The first code line, Option Explicit means (in simple terms) that all of your variables have to be explicitly declared by Dim statements. They can be any type, including object, integer, string, or even a variant.
This line: Dim envFrmwrkPath As Range is declaring the variable envFrmwrkPath of type Range. This means that you can only set it to a range.
This line: Set envFrmwrkPath = ActiveSheet.Range("D6").Value is attempting to set the Range type variable to a specific Value that is in cell D6. This could be a integer or a string for example (depends on what you have in that cell) but it’s not a range.
I’m assuming you want the value stored in a variable. Try something like this:
Dim MyVariableName As Integer
MyVariableName = ActiveSheet.Range("D6").Value
This assumes you have a number (like 5) in cell D6. Now your variable will have the value.
For simplicity sake of learning, you can remove or comment out the Option Explicit line and VBA will try to determine the type of variables at run time.
Try this to get through this part of your code
Dim envFrmwrkPath As String
Dim ApplicationName As String
Dim TestIterationName As String
Если вы используете Excel, вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой «Ошибка выполнения 424» с сообщением «Требуется объект».
Это ошибка в VBA (Visual Basic для приложений) и в основном проявляется, когда вы указываете на объект, который либо не существует, либо не находится за пределами текущей области.
Если вы видите ошибку, когда кто-то «обрабатывает» какой-то макрос/автоматизированную функцию в электронных таблицах Excel, вероятная проблема заключается в том, что вы называете объект «вне контекста». Это означает, что вы можете загрузить объект, но его содержимое может быть изменено или изменено. Есть также некоторые другие потенциальные проблемы, которые я объясню в этом руководстве…
причина
Ошибка, которую вы видите, будет иметь следующее сообщение:
Ошибка времени запуска «424»
Требуется объект
Чтобы объяснить, почему он показывает ошибку и что это значит, Microsoft выпустила свой пакет «Visual Basic» в конце 90-х.
Это обеспечивало основные возможности системы, позволяя разработчикам-любителям создавать простые приложения. VB имел большой успех.
Из-за этого Microsoft представила «VBA» (Visual Basic для приложений) в своем пакете программного обеспечения Office, а именно в Excel и Word. Это позволило типам разработчиков создавать автоматические функции в электронных таблицах Excel, указывать на «объекты» в самой электронной таблице и так далее.
Каждый раз, когда мы используем Visual Basic, мы вызываем ряд «объектов» в памяти. Эти объекты являются просто переменными, используемыми в ряде дополнительных функций, включая пользовательские функции и так далее. Проблема — и это относится к большинству языков программирования — в том, что если указать на объект, который не вызывается, приложение рухнет.
решение
Если вы хотите исправить проблему, вы должны сначала убедиться, что данные есть в системе, и тогда вы сможете правильно обращаться к ним. Этот урок объяснит, как:
1. Убедитесь, что переменные определены правильно
Основная проблема заключается в том, что вы вызываете метод для несуществующей переменной (объекта). Наиболее распространенная причина этого заключается в том, что вы просто неправильно вводите имя переменной и поэтому не объявляете ее в своем приложении VBA. Возьмем следующий пример:
Подтест ()
Application33.WorksheetFunction.Sum (диапазон (“A1: A100”))
Последняя подписка
Вышеприведенное вызовет ошибку, потому что вы пытаетесь вызвать метод WorksheetFunction для «Application33», указанного в объекте.
К сожалению, объект Application33 не существует в памяти, что не позволяет вашему приложению загрузить его. Чтобы исправить это, вам нужно просмотреть исходный код (почти всегда будут указаны неправильные ссылки) и исправить все имена объектов с ошибками.
2. Если вы используете Excel, убедитесь, что есть диапазоны/селекторы
Одна из наиболее распространенных причин ошибки заключается в том, что вы пытаетесь указать несуществующий объект или значение. Это типичная проблема при использовании одного из объектов VLookup или ActiveX. Если вы столкнулись с этой ошибкой, убедитесь, что код указывает только на существующие объекты:
Частный дополнительный тест ()
Это вызовет ошибку
Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(TeamName, Range (“TeamNameLookup”), 3, False).
Стоимость должна быть
Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(TeamName, Sheets (“YourSheetName”). Диапазон (“TeamNameLookup”), 3, False)
Последняя подписка
Вышеупомянутое означает, что вы пытаетесь вызвать разные рабочие листы, и их соответствующий «диапазон»/«значение» работает без поиска или объявления рабочих листов. Чтобы исправить это, вам нужно убедиться, что вы вызываете «диапазон» или «значение» для соответствующих объектов.
3. Убедитесь, что у вас есть правильные определения
Наконец, одна из наиболее распространенных причин ошибок заключается в том, что вы неправильно определяете свои переменные.
От неправильного определения переменных как неверных интерпретаций объектов до вызова «Option Explicit» вы можете пытаться указать переменные/объекты, которые не определены только потому, что они определены неправильно.
Например…
Вариант очевиден
Персональный дополнительный тест ()
Здесь вам нужно объявить переменные, прежде чем пытаться указать/заполнить их
Например…
Затемните your_path как строку
Установите your_path = “x/y/z”
Последняя подписка
В приведенном выше примере, если переменная «ваш_путь» не объявлена до ее установки, вы получите ошибку 424 (поскольку объект «ваш_путь» не существует). Отсюда вы также должны убедиться, что вы можете вызывать соответствующие объекты (если вы указываете значение рабочего листа, вы должны убедиться, что рабочий лист существует и может быть загружен).
Ясно, что есть много других случаев этой ошибки. Поскольку каждый код отличается, я не могу пройтись по каждому потенциалу. Надеюсь, вы видите, что ошибка вызвана указанием на неправильную переменную в вашей системе.
Home > VBA > VBA Object Required Error (Error 424)
When VBA is not able to recognize the object for which you are referring to the property or a method it shows you the Object Required error. In simple words, if you refer to an object, but the name of that object is not correct (that object is not in the VBA’s object hierarchy) it shows error 424, like the following.

