
Содержание
- Прямоугольные треугольники
- Закон синусов
- Закон косинусов
- Практика для мастерства
В математике изучение треугольников называется тригонометрией. Любые неизвестные значения углов и сторон могут быть обнаружены с использованием общих тригонометрических тождеств Синуса, Косинуса и Тангенса. Эти тождества представляют собой простые вычисления, используемые для преобразования соотношений сторон в градусы угла. Неизвестные углы называются угол тета и могут быть рассчитаны различными способами на основе известных сторон и углов.
Прямоугольные треугольники
Когда треугольник содержит угол 90 градусов, он известен как прямоугольный треугольники угол тета может быть определен с помощью аббревиатуры SOHCAHTOA.
Если разбить, это означает, что синус (S) равен длине бокового противоположного угла тета (O), деленной на длину гипотенузы (H), так что Sin (X) = Opp / Hyp. Точно так же косинус (C) равен длине соседней стороны (A), деленной на гипотенузу. (H) Cos (X) = Adj / Hyp. Касательная (T) равна противоположной (O), деленной на соседнюю (A). Tan (X) = Opp / Adj.
Чтобы решить эти отношения с помощью графического калькулятора, вы используете функции обратного триггера – известные как агсзш, агссоз а также агс – и представлены на калькуляторе как SIN ^ -1, COS ^ -1 и TAN ^ -1.
Если известна длина противоположной стороны, а также гипотенуза, соответствующая SOH в аббревиатуре, используйте функцию arcsin на калькуляторе, а затем введите две длины в дробной форме.
Например: если сторона противоположного угла тета имеет длину 4, а гипотенуза имеет длину 5, введите соотношение в калькулятор следующим образом:
SIN ^ -1 (4/5)
Это должно вывести значение примерно 53,13 градуса. Если нет, убедитесь, что калькулятор установлен в режим DEGREE, и повторите попытку.
Закон синусов
Если в треугольнике нет углов в 90 градусов, SOHCAHTOA не имеет смысла в определении углов. Однако, если угол и длина его противоположной стороны известны, Закон синусов может использоваться совместно с другой известной длиной стороны, чтобы найти недостающие углы. Закон гласит, что грех A / a = грех B / b = грех C / c.
Сломанный, это означает, что синус угла, разделенного на длину его противоположной стороны, прямо пропорционален синусу другого угла, разделенного на длину его противоположной стороны. Чтобы решить эту проблему, выделите синус неизвестного угла, умножив обе части уравнения на длину угла противоположной стороны.
Например: sin A / a = sin B / b становится (b * sin A) / a = sin B
В калькуляторе с заданной стороной a = 5, стороной b = 7 и углом A = 45 градусов это видно как SIN ^ -1 ((7 * SIN (45)) / 5). Это дает углу B значение приблизительно 81,87 градусов.
Закон косинусов
Закон косинусов работает на всех треугольниках, но в основном используется в тех случаях, когда известны длины всех сторон, но ни один из углов не известен. Формула похожа на Теорема Пифагора (a ^ 2 + b ^ 2 = c ^ 2) и состояния c ^ 2 = a ^ 2 + b ^ 2 – 2ab * cos (C). Но в целях нахождения тэты его легче прочитать как cos (C) = (a ^ 2 + b ^ 2 – c ^ 2) / 2ab.
Например, если у треугольника есть три стороны, измеряющие 5, 7 и 10, введите эти значения в графический калькулятор как cos ^ -1 ((5 ^ 2 + 7 ^ 2 – 10 ^ 2) / (2_5_7)). Этот расчет выводит значение примерно 111.80 градусов.
Практика для мастерства
Важно помнить, что все треугольники состоят из трех углов, общая сумма которых составляет 180 градусов. Практикуйте различные техники на разных треугольниках, пока процесс не станет знакомым. Иногда обнаружение тэты – это то же самое, что открывать новый способ решения проблемы.
Трапецеидальный синус
Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 20 июня 2019 года; проверки требует 1 правка.
Трапецеидальный синус — кусочно-гладкая функция действительной переменной с периодом 
![{displaystyle [0;2pi ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e830667d3083d42b27b4c32fc01820a0e3cf0c10)
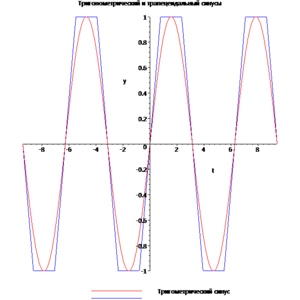
Трапецеидальный и тригонометрический синусы





Разложение в ряд ФурьеПравить
Как и любая кусочно-гладкая периодическая функция действительного аргумента, трапецеидальный синус может быть разложен в ряд Фурье. Из-за нечётности трапецеидального синуса его разложение в тригонометрический ряд Фурье не содержит членов с косинусом.
Кроме того, трапецеидальный синус не содержит в своём разложении чётных гармоник. Первые несколько коэффициентов разложения имеют вид:
Сходимость разложения трапецеидального синуса в ряд Фурье иллюстрируется графиком:
ПрименениеПравить
Трапецеидальный синус широко применяется в электротехнике, поскольку переменный ток такой формы достаточно просто получить из постоянного тока при большой мощности нагрузки[уточнить]. В частности, в современных ИБП и инверторах выходное напряжение чаще всего имеет форму трапецеидального синуса.[1] Также трапецеидальный синус применяется для анализа некоторых задач теории колебаний, где использование обычного (тригонометрического) синуса приводит к сильному усложнению конечных результатов.
[2]
СсылкиПравить
- ↑ http://www.web-logic.ru/eli-ms.htm Архивная копия от 13 ноября 2009 на Wayback Machine Трансформаторы — виды и различия
- ↑ Рабинович М. И., Трубецков Д. И. Введение в теорию колебаний и волн. — М.: Наука, 1984 г.

In mathematics, the trigonometric functions (also called circular functions, angle functions or goniometric functions[1][2]) are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. They are widely used in all sciences that are related to geometry, such as navigation, solid mechanics, celestial mechanics, geodesy, and many others. They are among the simplest periodic functions, and as such are also widely used for studying periodic phenomena through Fourier analysis.
The trigonometric functions most widely used in modern mathematics are the sine, the cosine, and the tangent. Their reciprocals are respectively the cosecant, the secant, and the cotangent, which are less used. Each of these six trigonometric functions has a corresponding inverse function, and an analog among the hyperbolic functions.
The oldest definitions of trigonometric functions, related to right-angle triangles, define them only for acute angles. To extend the sine and cosine functions to functions whose domain is the whole real line, geometrical definitions using the standard unit circle (i.e., a circle with radius 1 unit) are often used; then the domain of the other functions is the real line with some isolated points removed. Modern definitions express trigonometric functions as infinite series or as solutions of differential equations. This allows extending the domain of sine and cosine functions to the whole complex plane, and the domain of the other trigonometric functions to the complex plane with some isolated points removed.
Notation[edit]
Conventionally, an abbreviation of each trigonometric function’s name is used as its symbol in formulas. Today, the most common versions of these abbreviations are “sin” for sine, “cos” for cosine, “tan” or “tg” for tangent, “sec” for secant, “csc” or “cosec” for cosecant, and “cot” or “ctg” for cotangent. Historically, these abbreviations were first used in prose sentences to indicate particular line segments or their lengths related to an arc of an arbitrary circle, and later to indicate ratios of lengths, but as the function concept developed in the 17th–18th century, they began to be considered as functions of real-number-valued angle measures, and written with functional notation, for example sin(x). Parentheses are still often omitted to reduce clutter, but are sometimes necessary; for example the expression 


A positive integer appearing as a superscript after the symbol of the function denotes exponentiation, not function composition. For example 




However, the exponent 







Right-angled triangle definitions[edit]

In this right triangle, denoting the measure of angle BAC as A: sin A = a/c; cos A = b/c; tan A = a/b.

