort problem. It has already been mentioned that algorithmically you are not going to achieve better than O(n) for that case.
However, if you are looking at practical use, things get more interesting. You would then need to consider how large the array is, and the processes involved in adding and removing from the data set. In these cases, it can be best to take the computational ‘hit’ at insertion / removal time by sorting on the fly. Insertions into a pre-sorted array are not that expensive.
The quickest query response to the Min Max request will always be from a sorted array, because as others have mentioned, you simply take the first or last element – giving you an O(1) cost.
For a bit more of a technical explanation on the computational costs involved, and Big O notation, check out the Wikipedia article here.
Nick.
answered Jan 8, 2009 at 16:18
NickNick
2,2852 gold badges14 silver badges26 bronze badges
If you are building the array once and want to find the maximum just once, iterating is the best you can do.
When you want to modify the array and occasionally want to know the maximum element, you should use a Priority Queue. One of the best data structures for that is a Fibonacci Heap, if this is too complicated use a Binary Heap which is slower but still good.
To find minimum and maximum, just build two heaps and change the sign of the numbers in one of them.
answered Jan 8, 2009 at 16:12
martinusmartinus
17.7k15 gold badges72 silver badges92 bronze badges
Please take into account that sorting the array will only be faster that looping up to certain size of the array. If your array is small (and it will be like that any time) then your solution is perfectly fine. But if it might get too large you should use a conditional to use the sort approach when the array is small, and the normal iteration when it is too large
answered Jan 28, 2009 at 21:21
If you want to find both the min and max at the same time, the loop can be modified as follows:
int min = int.maxValue;
int max = int.minValue;
foreach num in someArray {
if(num < min)
min = num;
if(num > max)
max = num;
}
This should get achieve O(n) timing.
answered Jan 8, 2009 at 16:29
Matthew BrubakerMatthew Brubaker
3,0971 gold badge21 silver badges18 bronze badges
Shortest way :
Math.min.apply(null,array); //this will return min value from array
Math.max.apply(null,array); //this will return max value from array
otherway of getting min & max value from array
function maxVal(givenArray):Number
{
var max = givenArray[0];
for (var ma:int = 0; ma<givenArray.length; ma++)
{
if (givenArray[ma] > max)
{
max = givenArray[ma];
}
}
return max;
}
function minVal(givenArray):Number
{
var min = givenArray[0];
for (var mi:int = 0; mi<givenArray.length; mi++)
{
if (givenArray[mi] < min)
{
min = givenArray[mi];
}
}
return min;
}
As you can see, the code in both of these functions is very similar. The function sets a variable – max (or min) and then runs through the array with a loop, checking each next element. If the next element is higher than the current, set it to max (or min). In the end, return the number.
answered Feb 6, 2014 at 3:39
![]()
sajansajan
1,3451 gold badge14 silver badges18 bronze badges
Below is Solution with o(n):-
public static void findMaxAndMinValue(int A[]){
int min =0, max = 0;
if(A[0] > A[1] ){
min = A[1];
max = A[0];
}else{
max = A[1];
min = A[0];
}
for(int i = 2;i<A.length ;i++){
if(A[i] > max){
max = A[i];
}
if(min > A[i]){
min = A[i];
}
}
System.out.println("Maxinum Value is "+min+" & Minimum Value is "+max);
}
answered Jun 17, 2015 at 18:06
Ajay KumarAjay Kumar
4,6481 gold badge38 silver badges42 bronze badges
Amazed no-one mentioned parallelism here.
If you got really a huge array, you can use parallel-for, on sub ranges.
In the end compare all sub-ranges.
But parallelism comes width some penalty too, so this would not optimize on small arrays. However if you got huge datasets it starts to make sense, and you get a time division reduction nearing the amount of threads performing the test.
answered Mar 21, 2018 at 9:26
![]()
PeterPeter
2,0071 gold badge20 silver badges45 bronze badges
Find max values from a array
Let’s see how to obtain min, max values by using a single funtion
public void findMaxValue(){
int[] my_array = {1,2,,6,5,8,3,9,0,23};
int max = my_array[0];
for(int i=1; i<my_array.length; i++)
{
if(my_array[i] > max)
max = my_array[i];
}
return max;
}
same thing can do for find min value
answered Oct 24, 2018 at 16:00
After reading everyone’s comments (thank you for your interest), I found that the “best” way (least amount of code, best performing) to do this was to simply sort the Array, and then grab the first value in the Array:
var myArray:Array /* of Number */ = [2,3,3,4,2,2,5,6,7,2];
myArray.sort(Array.NUMERIC);
var minValue:int = myArray[0];
This also works for an Array of Objects – you simply use the Array.sortOn() function and specify a property:
// Sample data
var myArray:Array /* of XML */ =
[
<item level="2" name="a" />
<item level="3" name="b" />
<item level="3" name="c" />
<item level="2" name="d" />
<item level="5" name="e" />
]
// Perform a descending sort on the specified attribute in Array to get the maximum value
myArray.sortOn("@level", Array.DESCENDING | Array.NUMERIC);
var lowestLevel:int = myArray[0].@level;
I hope this helps someone else someday!
answered Jan 23, 2009 at 22:34
Eric BelairEric Belair
10.6k13 gold badges75 silver badges116 bronze badges
Часто встречаются задачи, где необходимо найти максимальный элемент в массиве. Рассмотрим общий алгоритм решения такой задачи.