In the above code, as you can see, I have misspelled the active cell object, and when VBA’s executes that line of code can’t that object because there’s no object with that name (as I have misspelled it).
Note: If you have used the Option Explicit statement in the module then with the same, you’ll get a different error (see image below).

Used “Set” Keyword for a Non-Object Variable
When you use a variable to assign an object to it, you need to use the keyword “Set”. In the following example, you have a myWKS for the worksheet and iVal for the value from cell A1.

As you can see, in the above code you have variables out of which one is declared as a worksheet object and the second as a string. But at the time of assigning the value, we have used the “Set” keyword to the variable “iVal” which is not declared as an object but as a string.
How to Fix Object Required (Error 424) in VBA
- Go to the Debug menu in your visual basic editor.
- Use the step to run the entire code step by step.
- The moment you reach the line where you have an error VBA will show you an error.
- Correct that line of code.

The other way could be going through the code line by line by reading it to make sure you are referring to the right objects and using the correct name of the variables and objects.
You can also use the GOTO statement to surpass an error or show a message to the users once an error occurred.
What is VBA
- VBA ERROR Handling
- VBA Automation Error (Error 440)
- VBA Error 400
- VBA Invalid Procedure Call Or Argument Error (Error 5)
- VBA Object Doesn’t Support this Property or Method Error (Error 438)
- VBA Out of Memory Error (Error 7)
- VBA Overflow Error (Error 6)
- VBA Runtime Error (Error 1004)
- VBA Subscript Out of Range Runtime Error (Error 9)
- VBA Type Mismatch Error (Error 13)
The Runtime error 424: Object required occurs when Excel is not able to recognize an object that you are referring to in a VBA code. The object can be a workbook, worksheet, range, variable, class, macro, etc. Some users have also reported that this error occurred when they tried to copy the values of the cells from one workbook to another.
Let’s understand the error through a small scenario. Suppose, I want to check the last field row in a table in a spreadsheet named “First” using the VBA code. To do this, I have added a command button and double-clicked on it and entered the below code in the backend:
Private Sub CommandButton2_Click()
Dim LRow As Integer
LRow = Worksheets(“First”).Cells(Rows.Count, 2).End(xlUp).Row
MsgBox (“Last Row ” & LRow)
End Sub
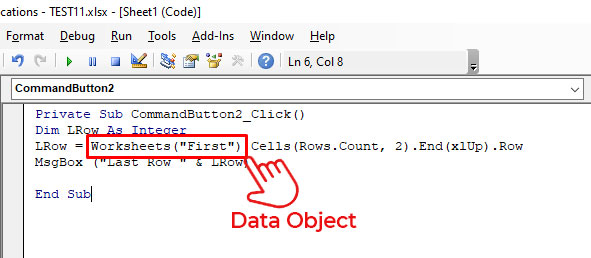
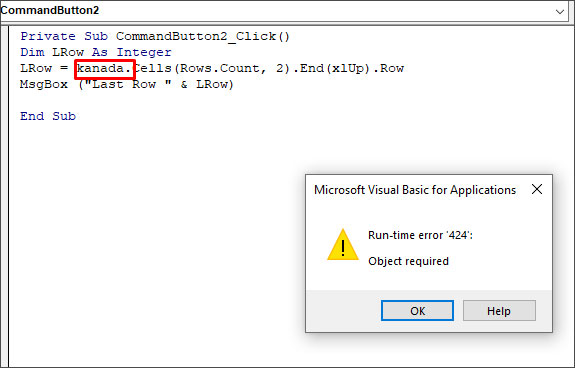
In this code, Worksheets(“First”) is a data object. If I mistakenly delete this data object and insert any random name (for example – kanada), then it will not be recognized by Excel. When I run this code, I will get the “Run-time error 424”.
Causes of Runtime Error 424 in Excel
The Runtime error 424: Object required can occur due to the following reasons:
- Incorrect name of the object you are trying to refer to in a code.
- You have provided an invalid qualifier to an object.
- You have not used the Set statement while assigning an object reference.
- The object is corrupted.
- Missing objects in a workbook.
- Objects you are trying to call in a code are mistakenly deleted or unavailable.
- You have used an incorrect syntax for object declaration.
- You are trying to perform an invalid action on an object in a code.
- Workbook is corrupted.
Solutions to Fix Runtime Error 424: Object Required in Excel
The VBA error ‘object required’ may occur due to different reasons. Based on the reason, you can follow the solutions mentioned below to fix the error.
1. Check the Name of the Object