Plot of the six trigonometric functions, the unit circle, and a line for the angle θ = 0.7 radians. The points labelled 1, Sec(θ), Csc(θ) represent the length of the line segment from the origin to that point. Sin(θ), Tan(θ), and 1 are the heights to the line starting from the x-axis, while Cos(θ), 1, and Cot(θ) are lengths along the x-axis starting from the origin.
If the acute angle θ is given, then any right triangles that have an angle of θ are similar to each other. This means that the ratio of any two side lengths depends only on θ. Thus these six ratios define six functions of θ, which are the trigonometric functions. In the following definitions, the hypotenuse is the length of the side opposite the right angle, opposite represents the side opposite the given angle θ, and adjacent represents the side between the angle θ and the right angle.[3][4]
In a right-angled triangle, the sum of the two acute angles is a right angle, that is, 90° or π/2 radians. Therefore 

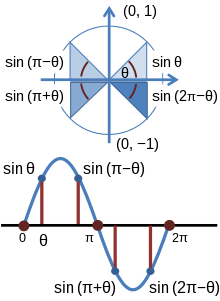
Top: Trigonometric function sin θ for selected angles θ, π − θ, π + θ, and 2π − θ in the four quadrants.
Bottom: Graph of sine function versus angle. Angles from the top panel are identified.
| Function | Description | Relationship | |
|---|---|---|---|
| using radians | using degrees | ||
| sine | opposite/hypotenuse | 
|

|
| cosine | adjacent/hypotenuse | 
|

|
| tangent | opposite/adjacent | 
|

|
| cotangent | adjacent/opposite | 
|

|
| secant | hypotenuse/adjacent | 
|

|
| cosecant | hypotenuse/opposite | 
|

|
Radians versus degrees[edit]
In geometric applications, the argument of a trigonometric function is generally the measure of an angle. For this purpose, any angular unit is convenient. One common unit is degrees, in which a right angle is 90° and a complete turn is 360° (particularly in elementary mathematics).
However, in calculus and mathematical analysis, the trigonometric functions are generally regarded more abstractly as functions of real or complex numbers, rather than angles. In fact, the functions sin and cos can be defined for all complex numbers in terms of the exponential function, via power series,[6] or as solutions to differential equations given particular initial values[7] (see below), without reference to any geometric notions. The other four trigonometric functions (tan, cot, sec, csc) can be defined as quotients and reciprocals of sin and cos, except where zero occurs in the denominator. It can be proved, for real arguments, that these definitions coincide with elementary geometric definitions if the argument is regarded as an angle given in radians.[6] Moreover, these definitions result in simple expressions for the derivatives and indefinite integrals for the trigonometric functions.[8] Thus, in settings beyond elementary geometry, radians are regarded as the mathematically natural unit for describing angle measures.
When radians (rad) are employed, the angle is given as the length of the arc of the unit circle subtended by it: the angle that subtends an arc of length 1 on the unit circle is 1 rad (≈ 57.3°), and a complete turn (360°) is an angle of 2π (≈ 6.28) rad. For real number x, the notations sin x, cos x, etc. refer to the value of the trigonometric functions evaluated at an angle of x rad. If units of degrees are intended, the degree sign must be explicitly shown (e.g., sin x°, cos x°, etc.). Using this standard notation, the argument x for the trigonometric functions satisfies the relationship x = (180x/π)°, so that, for example, sin π = sin 180° when we take x = π. In this way, the degree symbol can be regarded as a mathematical constant such that 1° = π/180 ≈ 0.0175.
Unit-circle definitions[edit]

In this illustration, the six trigonometric functions of an arbitrary angle θ are represented as Cartesian coordinates of points related to the unit circle. The ordinates of A, B and D are sin θ, tan θ and csc θ, respectively, while the abscissas of A, C and E are cos θ, cot θ and sec θ, respectively.

Signs of trigonometric functions in each quadrant. The mnemonic “all science teachers (are) crazy” lists the functions which are positive from quadrants I to IV.[9] This is a variation on the mnemonic “All Students Take Calculus”.
The six trigonometric functions can be defined as coordinate values of points on the Euclidean plane that are related to the unit circle, which is the circle of radius one centered at the origin O of this coordinate system. While right-angled triangle definitions allow for the definition of the trigonometric functions for angles between 0 and 
Let 











The trigonometric functions cos and sin are defined, respectively, as the x– and y-coordinate values of point A. That is,
and
[10]
In the range 


The other trigonometric functions can be found along the unit circle as
and
and
By applying the Pythagorean identity and geometric proof methods, these definitions can readily be shown to coincide with the definitions of tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant in terms of sine and cosine, that is

Trigonometric functions: Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosecant (dotted), Secant (dotted), Cotangent (dotted) – animation
Since a rotation of an angle of 


and
hold for any angle θ and any integer k. The same is true for the four other trigonometric functions. By observing the sign and the monotonicity of the functions sine, cosine, cosecant, and secant in the four quadrants, one can show that 



and
hold for any angle θ and any integer k.
Algebraic values[edit]

The unit circle, with some points labeled with their cosine and sine (in this order), and the corresponding angles in radians and degrees.
The algebraic expressions for the most important angles are as follows:
(zero angle)
(right angle)
Writing the numerators as square roots of consecutive non-negative integers, with a denominator of 2, provides an easy way to remember the values.[11]
Such simple expressions generally do not exist for other angles which are rational multiples of a right angle.
- For an angle which, measured in degrees, is a multiple of three, the exact trigonometric values of the sine and the cosine may be expressed in terms of square roots. These values of the sine and the cosine may thus be constructed by ruler and compass.
- For an angle of an integer number of degrees, the sine and the cosine may be expressed in terms of square roots and the cube root of a non-real complex number. Galois theory allows a proof that, if the angle is not a multiple of 3°, non-real cube roots are unavoidable.
- For an angle which, expressed in degrees, is a rational number, the sine and the cosine are algebraic numbers, which may be expressed in terms of nth roots. This results from the fact that the Galois groups of the cyclotomic polynomials are cyclic.
- For an angle which, expressed in degrees, is not a rational number, then either the angle or both the sine and the cosine are transcendental numbers. This is a corollary of Baker’s theorem, proved in 1966.
Simple algebraic values[edit]
The following table lists the sines, cosines, and tangents of multiples of 15 degrees from 0 to 90 degrees.
| Angle, θ, in | 
|

|

|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| radians | degrees | |||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
Undefined |
In calculus[edit]

Graphs of sine, cosine and tangent

The sine function (blue) is closely approximated by its Taylor polynomial of degree 7 (pink) for a full cycle centered on the origin.