Первое, что придётся сделать – создать массив. Как нам уже известно, нужно использовать цикл с параметром. Также удобнее будет создать массив случайным образом, если в условии задачи не оговорён способ задания массива.
Алгоритм нахождения максимального элемента массива выполняется следующим образом.
Сначала указываем, что первый элемент массива считается максимальным, иначе говоря – Max = A[i].
Потом начинаем процесс сравнивания последующих элементов массива с максимальным элементом в массиве.
Тут возможно два случая :
- Если максимальный элемент больше следующего, то ничего не меняем.
- Если максимальный элемент меньше следующего, то он становиться максимальным.
После этого выводим на экран максимальный элемент.
Блок-схема максимальный элемент массива
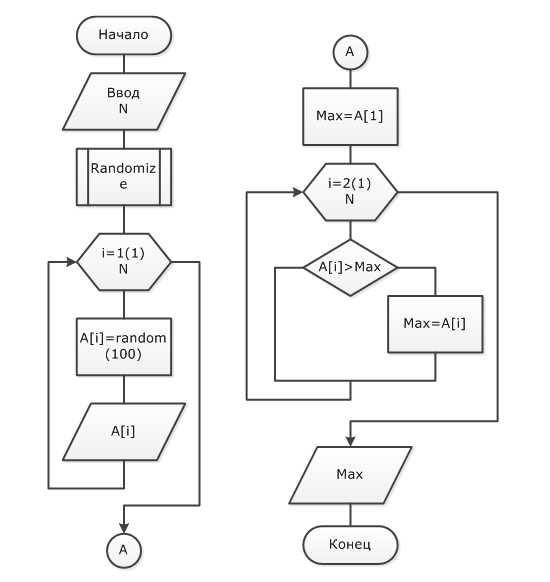
Программа максимальный элемент массива Pascal
Ниже представлен текст программы на языке Pascal, как найти максимальный элемент массива. Как было указанно в алгоритме выше, сначала создается сам массив (в моем случает любые целые числа от 0 до 100 включительно).
Program Max_element_massiva ;
Var i, n, max : integer ;
A : array [1..100] of integer;
Begin
Writeln('Введите количество элементов массива') ;
Readln(N) ;
Randomize;
For i := 1 to N do
begin
A[i] := Random(100);
Write(A[i]);
end;
Max := A[1];
For i := 2 to N do
if A[i]>Max then Max := A[i];
Writeln('Максимальный Элемент массива = ',Max) ;
Readln ;
End.
Какой алгоритм для поиска максимума в случайном массиве использовать? В статье собрано 5 эффективных must-have алгоритмов.
Если хочешь подтянуть свои знания, загляни на наш курс «Алгоритмы и структуры данных», на котором ты:
- углубишься в решение практических задач;
- узнаешь все про сложные алгоритмы, сортировки, сжатие данных и многое другое.
Ты также будешь на связи с преподавателем и другими студентами.
В итоге будешь браться за сложные проекты и повысишь чек за свою работу 🙂
Интересно, хочу попробовать
Самый быстрый и простейший алгоритм
Следует пояснить, что под “быстротой” алгоритма будет подразумеваться его асимптотическая сложность, а не физическое время выполнения.
В действительности, единственный способ точно найти самое большое число в случайном массиве будет перебор каждого числа в поисках максимума. Поэтому сложность такого алгоритма – O(N). Они называются линейными.
Простейшая реализация алгоритма на С:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int array[100];
int maximum, size, index = 0;
printf("Введите длину массива (не больше 100)n");
scanf("%d", &size);
printf("Введите %d целых чисел массиваn", size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
scanf("%d", &array[i]);
maximum = array[0]; // За изначальный максимум берем первый элемент массива
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++)
{
if (array[i] > maximum)
{
maximum = array[i];
index = i;
}
}
printf("Максимум находится в позиции %d и его значение %d.n", index, maximum);
return 0;
}
А как насчет распараллеливания?
После прочтения абзаца выше многие могут предложить поиск максимума с помощью параллельных вычислений, потому что он будет быстрее. И это так, если мы говорим о физическом времени. Но несмотря на то, сколько у вас есть процессов, вам всё равно придется просмотреть каждый элемент массива. Сложность алгоритма остается такой же, O(N).
Рассмотрим ситуацию на примере. Есть 200 карточек, на каждой из которых случайное число. Ваша задача найти карточку с самым большим числом. Допустим, друг согласился помочь, забрав половину карточек. Теперь каждый из вас ищет максимум из 100 карточек, вместо 200. Как только вы оба закончите, останется сравнить максимумы обеих половин. Время сократилось вдвое, но просмотреть пришлось все 200 карточек.
Сама по себе задача является так называемой чрезвычайно параллельной задачей, что ещё раз подтверждает возможность её решения именно распараллеливанием, без ущерба для конечного результата.