The Runtime error 424 can occur when you run the VBA code using an incorrect name of the object. For example, the object name is ‘MyObject’ but you’re using “Backcolor”.
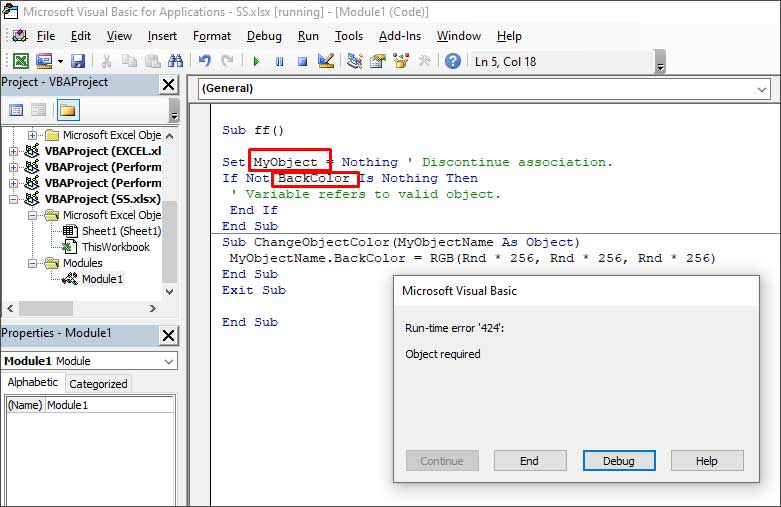
When you click the Debug button, the line with the error will highlight.
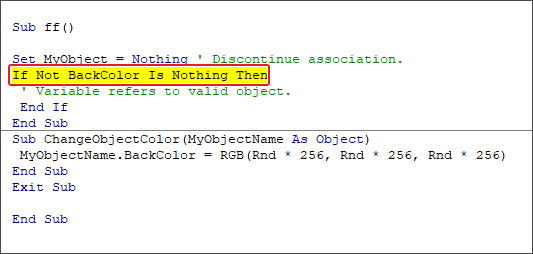
To fix the issue, you need to provide the correct name of the object.
2. Check if the Object is Missing
The Runtime error 424 can occur if the object you are referring to as a method is not available or you are using the wrong object in a code. In the below example, you can see that the error occurs when an object named “Employee” is not available in the Project list.
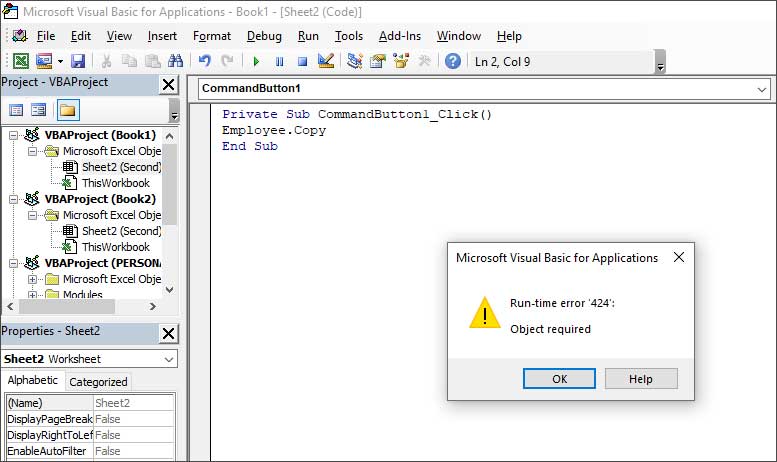
You can check and mention the object which is available. For instance, Sheet2 in the below code.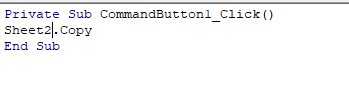
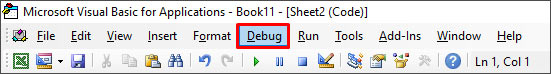
3. Check All References are Declared in the Code
You can get the Runtime error 424 if all the references are not declared. So, make sure you have declared all the references in the code. To verify this, you can use the debug mode by pressing F5 or clicking on the Debug option.
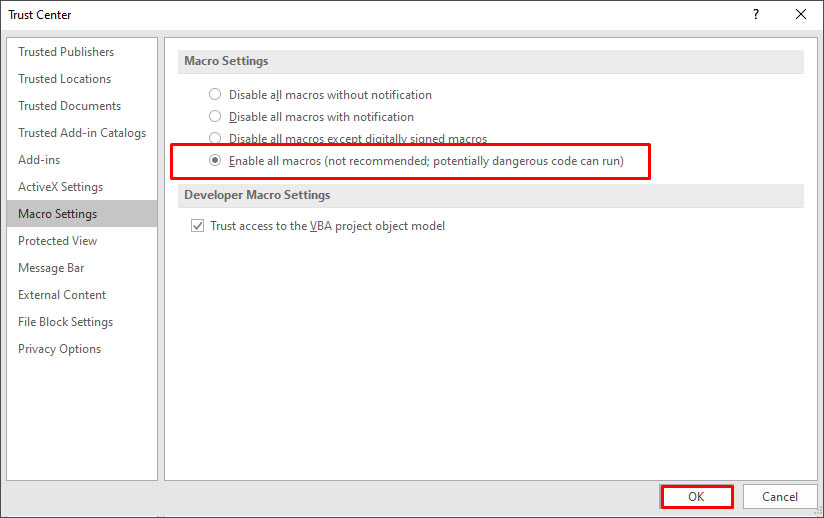
4. Check the Macro Security Settings
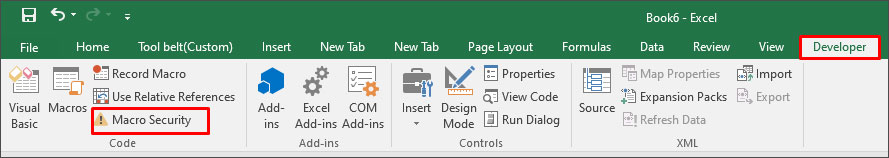
Sometimes, the error can occur if macros are disabled in the Macro Security settings. You can check and change the settings by following these steps:
- On the Developer tab, in the Code section, click Macro Security.
- In the Trust Center window, select Enable all macros.
- Click OK.
-
Repair your Workbook
Sometimes, the ‘Object required’ error can occur if your Excel file is damaged or corrupted. In such a case, you can try repairing the file using Microsoft’s in-built utility – Open and Repair. To use this utility, follow these steps:
- In Excel, go to File > Open > Browse.
- In the Open dialog box, click on the corrupted Excel file.
- Click the arrow next to the Open button and select Open and Repair from the dropdown.
- Select Repair to recover as much data from the file as possible.
If the Open and Repair utility fails or stops working, then you can try a professional Excel repair tool, such as Stellar Repair for Excel. It is an advanced tool that can repair severely corrupted Excel files (.xls, .xlsx, .xltm, .xltx, and .xlsm). It helps recover all the file components, including images, charts, tables, pivot tables, cell comments, chart sheets, formulas, etc., without impacting the original structure.
Conclusion
The Runtime error 424 usually occurs when there is an issue with the objects in your VBA code. In this article, we have covered some effective methods to resolve the “object required” error in Excel. If the error occurs due to corruption in Excel file, then you can repair the corrupt file using Stellar Repair for Excel. It is a reliable tool that can repair severely corrupted Excel file without changing its actual formatting. You can download the free trial version of the software to evaluate its functionality.
Object Required in Excel VBA
Mistakes are part and parcel of coding language. But the real genius lies in finding the error and fixing those errors. The first step in fixing those errors is the intelligence to find why those errors are occurring. If you can find why those errors are coming, then it is a very easy job to fix those errors without breaking a sweat. One such error in VBAVBA error handling refers to troubleshooting various kinds of errors encountered while working with VBA. read more coding is “Object Required.”
Table of contents
- Object Required in Excel VBA
- Why Object Required Error Occurs? (and… How to Fix it?)
- Example #1
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
- Why Object Required Error Occurs? (and… How to Fix it?)