Animation for the approximation of cosine via Taylor polynomials.


The modern trend in mathematics is to build geometry from calculus rather than the converse.[citation needed] Therefore, except at a very elementary level, trigonometric functions are defined using the methods of calculus.
Trigonometric functions are differentiable and analytic at every point where they are defined; that is, everywhere for the sine and the cosine, and, for the tangent, everywhere except at π/2 + kπ for every integer k.
The trigonometric function are periodic functions, and their primitive period is 2π for the sine and the cosine, and π for the tangent, which is increasing in each open interval (π/2 + kπ, π/2 + (k + 1)π). At each end point of these intervals, the tangent function has a vertical asymptote.
In calculus, there are two equivalent definitions of trigonometric functions, either using power series or differential equations. These definitions are equivalent, as starting from one of them, it is easy to retrieve the other as a property. However the definition through differential equations is somehow more natural, since, for example, the choice of the coefficients of the power series may appear as quite arbitrary, and the Pythagorean identity is much easier to deduce from the differential equations.
Definition by differential equations[edit]
Sine and cosine can be defined as the unique solution to the initial value problem:
Differentiating again, 

Applying the quotient rule to the tangent 
Power series expansion[edit]
Applying the differential equations to power series with indeterminate coefficients, one may deduce recurrence relations for the coefficients of the Taylor series of the sine and cosine functions. These recurrence relations are easy to solve, and give the series expansions[12]
The radius of convergence of these series is infinite. Therefore, the sine and the cosine can be extended to entire functions (also called “sine” and “cosine”), which are (by definition) complex-valued functions that are defined and holomorphic on the whole complex plane.
Being defined as fractions of entire functions, the other trigonometric functions may be extended to meromorphic functions, that is functions that are holomorphic in the whole complex plane, except some isolated points called poles. Here, the poles are the numbers of the form 

Recurrences relations may also be computed for the coefficients of the Taylor series of the other trigonometric functions. These series have a finite radius of convergence. Their coefficients have a combinatorial interpretation: they enumerate alternating permutations of finite sets.[13]
More precisely, defining
- Un, the nth up/down number,
- Bn, the nth Bernoulli number, and
- En, is the nth Euler number,
one has the following series expansions:[14]
Continued fraction expansion[edit]
The following expansions are valid in the whole complex plane:
The last one was used in the historically first proof that π is irrational.[15]
Partial fraction expansion[edit]
There is a series representation as partial fraction expansion where just translated reciprocal functions are summed up, such that the poles of the cotangent function and the reciprocal functions match:[16]
This identity can be proved with the Herglotz trick.[17]
Combining the (–n)th with the nth term lead to absolutely convergent series:
Similarly, one can find a partial fraction expansion for the secant, cosecant and tangent functions:
Infinite product expansion[edit]
The following infinite product for the sine is of great importance in complex analysis:
For the proof of this expansion, see Sine. From this, it can be deduced that
Relationship to exponential function (Euler’s formula)[edit]




Euler’s formula relates sine and cosine to the exponential function:
This formula is commonly considered for real values of x, but it remains true for all complex values.
Proof: Let 





One has
Solving this linear system in sine and cosine, one can express them in terms of the exponential function:
When x is real, this may be rewritten as
Most trigonometric identities can be proved by expressing trigonometric functions in terms of the complex exponential function by using above formulas, and then using the identity 
Definitions using functional equations[edit]
One can also define the trigonometric functions using various functional equations.
For example,[18] the sine and the cosine form the unique pair of continuous functions that satisfy the difference formula
and the added condition
In the complex plane[edit]
The sine and cosine of a complex number 
By taking advantage of domain coloring, it is possible to graph the trigonometric functions as complex-valued functions. Various features unique to the complex functions can be seen from the graph; for example, the sine and cosine functions can be seen to be unbounded as the imaginary part of 
|
|
|
|
Basic identities[edit]
Many identities interrelate the trigonometric functions. This section contains the most basic ones; for more identities, see List of trigonometric identities. These identities may be proved geometrically from the unit-circle definitions or the right-angled-triangle definitions (although, for the latter definitions, care must be taken for angles that are not in the interval [0, π/2], see Proofs of trigonometric identities). For non-geometrical proofs using only tools of calculus, one may use directly the differential equations, in a way that is similar to that of the above proof of Euler’s identity. One can also use Euler’s identity for expressing all trigonometric functions in terms of complex exponentials and using properties of the exponential function.
Parity[edit]
The cosine and the secant are even functions; the other trigonometric functions are odd functions. That is:
Periods[edit]
All trigonometric functions are periodic functions of period 2π. This is the smallest period, except for the tangent and the cotangent, which have π as smallest period. This means that, for every integer k, one has
Pythagorean identity[edit]
The Pythagorean identity, is the expression of the Pythagorean theorem in terms of trigonometric functions. It is
.
Dividing through by either 

and
.
Sum and difference formulas[edit]
The sum and difference formulas allow expanding the sine, the cosine, and the tangent of a sum or a difference of two angles in terms of sines and cosines and tangents of the angles themselves. These can be derived geometrically, using arguments that date to Ptolemy. One can also produce them algebraically using Euler’s formula.
- Sum
- Difference
When the two angles are equal, the sum formulas reduce to simpler equations known as the double-angle formulae.
These identities can be used to derive the product-to-sum identities.
By setting 


Together with
this is the tangent half-angle substitution, which reduces the computation of integrals and antiderivatives of trigonometric functions to that of rational fractions.
Derivatives and antiderivatives[edit]
The derivatives of trigonometric functions result from those of sine and cosine by applying quotient rule. The values given for the antiderivatives in the following table can be verified by differentiating them. The number C is a constant of integration.
 |
 |

|
|---|---|---|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
 |
 |

|
Note: For 






Alternatively, the derivatives of the ‘co-functions’ can be obtained using trigonometric identities and the chain rule:
Inverse functions[edit]
The trigonometric functions are periodic, and hence not injective, so strictly speaking, they do not have an inverse function. However, on each interval on which a trigonometric function is monotonic, one can define an inverse function, and this defines inverse trigonometric functions as multivalued functions. To define a true inverse function, one must restrict the domain to an interval where the function is monotonic, and is thus bijective from this interval to its image by the function. The common choice for this interval, called the set of principal values, is given in the following table. As usual, the inverse trigonometric functions are denoted with the prefix “arc” before the name or its abbreviation of the function.
| Function | Definition | Domain | Set of principal values |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |

|
 |
 |
 |

|
 |
 |
 |

|
 |
 |
 |

|
 |
 |
 |

|
 |
 |
 |

|
The notations sin−1, cos−1, etc. are often used for arcsin and arccos, etc. When this notation is used, inverse functions could be confused with multiplicative inverses. The notation with the “arc” prefix avoids such a confusion, though “arcsec” for arcsecant can be confused with “arcsecond”.
Just like the sine and cosine, the inverse trigonometric functions can also be expressed in terms of infinite series. They can also be expressed in terms of complex logarithms.
Applications[edit]
Angles and sides of a triangle[edit]
In this section A, B, C denote the three (interior) angles of a triangle, and a, b, c denote the lengths of the respective opposite edges. They are related by various formulas, which are named by the trigonometric functions they involve.
Law of sines[edit]
The law of sines states that for an arbitrary triangle with sides a, b, and c and angles opposite those sides A, B and C:
where Δ is the area of the triangle,
or, equivalently,
where R is the triangle’s circumradius.
It can be proved by dividing the triangle into two right ones and using the above definition of sine. The law of sines is useful for computing the lengths of the unknown sides in a triangle if two angles and one side are known. This is a common situation occurring in triangulation, a technique to determine unknown distances by measuring two angles and an accessible enclosed distance.
Law of cosines[edit]
The law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula or cosine rule) is an extension of the Pythagorean theorem:
or equivalently,
In this formula the angle at C is opposite to the side c. This theorem can be proved by dividing the triangle into two right ones and using the Pythagorean theorem.
The law of cosines can be used to determine a side of a triangle if two sides and the angle between them are known. It can also be used to find the cosines of an angle (and consequently the angles themselves) if the lengths of all the sides are known.
Law of tangents[edit]
The law of tangents says that:
.
Law of cotangents[edit]
If s is the triangle’s semiperimeter, (a + b + c)/2, and r is the radius of the triangle’s incircle, then rs is the triangle’s area. Therefore Heron’s formula implies that:
.
The law of cotangents says that:[19]
It follows that
Periodic functions[edit]