Задача о разборчивой невесте
Есть ещё один вариант нахождения максимума в случайном массиве.
Идем по первой половине всех значений в массиве. Запоминаем самое большое. Назовём его Х. Далее проходим по второй половине. Когда (и если) находим значение, которое больше Х, останавливаемся. Обозначим его Y. Какова вероятность того, что Y – максимум в массиве?
Чтобы это утверждение было истинным, Y должно находиться во второй половине массива. А так как значения в массиве случайны, шанс такого = 50%. Тогда если второй максимум присутствует в первой половине, это гарантирует, что найден правильный максимум.
Вероятность, что второй максимум в первой половине также = 50%. Посему вероятность, что и второй максимум в первой половине, и первый максимум во второй половине, равна 25%.
В итоге, такой алгоритм гарантирует точность 25% в нахождении максимума в массиве случайных чисел. Можно улучшить алгоритм, если искать второй максимум не в первой половине (1/2), а в 1/e (основание натурального логарифма) части массива. Этот способ впервые был предложен для решения задачи о разборчивой невесте или задачи секретаря (The Secretary Problem).
Аналоговый алгоритм
Спагетти-сортировка – прекрасный аналоговый алгоритм для решения задачи нахождения максимума в массиве.
Представим, что в массиве только N целых чисел. Возьмите N не приготовленных палочек спагетти, длина каждой сопоставляется с единственным значением в массиве.
Соберите спагетти в руку. Аккуратно, чтобы не сломать, поставьте горсть на ровную поверхность. В результате выше всех будет видна самая длинная (максимум) соломинка.
Асимптотическая сложность такого алгоритма – O(1). Но в цифровом мире он не применим.
Квантовый алгоритм
Алгоритм Гровера (или схема Гровера) используется в квантовых вычислениях для решения задач перебора. С его помощью сложность поиска максимума уменьшается до O(sqrt(N)) (большая О от корня N).
Данный способ решения может быть применен только на квантовом компьютере, что сильно умаляет его полезность в современном мире, но его нельзя не упомянуть.
Источник
Хотите дополнить? Ждём ваши предложения в комментариях 😉
 Задачи по нахождению минимального и/или максимального элемента в массиве очень часто встречаются в различных учебных пособиях по программированию и, как правило, вызывают трудности у начинающих программистов или просто студентов, получивших такое задание.
Задачи по нахождению минимального и/или максимального элемента в массиве очень часто встречаются в различных учебных пособиях по программированию и, как правило, вызывают трудности у начинающих программистов или просто студентов, получивших такое задание.
В данной статье вы узнаете, как написать реализацию программы на языке C++, которая находит максимальный и минимальный элемент в массиве и выводит на экран. А узнать множество решений других задач можно в разделе с решениями задач по программированию на языке C++.
Что такое максимальный и минимальный элемент массива
Для начала поймем, что же такое максимальный или минимальный элемент в массиве? Всё просто, максимальный элемент массива — это элемент, который имеет самое большое числовое значение, а минимальный элемент массива — это элемент, имеющий самое маленькое значение.
Пример: в массиве, состоящем из таких элементов: 3, 1, 0, -4, 16, 2 — максимальный элемент равен 16, т.к. это число больше других, а минимальный элемент равен -4, т.к. оно меньше остальных.
Поняв это, можно приступить к решению задачи.
Алгоритм решения задачи
— Инициализация массива, переменных, хранящих минимальное и максимальное значение.
— Заполнение массива случайными числами при помощи цикла и функции, возвращающей случайные числа.
— Вывод массива.
— Сравнение каждого элемента массива: Если элемент больше переменной с максимальным значением, то значение записывается в переменную; Если элемент меньше переменной с минимальным значением, то значение записывается в переменную.
— Вывод переменных с максимальным и минимальным элементом.
Алгоритм решения на языке C++
Для начала нужно подключить заголовок ввода/вывода <iostream>, заголовок стандартных функций <cstdlib> в ней имеется функция rand(), которая позволит заполнить массив случайными числами. Заполнение каждого элемента массива вручную требует времени, его можно сэкономить автоматизировав процесс. Подключаем пространство имён std. Создаём константу N, она будет определять количество элементов в массиве.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std; //Пространство имён std
const int N = 10;//Количество элементов в массиве
int main()
{
return 0;
}
В теле функции main() инициализируем массив целых чисел из N лементов, целочисленные переменные max и min, они будут хранить значение максимального и минимального элементов массива соответственно.
int mass[N], max, min;
Теперь заполним массив случайными числами. Для этого используем цикл от 0 до N (не включительно), который пройдется по каждому элементу массива и поместит случайное значение от 0 до 98. Это можно сделать, использовав функцию rand(), которая возвращает случайное число. Поделить возвращаемое значение на 99 и внести в ячейку остаток от деления, таким образом значение ячейки будет иметь значение в диапазоне от 0 до 99(не включая 99, т.к. остаток от деления не может быть кратным делителю). При этом выведем значения элементов массива на экран.
cout << "Элементы: |";
for(int r = 0; r<N; r++) // Цикл от 0 до N
{
mass[r] = rand()%99; // Заполнение случайным числом
cout << mass[r] << "|"; // Вывод значения
}
cout << endl;
В результате программа выведет на экран значения элементов массива, разделенное вертикальными чертами:
Элементы: |28|43|72|79|23|70|55|39|69|1|
Обратите внимание! Если вы программируете под Windows и у Вас не отображаются русские символы в консоли, то советую Вам почитать о решении этой проблемы в статье Русские символы(буквы) при вводе/выводе в консоль на C++.