If you remember, while learning variables and assigning data types to those variables, we have “Object” data types as well. So, when the object data type is assigned, and if that object does not exist in the worksheet or workbook we refer to, we will get the VBA error message as “Object required.” So, as a new coder, it is common to panic in those situations because, at the starting level, a beginner cannot find the cause for this error.
Why does Object Required Error Occur? (and… How to Fix it?)
It takes two or three examples to understand why this error occurs and how to fix it.
You can download this VBA Object Required Excel Template here – VBA Object Required Excel Template
For example, look at the below code.
Code:
Sub Last_Row() Dim Wb As Workbook Dim Ws As Worksheet Dim MyToday As Date Set Wb = ThisWorkbook Set Ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Data") Set MyToday = Wb.Ws.Cells(1, 1) MsgBox MyToday End Sub
Let me explain to you the above code for you.
We have declared three variables, and the first two refer to the “Workbook” and “Worksheet” objects. The third variable refers to the “Date” data type.
When the “Object” data types assign the variable, we need to use the word “Set” key to assign the object’s reference to the variable. So, in the next two lines, by using the “Set” keyword, we have assigned the reference of “ThisWorkbook” to the variable “Wb” because this variable holds the object data type as “Workbook.” For the variable “Ws,” we have assigned the worksheet object of the “Data” worksheet in this workbook.
Set Wb = ThisWorkbook
Set Ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Data")
- In the next line for the “Date” data type variable also, we have used the “Set” keyword to assign the value of the cell A1 value in this workbook (Wb) and the worksheet “Data” (Ws).
Set MyToday = Wb.Ws.Cells(1, 1)
- In the next line, we show the value of the “MyDate” variable value of cell A1 in the message box in VBA.
MsgBox MyToday
- Let us run this code and see what we get.