Sinusoidal basis functions (bottom) can form a sawtooth wave (top) when added. All the basis functions have nodes at the nodes of the sawtooth, and all but the fundamental (k = 1) have additional nodes. The oscillation seen about the sawtooth when k is large is called the Gibbs phenomenon
The trigonometric functions are also important in physics. The sine and the cosine functions, for example, are used to describe simple harmonic motion, which models many natural phenomena, such as the movement of a mass attached to a spring and, for small angles, the pendular motion of a mass hanging by a string. The sine and cosine functions are one-dimensional projections of uniform circular motion.
Trigonometric functions also prove to be useful in the study of general periodic functions. The characteristic wave patterns of periodic functions are useful for modeling recurring phenomena such as sound or light waves.[20]
Under rather general conditions, a periodic function f (x) can be expressed as a sum of sine waves or cosine waves in a Fourier series.[21] Denoting the sine or cosine basis functions by φk, the expansion of the periodic function f (t) takes the form:
For example, the square wave can be written as the Fourier series
In the animation of a square wave at top right it can be seen that just a few terms already produce a fairly good approximation. The superposition of several terms in the expansion of a sawtooth wave are shown underneath.
History[edit]
While the early study of trigonometry can be traced to antiquity, the trigonometric functions as they are in use today were developed in the medieval period. The chord function was discovered by Hipparchus of Nicaea (180–125 BCE) and Ptolemy of Roman Egypt (90–165 CE). The functions of sine and versine (1 – cosine) can be traced back to the jyā and koti-jyā functions used in Gupta period Indian astronomy (Aryabhatiya, Surya Siddhanta), via translation from Sanskrit to Arabic and then from Arabic to Latin.[22] (See Aryabhata’s sine table.)
All six trigonometric functions in current use were known in Islamic mathematics by the 9th century, as was the law of sines, used in solving triangles.[23] With the exception of the sine (which was adopted from Indian mathematics), the other five modern trigonometric functions were discovered by Persian and Arab mathematicians, including the cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant.[23] Al-Khwārizmī (c. 780–850) produced tables of sines, cosines and tangents. Circa 830, Habash al-Hasib al-Marwazi discovered the cotangent, and produced tables of tangents and cotangents.[24][25] Muhammad ibn Jābir al-Harrānī al-Battānī (853–929) discovered the reciprocal functions of secant and cosecant, and produced the first table of cosecants for each degree from 1° to 90°.[25] The trigonometric functions were later studied by mathematicians including Omar Khayyám, Bhāskara II, Nasir al-Din al-Tusi, Jamshīd al-Kāshī (14th century), Ulugh Beg (14th century), Regiomontanus (1464), Rheticus, and Rheticus’ student Valentinus Otho.
Madhava of Sangamagrama (c. 1400) made early strides in the analysis of trigonometric functions in terms of infinite series.[26] (See Madhava series and Madhava’s sine table.)
The tangent function was brought to Europe by Giovanni Bianchini in 1467 in trigonometry tables he created to support the calculation of stellar coordinates.[27]
The terms tangent and secant were first introduced by the Danish mathematician Thomas Fincke in his book Geometria rotundi (1583).[28]
The 17th century French mathematician Albert Girard made the first published use of the abbreviations sin, cos, and tan in his book Trigonométrie.[29]
In a paper published in 1682, Gottfried Leibniz proved that sin x is not an algebraic function of x.[30] Though introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and thus appearing to be rational functions, Leibnitz result established that they are actually transcendental functions of their argument. The task of assimilating circular functions into algebraic expressions was accomplished by Euler in his Introduction to the Analysis of the Infinite (1748). His method was to show that the sine and cosine functions are alternating series formed from the even and odd terms respectively of the exponential series. He presented “Euler’s formula”, as well as near-modern abbreviations (sin., cos., tang., cot., sec., and cosec.).[22]
A few functions were common historically, but are now seldom used, such as the chord, the versine (which appeared in the earliest tables[22]), the coversine, the haversine,[31] the exsecant and the excosecant. The list of trigonometric identities shows more relations between these functions.
- crd(θ) = 2 sin(θ/2)
- versin(θ) = 1 − cos(θ) = 2 sin2(θ/2)
- coversin(θ) = 1 − sin(θ) = versin(π/2 − θ)
- haversin(θ) = 1/2versin(θ) = sin2(θ/2)
- exsec(θ) = sec(θ) − 1
- excsc(θ) = exsec(π/2 − θ) = csc(θ) − 1
Etymology[edit]
The word sine derives[32] from Latin sinus, meaning “bend; bay”, and more specifically “the hanging fold of the upper part of a toga”, “the bosom of a garment”, which was chosen as the translation of what was interpreted as the Arabic word jaib, meaning “pocket” or “fold” in the twelfth-century translations of works by Al-Battani and al-Khwārizmī into Medieval Latin.[33]
The choice was based on a misreading of the Arabic written form j-y-b (جيب), which itself originated as a transliteration from Sanskrit jīvā, which along with its synonym jyā (the standard Sanskrit term for the sine) translates to “bowstring”, being in turn adopted from Ancient Greek χορδή “string”.[34]
The word tangent comes from Latin tangens meaning “touching”, since the line touches the circle of unit radius, whereas secant stems from Latin secans—”cutting”—since the line cuts the circle.[35]
The prefix “co-” (in “cosine”, “cotangent”, “cosecant”) is found in Edmund Gunter’s Canon triangulorum (1620), which defines the cosinus as an abbreviation for the sinus complementi (sine of the complementary angle) and proceeds to define the cotangens similarly.[36][37]
See also[edit]
- All Students Take Calculus – a mnemonic for recalling the signs of trigonometric functions in a particular quadrant of a Cartesian plane
- Bhaskara I’s sine approximation formula
- Small-angle approximation
- Differentiation of trigonometric functions
- Generalized trigonometry
- Generating trigonometric tables
- Hyperbolic function
- List of integrals of trigonometric functions
- List of periodic functions
- List of trigonometric identities
- Polar sine – a generalization to vertex angles
- Proofs of trigonometric identities
- Versine – for several less used trigonometric functions
Notes[edit]
- ^ Klein, Christian Felix (1924) [1902]. Elementarmathematik vom höheren Standpunkt aus: Arithmetik, Algebra, Analysis (in German). Vol. 1 (3rd ed.). Berlin: J. Springer.
- ^ Klein, Christian Felix (2004) [1932]. Elementary Mathematics from an Advanced Standpoint: Arithmetic, Algebra, Analysis. Translated by Hedrick, E. R.; Noble, C. A. (Translation of 3rd German ed.). Dover Publications, Inc. / The Macmillan Company. ISBN 978-0-48643480-3. Archived from the original on 2018-02-15. Retrieved 2017-08-13.
- ^ Protter & Morrey (1970, pp. APP-2, APP-3)
- ^ “Sine, Cosine, Tangent”. www.mathsisfun.com. Retrieved 2020-08-29.
- ^ Protter & Morrey (1970, p. APP-7)
- ^ a b Rudin, Walter, 1921–2010. Principles of mathematical analysis (Third ed.). New York. ISBN 0-07-054235-X. OCLC 1502474.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Diamond, Harvey (2014). “Defining Exponential and Trigonometric Functions Using Differential Equations”. Mathematics Magazine. 87 (1): 37–42. doi:10.4169/math.mag.87.1.37. ISSN 0025-570X. S2CID 126217060.
- ^ Spivak, Michael (1967). “15”. Calculus. Addison-Wesley. pp. 256–257. LCCN 67-20770.
- ^ Heng, H. H.; Cheng, Khoo; Talbert, J. F. (2001). Additional Mathematics. Pearson Education South Asia. ISBN 978-981-235-211-8.
- ^ Bityutskov, V.I. (2011-02-07). “Trigonometric Functions”. Encyclopedia of Mathematics. Archived from the original on 2017-12-29. Retrieved 2017-12-29.
- ^ Larson, Ron (2013). Trigonometry (9th ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 153. ISBN 978-1-285-60718-4. Archived from the original on 2018-02-15. Extract of page 153 Archived 15 February 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ See Ahlfors, pp. 43–44.
- ^ Stanley, Enumerative Combinatorics, Vol I., p. 149
- ^ Abramowitz; Weisstein.
- ^ Lambert, Johann Heinrich (2004) [1768], “Mémoire sur quelques propriétés remarquables des quantités transcendantes circulaires et logarithmiques”, in Berggren, Lennart; Borwein, Jonathan M.; Borwein, Peter B. (eds.), Pi, a source book (3rd ed.), New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 129–140, ISBN 0-387-20571-3
- ^ Aigner, Martin; Ziegler, Günter M. (2000). Proofs from THE BOOK (Second ed.). Springer-Verlag. p. 149. ISBN 978-3-642-00855-9. Archived from the original on 2014-03-08.
- ^ Remmert, Reinhold (1991). Theory of complex functions. Springer. p. 327. ISBN 978-0-387-97195-7. Archived from the original on 2015-03-20. Extract of page 327 Archived 20 March 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Kannappan, Palaniappan (2009). Functional Equations and Inequalities with Applications. Springer. ISBN 978-0387894911.
- ^ The Universal Encyclopaedia of Mathematics, Pan Reference Books, 1976, pp. 529–530. English version George Allen and Unwin, 1964. Translated from the German version Meyers Rechenduden, 1960.
- ^ Farlow, Stanley J. (1993). Partial differential equations for scientists and engineers (Reprint of Wiley 1982 ed.). Courier Dover Publications. p. 82. ISBN 978-0-486-67620-3. Archived from the original on 2015-03-20.
- ^ See for example, Folland, Gerald B. (2009). “Convergence and completeness”. Fourier Analysis and its Applications (Reprint of Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole 1992 ed.). American Mathematical Society. pp. 77ff. ISBN 978-0-8218-4790-9. Archived from the original on 2015-03-19.
- ^ a b c Boyer, Carl B. (1991). A History of Mathematics (Second ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 0-471-54397-7, p. 210.
- ^ a b Gingerich, Owen (1986). “Islamic Astronomy”. Scientific American. Vol. 254. p. 74. Archived from the original on 2013-10-19. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ^ Jacques Sesiano, “Islamic mathematics”, p. 157, in Selin, Helaine; D’Ambrosio, Ubiratan, eds. (2000). Mathematics Across Cultures: The History of Non-western Mathematics. Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4020-0260-1.
- ^ a b “trigonometry”. Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ^ O’Connor, J. J.; Robertson, E. F. “Madhava of Sangamagrama”. School of Mathematics and Statistics University of St Andrews, Scotland. Archived from the original on 2006-05-14. Retrieved 2007-09-08.
- ^ Van Brummelen, Glen (2018). “The end of an error: Bianchini, Regiomontanus, and the tabulation of stellar coordinates”. Archive for History of Exact Sciences. 72 (5): 547–563. doi:10.1007/s00407-018-0214-2. JSTOR 45211959. S2CID 240294796.
- ^ “Fincke biography”. Archived from the original on 2017-01-07. Retrieved 2017-03-15.
- ^ O’Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., “Trigonometric functions”, MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews
- ^ Bourbaki, Nicolás (1994). Elements of the History of Mathematics. Springer. ISBN 9783540647676.
- ^ Nielsen (1966, pp. xxiii–xxiv)
- ^ The anglicized form is first recorded in 1593 in Thomas Fale’s Horologiographia, the Art of Dialling.
- ^ Various sources credit the first use of sinus to either
- Plato Tiburtinus’s 1116 translation of the Astronomy of Al-Battani
- Gerard of Cremona’s translation of the Algebra of al-Khwārizmī
- Robert of Chester’s 1145 translation of the tables of al-Khwārizmī
See Merlet, A Note on the History of the Trigonometric Functions in Ceccarelli (ed.), International Symposium on History of Machines and Mechanisms, Springer, 2004
See Maor (1998), chapter 3, for an earlier etymology crediting Gerard.