Далее определим максимальный и минимальный элемент в массиве, для этого вновь пройдемся по массиву циклом. При помощи условия определим максимальный и минимальный элемент массива.
Перед циклом нужно будет занести первый элемент массива в переменные min и max, они будут хранить минимальное и максимальное значение изначально, а во время цикла поменяют его, если найдётся значение меньше для min или больше для max.
max = mass[0];//Помещаем значения 1-го элемента
min = mass[0];//массива в переменные
for(int r = 1; r<N; r++)
{
if(max < mass[r]) max = mass[r]; //если значение элемента больше значения переменной max, то записываем это значение в переменную
if(min > mass[r]) min = mass[r]; //аналогично и для min
}
После цикла выведем значения min и max.
cout << "Min: " << min << endl; cout << "Max: " << max << endl;
После компиляции и запуска прогамма выводит следующее
Элементы: |28|43|72|79|23|70|55|39|69|1| Min: 1 Max: 79
Пробегаемся по элементам массива глазами и видим, что минимальное значение — 1, а максимальное — 79. Переменные min и max имеют эти же значения соответственно, следовательно алгоритм работает.
Весь листинг программы на C++
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int main()
{
int mass[N], max, min;
cout << "Элементы: |";
for(int r = 0; r<N; r++)
{
mass[r] = rand()%99;
cout << mass[r] << "|";
}
cout << endl;
max = mass[0];
min = mass[0];
for(int r = 1; r<N; r++)
{
if(max < mass[r]) max = mass[r];
if(min > mass[r]) min = mass[r];
}
cout << "Min: " << min << endl;
cout << "Max: " << max << endl;
return 0;
}
How about augmenting the built-in Array object to use Math.max/Math.min instead:
Array.prototype.max = function() {
return Math.max.apply(null, this);
};
Array.prototype.min = function() {
return Math.min.apply(null, this);
};
let p = [35,2,65,7,8,9,12,121,33,99];
console.log(`Max value is: ${p.max()}` +
`nMin value is: ${p.min()}`);Here is a JSFiddle.
Augmenting the built-ins can cause collisions with other libraries (some see), so you may be more comfortable with just apply‘ing Math.xxx() to your array directly:
var min = Math.min.apply(null, arr),
max = Math.max.apply(null, arr);
Alternately, assuming your browser supports ECMAScript 6, you can use spread syntax which functions similarly to the apply method:
var min = Math.min( ...arr ),
max = Math.max( ...arr );
RobG
141k31 gold badges171 silver badges209 bronze badges
answered Nov 3, 2009 at 18:23
Roatin MarthRoatin Marth
23.4k3 gold badges51 silver badges55 bronze badges
15
Using spread operator (ES6)
Math.max(...array) // The same with "min" => Math.min(...array)
![]()
Gass
6,7622 gold badges34 silver badges38 bronze badges
answered Aug 23, 2016 at 16:37
![]()
Abdennour TOUMIAbdennour TOUMI
85.2k38 gold badges242 silver badges250 bronze badges
9
For big arrays (~10⁷ elements), Math.min and Math.max both produces the following error in Node.js.
RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded
A more robust solution is to not add every element to the call stack, but to instead pass an array:
function arrayMin(arr) {
return arr.reduce(function (p, v) {
return ( p < v ? p : v );
});
}
function arrayMax(arr) {
return arr.reduce(function (p, v) {
return ( p > v ? p : v );
});
}
If you are concerned about speed, the following code is ~3 times faster then Math.max.apply is on my computer. See https://jsben.ch/JPOyL.
function arrayMin(arr) {
var len = arr.length, min = Infinity;
while (len--) {
if (arr[len] < min) {
min = arr[len];
}
}
return min;
};
function arrayMax(arr) {
var len = arr.length, max = -Infinity;
while (len--) {
if (arr[len] > max) {
max = arr[len];
}
}
return max;
};
If your arrays contains strings instead of numbers, you also need to coerce them into numbers. The below code does that, but it slows the code down ~10 times on my machine. See https://jsben.ch/uPipD.
function arrayMin(arr) {
var len = arr.length, min = Infinity;
while (len--) {
if (Number(arr[len]) < min) {
min = Number(arr[len]);
}
}
return min;
};
function arrayMax(arr) {
var len = arr.length, max = -Infinity;
while (len--) {
if (Number(arr[len]) > max) {
max = Number(arr[len]);
}
}
return max;
};
![]()
answered Nov 18, 2012 at 14:00
Linus UnnebäckLinus Unnebäck
22.5k14 gold badges72 silver badges89 bronze badges
6
tl;dr
// For regular arrays:
var max = Math.max(...arrayOfNumbers);
// For arrays with tens of thousands of items:
let max = testArray[0];
for (let i = 1; i < testArrayLength; ++i) {
if (testArray[i] > max) {
max = testArray[i];
}
}
MDN solution
The official MDN docs on Math.max() already covers this issue:
The following function uses Function.prototype.apply() to find the maximum element in a numeric array.