As you can see above, it shows the VBA error message as “Object required.” Therefore, it is time to examine why we are getting this error message.
- In the above error message image in the code section, while showing the error message, it has highlighted the error part of the code with blue color.

- So, the question remains why we got this error. The first thing we need to see is this particular variable data type. Go back to the previous code line, assigning the data type to the variable “MyDate.”

- We have assigned the variable data type as “Date” and now return to the error line.

In this line, we have used the keyword “Set,” whereas our data type isn’t the “Object” data type. So the moment VBA code sees the keyword “Set,” it assumes it is an object data type and says it requires an object reference.
So, the bottom line is the “Set” keyword one may use to refer only to reference the object variables like Worksheet, Workbook, etc.
Example #1
Now take a look at the below code.
Code:
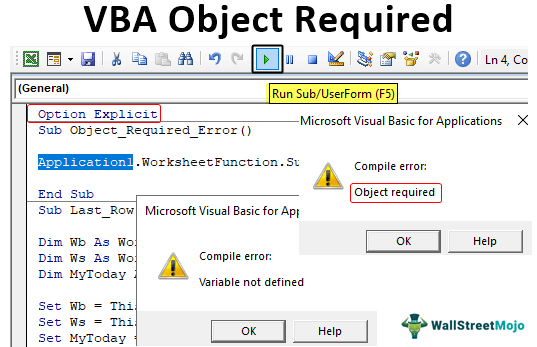
Sub Object_Required_Error() Range("A101").Value = Application1.WorksheetFunction.Sum(Range("A1:A100")) End Sub
In the above code, we have used the worksheet function “SUM” to get the total of the cell values from A1 to A100. When you run this code, we will encounter the below error.

It says, “Run-time error ‘424’: Object required.”
Now, let us closely look at the code now.

Instead of using “Application,” we mistakenly used “Application1”, so this encountered the error of “Object required” in the VBA code.
If the word “Option ExplicitVBA option explicitly makes a user mandatory to declare all the variables before using them; any undefined variable will throw an error while coding execution. We can enable it for all codes from options to require variable declaration.read more” is enabled, we will get the “Variable not defined” error.

Things to Remember
- The “Object required” means object data type reference needs to be accurate.
- When the Option Explicit word is unenabled in the coding, we will get an “Object Required” error for misspelled variable words. If Option Explicit is enabled, we will get the variable not defined error for misspelled variable words.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA Object Required. Here, we learn why the object required an error in Excel VBA and some examples and download the Excel template. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
- VBA Login User Form
- CreateObject in VBA
- OverFlow Error in VBA
- 1004 Error in VBA
- VBA COUNTA