See Katx, Victor (July 2008). A history of mathematics (3rd ed.). Boston: Pearson. p. 210 (sidebar). ISBN 978-0321387004. - ^ See Plofker, Mathematics in India, Princeton University Press, 2009, p. 257
See “Clark University”. Archived from the original on 2008-06-15.
See Maor (1998), chapter 3, regarding the etymology. - ^ Oxford English Dictionary
- ^ Gunter, Edmund (1620). Canon triangulorum.
- ^ Roegel, Denis, ed. (2010-12-06). “A reconstruction of Gunter’s Canon triangulorum (1620)” (Research report). HAL. inria-00543938. Archived from the original on 2017-07-28. Retrieved 2017-07-28.
References[edit]
- Abramowitz, Milton; Stegun, Irene Ann, eds. (1983) [June 1964]. Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables. Applied Mathematics Series. Vol. 55 (Ninth reprint with additional corrections of tenth original printing with corrections (December 1972); first ed.). Washington D.C.; New York: United States Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards; Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-61272-0. LCCN 64-60036. MR 0167642. LCCN 65-12253.
- Lars Ahlfors, Complex Analysis: an introduction to the theory of analytic functions of one complex variable, second edition, McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, 1966.
- Boyer, Carl B., A History of Mathematics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2nd edition. (1991). ISBN 0-471-54397-7.
- Cajori, Florian (1929). “§2.2.1. Trigonometric Notations”. A History of Mathematical Notations. Vol. 2. Open Court. pp. 142–179 (¶511–537).
- Gal, Shmuel and Bachelis, Boris. An accurate elementary mathematical library for the IEEE floating point standard, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (1991).
- Joseph, George G., The Crest of the Peacock: Non-European Roots of Mathematics, 2nd ed. Penguin Books, London. (2000). ISBN 0-691-00659-8.
- Kantabutra, Vitit, “On hardware for computing exponential and trigonometric functions,” IEEE Trans. Computers 45 (3), 328–339 (1996).
- Maor, Eli, Trigonometric Delights, Princeton Univ. Press. (1998). Reprint edition (2002): ISBN 0-691-09541-8.
- Needham, Tristan, “Preface”” to Visual Complex Analysis. Oxford University Press, (1999). ISBN 0-19-853446-9.
- Nielsen, Kaj L. (1966), Logarithmic and Trigonometric Tables to Five Places (2nd ed.), New York: Barnes & Noble, LCCN 61-9103
- O’Connor, J. J., and E. F. Robertson, “Trigonometric functions”, MacTutor History of Mathematics archive. (1996).
- O’Connor, J. J., and E. F. Robertson, “Madhava of Sangamagramma”, MacTutor History of Mathematics archive. (2000).
- Pearce, Ian G., “Madhava of Sangamagramma” Archived 2006-05-05 at the Wayback Machine, MacTutor History of Mathematics archive. (2002).
- Protter, Murray H.; Morrey, Charles B. Jr. (1970), College Calculus with Analytic Geometry (2nd ed.), Reading: Addison-Wesley, LCCN 76087042
- Weisstein, Eric W., “Tangent” from MathWorld, accessed 21 January 2006.
External links[edit]
- “Trigonometric functions”, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001 [1994]
- Visionlearning Module on Wave Mathematics
- GonioLab Visualization of the unit circle, trigonometric and hyperbolic functions
- q-Sine Article about the q-analog of sin at MathWorld
- q-Cosine Article about the q-analog of cos at MathWorld
Тригонометрия – раздел математической науки, в котором изучаются тригонометрические функции и их использование в геометрии. Развитие тригонометрии началось еще во времена античной Греции. Во времена средневековья важный вклад в развитие этой нужной науки внесли ученые Ближнего Востока и Индии, которые придумали наиболее важные понятия, объяснили многие свойства, предложили варианты измерения и др.
Данная статья посвящена базовым понятиям и дефинициям тригонометрии. В ней рассмотрены определения основных тригонометрических функций: синуса, косинуса, тангенса и котангенса. Разъяснен и проиллюстрирован их смысл в контексте геометрии без таблиц и графиков.
Синус, косинус, тангенс и котангенс. Определения
Зачем разделять понятия синуса, косинуса, тангенса и котангенса?
Изначально определения тригонометрических функций, аргументом которых является угол, выражались через соотношения сторон прямоугольного треугольника.
Что такое синус?
Синус угла (sin α) – это отношение противолежащего этому углу катета к гипотенузе.
Что такое косинус?
Косинус угла (cosα) – это отношение прилежащего катета к гипотенузе.
Что такое тангенс?
Тангенс угла (tg α) – это отношение противолежащего катета к прилежащему.
Котангенс угла (ctg α) – отношение прилежащего катета к противолежащему.
Данные определения даны для острого угла прямоугольного треугольника!
Синус и косинус можно представить через экспоненту (экспоненциальная функция).
Приведем иллюстрацию.
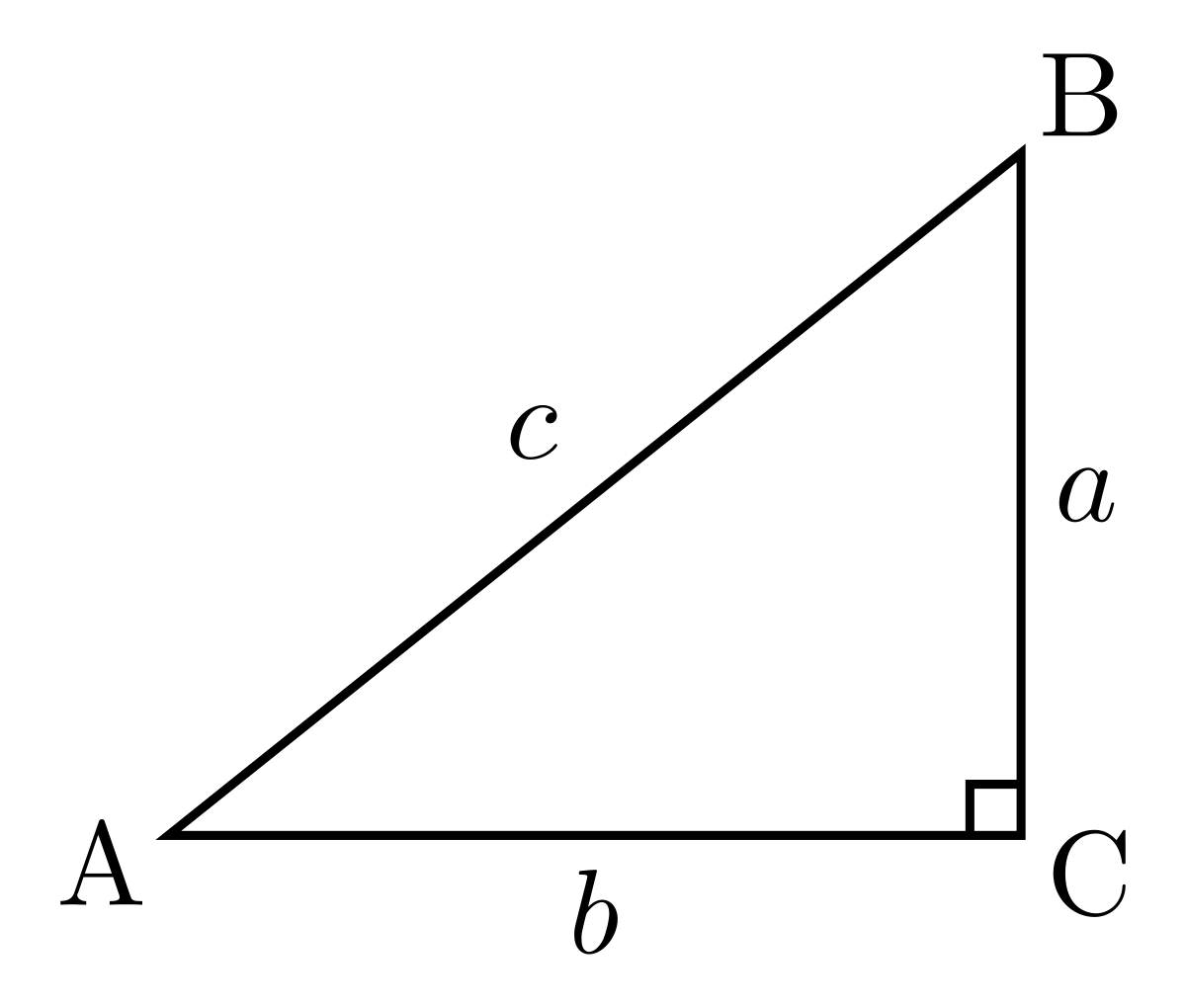
В треугольнике ABC с прямым углом С синус угла А равен отношению катета BC к гипотенузе AB.
Означения синуса, косинуса, тангенса и котангенса позволяют вычислять (находить) значения этих функций по известным длинам сторон треугольника.
Что и почему важно и принято помнить в ходе такого нахождения?
Область значений синуса и косинуса: от -1 до 1. Иными словами синус и косинус принимают значения от -1 до 1. Область значений тг и ктг – вся числовая прямая, то есть эти функции могут принимать любые значения.
Как найти синус? Для начала нужно определиться, какой перед нами треугольник: прямоугольный или произвольный. В первом случае можно использовать обычный тригонометрический метод, а во втором – теорему косинусов.
Как найти косинус? Соответственно, нам нужно знать значения прилежающего катета и гипотенузы.
Как найти тангенс? Если треугольник прямоугольный, то тангенс вычисляется при помощи значений противоположного катета и прилежащего (в уравнении нужно поделить одно на другое). Если речь идет о числах, тупых, развернутых углов и углов, превышающих 360 градусов, то тангенс определяется при помощи синуса и косинуса (посредством их отношения и деления).
Теорема синусов и косинусов используется для того чтобы искать элементы в произвольном треугольнике. Такой поиск используется часто.
Угол поворота
Определения, данные выше, относятся к острым углам. В тригонометрии вводится понятие угла поворота, величина которого, в отличие от острого угла, не ограничена рамками от 0 до 90 градусов.Угол поворота в градусах или радианах выражается любым действительным числом от -∞ до +∞.
В данном контексте можно дать определение синуса, косинуса, тангенса и котангенса угла произвольной величины. Представим единичную окружность (круг) с центром в начале декартовой системы координат.
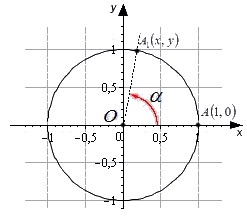
Начальная точка A с координатами (1, 0) поворачивается вокруг центра единичной окружности на некоторый угол α и переходит в точку A1. Определение дается через координаты точки A1(x , y).
Синус угла поворота α – это ордината точки A1(x , y). sin α=y
Косинус угла поворота α – это абсцисса точки A1(x , y). cos α=икс
Тангенс угла поворота α – это отношение ординаты точки A1(x , y) к ее абсциссе. tg α=yx
Котанг угла поворота α – это отношение абсциссы точки A1(x , y) к ее ординате. ctg α=xy
Синус и косинус определены для любого угла поворота. Это логично, ведь абсциссу и ординату точки после поворота можно определить при любом угле. Иначе обстоит дело с тангенсом и котангенсом. Тангенс не определен, когда точка после поворота переходит в точку с нулевой абсциссой (0, 1) и (0, -1). В таких случаях выражение для тангенса tg α=yx просто не имеет смысла, так как в нем присутствует деление на ноль. Аналогична ситуация с котангенсом. Отличие состоит в том, что котангенс не определен в тех случаях, когда в ноль обращается ордината точки.
Простое правило: синус и косинус определены для любых углов α.
Тангенс определен для всех углов, кроме α=90°+180°·k, k∈Z (α=π2+π·k, k∈Z)
Котангенс определен для всех углов, кроме α=180°·k, k∈Z (α=π·k, k∈Z)
При решении практических примеров не говорят “синус угла поворота α”. Слова “угол поворота” просто опускают, подразумевая, что из контекста и так понятно, о чем идет речь.
Числа
Как быть с определением синуса, косинуса, тангенса и котангенса числа, а не угла поворота?
Синусом, косинусом, тангенсом и котангенсом числа t называется число, которое соответственно равно синусу, косинусу, тангенсу и котангенсу в t радиан.
Например, синус числа 10π равен синусу угла поворота величиной 10π рад.
Существует и другой подход к определению синуса, косинуса, тангенса и котангенса числа. Рассмотрим его подробнее.
Любому действительному числу t ставится в соответствие точка на единичной окружности с центром в начале прямоугольной декартовой системы координат. Синус, косинус, тангенс и котангенс определяются через координаты этой точки.
Начальная точка на окружности – точка A c координатами (1, 0).
Положительному числу t соответствует точка, в которую перейдет начальная точка, если будет двигаться по окружности против часовой стрелки и пройдет путь t.
Отрицательному числу t соответствует точка, в которую перейдет начальная точка, если будет двигаться по окружности против часовой стрелки и пройдет путь t.
Теперь, когда связь числа и точки на окружности установлена, переходим к определению синуса, косинуса, тангенса и котангенса.
Синус числа t – ордината точки единичной окружности, соответствующей числу t. sin t=y
Косинус числа t – абсцисса точки единичной окружности, соответствующей числу t. cos t=x
Тангенс числа t – отношение ординаты к абсциссе точки единичной окружности, соответствующей числу t. tg t=yx=sin tcos t
Последние определения находятся в соответствии и не противоречат определению, данному в начале это пункта. Точка на окружности, соответствующая числу t, совпадает с точкой, в которую переходит начальная точка после поворота на угол t радиан.
Тригонометрические функции углового и числового аргумента
Каждому значению угла α соответствует определенное значение синуса и косинуса этого угла. Также, как всем углам α, отличным от α = 90 ° + 180 ° · k , k ∈ Z ( α = π 2 + π · k , k ∈ Z ) соответствует определенное значение тангенса. Котангенс, как сказано выше, определен для всех α, кроме α = 180 ° · k , k ∈ Z ( α = π · k , k ∈ Z ).
Можно сказать, что sin α, cos α, tg α, ctg α – это функции угла альфа, или функции углового аргумента.
Аналогично можно говорить о синусе, косинусе, тангенсе и котангенсе, как о функциях числового аргумента. Каждому действительному числу t соответствует определенное значение синуса или косинуса числа t. Всем числам, отличным от π 2 + π · k , k ∈ Z соответствует значение тангенса. Котангенс, аналогично, определен для всех чисел, кроме π · k , k ∈ Z.
Синус, косинус, тангенс и котангенс – основные тригонометрические функции.
Из контекста обычно понятно, с каким аргументом тригонометрической функции (угловой аргумент или числовой аргумент) мы имеем дело.
Связь определений sin, cos, tg и ctg из геометрии и тригонометрии
Вернемся к данным в самом начале определениям и углу альфа, лежащему в пределах от 0 до 90 градусов. Тригонометрические определения синуса, косинуса, тангенса и котангенса полностью согласуются с геометрическими определениями, данными с помощью соотношений сторон прямоугольного треугольника. Покажем это.
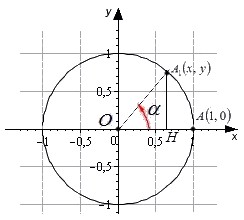
Возьмем единичную окружность с центром в прямоугольной декартовой системе координат. Повернем начальную точку A(1,0) на угол величиной до 90 градусов и проведем из полученной точки A1(x,y) перпендикуляр к оси абсцисс. В полученном прямоугольном треугольнике угол A1OH равен углу поворота α, длина катета OH равна абсциссе точки A1(x,y). Длина катета, противолежащего углу, равна ординате точки A1(x,y), а длина гипотенузы равна единице, так как она является радиусом единичной окружности.
В соответствии с определением из геометрии, синус угла α равен отношению противолежащего катета к гипотенузе.
sin α=A1HOA1=y1=y
Значит, определение синуса острого угла в прямоугольном треугольнике через соотношение сторон эквивалентно определению синуса угла поворота α, при альфа лежащем в пределах от 0 до 90 градусов.
Аналогично соответствие определений можно показать для косинуса, тангенса и котангенса.
Синус, косинус, тангенс и котангенс: основные формулы
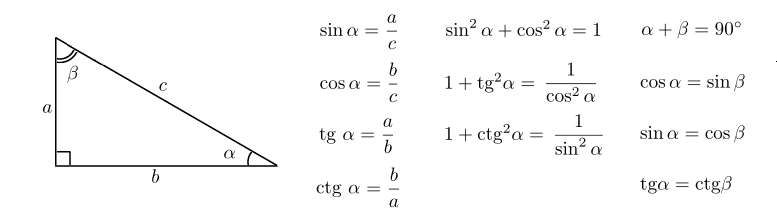