getMaxOfArray([1, 2, 3])is equivalent toMath.max(1, 2, 3), but you can usegetMaxOfArray()on programmatically constructed arrays of any size.function getMaxOfArray(numArray) { return Math.max.apply(null, numArray); }Or with the new spread operator, getting the maximum of an array becomes a lot easier.
var arr = [1, 2, 3]; var max = Math.max(...arr);
Maximum size of an array
According to MDN the apply and spread solutions had a limitation of 65536 that came from the limit of the maximum number of arguments:
But beware: in using apply this way, you run the risk of exceeding the JavaScript engine’s argument length limit. The consequences of applying a function with too many arguments (think more than tens of thousands of arguments) vary across engines (JavaScriptCore has hard-coded argument limit of 65536), because the limit (indeed even the nature of any excessively-large-stack behavior) is unspecified. Some engines will throw an exception. More perniciously, others will arbitrarily limit the number of arguments actually passed to the applied function. To illustrate this latter case: if such an engine had a limit of four arguments (actual limits are of course significantly higher), it would be as if the arguments 5, 6, 2, 3 had been passed to apply in the examples above, rather than the full array.
They even provide a hybrid solution which doesn’t really have good performance compared to other solutions. See performance test below for more.
In 2019 the actual limit is the maximum size of the call stack. For modern Chromium based desktop browsers this means that when it comes to finding min/max with apply or spread, practically the maximum size for numbers only arrays is ~120000. Above this, there will be a stack overflow and the following error will be thrown:
RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded
With the script below (based on this blog post), by catching that error you can calculate the limit for your specific environment.
Warning! Running this script takes time and depending on the performance of your system it might slow or crash your browser/system!
let testArray = Array.from({length: 10000}, () => Math.floor(Math.random() * 2000000));
for (i = 10000; i < 1000000; ++i) {
testArray.push(Math.floor(Math.random() * 2000000));
try {
Math.max.apply(null, testArray);
} catch (e) {
console.log(i);
break;
}
}Performance on large arrays
Based on the test in EscapeNetscape’s comment I created some benchmarks that tests 5 different methods on a random number only array with 100000 items.
In 2019, the results show that the standard loop (which BTW doesn’t have the size limitation) is the fastest everywhere. apply and spread comes closely after it, then much later MDN’s hybrid solution then reduce as the slowest.
Almost all tests gave the same results, except for one where spread somewhy ended up being the slowest.
If you step up your array to have 1 million items, things start to break and you are left with the standard loop as a fast solution and reduce as a slower.
JSPerf benchmark

JSBen benchmark

JSBench.me benchmark

Benchmark source code
answered Jun 14, 2015 at 21:22
totymedlitotymedli
28.9k22 gold badges130 silver badges163 bronze badges
4
If you’re paranoid like me about using Math.max.apply (which could cause errors when given large arrays according to MDN), try this:
function arrayMax(array) {
return array.reduce(function(a, b) {
return Math.max(a, b);
});
}
function arrayMin(array) {
return array.reduce(function(a, b) {
return Math.min(a, b);
});
}
Or, in ES6:
function arrayMax(array) {
return array.reduce((a, b) => Math.max(a, b));
}
function arrayMin(array) {
return array.reduce((a, b) => Math.min(a, b));
}
The anonymous functions are unfortunately necessary (instead of using Math.max.bind(Math) because reduce doesn’t just pass a and b to its function, but also i and a reference to the array itself, so we have to ensure we don’t try to call max on those as well.
answered Jul 27, 2015 at 1:00
7
Alternative Methods
The Math.min and Math.max are great methods to get the minimum and maximum item out of a collection of items, however it’s important to be aware of some cavities that can comes with it.
Using them with an array that contains large number of items (more than ~10⁷ items, depends on the user’s browser) most likely will crash and give the following error message:
const arr = Array.from(Array(1000000).keys());
Math.min(arr);
Math.max(arr);
Uncaught RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded
UPDATE
Latest browsers might return NaN instead. That might be a better way to handle errors, however it doesn’t solve the problem just yet.
Instead, consider using something like so:
function maxValue(arr) {
return arr.reduce((max, val) => max > val ? max : val)
}
Or with better run-time:
function maxValue(arr) {
let max = arr[0];
for (let val of arr) {
if (val > max) {
max = val;
}
}
return max;
}
Or to get both Min and Max:
function getMinMax(arr) {
return arr.reduce(({min, max}, v) => ({
min: min < v ? min : v,
max: max > v ? max : v,
}), { min: arr[0], max: arr[0] });
}
Or with even better run-time*:
function getMinMax(arr) {
let min = arr[0];
let max = arr[0];
let i = arr.length;
while (i--) {
min = arr[i] < min ? arr[i] : min;
max = arr[i] > max ? arr[i] : max;
}
return { min, max };
}
* Tested with 1,000,000 items:
Just for a reference, the 1st function run-time (on my machine) was 15.84ms vs 2nd function with only 4.32ms.
answered Oct 2, 2018 at 17:34
Lior ElromLior Elrom
19.4k16 gold badges80 silver badges92 bronze badges
3
Two ways are shorter and easy:
let arr = [2, 6, 1, 0]
Way 1:
let max = Math.max.apply(null, arr)
Way 2:
let max = arr.reduce(function(a, b) {
return Math.max(a, b);
});
answered May 18, 2018 at 1:37
3
.apply is often used when the intention is to invoke a variadic function with a list of argument values, e.g.
The Math.max([value1[,value2, ...]]) function returns the largest of zero or more numbers.
Math.max(10, 20); // 20
Math.max(-10, -20); // -10
Math.max(-10, 20); // 20
The Math.max() method doesn’t allow you to pass in an array. If you have a list of values of which you need to get the largest, you would normally call this function using Function.prototype.apply(), e.g.
Math.max.apply(null, [10, 20]); // 20
Math.max.apply(null, [-10, -20]); // -10
Math.max.apply(null, [-10, 20]); // 20
However, as of the ECMAScript 6 you can use the spread operator:
The spread operator allows an expression to be expanded in places where multiple arguments (for function calls) or multiple elements (for array literals) are expected.
Using the spread operator, the above can be rewritten as such:
Math.max(...[10, 20]); // 20
Math.max(...[-10, -20]); // -10
Math.max(...[-10, 20]); // 20
When calling a function using the variadic operator, you can even add additional values, e.g.
Math.max(...[10, 20], 50); // 50
Math.max(...[-10, -20], 50); // 50
Bonus:
Spread operator enables you to use the array literal syntax to create new arrays in situations where in ES5 you would need to fall back to imperative code, using a combination of push, splice, etc.
let foo = ['b', 'c'];
let bar = ['a', ...foo, 'd', 'e']; // ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
answered Dec 18, 2014 at 1:38
GajusGajus
67.7k70 gold badges270 silver badges434 bronze badges
1
You do it by extending the Array type:
Array.max = function( array ){
return Math.max.apply( Math, array );
};
Array.min = function( array ){
return Math.min.apply( Math, array );
};
Boosted from here (by John Resig)
answered Nov 3, 2009 at 18:35
brettkellybrettkelly
27.6k8 gold badges56 silver badges71 bronze badges
A simple solution to find the minimum value over an Array of elements is to use the Array prototype function reduce:
A = [4,3,-9,-2,2,1];
A.reduce((min, val) => val < min ? val : min, A[0]); // returns -9
or using JavaScript’s built-in Math.Min() function (thanks @Tenflex):
A.reduce((min,val) => Math.min(min,val), A[0]);
This sets min to A[0], and then checks for A[1]...A[n] whether it is strictly less than the current min. If A[i] < min then min is updated to A[i]. When all array elements has been processed, min is returned as the result.
EDIT: Include position of minimum value:
A = [4,3,-9,-2,2,1];
A.reduce((min, val) => val < min._min ? {_min: val, _idx: min._curr, _curr: min._curr + 1} : {_min: min._min, _idx: min._idx, _curr: min._curr + 1}, {_min: A[0], _idx: 0, _curr: 0}); // returns { _min: -9, _idx: 2, _curr: 6 }
answered Oct 29, 2017 at 11:26
2
For a concise, modern solution, one can perform a reduce operation over the array, keeping track of the current minimum and maximum values, so the array is only iterated over once (which is optimal). Destructuring assignment is used here for succinctness.
let array = [100, 0, 50];
let [min, max] = array.reduce(([prevMin,prevMax], curr)=>
[Math.min(prevMin, curr), Math.max(prevMax, curr)], [Infinity, -Infinity]);
console.log("Min:", min);
console.log("Max:", max);To only find either the minimum or maximum, we can use perform a reduce operation in much the same way, but we only need to keep track of the previous optimal value. This method is better than using apply as it will not cause errors when the array is too large for the stack.
const arr = [-1, 9, 3, -6, 35];
//Only find minimum
const min = arr.reduce((a,b)=>Math.min(a,b), Infinity);
console.log("Min:", min);//-6
//Only find maximum
const max = arr.reduce((a,b)=>Math.max(a,b), -Infinity);
console.log("Max:", max);//35answered Aug 20, 2020 at 22:47
UnmitigatedUnmitigated
69.5k8 gold badges56 silver badges76 bronze badges
Others have already given some solutions in which they augment Array.prototype. All I want in this answer is to clarify whether it should be Math.min.apply( Math, array ) or Math.min.apply( null, array ). So what context should be used, Math or null?