![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}sin x&=x-{frac {x^{3}}{3!}}+{frac {x^{5}}{5!}}-{frac {x^{7}}{7!}}+cdots \[6mu]&=sum _{n=0}^{infty }{frac {(-1)^{n}}{(2n+1)!}}x^{2n+1}\[8pt]cos x&=1-{frac {x^{2}}{2!}}+{frac {x^{4}}{4!}}-{frac {x^{6}}{6!}}+cdots \[6mu]&=sum _{n=0}^{infty }{frac {(-1)^{n}}{(2n)!}}x^{2n}.end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/396790dc41b52c5381ef1683a279d05ba5d64f79)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}tan x&{}=sum _{n=0}^{infty }{frac {U_{2n+1}}{(2n+1)!}}x^{2n+1}\[8mu]&{}=sum _{n=1}^{infty }{frac {(-1)^{n-1}2^{2n}left(2^{2n}-1right)B_{2n}}{(2n)!}}x^{2n-1}\[5mu]&{}=x+{frac {1}{3}}x^{3}+{frac {2}{15}}x^{5}+{frac {17}{315}}x^{7}+cdots ,qquad {text{for }}|x|<{frac {pi }{2}}.end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d0de1a2399f8c3b723b71c5e24e8f0136fd4bb18)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}csc x&=sum _{n=0}^{infty }{frac {(-1)^{n+1}2left(2^{2n-1}-1right)B_{2n}}{(2n)!}}x^{2n-1}\[5mu]&=x^{-1}+{frac {1}{6}}x+{frac {7}{360}}x^{3}+{frac {31}{15120}}x^{5}+cdots ,qquad {text{for }}0<|x|<pi .end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bd4b74fe732906b09b6205ecfa81326222ae0320)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}sec x&=sum _{n=0}^{infty }{frac {U_{2n}}{(2n)!}}x^{2n}=sum _{n=0}^{infty }{frac {(-1)^{n}E_{2n}}{(2n)!}}x^{2n}\[5mu]&=1+{frac {1}{2}}x^{2}+{frac {5}{24}}x^{4}+{frac {61}{720}}x^{6}+cdots ,qquad {text{for }}|x|<{frac {pi }{2}}.end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1e8d1437d98b6b4d05d4da50fe2e18bd39a7ff9e)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}cot x&=sum _{n=0}^{infty }{frac {(-1)^{n}2^{2n}B_{2n}}{(2n)!}}x^{2n-1}\[5mu]&=x^{-1}-{frac {1}{3}}x-{frac {1}{45}}x^{3}-{frac {2}{945}}x^{5}-cdots ,qquad {text{for }}0<|x|<pi .end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4c6645779d6fe606694a0ac157fcdee271c7e795)