When passing null as a context to apply, then the context will default to the global object (the window object in the case of browsers). Passing the Math object as the context would be the correct solution, but it won’t hurt passing null either. Here’s an example when null might cause trouble, when decorating the Math.max function:
// decorate Math.max
(function (oldMax) {
Math.max = function () {
this.foo(); // call Math.foo, or at least that's what we want
return oldMax.apply(this, arguments);
};
})(Math.max);
Math.foo = function () {
print("foo");
};
Array.prototype.max = function() {
return Math.max.apply(null, this); // <-- passing null as the context
};
var max = [1, 2, 3].max();
print(max);
The above will throw an exception because this.foo will be evaluated as window.foo, which is undefined. If we replace null with Math, things will work as expected and the string “foo” will be printed to the screen (I tested this using Mozilla Rhino).
You can pretty much assume that nobody has decorated Math.max so, passing null will work without problems.
answered Nov 3, 2009 at 18:39
Ionuț G. StanIonuț G. Stan
175k18 gold badges188 silver badges201 bronze badges
2
One more way to do it:
var arrayMax = Function.prototype.apply.bind(Math.max, null);
Usage:
var max = arrayMax([2, 5, 1]);
![]()
gion_13
41k10 gold badges95 silver badges107 bronze badges
answered Sep 26, 2012 at 18:43
sbrsbr
4,6955 gold badges42 silver badges48 bronze badges
2
I am surprised not one mentiond the reduce function.
var arr = [1, 10, 5, 11, 2]
var b = arr.reduce(function(previous,current){
return previous > current ? previous:current
});
b => 11
arr => [1, 10, 5, 11, 2]
2
This may suit your purposes.
Array.prototype.min = function(comparer) {
if (this.length === 0) return null;
if (this.length === 1) return this[0];
comparer = (comparer || Math.min);
var v = this[0];
for (var i = 1; i < this.length; i++) {
v = comparer(this[i], v);
}
return v;
}
Array.prototype.max = function(comparer) {
if (this.length === 0) return null;
if (this.length === 1) return this[0];
comparer = (comparer || Math.max);
var v = this[0];
for (var i = 1; i < this.length; i++) {
v = comparer(this[i], v);
}
return v;
}
answered Nov 3, 2009 at 18:21
ChaosPandionChaosPandion
77.2k18 gold badges118 silver badges156 bronze badges
5
let array = [267, 306, 108]
let longest = Math.max(…array);
answered Oct 3, 2020 at 15:10
![]()
Trilok SinghTrilok Singh
1,17712 silver badges9 bronze badges
1
I thought I’d share my simple and easy to understand solution.
For the min:
var arr = [3, 4, 12, 1, 0, 5];
var min = arr[0];
for (var k = 1; k < arr.length; k++) {
if (arr[k] < min) {
min = arr[k];
}
}
console.log("Min is: " + min);And for the max:
var arr = [3, 4, 12, 1, 0, 5];
var max = arr[0];
for (var k = 1; k < arr.length; k++) {
if (arr[k] > max) {
max = arr[k];
}
}
console.log("Max is: " + max);answered Oct 13, 2016 at 16:37
![]()
Ionut NeculaIonut Necula
11k4 gold badges45 silver badges69 bronze badges
9
For big arrays (~10⁷ elements), Math.min and Math.max procuces a RangeError (Maximum call stack size exceeded) in node.js.
For big arrays, a quick & dirty solution is:
Array.prototype.min = function() {
var r = this[0];
this.forEach(function(v,i,a){if (v<r) r=v;});
return r;
};
answered Jan 24, 2012 at 12:43
PeterPeter
5,0985 gold badges29 silver badges38 bronze badges
For an array containing objects instead of numbers:
arr = [
{ name: 'a', value: 5 },
{ name: 'b', value: 3 },
{ name: 'c', value: 4 }
]
You can use reduce to get the element with the smallest value (min)
arr.reduce((a, b) => a.value < b.value ? a : b)
// { name: 'b', value: 3 }
or the largest value (max)
arr.reduce((a, b) => a.value > b.value ? a : b)
// { name: 'a', value: 5 }
answered Aug 6, 2020 at 12:17
![]()
laktaklaktak
56.1k17 gold badges134 silver badges164 bronze badges
Aside using the math function max and min, another function to use is the built in function of sort(): here we go
const nums = [12, 67, 58, 30].sort((x, y) =>
x - y)
let min_val = nums[0]
let max_val = nums[nums.length -1]
![]()
answered Feb 14, 2020 at 15:29
![]()
1
I had the same problem, I needed to obtain the minimum and maximum values of an array and, to my surprise, there were no built-in functions for arrays. After reading a lot, I decided to test the “top 3” solutions myself:
- discrete solution: a FOR loop to check every element of the array against the current max and/or min value;
- APPLY solution: sending the array to the Math.max and/or Math.min internal functions using apply(null,array);
- REDUCE solution: recursing a check against every element of the array using reduce(function).