![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}e^{ix}&=cos x+isin x\[5pt]e^{-ix}&=cos x-isin x.end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8d374fafbe34908c7766b67e4c51797589906940)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}sin x&={frac {e^{ix}-e^{-ix}}{2i}}\[5pt]cos x&={frac {e^{ix}+e^{-ix}}{2}}.end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/590e4a1bbe3ccdb7521fe06a6e5b56e538d4e729)



![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}sin z&=sin xcosh y+icos xsinh y\[5pt]cos z&=cos xcosh y-isin xsinh yend{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c1646655eab602e234f42df85cae241ffbb867cf)















![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}sin left(x+yright)&=sin xcos y+cos xsin y,\[5mu]cos left(x+yright)&=cos xcos y-sin xsin y,\[5mu]tan(x+y)&={frac {tan x+tan y}{1-tan xtan y}}.end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7a94648d4600a711a8851dfaea622a269be4eda5)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}sin left(x-yright)&=sin xcos y-cos xsin y,\[5mu]cos left(x-yright)&=cos xcos y+sin xsin y,\[5mu]tan(x-y)&={frac {tan x-tan y}{1+tan xtan y}}.end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0a627a03bba700c34bee8de20cfa09d78b127716)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}sin 2x&=2sin xcos x={frac {2tan x}{1+tan ^{2}x}},\[5mu]cos 2x&=cos ^{2}x-sin ^{2}x=2cos ^{2}x-1=1-2sin ^{2}x={frac {1-tan ^{2}x}{1+tan ^{2}x}},\[5mu]tan 2x&={frac {2tan x}{1-tan ^{2}x}}.end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d631768e76acdd703625fbcaf9cdf8b8e3e9200f)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}sin theta &={frac {2t}{1+t^{2}}},\[5mu]cos theta &={frac {1-t^{2}}{1+t^{2}}},\[5mu]tan theta &={frac {2t}{1-t^{2}}}.end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c9eb5a515edf456acce4c943b43121632bef4d27)