The test code was this:
function GetMaxDISCRETE(A)
{ var MaxX=A[0];
for (var X=0;X<A.length;X++)
if (MaxX<A[X])
MaxX=A[X];
return MaxX;
}
function GetMaxAPPLY(A)
{ return Math.max.apply(null,A);
}
function GetMaxREDUCE(A)
{ return A.reduce(function(p,c)
{ return p>c?p:c;
});
}
The array A was filled with 100,000 random integer numbers, each function was executed 10,000 times on Mozilla Firefox 28.0 on an intel Pentium 4 2.99GHz desktop with Windows Vista. The times are in seconds, retrieved by performance.now() function. The results were these, with 3 fractional digits and standard deviation:
- Discrete solution: mean=0.161s, sd=0.078
- APPLY solution: mean=3.571s, sd=0.487
- REDUCE solution: mean=0.350s, sd=0.044
The REDUCE solution was 117% slower than the discrete solution. The APPLY solution was the worse, 2,118% slower than the discrete solution. Besides, as Peter observed, it doesn’t work for large arrays (about more than 1,000,000 elements).
Also, to complete the tests, I tested this extended discrete code:
var MaxX=A[0],MinX=A[0];
for (var X=0;X<A.length;X++)
{ if (MaxX<A[X])
MaxX=A[X];
if (MinX>A[X])
MinX=A[X];
}
The timing: mean=0.218s, sd=0.094
So, it is 35% slower than the simple discrete solution, but it retrieves both the maximum and the minimum values at once (any other solution would take at least twice that to retrieve them). Once the OP needed both values, the discrete solution would be the best choice (even as two separate functions, one for calculating maximum and another for calculating minimum, they would outperform the second best, the REDUCE solution).
answered Apr 2, 2014 at 17:46
CyberknightCyberknight
1562 silver badges6 bronze badges
Iterate through, keeping track as you go.
var min = null;
var max = null;
for (var i = 0, len = arr.length; i < len; ++i)
{
var elem = arr[i];
if (min === null || min > elem) min = elem;
if (max === null || max < elem) max = elem;
}
alert( "min = " + min + ", max = " + max );
This will leave min/max null if there are no elements in the array. Will set min and max in one pass if the array has any elements.
You could also extend Array with a range method using the above to allow reuse and improve on readability. See a working fiddle at http://jsfiddle.net/9C9fU/
Array.prototype.range = function() {
var min = null,
max = null,
i, len;
for (i = 0, len = this.length; i < len; ++i)
{
var elem = this[i];
if (min === null || min > elem) min = elem;
if (max === null || max < elem) max = elem;
}
return { min: min, max: max }
};
Used as
var arr = [3, 9, 22, -7, 44, 18, 7, 9, 15];
var range = arr.range();
console.log(range.min);
console.log(range.max);
answered Nov 3, 2009 at 18:23
tvanfossontvanfosson
522k99 gold badges697 silver badges794 bronze badges
1
You can use the following function anywhere in your project:
function getMin(array){
return Math.min.apply(Math,array);
}
function getMax(array){
return Math.max.apply(Math,array);
}
And then you can call the functions passing the array:
var myArray = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7];
var maximo = getMax(myArray); //return the highest number
![]()
falsarella
12.2k9 gold badges69 silver badges115 bronze badges
answered Aug 26, 2014 at 16:57
![]()
The following code works for me :
var valueList = [10,4,17,9,3];
var maxValue = valueList.reduce(function(a, b) { return Math.max(a, b); });
var minValue = valueList.reduce(function(a, b) { return Math.min(a, b); });
Gogol
3,0334 gold badges28 silver badges57 bronze badges
answered May 26, 2017 at 12:40
![]()
0
array.sort((a, b) => b - a)[0];
Gives you the maximum value in an array of numbers.
array.sort((a, b) => a - b)[0];
Gives you the minimum value in an array of numbers.
let array = [0,20,45,85,41,5,7,85,90,111];
let maximum = array.sort((a, b) => b - a)[0];
let minimum = array.sort((a, b) => a - b)[0];
console.log(minimum, maximum)answered Jun 20, 2020 at 20:33
Adam BelekoAdam Beleko
6287 silver badges14 bronze badges
let arr=[20,8,29,76,7,21,9]
Math.max.apply( Math, arr ); // 76
answered Oct 28, 2020 at 21:53
![]()
Simple stuff, really.
var arr = [10,20,30,40];
arr.max = function() { return Math.max.apply(Math, this); }; //attach max funct
arr.min = function() { return Math.min.apply(Math, this); }; //attach min funct
alert("min: " + arr.min() + " max: " + arr.max());
![]()
falsarella
12.2k9 gold badges69 silver badges115 bronze badges
answered Sep 23, 2014 at 7:48
![]()
BrianBrian
3,6431 gold badge22 silver badges33 bronze badges
Here’s one way to get the max value from an array of objects. Create a copy (with slice), then sort the copy in descending order and grab the first item.
var myArray = [
{"ID": 1, "Cost": 200},
{"ID": 2, "Cost": 1000},
{"ID": 3, "Cost": 50},
{"ID": 4, "Cost": 500}
]
maxsort = myArray.slice(0).sort(function(a, b) { return b.ID - a.ID })[0].ID;
![]()
falsarella
12.2k9 gold badges69 silver badges115 bronze badges
answered Jan 9, 2014 at 18:46
BenBen
5849 silver badges8 bronze badges
